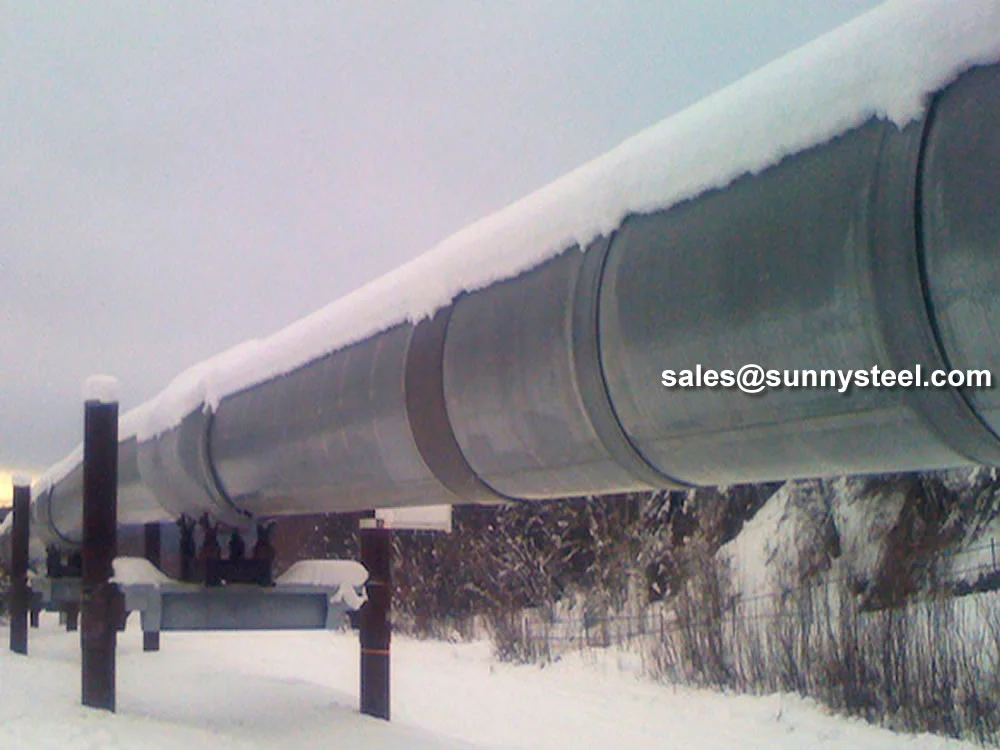
Low-Temperature Carbon Steel Pipe is specially designed to perform in cryogenic and subzero
conditions, offering outstanding impact toughness, ductility, and corrosion
resistance. Conforming to ASTM A333 standards, this seamless carbon steel pipe is ideal
for applications in LNG facilities, chemical plants, and power generation systems where temperatures drop below -50°C.
Cryogenic Performance
Maintains structural integrity and mechanical strength even at extreme cold temperatures down to -45°C
(-50°F).
These ASTM A333 LTCS Seamless Pipes are produced through controlled rolling and heat treatment
processes to ensure mechanical integrity at low temperatures. Available in multiple grades, such as Grade 1 and
Grade 6, these pipes deliver reliable performance in structural, fluid, and gas transmission lines operating in
subzero climates. The carbon-manganese alloy composition ensures high strength and resilience under
thermal cycling and pressure variations.
LTCS Pipes are known for their weldability and ease of fabrication, making them suitable for
complex boiler systems, heat exchangers, and refrigeration units. Pipes undergo strict quality checks, including
Charpy V-Notch impact testing at -45°C, hydrostatic testing, and ultrasonic inspections to ensure compliance with
industrial safety and durability standards.
Whether you're building a pipeline for arctic exploration or retrofitting industrial equipment in cold regions,
Low Temperature Carbon Steel Pipes provide the mechanical robustness and thermal stability needed
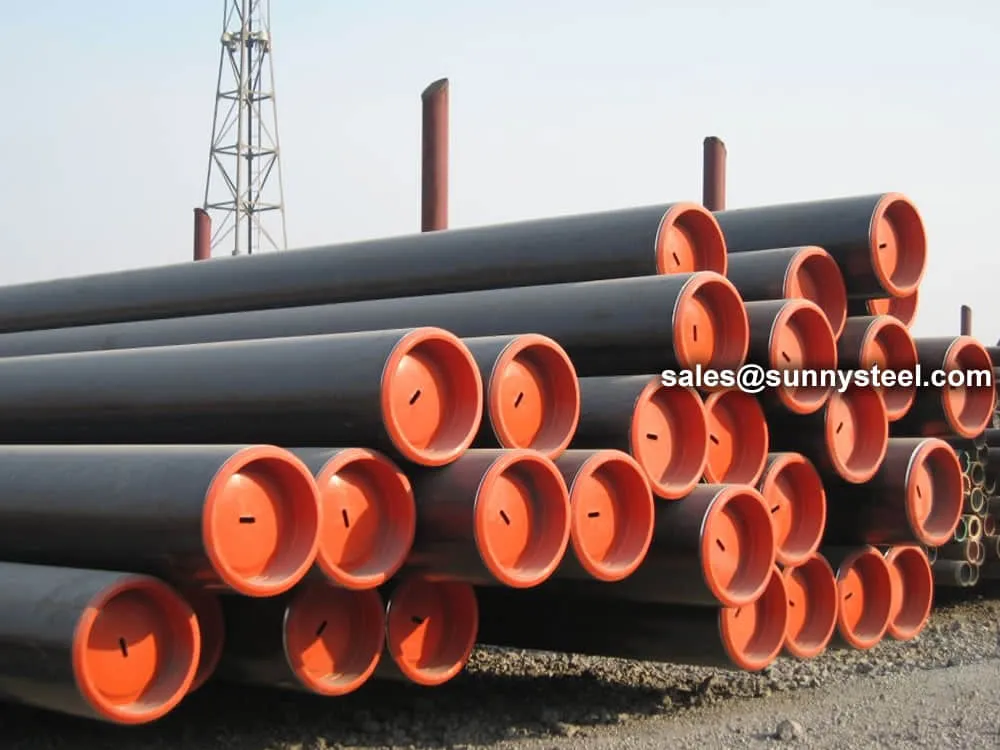
for long-term operation. Available in sizes from 1/2” to 48” and various wall thicknesses (SCH 40 to SCH 160), they
can be custom-manufactured with plain, beveled, or threaded ends.
Combined with surface treatments such as galvanized coating, 3LPE, or epoxy painting, these pipes enhance longevity
and corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Their high strength-to-weight ratio also minimizes structural load
while maintaining safety under cryogenic conditions.
International Steel Grade Equivalents and Applications
| Steel Grade Category |
GB (China) |
ASME(USA) |
DIN/EN (Euro) |
JIS (Japan) |
Application |
| Carbon steel |
10 |
A106 |
St35.8 |
STB340 |
Economizer tube, Water wall tube, pipeline, header pipe, Petrochemical furnace tube, heat
exchange tube |
| 20 |
SA-106B |
St45.8 |
STB410 |
| 20G |
SA-106C |
P235GH |
STB510 |
| 20MnG |
SA-192 |
P265GH |
- |
| 25MnG |
SA-210A1 |
- |
- |
| Q345B/C/D/E |
SA-210C |
- |
- |
| Mo steel |
15MoG |
SA-209 T1 |
16Mo3 |
15Mo3 |
Water wall tube
Superheater tube
Reheater tube |
| 20MoG |
SA-209 T1a |
- |
16Mo3 |
| - |
SA-209 T1b |
- |
- |
| Cr-Mo Steel |
12Cr1MoG |
- |
12Cr1MoV |
- |
Superheater tube
Reheater tube,
Pipeline, Header pipe, Petrochemical furnace tube, Heat
exchange tube |
| Cr-Mo-V steel |
12Cr2MoWVTiB |
- |
14MoV63 |
- |
| Cr-Mo-Steel |
12CrMoG |
T11/P11 |
10CrMo5-5 |
STB20 |
| Cr-Mo-W Steel |
15CrMoG |
T12/P12 |
12CrMo4-5 |
STB22 |
| Cr-Mo Steel |
12Cr2MoG |
T22/P22 |
10CrMo9-10 |
STB23 |
Superheater tube, Reheater tube, Main steam pipe, Pipleline, Header pip, Petrochemical furnace
tube, Heat exchange tube |
| Cr-Mo-W steel |
10Cr9Mo1VNbN |
T23/P23 |
7CrWVMoNb9-6 |
STB24 |
| 10Cr9MoW2VNbBN |
T24/P24 |
7CrMoVTIB10-10 |
STB25 |
| 12Cr1Mo |
T5/P5 |
X10CrMoVNb9-1 |
STB26 |
| 12Cr5Mol/NT |
T9/P9 |
X10CrWMoVNb9-2 |
- |
| 12Cr9Mol/NT |
T91/P91 |
X11CrMo5+l/NT |
- |
| - |
T92/P92 |
X11CrMo9-1+l/NT |
- |
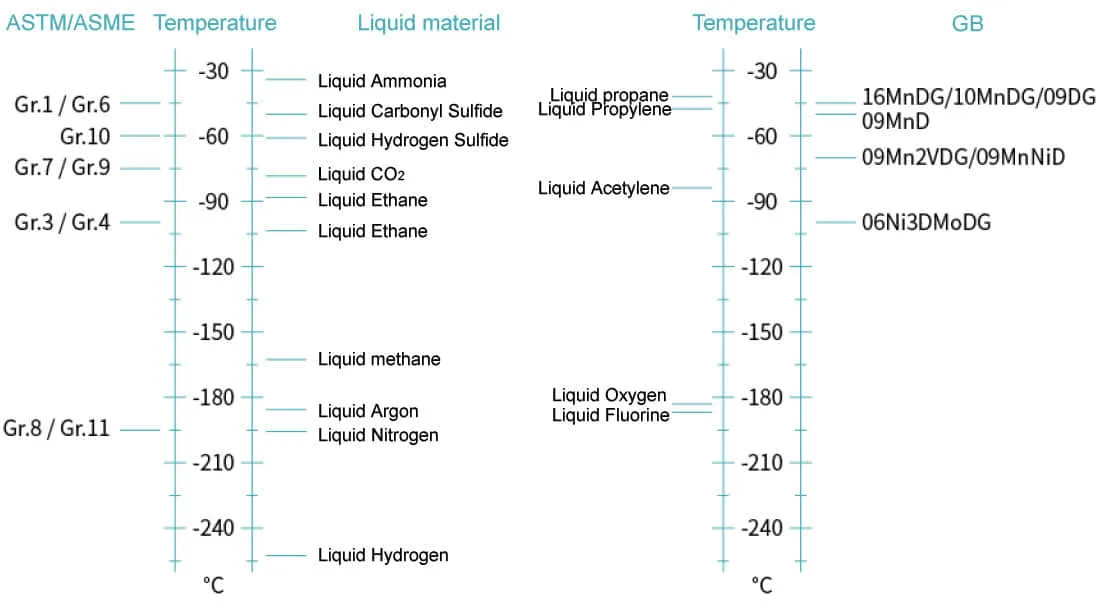
| Carbon steel |
16MnDG |
A333-1 |
- |
STPL380 |
Tube & pipe for Low-temperature service |
| Ni steel |
10MnDG |
SA-333-1 |
- |
STPL450 |
| 09DG |
A333-6 |
- |
- |
| - |
SA-333-6 |
- |
- |
| - |
A333-3 |
- |
- |
| - |
SA-333-3 |
- |
- |
| Austentic Stainless steel |
--- |
AP304 TP304H |
- |
--- |
Superheater tube, Reheater tube |
| - |
TP321 TP321H |
- |
- |
| - |
TP347 TP347H |
- |
- |
| - |
TP316 TP316H |
- |
- |
| - |
S30432 TP310HCbN |
- |
- |
Sizes & Specifications
Size Range
Outer Diameter (O.D.): 1/4” Nominal to 24”
Wall Thickness: Schedule 10 through XXH (Extra Extra Heavy)
Pipe Specifications & Grades
Standards: ASTM A333 / ASME SA333
Grades Available: Grade 1, Grade 3, Grade 6
Welded Alternative: ASTM A671 EFW (for sizes over 24" O.D.)
Flanges & Forged Fittings
Standard: ASTM A350 / ASME SA350
Grades: LF2, LF3 (Low Temperature Service)
Buttweld Pipe Fittings
Standard: ASTM A420 / ASME SA420
Grades: WPL6, WPL3
Effect of Alloying Elements on Cryogenic Steels
Alloying elements significantly influence the performance of cryogenic steels, used from -10°C
to -273°C, including aluminum-killed C-Mn steels (e.g., 06MnVTi), low-alloy ferritic steels (e.g., 0.5Ni),
martensitic steels (e.g., 9Ni), and austenitic steels (e.g., 1Cr18Ni9Ti).
Mn (Manganese)
Enhances low-temperature toughness by forming a solid solution, expanding the austenite region, lowering
transformation temperatures (A1 and A3), and refining ferrite and pearlite grains. An Mn/C ratio of 3
optimizes toughness and compensates for reduced mechanical properties due to lower carbon.
Ni (Nickel)
Reduces brittle transition temperature by 10°C per 1% increase (five times more effective than Mn),
refines microstructure, and boosts toughness. Enables 9Ni steel for -196°C and 5Ni for -162°C to -196°C
due to increased movable dislocations.
C (Carbon)
Increases brittle transition temperature and reduces weldability, limiting its content to below 0.2% in
cryogenic steels.
P, S, Sn, Pb, Sb (Phosphorus, Sulfur, Tin, Lead, Antimony)
Harmful to toughness, these elements segregate at grain boundaries, lowering resistance and causing
brittle cracks. Phosphorus boosts strength but increases brittleness, requiring strict limits.
O, H, N (Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen)
Raise brittle transition temperature. Aluminum-killed steels offer better toughness than silicon-killed
steels, as silicon increases the transition temperature.
Summary
Alloying elements like Mn and Ni enhance toughness, while C, P, S, Sn, Pb, Sb, O, H, and N can degrade it
by increasing brittle transition temperatures or promoting brittleness. Optimal composition is key for
cryogenic performance.









