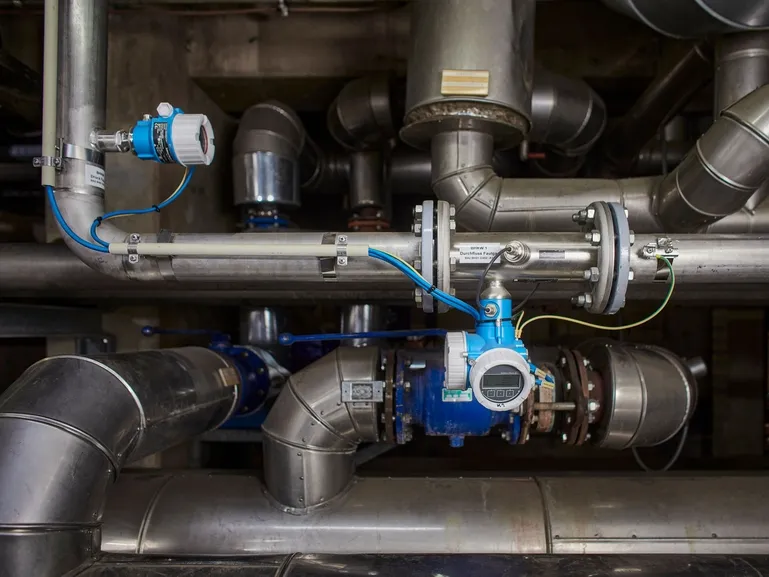
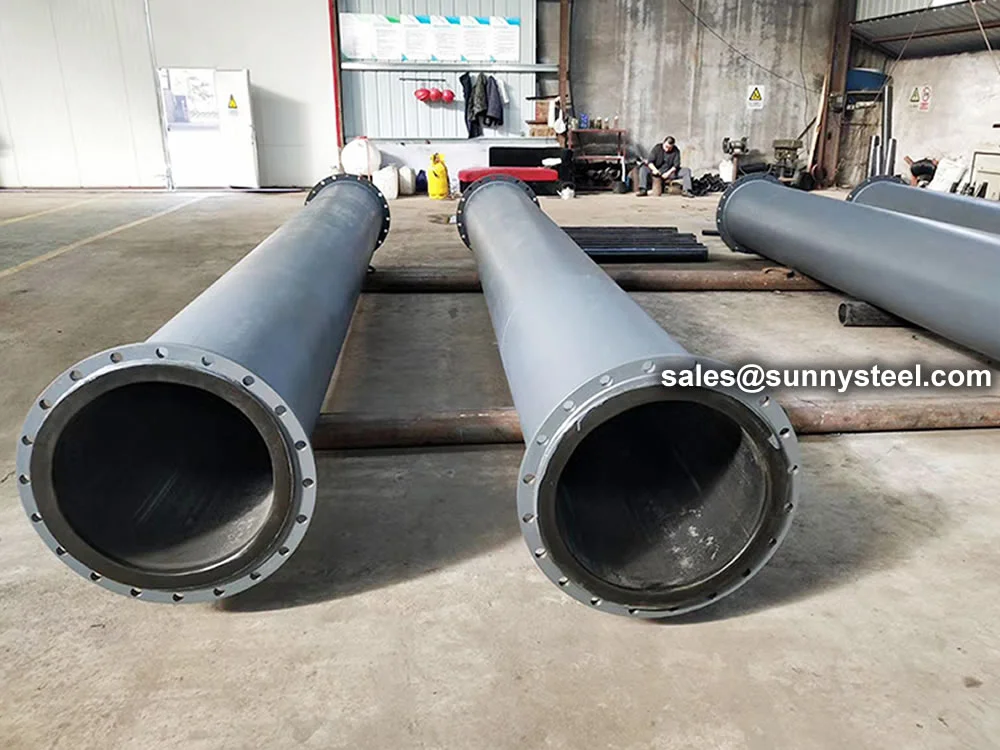
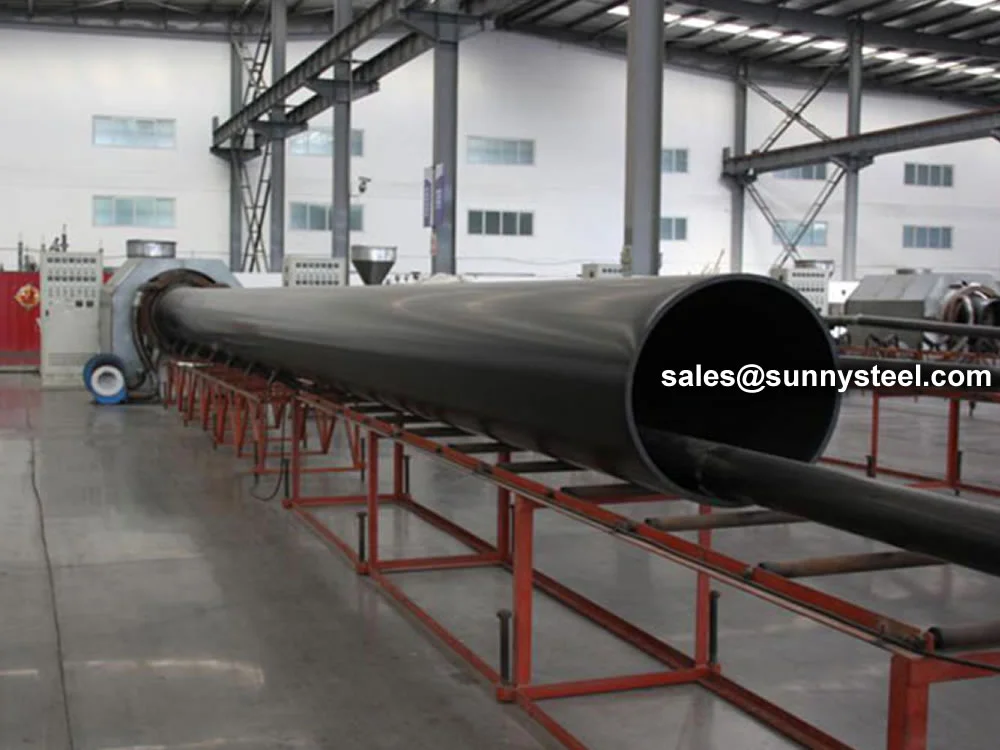
Mining Sludge Pipelines are specially engineered piping systems designed to transport abrasive, corrosive, and highly viscous sludge generated during mining and mineral processing activities. These pipelines play a vital role in moving materials such as mine tailings, concentrates, wastewater, and chemical-laden slurry over long distances to disposal or treatment locations.
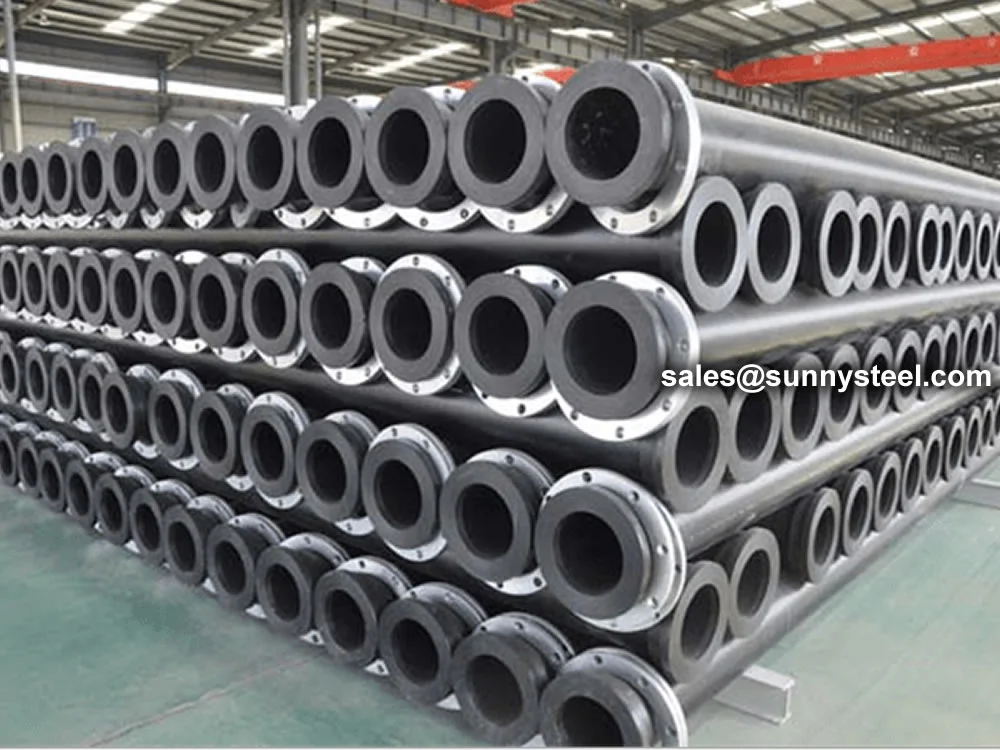
To meet the rigorous demands of these environments, mining sludge pipelines are often constructed using wear-resistant liners such as UHMWPE (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene), alumina ceramics, rubber, or cast basalt, integrated within a carbon steel or alloy steel outer shell for structural integrity.
The pipeline’s internal surface offers exceptional resistance to abrasion, often 6–10 times higher than standard steel, while also resisting chemical degradation caused by acidic or alkaline content in the slurry. The result is a long-lasting, low-maintenance solution that reduces operational downtime, pipe replacement frequency, and total cost of ownership.
Additionally, mining sludge pipelines can be configured in straight runs, elbows, tees, reducers, and expansion joints to suit various layout requirements in processing plants, flotation circuits, or tailings dams.
What pipes are used in the mining industry?
For more than 30 years, polyethylene (PE) pipe's unique characteristics have made it the product of choice for numerous applications in the mining industry. Heat-fused joints create a monolithic structure that allows long lengths of pipe to be pulled from one area to another.
Installation Guidelines
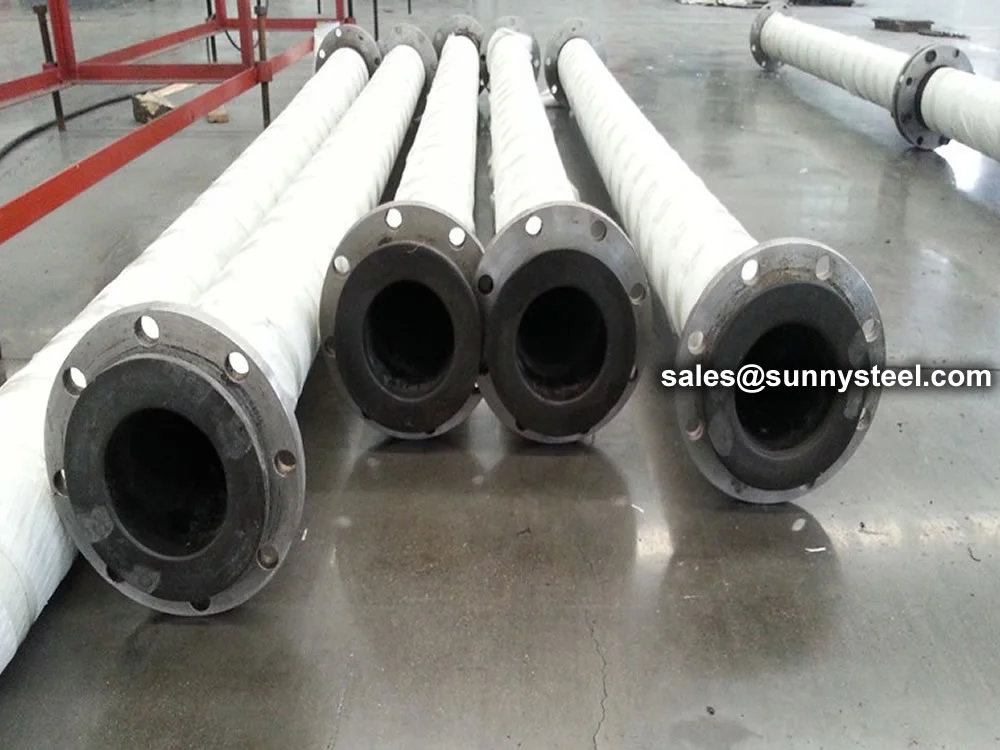
- Connect UHMWPE dredging pipe with floaters and rubber hoses.
- Each 12-meter pipe section requires 3 pairs of floaters for proper buoyancy.
- Every three pipe sections should be connected to one rubber hose to buffer distortion caused by wind and wave action.
Key Advantages of UHMWPE Dredging Pipe
High Wear Resistance
4–7× that of Q235 steel and 2.7× that of 16Mn steel. Increases pipe flow rate and improves transmission efficiency by over 20%.
Superior Impact Resistance
5× that of HDPE, 2× PC, and 10× PTFE. Resists heavy water hammer impact during pump starts.
Energy Efficient
Low friction coefficient (0.009 vs. 0.013 for steel). Saves up to 25% in energy with same flow rate.
Anti-Scaling
Inner wall roughness of 0.00022 ensures no scaling, eliminating the need for acid cleaning.
High Flexibility
Elongation ≥ 350%. Adapts to crustal settlement and seismic areas without cracking.