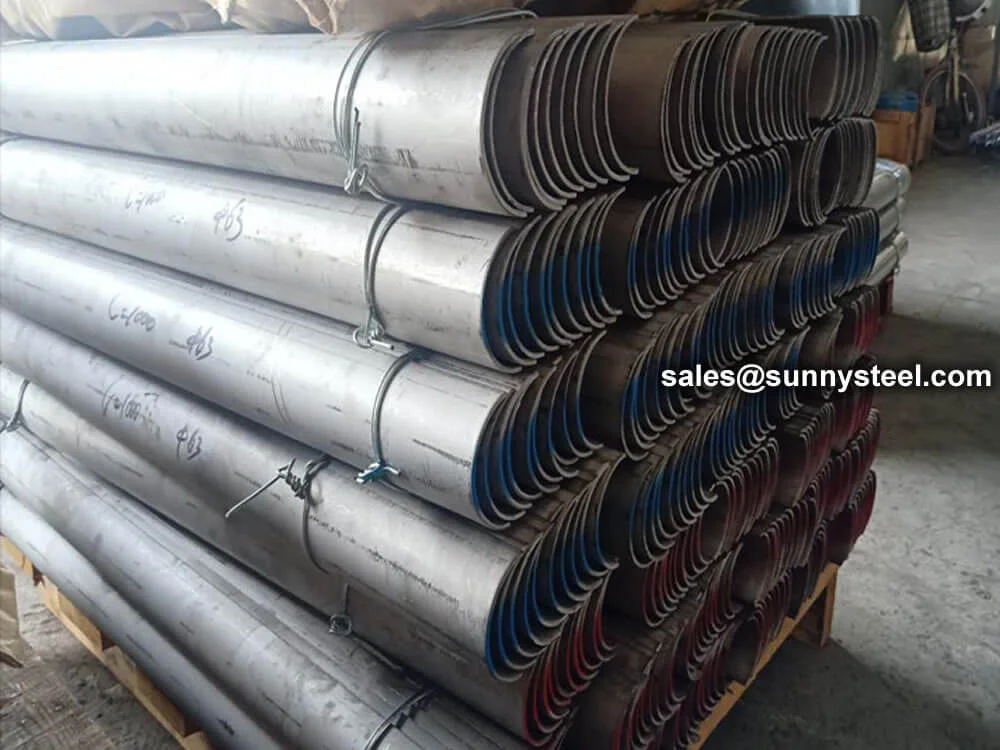

Corrosion-resistant Protection For Industrial Boiler Tubes
304 stainless tube shields provide effective erosion and corrosion protection for boiler tubes in high-temperature, humid, and chemically active industrial environments.
Corrosion-resistant Protection For Industrial Boiler Tubes
304 stainless tube shields provide effective erosion and corrosion protection for boiler tubes in high-temperature, humid, and chemically active industrial environments.
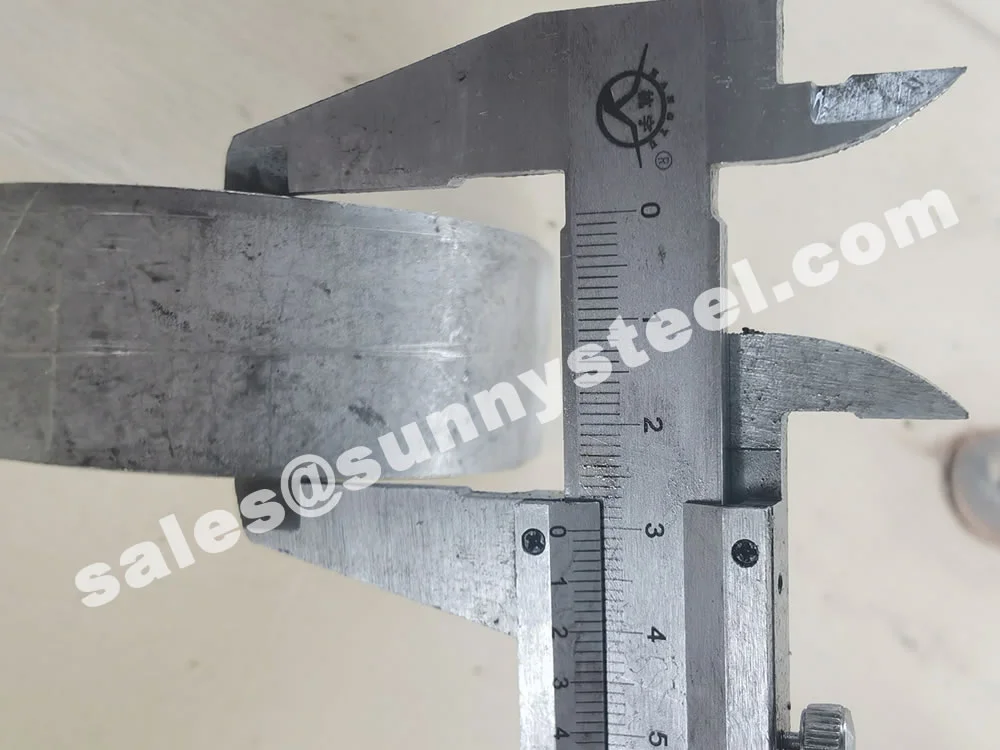
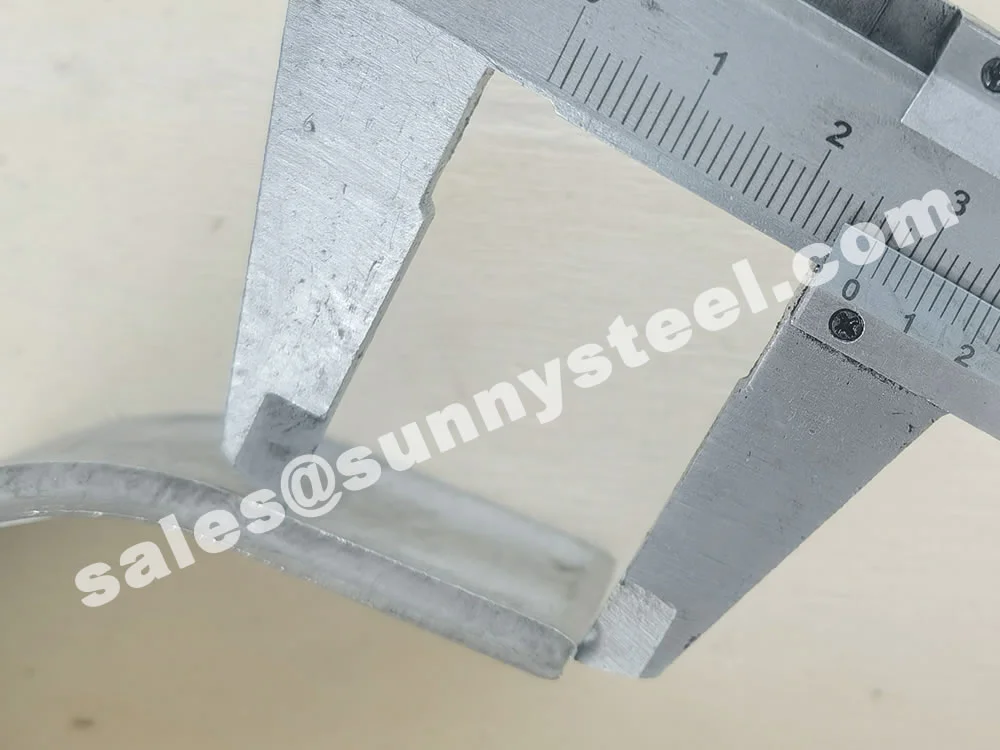
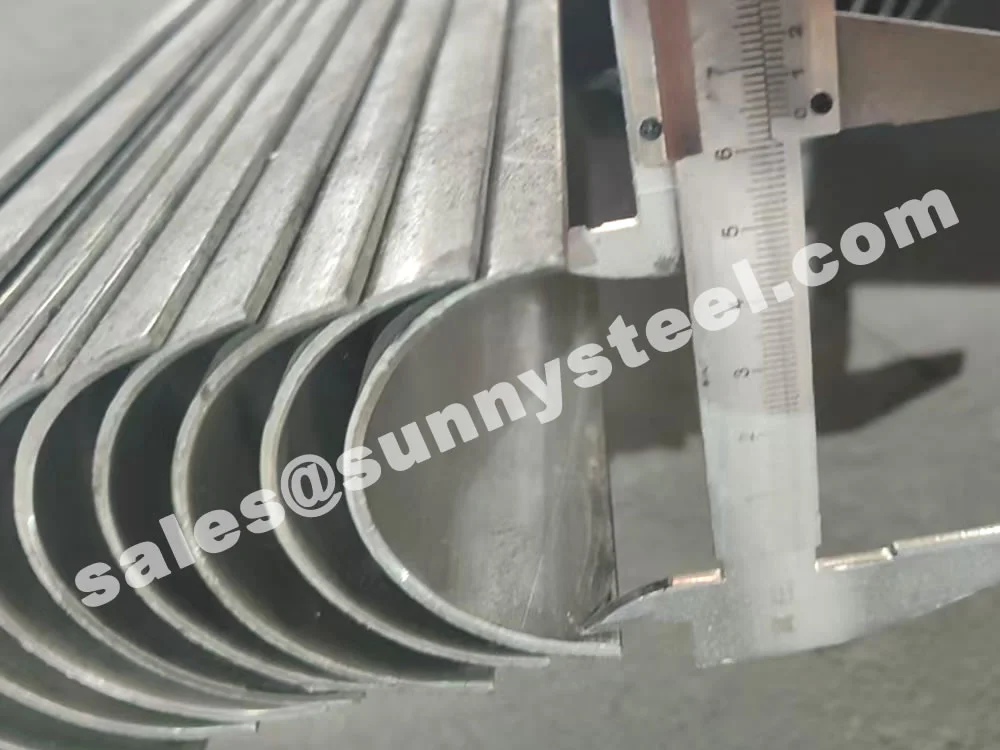
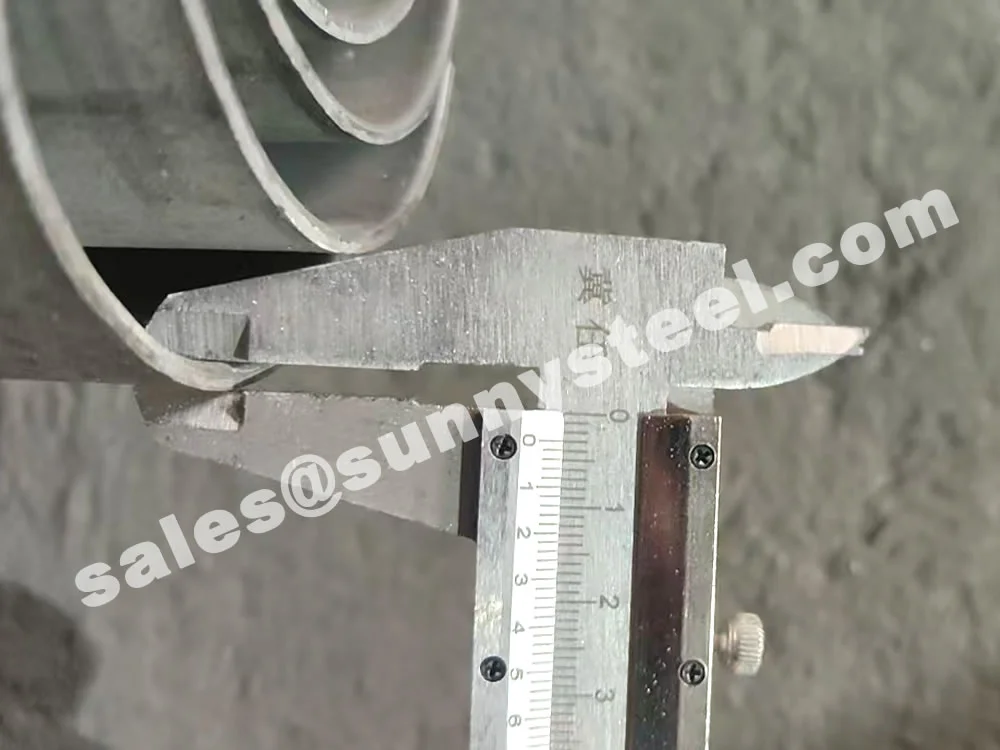


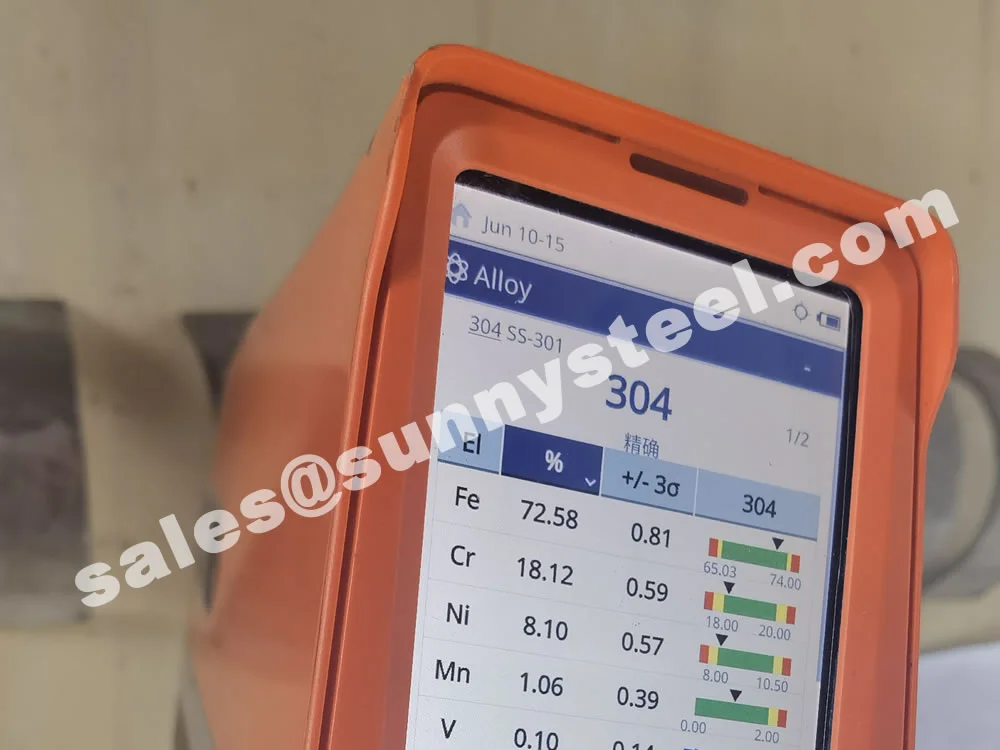



304 Stainless Tube Shields are robust protective components fabricated from SS304, the most widely used austenitic stainless steel grade. These shields are engineered to protect boiler tubes and heat-exposed pipe surfaces from mechanical erosion, flue gas abrasion, and chemical corrosion—especially in power generation, waste heat recovery, and petrochemical applications.
SS304 contains approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel, providing excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion in moist or mildly acidic environments. This makes it ideal for shielding tube surfaces subject to flue gas flow, ash erosion, and steam-side oxidation.
SS304 tube shields offer an ideal balance between cost-efficiency and protective performance. While they may not provide the extreme heat resistance of specialty alloys like 1Cr25Ni20Si2, they are more than sufficient in environments involving moderate temperatures and humid flue gas conditions. They extend boiler tube service life, minimize erosion damage, and reduce overall maintenance intervals.
Due to their excellent workability and weldability, SS304 shields are easy to fabricate, install, and replace—making them a go-to solution for general industrial boiler systems where routine protection is critical for operational efficiency and safety.
There are hundreds of different grades of stainless steel on the market. Each formulation offers enhanced corrosion resistance over plain carbon steel. Grade 304, 304L, and 304H are chemically similar but vary in carbon content, impacting their strength and weldability.
The similarity in naming can lead to confusion, especially between 304 and 304L. Understanding their composition and application is key.
| Element | Grade | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 304L | 304H | |
| Carbon (C) | 0.08 | 0.030 | 0.04 – 0.10 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 18.00 – 20.00 | 18.00 – 20.00 | 18.00 – 20.00 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 8.00 – 10.50 | 8.00 – 12.00 | 8.00 – 10.50 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Grade | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (0.2%, N/mm²) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Annealed | 500–700 | 195 | 40 |
| 304L Annealed | 460–680 | 180 | 40 |
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8 g/cm³ | 0.289 lb/in³ |
| Property | Metric | Imperial | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness, Brinell | 123 | 123 | Converted from Rockwell B |
| Hardness, Knoop | 138 | 138 | Converted from Rockwell B |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 70 | 70 | |
| Hardness, Vickers | 129 | 129 | Converted from Rockwell B |
| Tensile Strength, Ultimate | 505 MPa | 73,200 psi | |
| Tensile Strength, Yield | 215 MPa | 31,200 psi | 0.2% offset |
| Elongation at Break | 70% | 70% | in 50 mm |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 193 – 200 GPa | 28,000 – 29,000 ksi | |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.29 | 0.29 | |
| Charpy Impact | 325 J | 240 ft-lb | |
| Shear Modulus | 86 GPa | 12,500 ksi |
| Property | Value (Metric) | Value (Imperial) | Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | 7.2 × 10⁻⁵ Ω·cm | 7.2 × 10⁻⁵ Ω·cm | At 20°C; increases at 650°C |
| Magnetic Permeability | 1.008 | 1.008 | At room temperature |
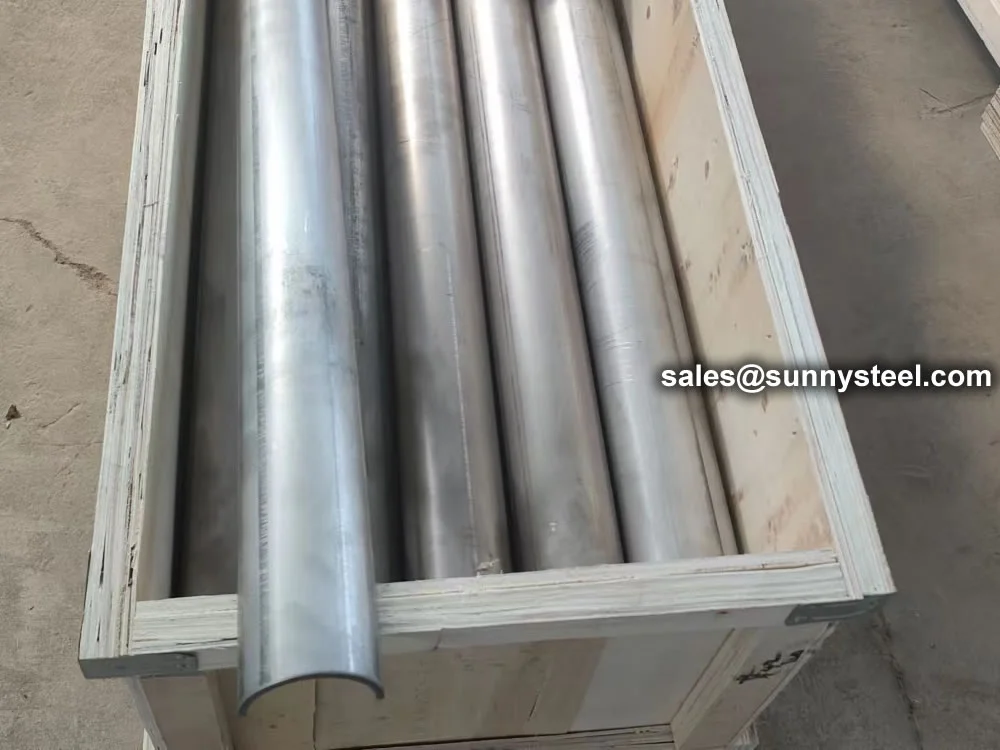

Ss 309 shields protect boiler tubes from erosion a...
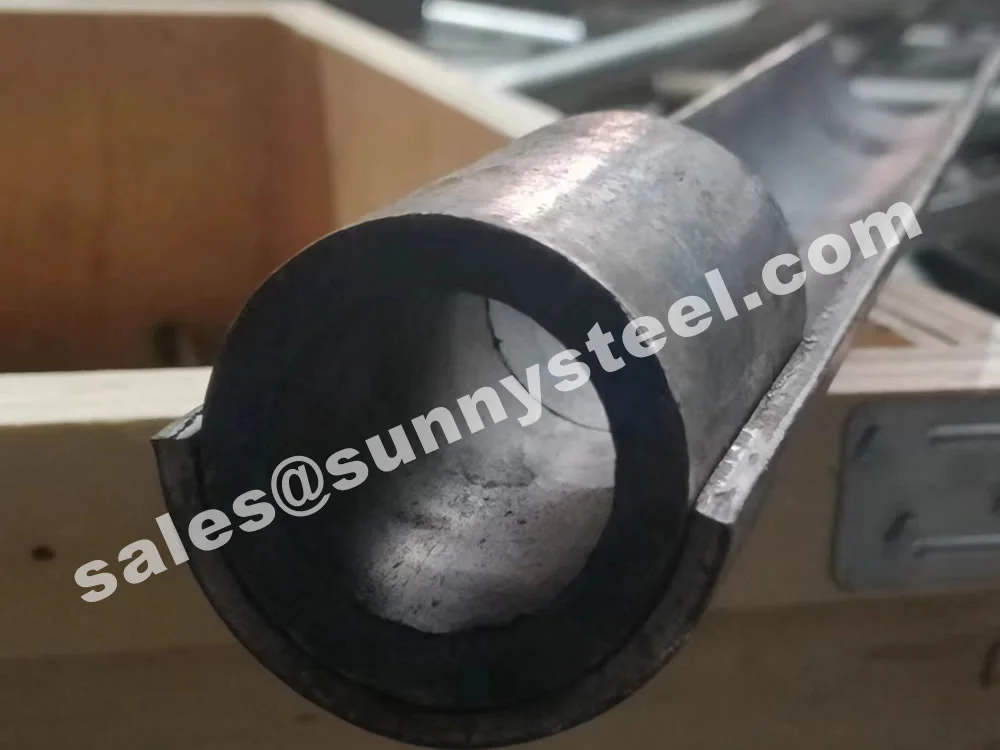

Q235 tube shields offer reliable and economical er...
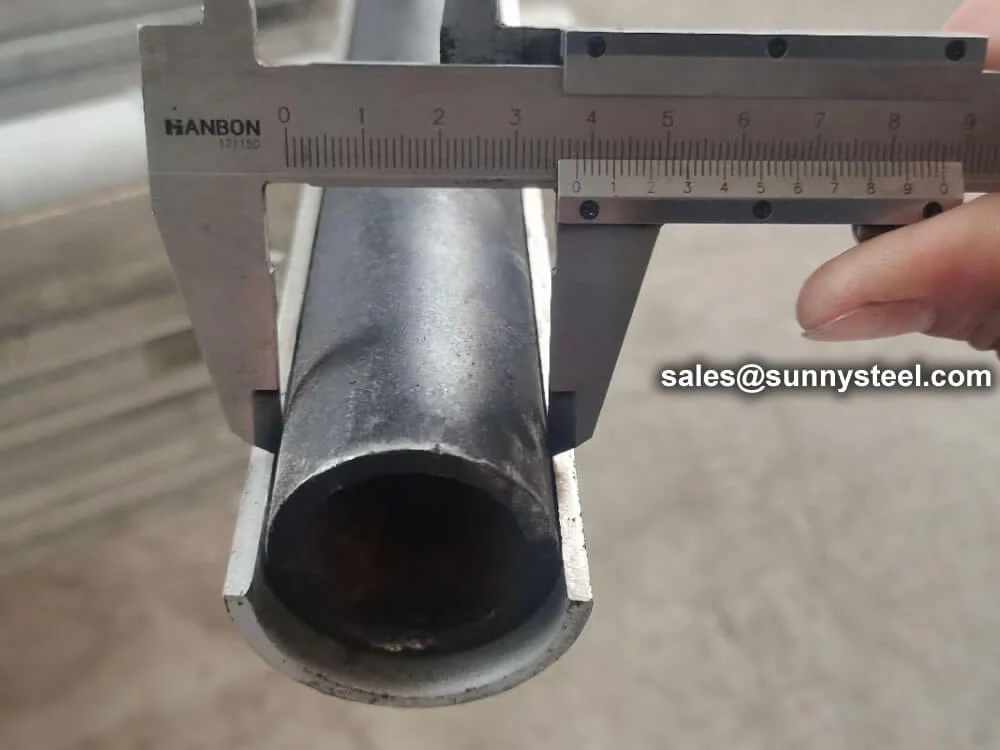

1cr18ni9ti tube shields offer excellent resistance...
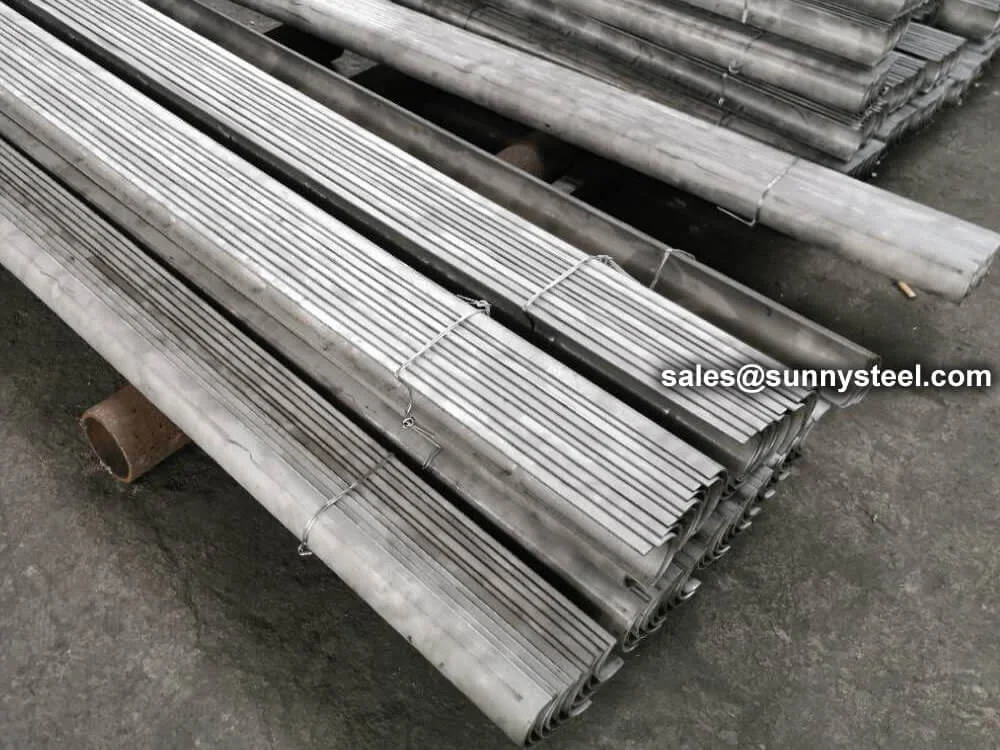

316 stainless steel tube shields protect boiler tu...
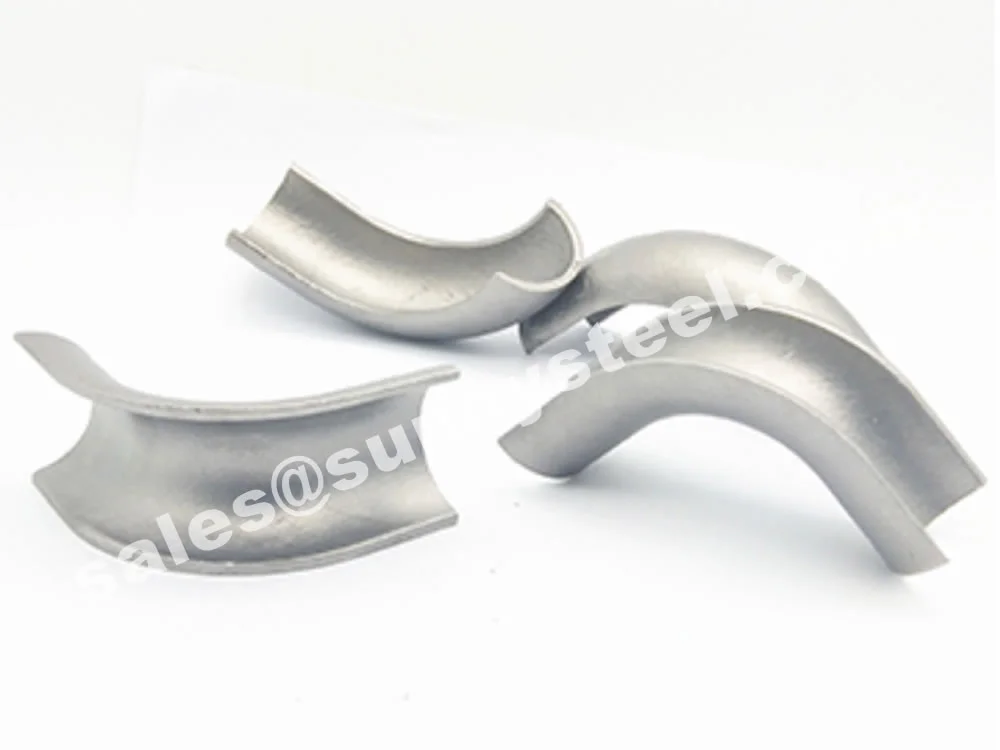

Premium 316l stainless steel tube shields provide ...