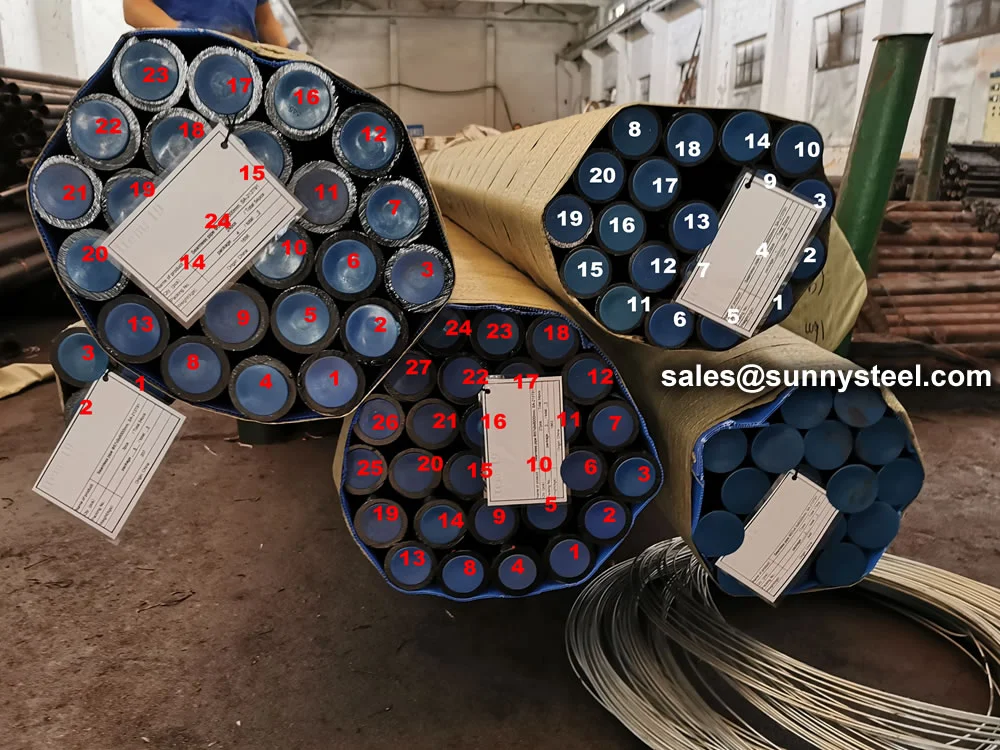

Astm A213 T91 Seamless Alloy Tube
Astm a213 t91 seamless alloy tubes offer superior creep strength and corrosion resistance, ideal for high-temperature applications in supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers, superheaters, and heat exchangers in power plants and petrochemical industries.
Astm A213 T91 Seamless Alloy Tube
Astm a213 t91 seamless alloy tubes offer superior creep strength and corrosion resistance, ideal for high-temperature applications in supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers, superheaters, and heat exchangers in power plants and petrochemical industries.
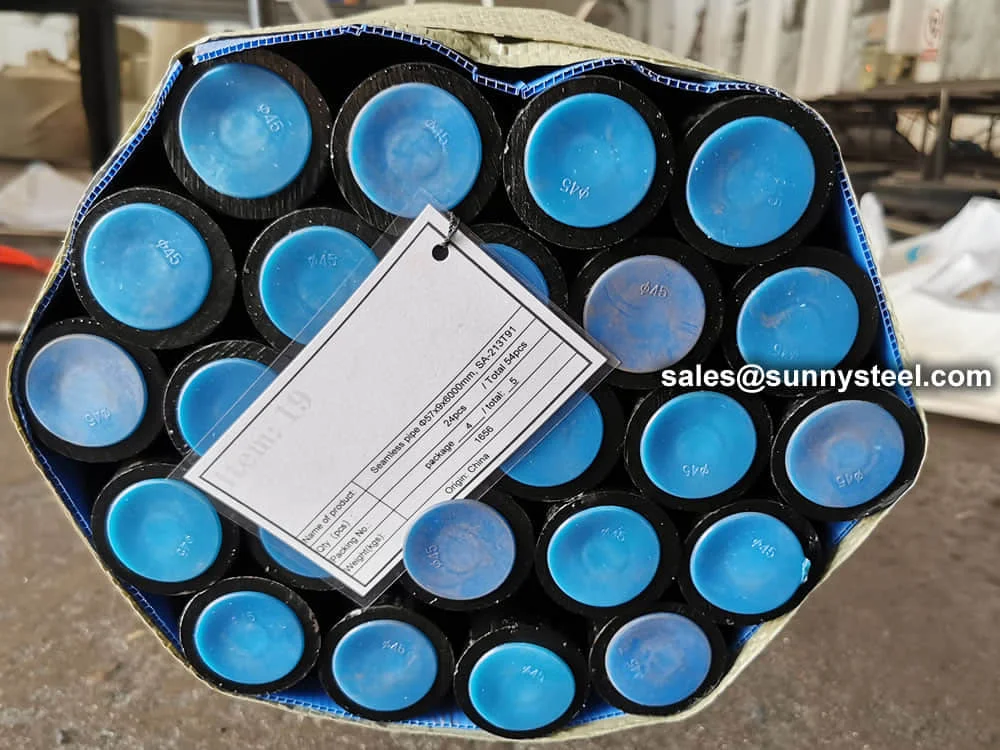








ASTM A213 T91 Seamless Alloy Tube is a high-performance ferritic alloy steel tube used in critical high-temperature applications such as boilers, superheaters, and heat exchangers. It offers excellent creep resistance, strength retention, and corrosion protection under extreme heat and pressure.
Manufactured according to ASTM A213 and ASME SA213 standards, T91 tubes are composed of Chromium (Cr), Molybdenum (Mo), and Vanadium (V) with nitrogen control, delivering superior oxidation resistance and creep strength. These tubes are ideal for ultra-supercritical power plants and petrochemical environments where service temperatures exceed 600°C.
T91 seamless alloy tubes are produced by hot finished or cold drawn methods, followed by normalized and tempered heat treatments to meet strict mechanical and metallurgical requirements. This grade is suitable for pressure-bearing and load-carrying operations in harsh thermal cycles.
The enhanced mechanical strength of ASTM A213 T91 makes it highly resistant to deformation and cracking during welding and long-term service. Applications include boiler tube banks, reheaters, superheaters, and chemical reactor piping systems in power generation and refining sectors.
Available in outer diameters from 10.2 mm to 114.3 mm, and thicknesses from 1 mm to 12 mm, these seamless tubes are supplied in lengths up to 12 meters with plain, beveled, or threaded ends. Protective coatings such as black paint, anti-rust oil, or 3LPE can be applied as per project requirements.
T91 has higher chromium (8.0–9.5% vs. 1.0–1.5%), higher molybdenum (0.85–1.05% vs. 0.44–0.65%), and includes vanadium and niobium for superior creep strength. T91 supports higher temperatures (up to 650°C vs. 560°C) and has higher strength (585/415 MPa vs. 415/205 MPa).
T91 has higher chromium (8.0–9.5% vs. 0.8–1.25%), higher molybdenum (0.85–1.05% vs. 0.44–0.65%), and includes vanadium and niobium, offering better corrosion and creep resistance. T91 is suited for ultra-supercritical boilers (up to 650°C vs. 550°C) with higher strength (585/415 MPa vs. 415/220 MPa).
T91 has higher chromium (8.0–9.5% vs. 1.9–2.6%) and similar molybdenum (0.85–1.05% vs. 0.87–1.13%) but includes vanadium and niobium for enhanced creep resistance. T91 supports higher temperatures (650°C vs. 593°C) and has higher strength (585/415 MPa vs. 415/205 MPa).
T91 has similar chromium (8.0–9.5% vs. 8.0–10.0%) and molybdenum (0.85–1.05% vs. 0.9–1.1%) but includes vanadium and niobium for superior creep resistance. T91 has higher strength (585/415 MPa vs. 415/205 MPa) and is suited for ultra-supercritical boilers (up to 650°C vs. 620°C).
T92 is an enhanced version of T91, with added tungsten (1.5–2.0%) and boron (0.001–0.006%) for improved creep strength, but similar chromium (8.5–9.5% vs. 8.0–9.5%) and slightly higher strength (620/440 MPa vs. 585/415 MPa). Both are used in ultra-supercritical boilers (up to 650°C).
T91 has higher chromium (8.0–9.5% vs. 2.2–2.6%) but similar vanadium and niobium, while T24 includes titanium and boron. T91 is suited for ultra-supercritical boilers (up to 650°C vs. 600°C) with similar strength (585/415 MPa).
T91 (ASTM A213) is a seamless tube for heat transfer components (thinner walls, OD 1/8” to 5”), while P91 (ASTM A335) is a pipe for structural and pressure piping (OD 1/8” to 48”). Both share the same 9Cr–1Mo–V–Nb chemistry but are used in different applications.
The ASTM A213 T91 Seamless Alloy Tube addresses critical challenges like corrosion, creep, and thermal stress in high-throughput industrial systems. Its advanced alloy composition and seamless construction make it a premium choice for engineers seeking durable boiler tubes and heat exchanger tubes for extreme environments.
Dimensions and performance data for ASTM A213 T91 Seamless Alloy Tube
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.08-0.12 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.30-0.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤0.020 |
| Sulfur (S) | ≤0.010 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.20-0.50 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 8.00-9.50 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.85-1.05 |
| Vanadium (V) | 0.18-0.25 |
| Nitrogen (N) | 0.03-0.07 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) | 585 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) | 415 |
| Elongation, min (%) | 20 (Longitudinal) |
| Hardness, max (HB) | 217 |
| Parameter | Range | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Inside Diameter | 1/8" to 5" | 3.2 mm to 127 mm |
| Wall Thickness | 0.015" to 0.500" | 0.4 mm to 12.7 mm |
| Length | 5–7 m / 9–13 m | SRL / DRL |
| Schedule | 40 to 160 | STD, XS, XXS |
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Max Service Temperature | 650 | °C |
| Tensile Strength | 415–690 | MPa |
| Yield Strength | 205–520 | MPa |
| Elongation | 20–30 | % |

ASTM A213 T91 Seamless Alloy Tube are widely used in various industries due to their excellent high-temperature and high-pressure performance.
Utilized in boilers, superheaters, and reheaters within steam power plants due to their high-temperature resistance and durability.
Employed in refineries and chemical plants for transporting high-temperature fluids and gases, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Ideal for use in heat exchangers where thermal stability and corrosion resistance are critical under fluctuating temperatures.
Commonly used in high-pressure boilers and superheaters, offering excellent performance under extreme thermal conditions.
Applied in the extraction and processing of oil and gas, handling high-pressure and high-temperature fluids effectively.
Suitable for equipment in chemical industries where resistance to corrosive substances and high temperatures is essential.

Astm a213 t91 alloy steel boiler tubes offer high ...

Sa213 t91 boiler tubes are seamless alloy steel tu...