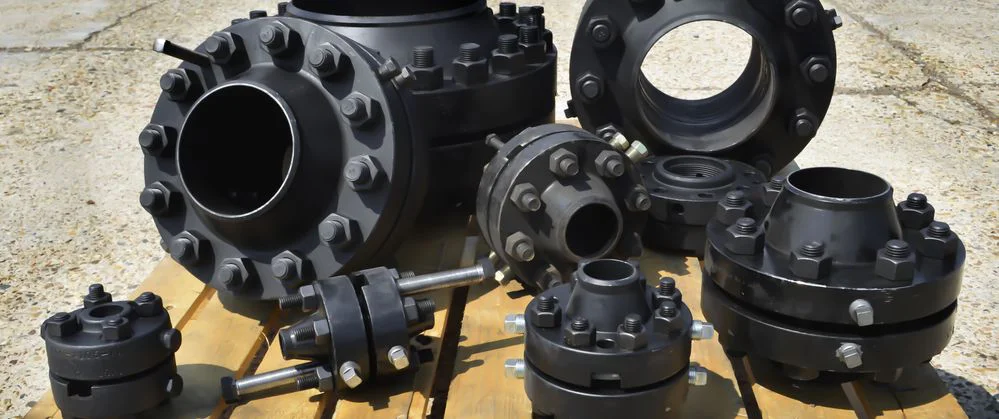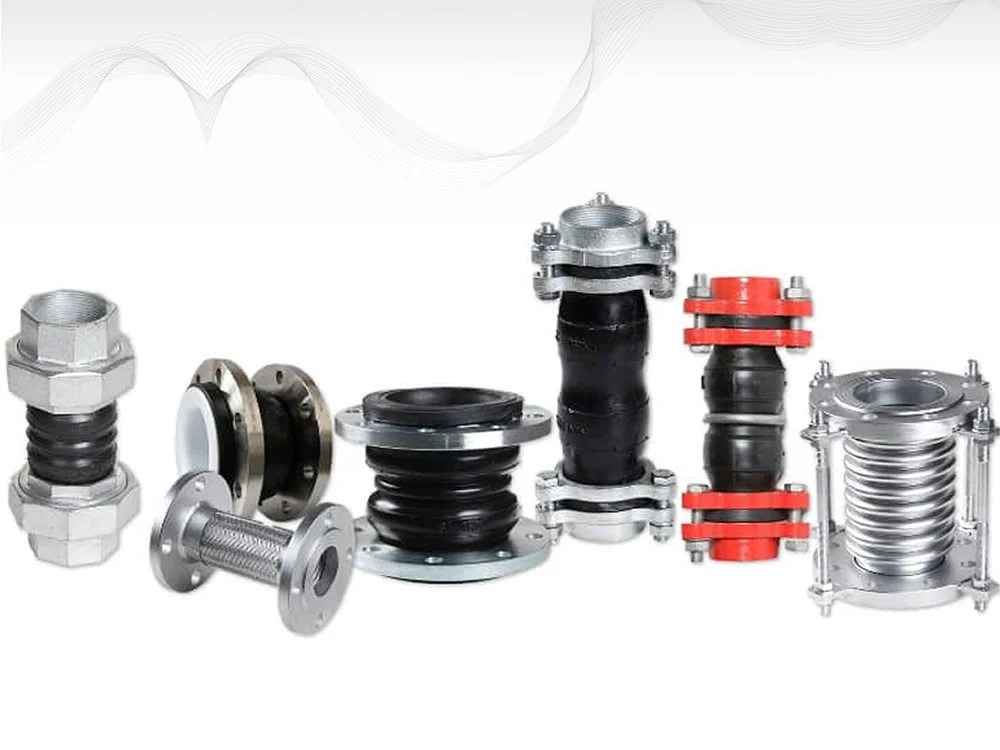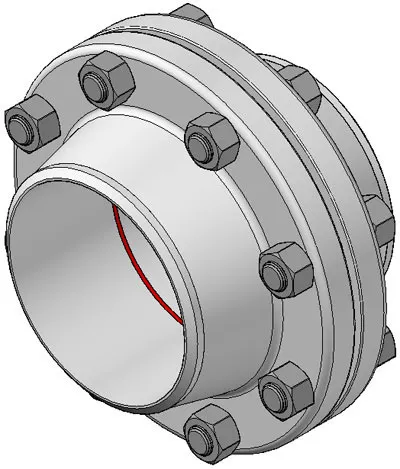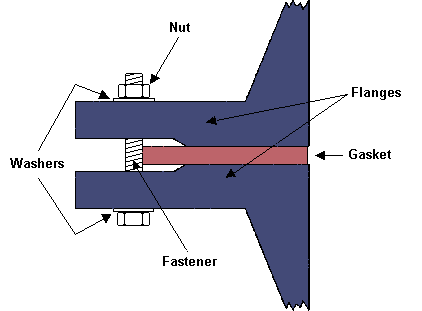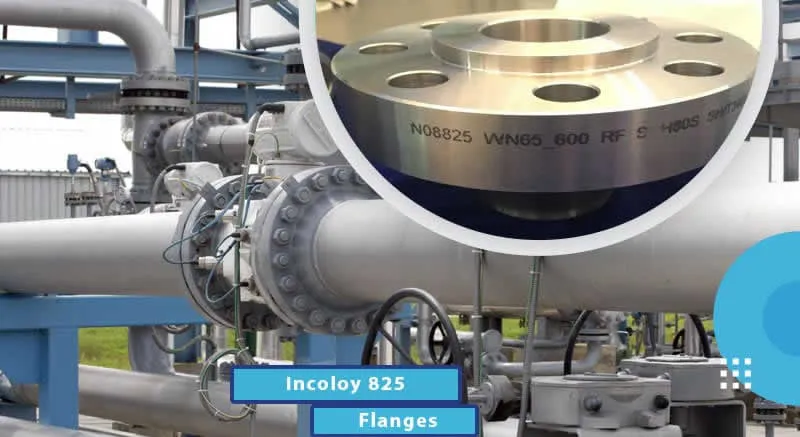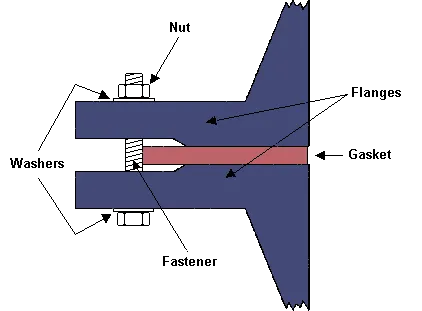
A flanged connection includes Pipe Flanges, gaskets (full-face or ring types),
and bolts, all matched in material (e.g., steel or alloys) for secure, leak-proof joints per
industry standards.
There are many ways to connect flanges, including threading, welding or bolting. The threaded
flange is best for low pressure or smaller pipelines because it can maintain its seal. When
your pipeline is larger or high pressure, then the welded flange is preferable. A boiler
room is one place where welded blind flanges might be used, due to the high pressure
involved.
A flange is a external rib at the end of pipes, valves and other flow devices to assemble
them.
Dimensions of the flanges are up to specific Standards : DIN, ANSI, AS, BS, JIS
A flanged connection requires two flanges (the “main” and the “companion”), a set of bolts
and nuts (whose number depends on the flange diameter and class) and two sealing gaskets.
Flanged connections have to be executed and supervised by trained personnel, as the quality
of the joint has a critical impact on the performance of the piping system / pipeline (the
standard TSE – TS EN 1591 Part 1-4, “Flanges and their joints”, defines a number of
requirements for the execution of proper flanged connections). Whereas all elements of the
joint are critical, experience shows most leaks are originated by the improper installation
of the sealing elements, i.e. the gaskets.
The typical pipe to flange connections are welded or threaded. Welded flanges are used for pipelines and piping systems with high pressures and temperatures, and with diameters above 2 inches.
Threaded connections are instead used for installations of smaller diameter and not subject to severe mechanical forces such as expansion, vibration, contraction, oscillation (forces that would crack the threaded joint). In all these critical cases, butt weld connections are recommended.