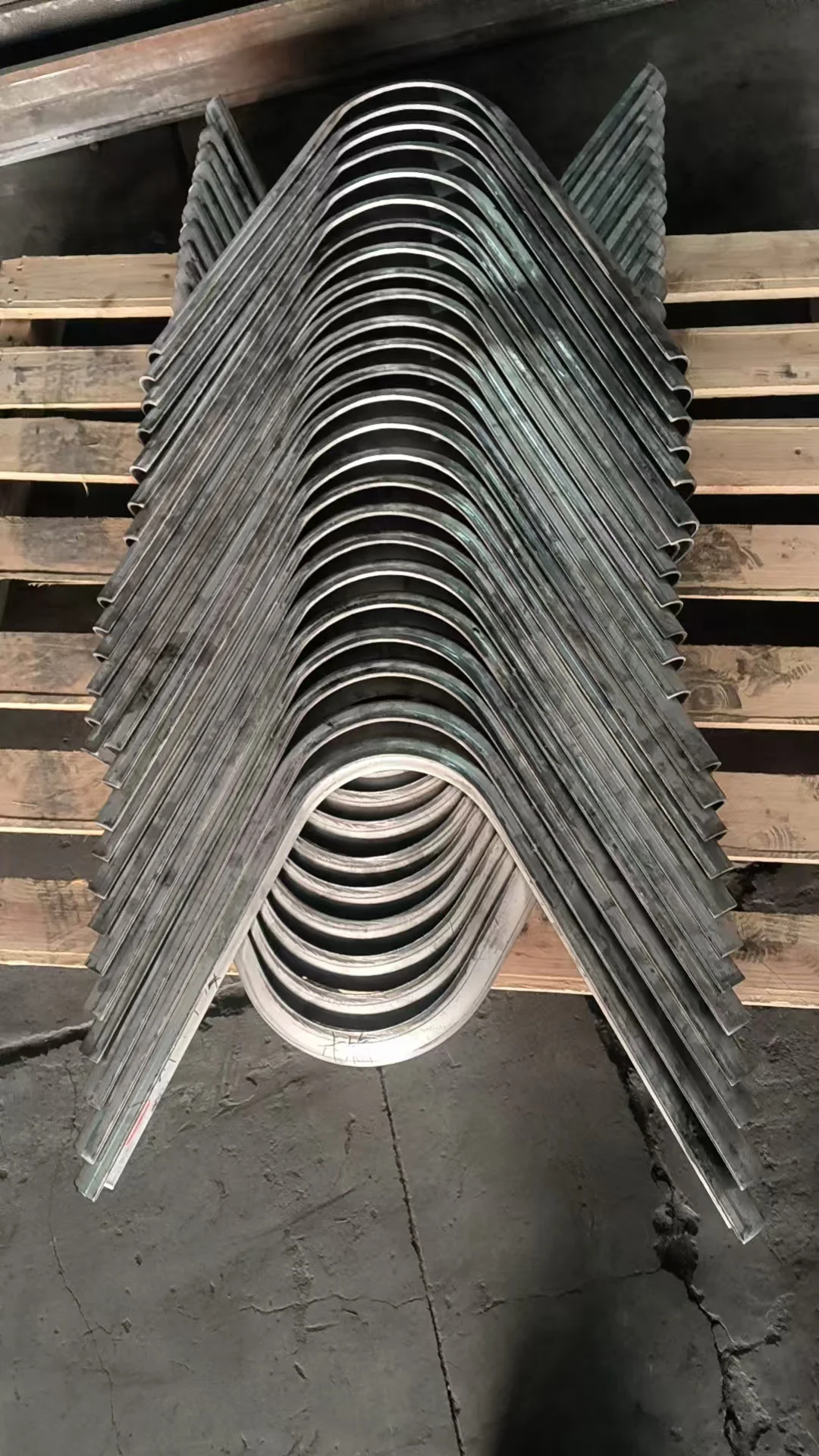
Protection For Boiler And Heat Exchanger Elbow Sections
Bend tube shields are curved protective sleeves that prevent erosion and corrosion in boiler and heat exchanger elbow sections.
Protection For Boiler And Heat Exchanger Elbow Sections
Bend tube shields are curved protective sleeves that prevent erosion and corrosion in boiler and heat exchanger elbow sections. custom-formed for precise fit and lasting durability.
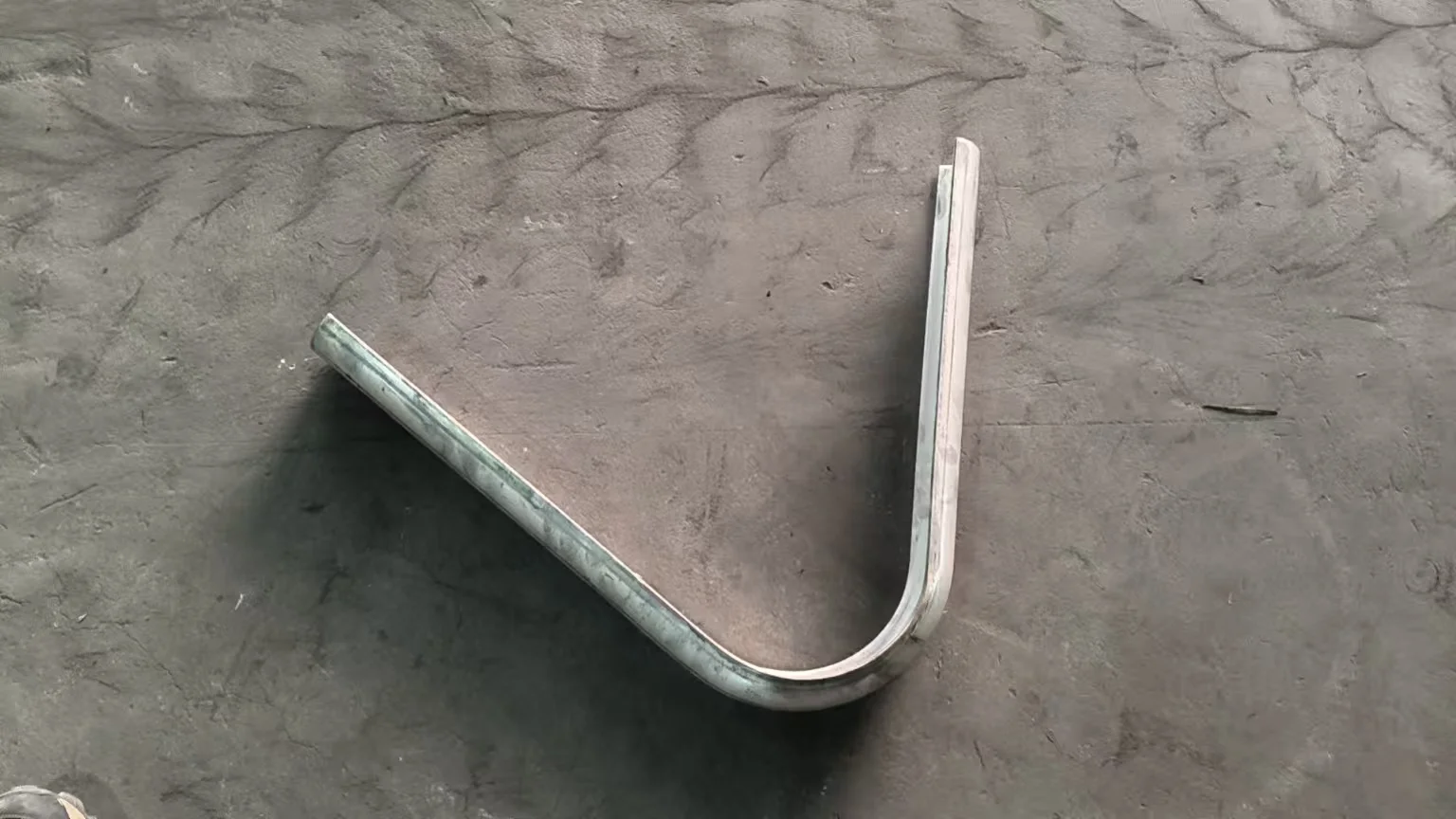
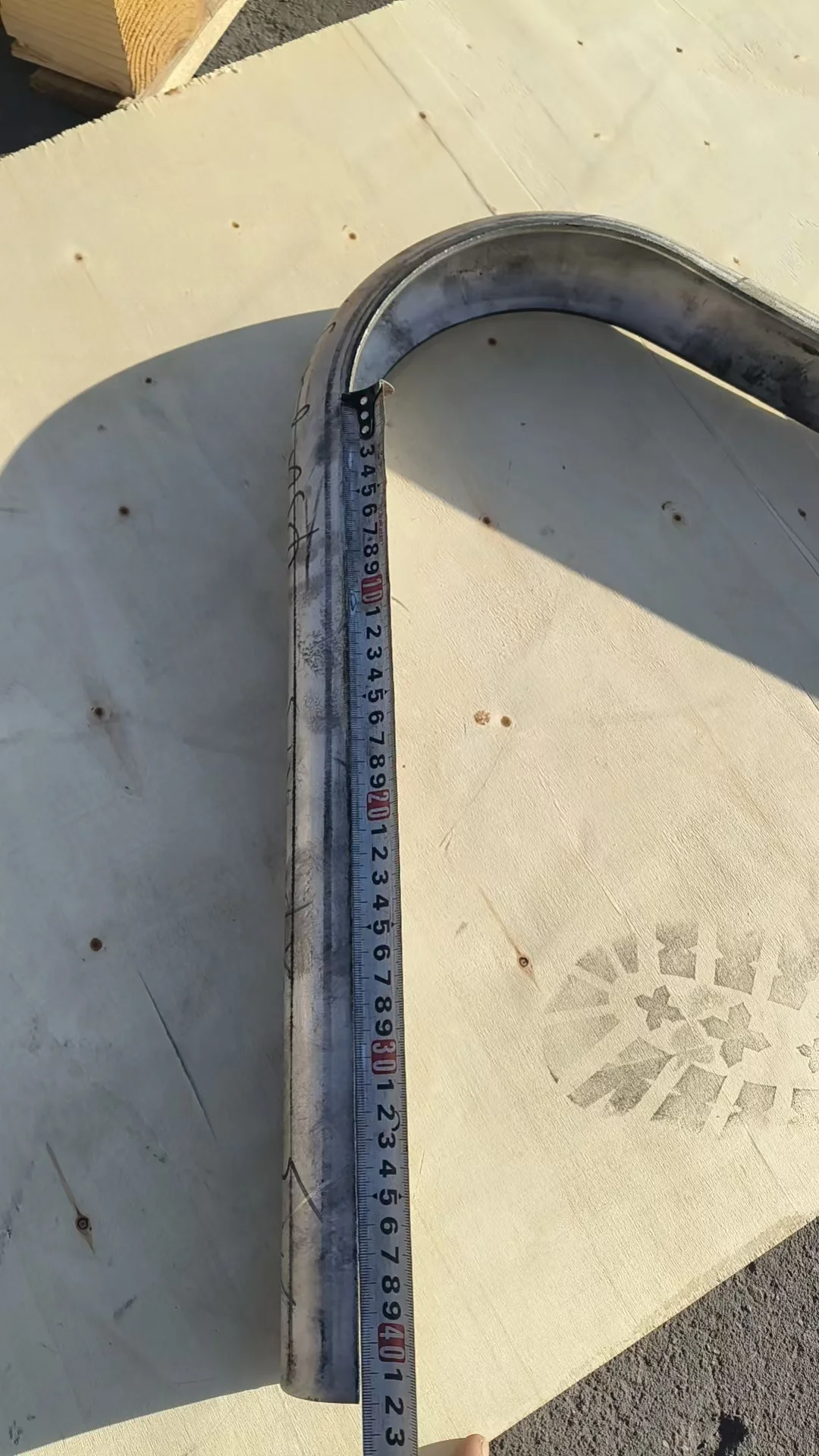







Bend Tube Shields are precision-engineered sleeves designed to protect curved, elbowed, or bent sections of boiler tubes and heat exchanger pipes. These vulnerable areas often face flue gas erosion, ash impact, and corrosion due to directional flow changes and high-temperature fluctuations.
Fabricated from corrosion- and heat-resistant alloys such as 304, 316, 1Cr13, 310S, and Cr25Ni20, these shields are CNC-formed or rolled to match tube curvature. They are ideal for use in power stations, petrochemical refineries, and waste-to-energy facilities.
| Application Area | Exposure Type | Suggested Material |
|---|---|---|
| Superheater Tube Elbows | High-velocity flue gas erosion | 310S / Cr25Ni20 |
| Economizer Return Bends | Ash + Moisture Attack | 1Cr13 / 304 |
| Preheater Curved Tubes | Thermal Cycling | 304H / 316L |
| Marine Boiler Turns | Salt-laden Exhaust | 316L / Duplex |
| Waste Gas Path Bends | Corrosive + Dusty Flows | Cr25Ni20 / Inconel |
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Form | U-type, segmented wrap, or saddle-fit |
| Thickness Range | 1.2 mm – 3.0 mm |
| Radius Compatibility | Custom-fit based on drawing or tube sample |
| Material Grades | 304, 316, 1Cr13, 310S, Cr25Ni20, Inconel |
| Attachment Options | Spot weld, clamp, full weld, band-fastening |
| Finish Options | Pickled, passivated, sandblasted |
Technical specifications including chemical composition, mechanical and thermal properties.
| Grade | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS 309 | 0.20 max | 2.0 max | 0.75 max | 0.045 max | 0.030 max | 22.0 – 24.0 | 12.0 – 15.0 | Balance |
| SS 309S | 0.08 max | 2.0 max | 0.75 max | 0.045 max | 0.030 max | 22.0 – 24.0 | 12.0 – 15.0 | Balance |
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8 g/cm3 | 0.289 lb/in3 |
| Melting Point | 1455°C | 2650°F |
Physical properties of SS 309 stainless steels, including density, thermal expansion, and specific heat.
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 620 MPa | 89,900 psi |
| Yield Strength (0.2%) | 310 MPa | 45,000 psi |
| Izod Impact | 120–165 J | 88.5–122 ft-lb |
| Shear Modulus | 77 GPa | 11,200 ksi |
| Elastic Modulus | 200 GPa | 29,008 ksi |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.27 – 0.30 | 0.27 – 0.30 |
| Elongation at Break | 45% | 45% |
| Hardness, Brinell | 147 | 147 |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 85 | 85 |
| Hardness, Vickers | 169 | 169 |
| Property | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient (0–100°C) | 14.9 μm/m·°C | 8.28 μin/in·°F |
| Thermal Conductivity (0–100°C) | 15.6 W/m·K | 108 BTU in/hr·ft²·°F |
| Standard 1 | Standard 2 | Standard 3 | Standard 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A167 | ASME SA249 | ASTM A314 | ASTM A580 |
| ASTM A249 | ASME SA312 | ASTM A358 | FED QQ-S-763 |
| ASTM A276 | ASME SA358 | ASTM A403 | FED QQ-S-766 |
| ASTM A473 | ASME SA403 | ASTM A409 | MIL-S-862 |
| ASTM A479 | ASME SA409 | ASTM A511 | SAE J405 (30309) |
| DIN 1.4828 | ASTM A312 | ASTM A554 | SAE 30309 |
| 309 | 309S | 309H |
|---|---|---|
| UNS S30900 | UNS S30908 | UNS S30909 |
| ASTM A240 | ASTM A240 | ASTM A240 |
| ASTM A480 | ASTM A480 | ASTM A480 |
| ASME SA240 | ASME SA240 | ASME SA240 |
| AMS 5523 | AMS 5523 | AMS 5523 |
Manufactured to exacting standards using high-pressure pressing technology
Advanced equipment and precision moulds ensure optimal welding performance, smooth surfaces, and rapid turnaround times [[2, 5]].
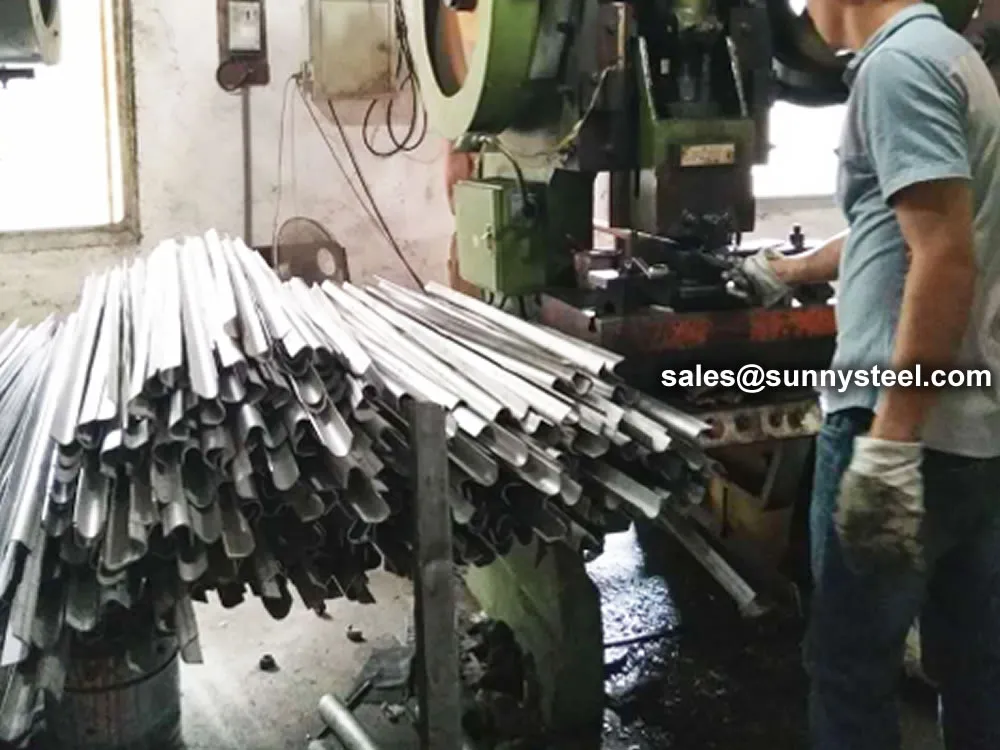

Arc-shaped wear-resistant tiles are formed using specialized moulds on high-pressure presses or pipe benders [[2, 9]].
This process delivers:

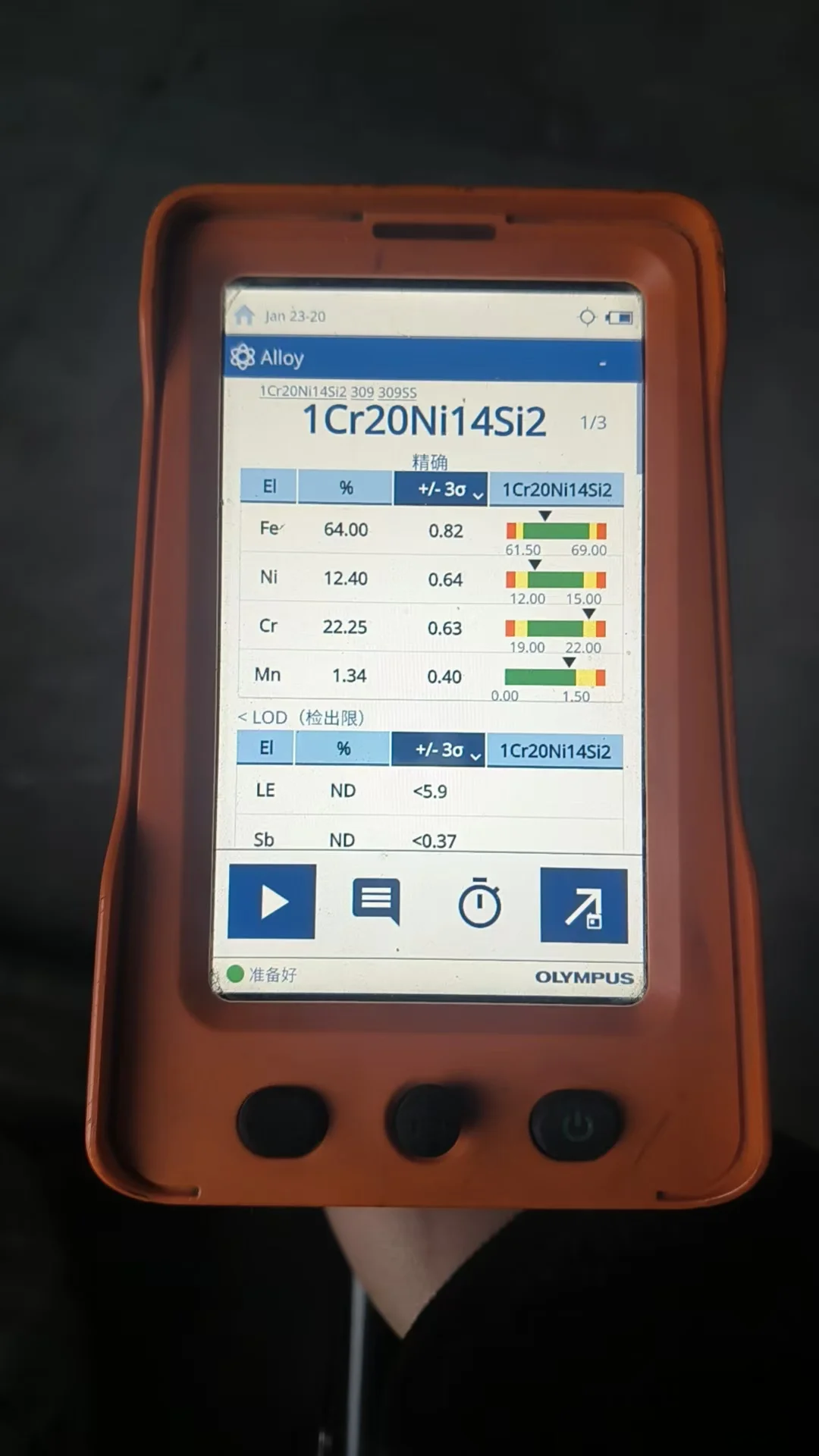
Positive Material Identification (PMI) testing verifies stainless steel composition before production, ensuring compliance with API 578 standards [[1, 3]].
Raw materials are sourced directly from certified steel mills with Mill Test Certificates (MTC). Excess material is repurposed into snap rings for zero-waste manufacturing [[5, 15]].
Explore detailed material grades, dimensional standards, and configuration types for stainless steel tube shields used in high-temperature boiler environments.
Boiler tube erosion shields are manufactured using heat- and corrosion-resistant alloys for superior durability in demanding thermal systems such as superheaters, economizers, and reheaters.
| Material Grade | Operating Temp | Chromium (%) | Nickel (%) | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS 304 | Up to 600°C | 18% | 8% | General boiler protection |
| SS 316 | Up to 650°C | 16–18% | 10–14% | Corrosive steam systems |
| SS 309 | Up to 750°C | 22–24% | 12–15% | High-temp gas zones |
| SS 310S | Up to 1000°C | 24–26% | 19–22% | Extreme flue gas exposure |
| SS 310 | Up to 1200°C | 24–26% | 19–22% | Aggressive chemical plants |
| Carbon Steel | Up to 1400°C | 26–28% | 22–25% | High-temperature gas systems |
| Inconel 600 | Up to 1200°C | 15% | 72% | Aggressive chemical plants |
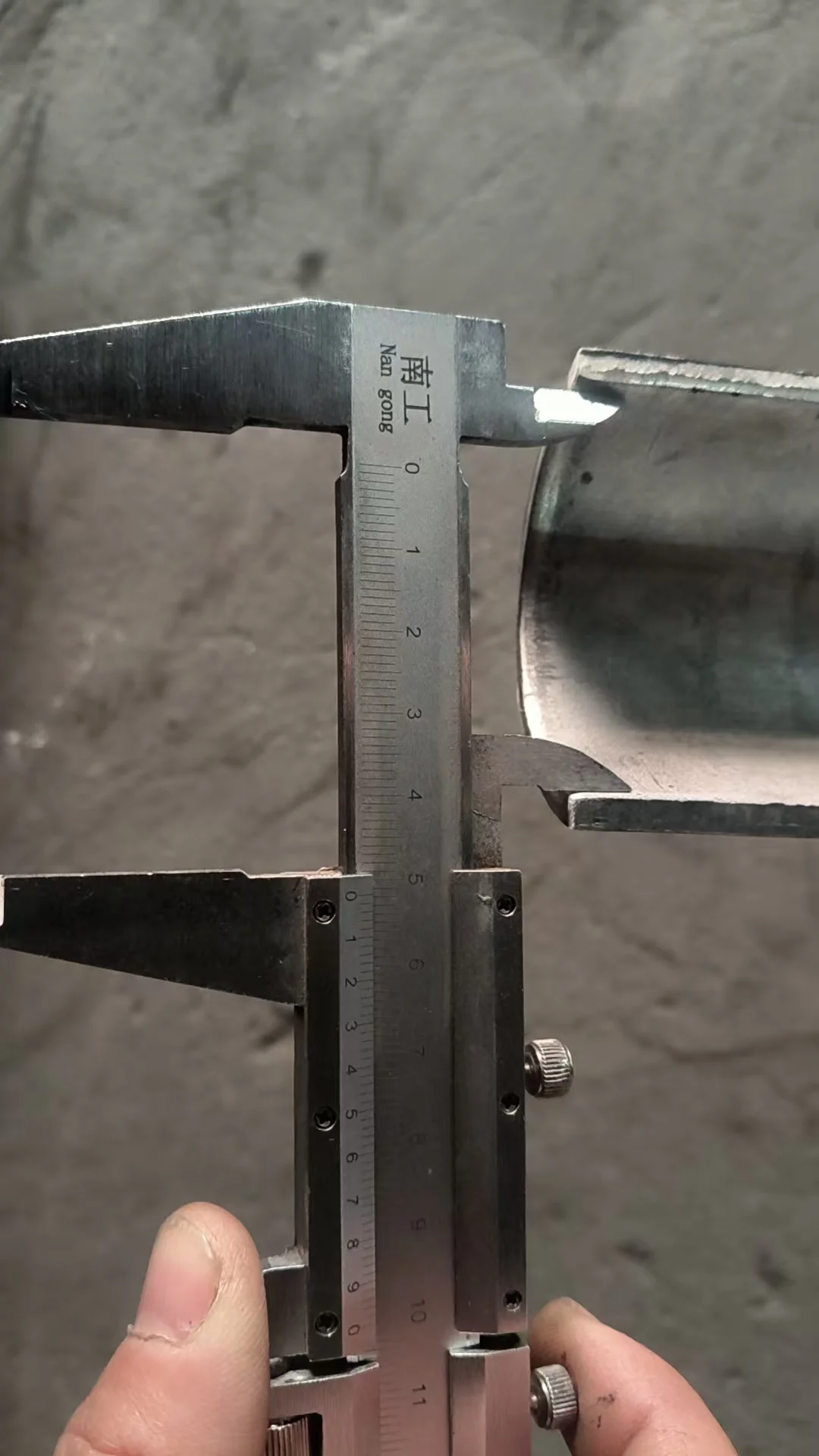
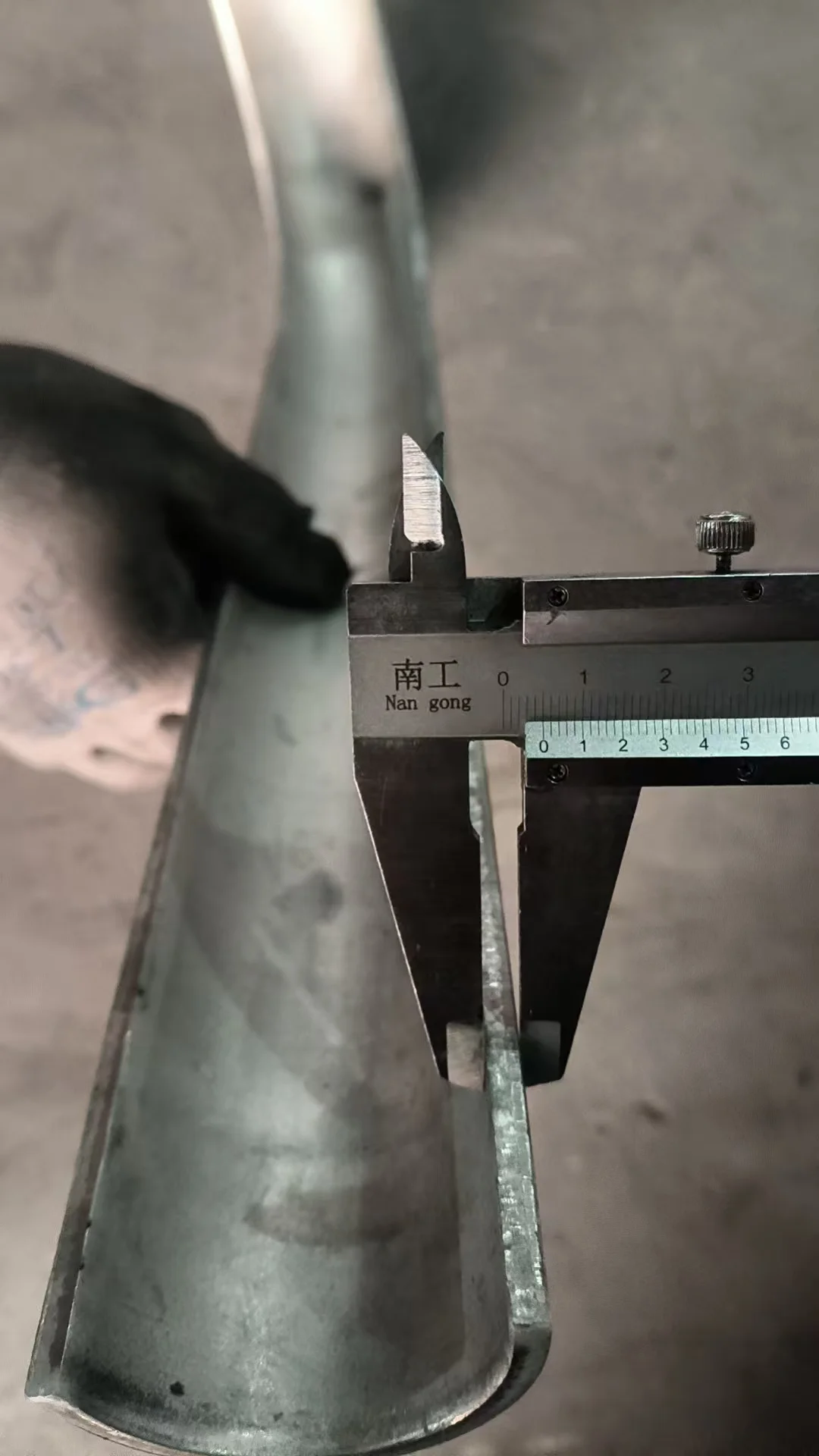
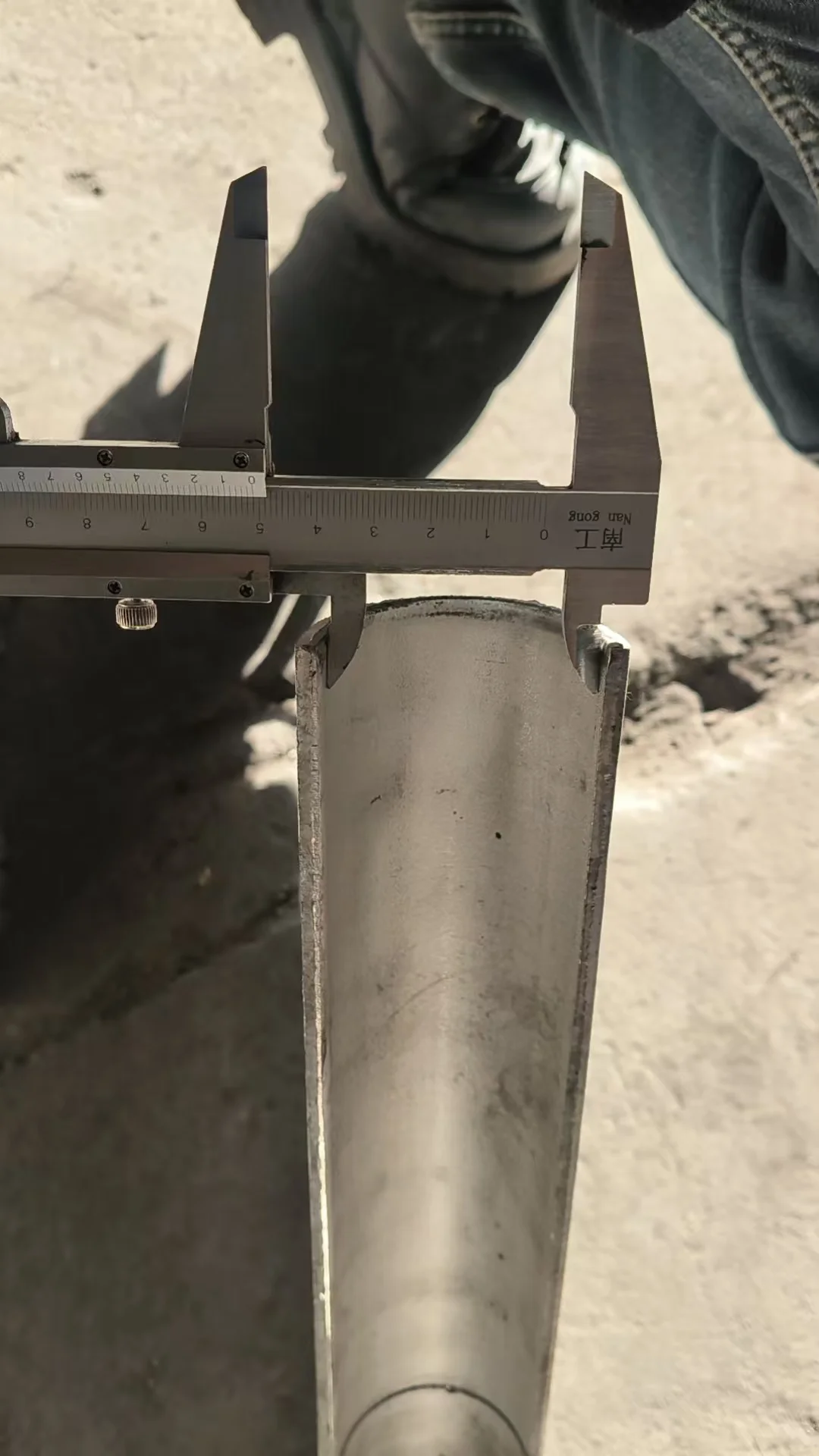
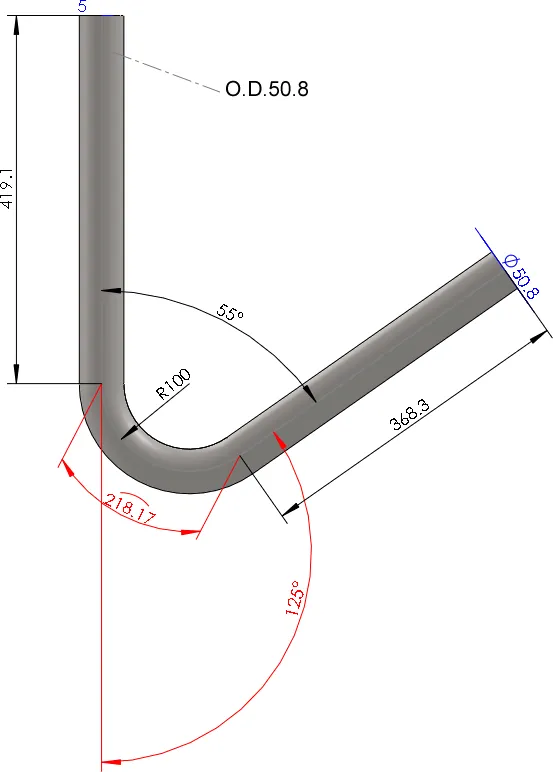
Tube erosion shields are precision-engineered to match a wide range of pipe diameters and curvature profiles, ensuring exact fit and reliable performance in erosive gas flows.
| Specification | Standard Range | Common Sizes | Customization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tube Outer Diameter | 32–89mm | 38, 42, 48, 51, 57, 63.5, 76mm | Other diameters available |
| Shield Length | 20–3000mm | 1000–2000mm | As per project requirement |
| Shield Thickness | 2–5mm | 3mm, 4mm | Based on wear conditions |
| Coverage Angle | 120°–240° | 180° (Semi-circular) | Tailored arcs for complex bends |
| Shield Clearance | 1–3mm | 2mm typical | For thermal expansion fit |
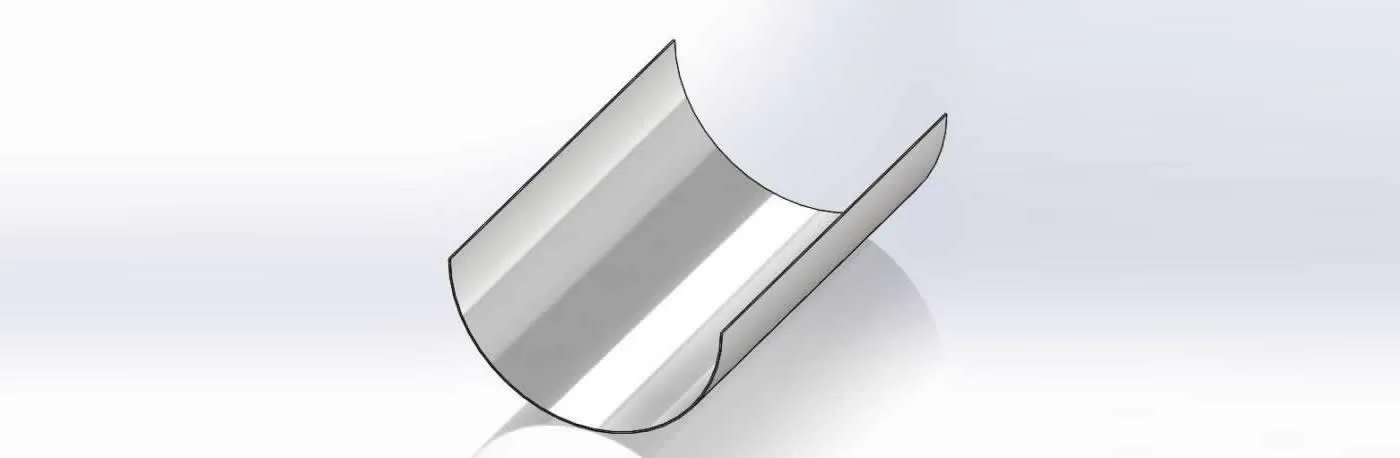
Tube erosion shields are precision-engineered to fit straight sections, tube bends, finned pipes, and other complex geometries, providing long-term protection in high-wear boiler zones.
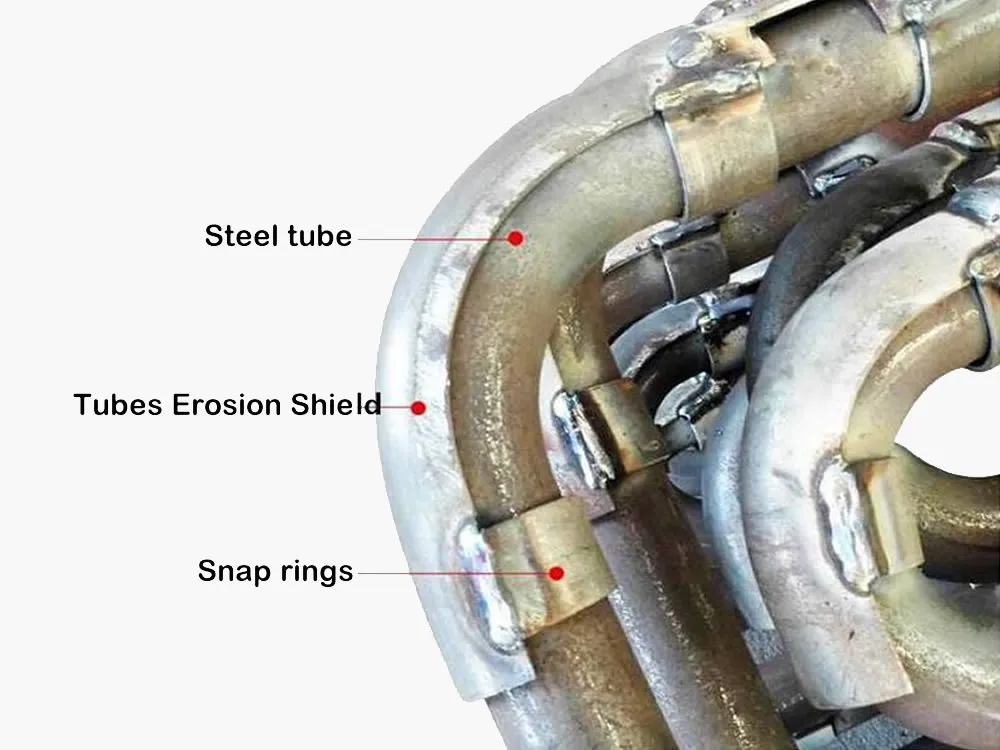
Also known as anti-wear plates, anti-corrosion shields, boiler tube protection covers, or snap-on climbing plates, these components are typically paired with snap rings to ensure firm and efficient installation on boiler surfaces.
Each erosion shield is manufactured using a high-pressure pressing process with precision moulds. The result is a smooth surface finish, excellent weldability, and strong attachment performance without risk of separation under thermal stress.
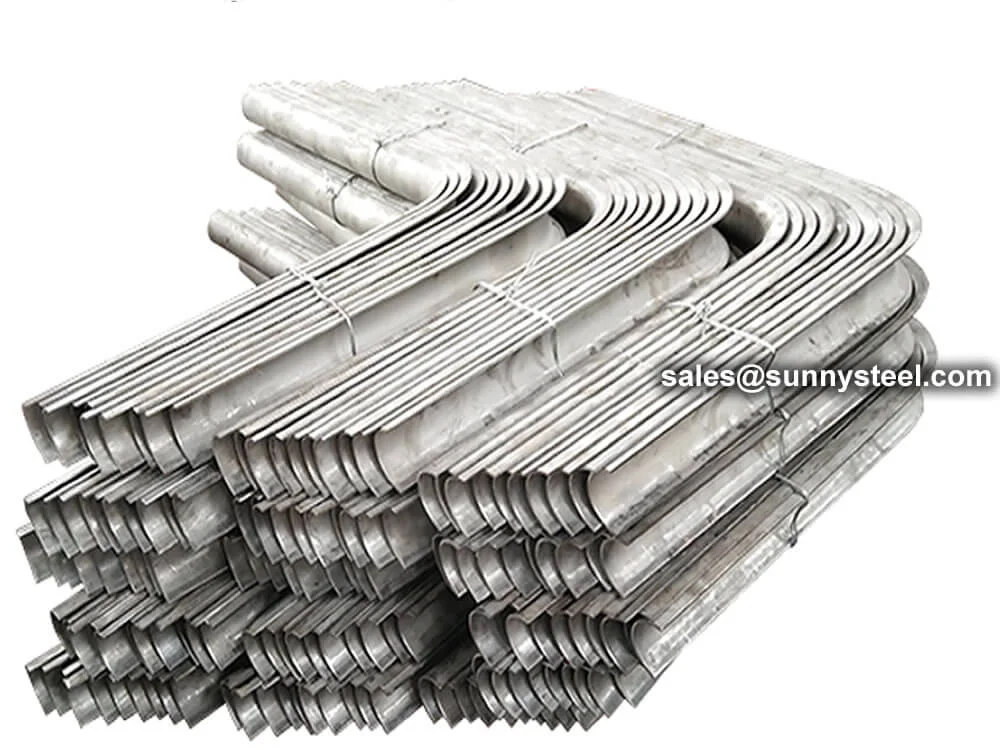
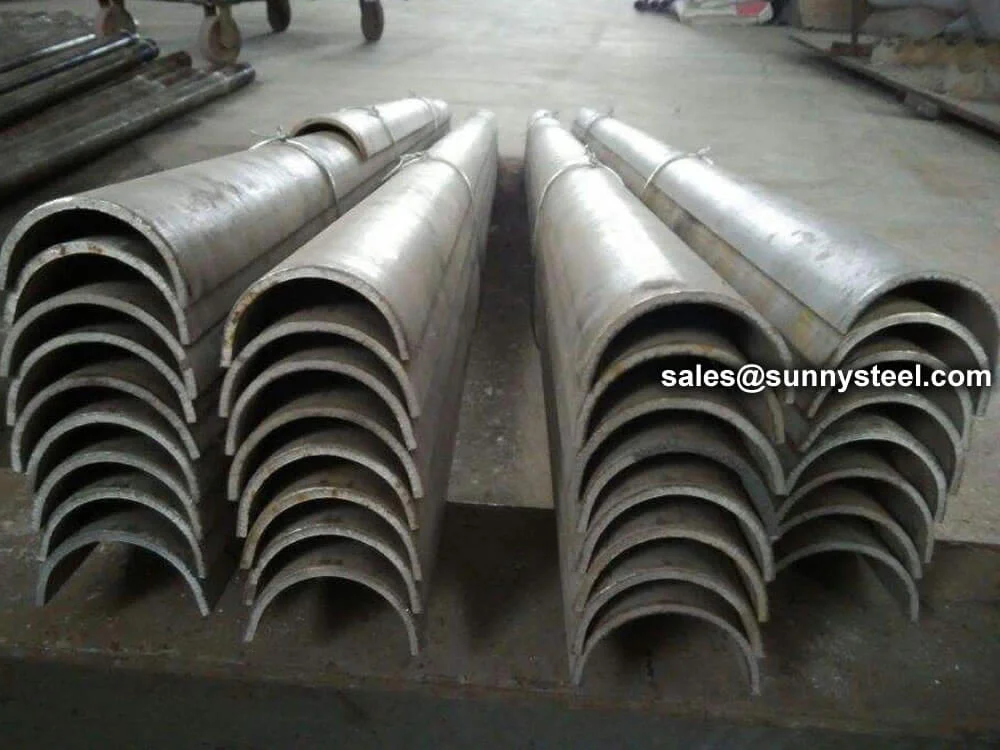
Curved tube shields are shaped using custom tube benders or formed under pressure, making them ideal for use in elbows, U-bends, and complex heat exchanger tube paths. The shields effectively absorb erosive wear from sootblowers, high-speed flue gas, and abrasive particles.
By preventing localized thinning and cracking, these shields significantly reduce boiler downtime, extend tube life, and lower maintenance costs, especially in CFB boilers, waste heat recovery systems, and coal-fired power plants.
Proper installation of boiler tube erosion shields is essential for preventing wear, prolonging service life, and avoiding critical failures like boiler explosions.
Erosion shields are installed primarily to protect the heating surfaces of boiler tubes from high-velocity flue gases and abrasive particles. They reduce wear and enhance heat transfer efficiency in high-stress environments such as CFB boilers and waste heat recovery units.
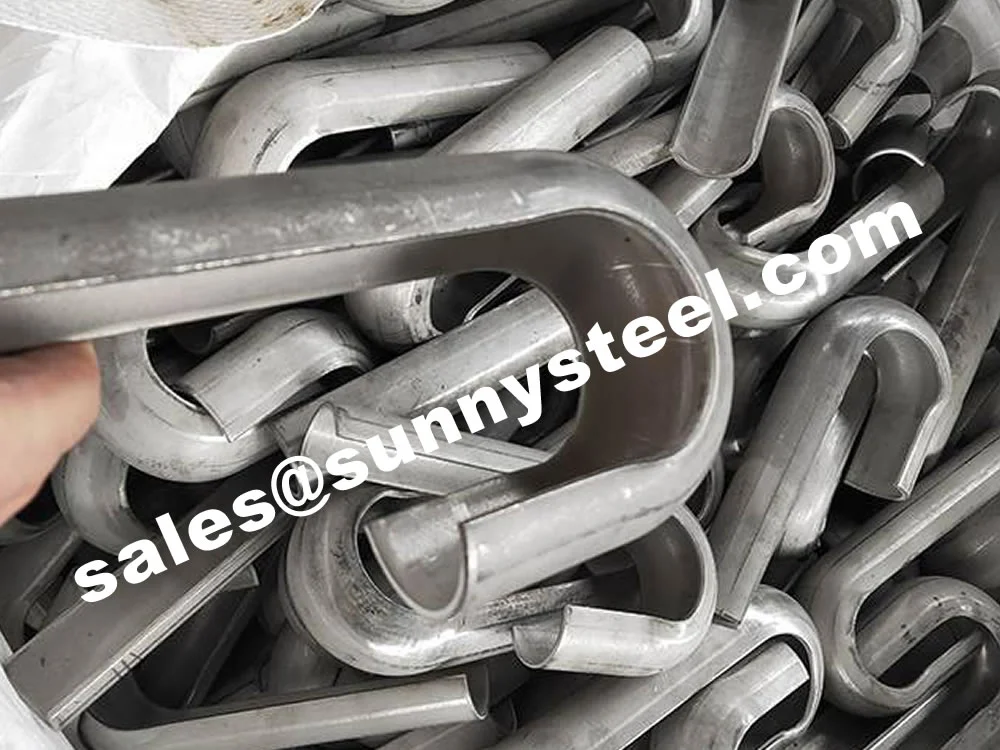
A snap ring is used to affix the erosion shield securely to the tube surface. It typically overlaps the shield slightly—usually with a 190°–200° arc—allowing it to clamp firmly while leaving space for welding. The ring width must be no less than 20mm for adequate support.
Each erosion shield requires 2–4 snap rings spaced at 200–500mm intervals. The rings and shield must be fully spot welded to prevent displacement from thermal expansion and vibrations during operation.
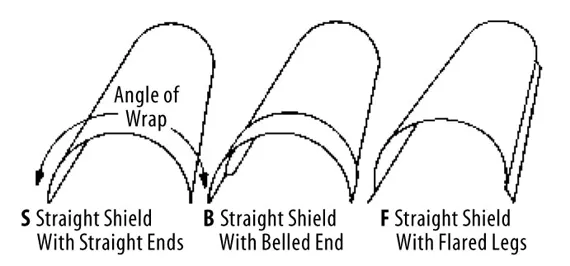
The installation procedure varies slightly for different shapes—straight, curved, or S-type. All joints must be secure, sealed, and aligned to ensure continuous protection without gaps.


Boiler tube erosion shields are typically attached using the following methods:
Yes,
we provide custom straight boiler tube shields based on customer requirements.
These can be tailored in shape, size, and material to suit specific boiler configurations.
Boiler tubes erosion shields protect critical boiler components from wear and corrosion, ensuring durability and efficiency across multiple industries.
Protects boiler tubes in coal-fired, natural gas, biomass, and waste-to-energy plants from abrasive flue gases and high temperatures.
Shields tubes in petrochemical, pulp and paper, food processing, and manufacturing boilers, reducing wear and maintenance costs.
Provides corrosion-resistant protection for marine boiler systems and offshore platform boilers in harsh, corrosive environments.
Enhances tube durability in gas turbine exhausts and industrial process systems, improving energy efficiency and longevity.
Reduces downtime with easy-to-install shields for straight, bent, and finned tubes, ensuring long-term boiler reliability.
Custom shields for unique boiler configurations, protecting against abrasive particles and high-pressure conditions.
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Coal-Fired Power Plants | Protects superheaters, reheaters, and economizers from abrasive ash and flue gas erosion. |
| Natural Gas Combined Cycle | Shields tubes in high-pressure boilers from wear caused by high-velocity gas flows. |
| Biomass Power Stations | Reduces tube wear in boilers handling abrasive biomass materials like wood chips. |
| Waste-to-Energy Plants | Protects tubes from corrosion and erosion in incineration and waste processing systems. |
| Petrochemical Facilities | Ensures durability of boiler tubes in high-temperature, corrosive chemical environments. |
| Pulp and Paper Mills | Shields boiler tubes from wear in steam generation systems for paper production. |
| Food Processing Plants | Protects steam boiler tubes from wear and corrosion in hygienic processing environments. |
| Marine Boiler Systems | Provides corrosion-resistant protection for tubes in harsh marine environments. |
| Offshore Platform Boilers | Ensures tube longevity in remote, corrosive offshore conditions with minimal maintenance. |
| Heat Recovery Steam Generators | Enhances tube life in systems recovering heat from gas turbine exhausts. |
| Industrial Process Exhausts | Protects tubes in waste heat recovery systems handling variable, abrasive exhausts. |
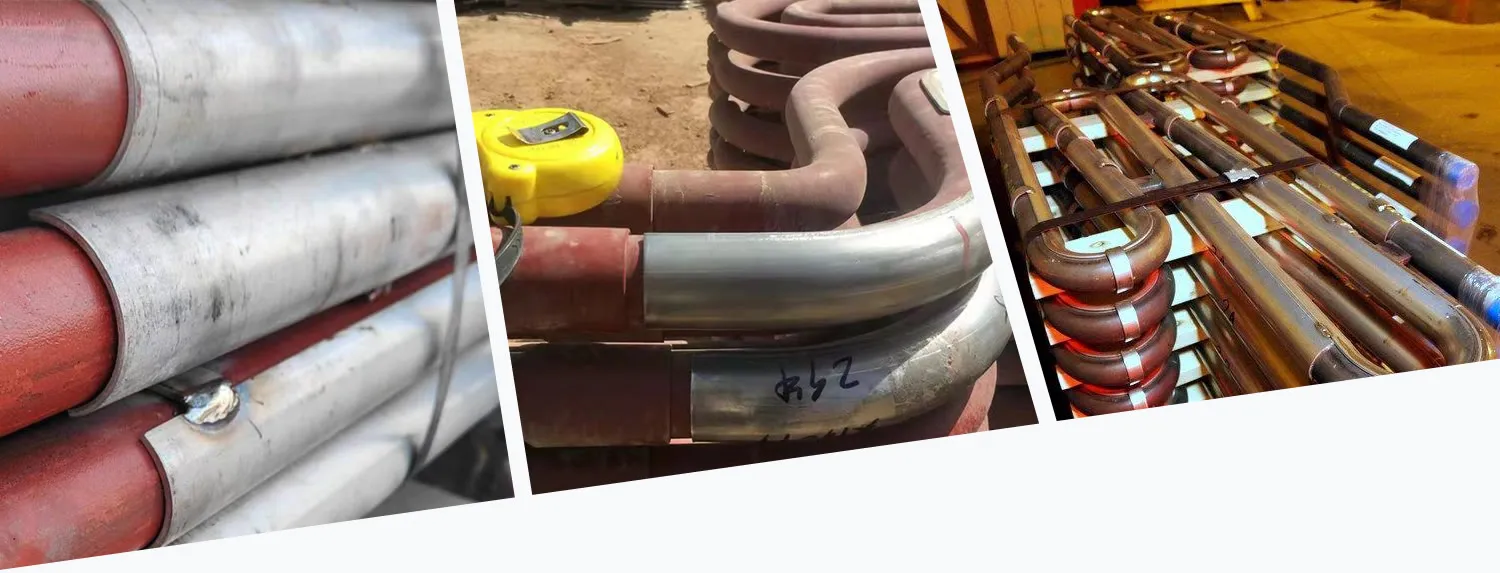

The service life of boiler tube erosion shields varies depending on boiler type and installation location.
Normally, shields last throughout one overhaul cycle (3–5 years). During major maintenance, shields are inspected and replaced if:
In sections such as superheaters and economizers, erosion shields are placed on the flue gas flow-facing side of the tubes to protect against high-temperature abrasion. Curved shields are essential for elbows and U-bends to prevent wear in circulating fluidized bed (CFB) boilers, where demand is increasing.
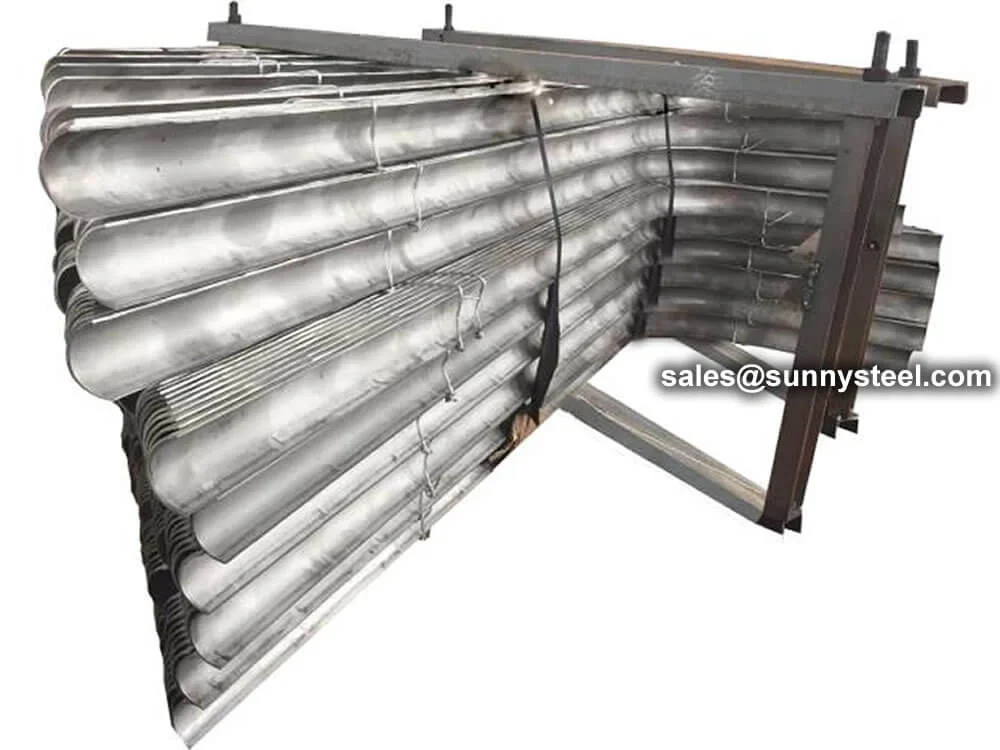

Outside-of-bend tube shields offer robust protecti...

Inside-of-bend tube shields protect the internal c...

U-type outer half-round tube shields offer robust ...

Custom straight tube shields are designed for boil...
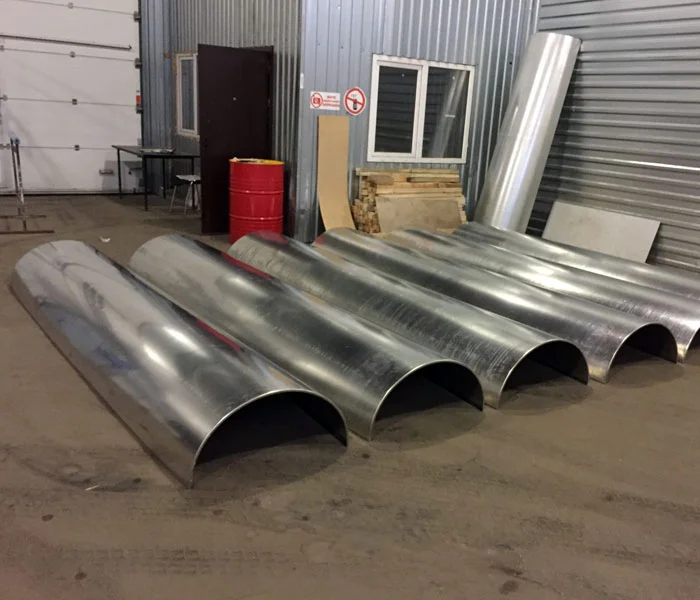

Custom curved tube shields are designed to protect...