Industrial Materials
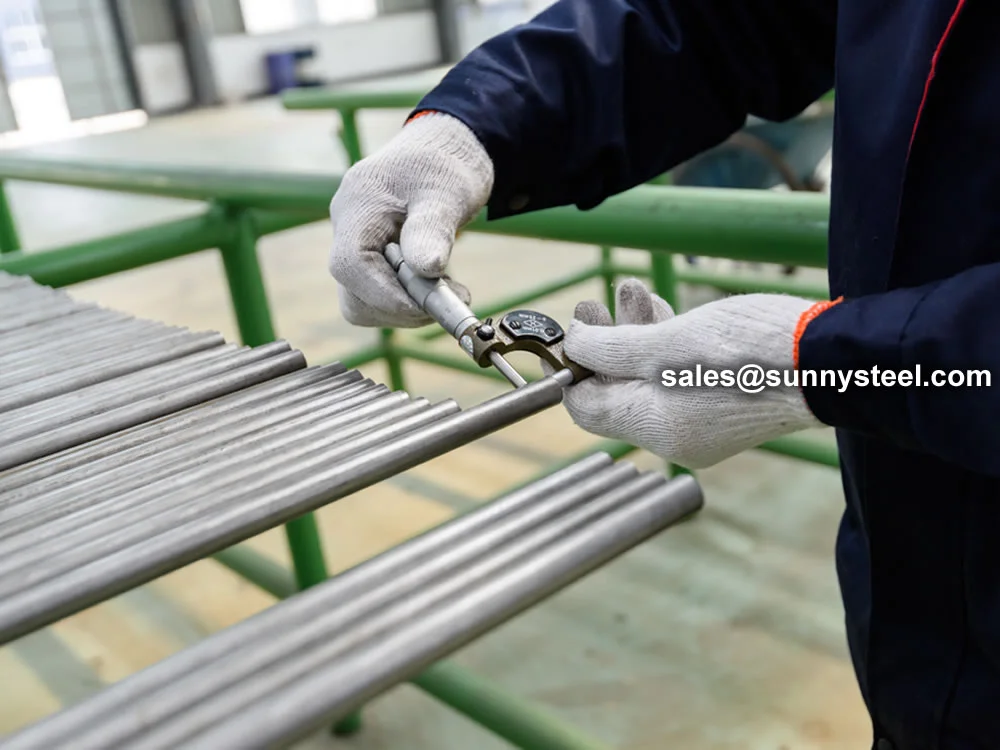
What Is a Seamless Pipe?
Seamless pipes, manufactured without welds or seams, offer exceptional strength and reliability for high-pressure and high-temperature applications across various industries.
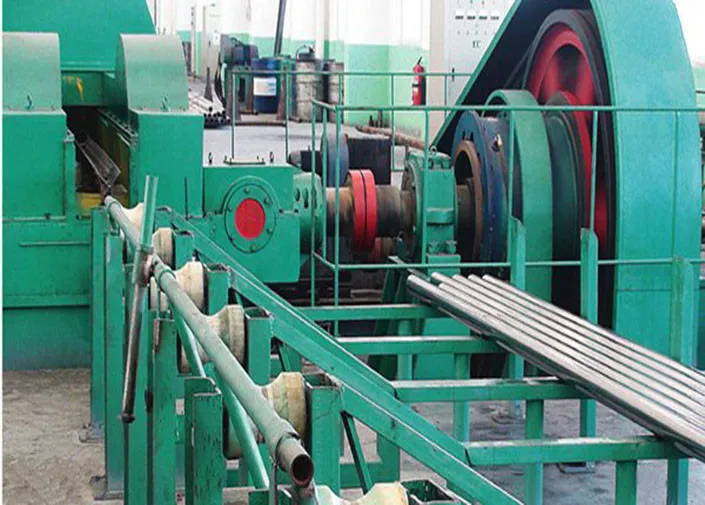
Seamless steel pipes are produced from solid steel billets that are heated and extruded through hot rolling or cold drawing to form a hollow pipe. This weld-free construction ensures uniformity, strength, and leak-proof performance, making them ideal for demanding environments in oil and gas, petrochemicals, power generation, and construction.
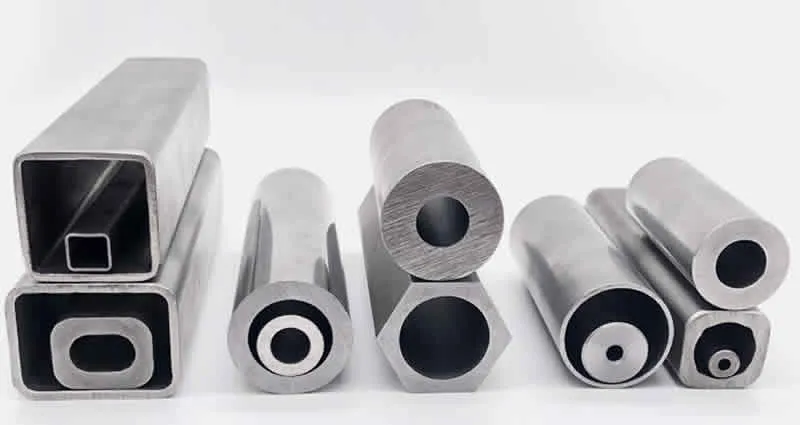
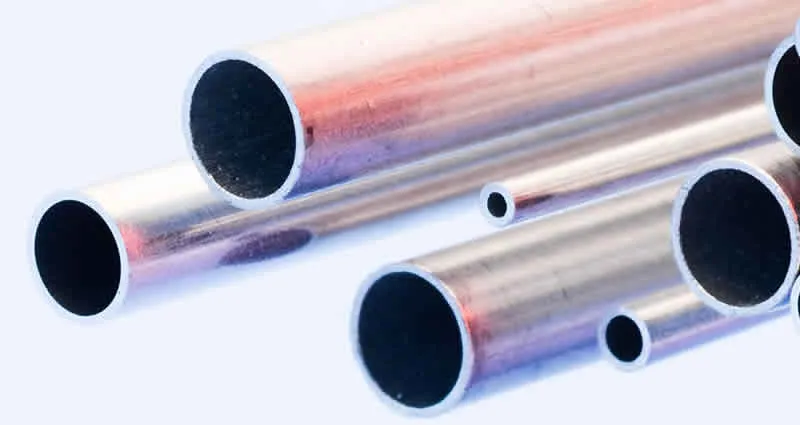
Available in carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel variants, these pipes meet stringent standards such as ASTM A106, A335, API 5L, and DIN 17175. They are designed for fluid and gas transport, structural applications, and specialized uses, providing robust and long-lasting solutions for industrial piping needs.
With their superior strength and versatility, seamless pipes are a preferred choice for reliable piping systems, ensuring safe and efficient performance in critical applications.