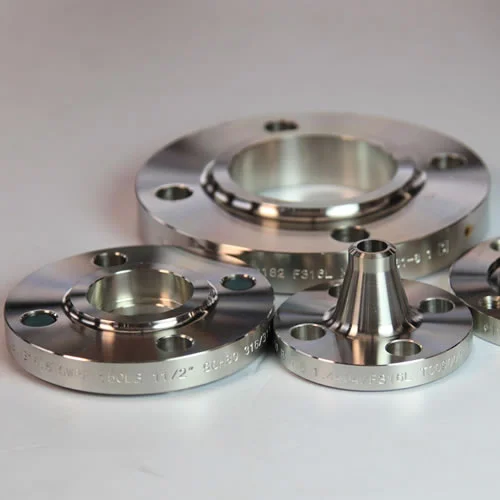
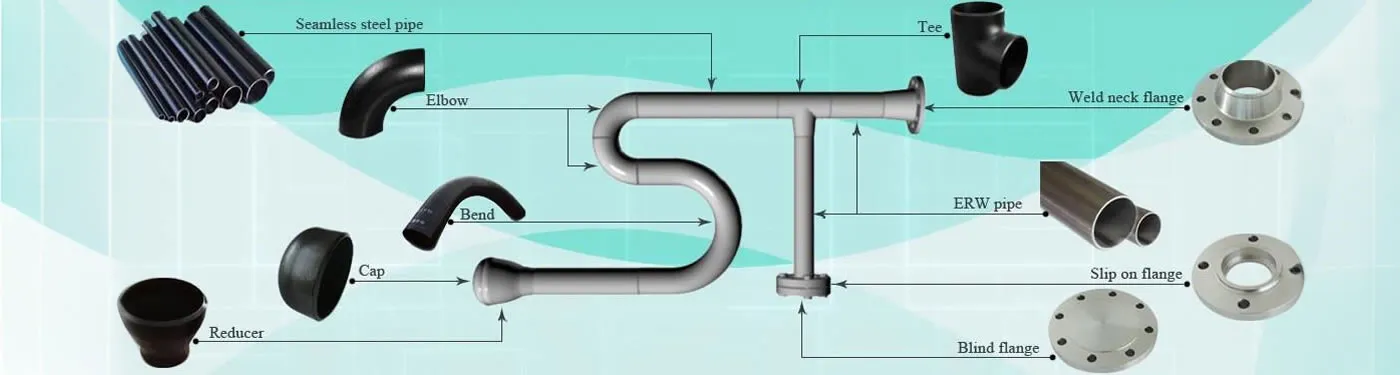
What are Butt Weld Pipe Fittings?
Butt weld pipe fittings are weldable components designed to be joined to pipes, valves, and other equipment by butt welding, creating strong, leak-proof, and permanent connections.
Weldable Components
Designed to be permanently welded to pipes, creating strong and reliable connections for various piping applications.
Size Range
Available in sizes from ½" to 72", offering significant advantages over threaded and socket weld fittings for larger applications.
ASME B16.9
Manufactured in accordance with ASME B16.9 standards, ensuring consistent dimensions, tolerances, and quality.
Butt Weld Pipe Fittings are durable fittings designed for seamless piping connections, adhering to ASME B16.9 standards as of August 26, 2025, 01:39 AM PDT. These Seamless Pipe Fittings ensure strength.
Available in sizes from 1/2” to 48” with pressure ratings up to Class 6000, Butt Weld Pipe Fittings handle temperatures up to 600°C, depending on material, for versatile use.
Manufactured through hot forming or cold forming, these fittings offer a strong, leak-proof joint, with coatings like 3LPE enhancing corrosion resistance as of August 2025. Reliability is key.
Compared to threaded fittings, Butt Weld Pipe Fittings provide superior strength and longevity, with a service life of 20–40 years with proper maintenance and protective measures.
Butt Weld Pipe Fittings address challenges like leaks and pressure loss, delivering robust industrial butt weld fittings as of August 26, 2025.
How are Butt weld Joints made
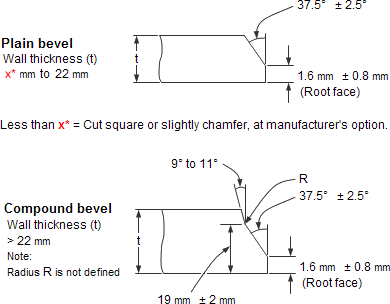
The end of the pipe is beveled as shown in figure below. Fittings are similarly supplied with beveled ends by the manufacturer. Butt weld fittings have beveled ends (BE) configured as per ASME B16.25. In piping material specifications the fittings are specified with equivalent material and same wall thickness as the matching pipe. The two parts are aligned with a proper gap, usually 1.6mm (1/16") root gap. The two parts are tack welded and then a continuous weld is made to complete the joint. The first pass of weld is called the root weld. Butt weld fittings must not be supplied with lower wall thickness than the run pipe as this can affect the integrity of the weld joint. When pipes and fittings are supplied with different wall thickness, one of the components must be machined or ground internally to align the butt joints. The internal machining will reduce the wall thickness and the pipe wall thickness at the weld joint may not be suitable for the design conditions. Hence, the designer must pay close attention to this requirement.
Sketch below shows typical piping assembly with pipes and fittings.
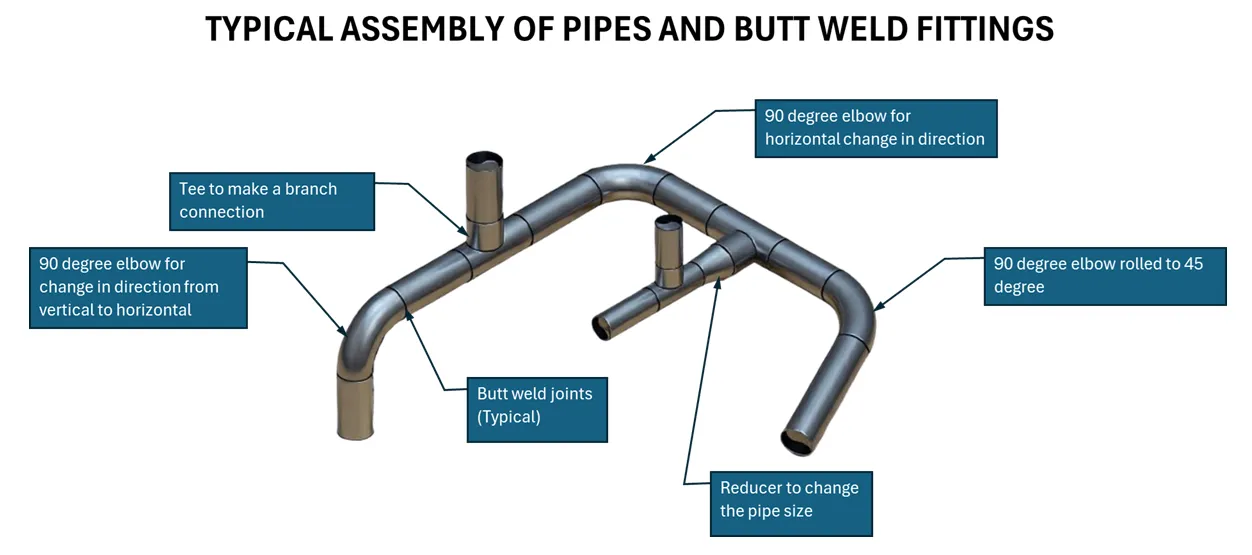
Butt Weld Pipe Fitting
Beveled Ends
As per ASME B16.25, all fittings have beveled ends for full penetration welds without extra preparation.
Robust Welded Joint
Welded connections create a continuous metal structure, adding strength and reliability to piping systems.
Seamless Flow
Matching pipe schedules ensure smooth internal flow, with gradual transitions via elbows and reducers.
Flexible Design
Available in SR, LR, and 3R elbows, offering multiple turn radius options for different layouts.
Cost Effective
More economical than threaded or socket weld fittings, while still delivering high durability and performance.
Stainless Steel Range
Available in SCH 10 & SCH 40 configurations, offering thinner or standard wall thickness options.