
High-strength, Corrosion-resistant Piping For Nuclear Applications
Seamless pipes for nuclear power stations ensure safe, reliable transport of high-pressure steam and coolant, offering superior strength and corrosion resistance.
High-strength, Corrosion-resistant Piping For Nuclear Applications
Seamless pipes for nuclear power stations ensure safe, reliable transport of high-pressure steam and coolant, offering superior strength and corrosion resistance.
Seamless Pipes for Nuclear Power Stations are engineered to meet the rigorous demands of nuclear facilities, ensuring safe and reliable transport of high-pressure steam, coolant, and other fluids in extreme conditions. These nuclear power piping systems comply with standards like ASME B&PV Code Section III and GB 24512.1, offering exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and radiation resistance for pressurized water reactors (PWRs) and boiling water reactors (BWRs). Their seamless design eliminates weld-related weaknesses, ensuring safety in critical environments.
Made from high-quality materials like stainless steel (304L, 316L) or nickel-based alloys (e.g., Inconel 625), stainless steel nuclear pipes are designed for high-pressure (up to 150 bar) and high-temperature (exceeding 300°C) conditions. Available in sizes from 1/2” to 12” (DN15–DN300) with wall thicknesses from SCH 40 to SCH 160, these pipes are used in reactor coolant systems, steam generators, and emergency cooling. Cold-drawing or hot-rolling processes ensure precision, while passivation or specialized coatings enhance corrosion resistance against seawater or acidic environments.
Inconel seamless tubes undergo stringent testing, including ultrasonic, eddy current, and hydrostatic tests, to ensure defect-free performance. With tensile strengths from 485 MPa (316L SS) to 690 MPa (Inconel 625), they resist stress corrosion cracking and radiation-induced degradation. These pipes are critical for transporting cooling water, steam, and hydrogen gas, ensuring operational safety and efficiency. Their high nickel content provides excellent resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, ideal for coastal nuclear plants.
Unlike welded pipes, high-pressure nuclear piping offers superior integrity, reducing risks of leaks or failures. They are customizable for applications like main steam pipelines, fuel cladding, or heat exchanger tubes, meeting tight dimensional tolerances. These pipes withstand thermal cycling and radioactive exposure, ensuring long-term reliability in nuclear systems. Their versatility extends to auxiliary systems like fire sprinklers and emergency fuel lines.
By addressing challenges like corrosion, high-pressure demands, and radiation exposure, corrosion-resistant nuclear tubes ensure reliable operation in nuclear power stations. From reactor coolant systems to steam generators, these pipes deliver unmatched safety, durability, and performance, making them essential for clean energy production in nuclear facilities worldwide.
| Size | Steel Grade | Specification | Typical Application | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD(mm) | WT(mm) | |||
| 48 - 720 | 4.5 - 130 | HD245, HD245Cr | GB 24512.1 GB 24512.2 |
Carbon and alloy seamless steel pipe for Nuclear Station Island and Conventional Island |
| HD265, HD265Cr | ||||
| HD280, HD280Cr | ||||
| HD12Cr2Mo | ||||
| HD15Ni1MnMoNbCu | ||||
| TUE250B | RCC-M | |||
| TU42C | ||||
| TU48C | ||||
| P280GH | ||||
| SA106B/C | ASME SA-106/SA-106M | |||
| P11 | ASME SA-335/SA-335M | |||
| P22 | ||||
| P36 | ||||
| P91 | ||||
Nuclear power is a technology which extracts usable energy from atomic nuclei via controlled nuclear reactions – normally atomic fission.
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | Nb | N | Cu | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD12Cr2Mo | 0.07-0.16 | ≤0.54 | 0.37-0.73 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.02 | 1.9-2.6 | 0.86-1.24 | ≤0.30 | - | - | ≤0.20 | ≤0.08 |
| HD15Ni1MnMoNbCu | 0.09-0.18 | 0.21-0.54 | 0.76-1.24 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.020 | 0.14-0.35 | 0.21-0.44 | 0.95-1.35 | 0.010-0.030 | ≤0.020 | 0.45-0.85 | ≤0.02 |
| Grade | Tensile Strength, [MPa] | Yield Strength, [MPa] | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HD12Cr2Mo | 450-600 | ≥280 | ≥22 |
| HD15Ni1MnMoNbCu | 620-780 | ≥440 | ≥19 |
RCC-M steel pipe for nuclear industry equipment.
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | Al | Ceq | Cu | Sn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TU48C | ≤0.24 | 0.09-0.40 | 0.60-1.30 | ≤0.040 | ≤0.040 | - | - | - | - | - | ≤0.25 | ≤0.030 |
| P280GH | ≤0.22 | 0.10-0.40 | 0.80-1.60 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.020 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.50 | 0.020-0.050 | ≤0.48 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.030 |
| Grade | Tensile Strength, [MPa] | Yield Strength, [MPa] | Elongation |
|---|---|---|---|
| TU48C | 470-570 | ≥275 | Rm(A-2)≥10500 |
| P280GH | 470-570 | ≥275 | Rm(A-2)≥10500 |
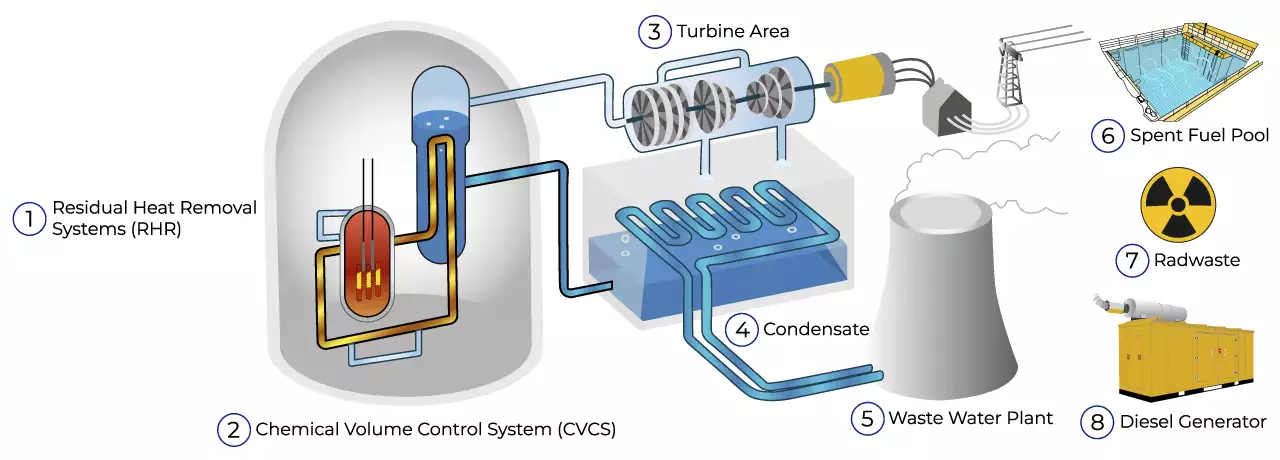
The process takes place in a nuclear-fuelled power plant, where – much like in a fossil-fuelled power plant – water is turned into steam, which drives turbine generators to produce electricity. The difference between the two power plants is the heat source. Nuclear power produces electricity by splitting uranium atoms which generate phenomenal heat. This is called fission. This heat is used to create the steam which powers the generators. There is no combustion in a nuclear reactor, just the constant splitting of atoms which produces manageable heat.
Either a pressurised water reactor or boiling water reactor is used, but regardless which type of reactor is used to generate heat, the conditions under which they do are extremely hostile. This means that the finest Stainless Steel pipes and tubing are required so that they can deal with constantly high pressures and temperatures.
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | Sn | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HD245 | ≤0.22 | 0.15-0.39 | ≤1.04 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.20 |
| HD245Cr | ≤0.22 | 0.15-0.39 | ≤1.04 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.02 | 0.18-0.33 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.20 |
| HD265 | ≤0.22 | ≤0.44 | ≤1.44 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.20 |
| HD265Cr | ≤0.22 | ≤0.44 | ≤1.44 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.02 | 0.15-0.3 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.20 |
| HD280 | ≤0.22 | 0.1-0.4 | 0.8-1.6 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.02 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.20 |
| HD280Cr | ≤0.22 | 0.1-0.4 | 1.0-1.6 | ≤0.025 | ≤0.02 | 0.15-0.33 | ≤0.1 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.20 |
GB24512.1 seamless tubes and pipes for nuclear power plant.
| Grade | Standard | OD (mm) | WT (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HD245, HD245Cr | GB 24512.1 | 48–720 | 4.5–130 |
| HD265, HD265Cr | GB 24512.2 | 48–720 | 4.5–130 |
| TU48C, P280GH | RCC‑M / ASME SA‑335M | 219–1200 | 8–130 |
Explore the dimensional ranges and common applications of various seamless pipe types.
| Type | Outer Diameter | Wall Thickness | Length | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hot-Rolled Seamless | Above 32 mm | 2.5 – 200 mm | Up to 12 m | General industrial, structural |
| Cold-Rolled Seamless | 6 – 650 mm | 0.25 – 50 mm | Up to 12 m | Precision applications |
| Thin-Walled Pipe | 5 – 100 mm | Less than 0.25 mm | Up to 6 m | Instrumentation, automotive |
| Heavy Wall Pipe | 50 – 650 mm | 10 – 200 mm | Up to 12 m | High pressure, structural |
| DN | NB (inch) | OD (mm) | Nominal Wall Thickness (mm) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCH10 | SCH20 | SCH30 | STD | SCH40 | SCH60 | XS | SCH80 | SCH100 | SCH120 | SCH140 | SCH160 | XXS | |||
| 15 | 1/2" | 21.3 | 2.11 | 2.41 | 2.77 | 2.77 | 3.73 | 3.73 | 4.78 | 7.47 | |||||
| 20 | 3/4" | 26.7 | 2.11 | 2.41 | 2.87 | 2.87 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 5.56 | 7.82 | |||||
| 25 | 1" | 33.4 | 2.77 | 2.90 | 3.38 | 3.38 | 4.55 | 4.55 | 6.35 | 9.09 | |||||
| 32 | 1.1/4" | 42.2 | 2.77 | 2.97 | 3.56 | 3.56 | 4.85 | 4.85 | 6.35 | 9.70 | |||||
| 40 | 1.1/2" | 48.3 | 2.77 | 3.18 | 3.68 | 3.68 | 5.08 | 5.08 | 7.14 | 10.15 | |||||
| 50 | 2" | 60.3 | 2.77 | 3.18 | 3.91 | 3.91 | 5.54 | 5.54 | 8.74 | 11.07 | |||||
| 65 | 2.1/2" | 73 | 3.05 | 4.78 | 5.16 | 5.16 | 7.01 | 7.01 | 9.53 | 14.02 | |||||
| 80 | 3" | 88.9 | 3.05 | 4.78 | 5.49 | 5.49 | 7.62 | 7.62 | 11.13 | 15.25 | |||||
| 90 | 3.1/2" | 101.6 | 3.05 | 4.78 | 5.74 | 5.74 | 8.08 | 8.08 | |||||||
| 100 | 4" | 114.3 | 3.05 | 4.78 | 6.02 | 6.02 | 8.56 | 8.56 | 13.49 | 17.12 | |||||
| 125 | 5" | 141.3 | 3.4 | 6.55 | 6.55 | 9.53 | 9.53 | 12.7 | 15.88 | 19.05 | |||||
| 150 | 6" | 168.3 | 3.4 | 7.11 | 7.11 | 10.97 | 10.97 | 14.27 | 18.26 | 21.95 | |||||
| 200 | 8" | 219.1 | 3.76 | 6.35 | 7.04 | 8.18 | 8.18 | 10.31 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 15.09 | 18.26 | 20.62 | 23.01 | 22.23 |
| 250 | 10" | 273 | 4.19 | 6.35 | 7.8 | 9.27 | 9.27 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 15.09 | 18.26 | 21.44 | 25.4 | 28.58 | 25.4 |
| 300 | 12" | 323.8 | 4.57 | 6.35 | 8.38 | 9.53 | 10.31 | 14.27 | 12.7 | 17.48 | 21.44 | 25.4 | 28.58 | 33.32 | 25.4 |
| 350 | 14" | 355.6 | 6.35 | 7.92 | 9.53 | 9.53 | 11.13 | 15.09 | 12.7 | 19.05 | 23.83 | 27.79 | 31.75 | 35.71 | |
| 400 | 16" | 406.4 | 6.35 | 7.92 | 9.53 | 9.53 | 12.7 | 16.66 | 12.7 | 21.44 | 26.19 | 30.96 | 36.53 | 40.19 | |
| 450 | 18" | 457.2 | 6.35 | 7.92 | 11.13 | 9.53 | 14.27 | 19.05 | 12.7 | 23.83 | 39.36 | 34.93 | 39.67 | 45.24 | |
| 500 | 20" | 508 | 6.35 | 9.53 | 12.7 | 9.53 | 15.09 | 20.62 | 12.7 | 26.19 | 32.54 | 38.1 | 44.45 | 50.01 | |
| 550 | 22" | 558.8 | 6.35 | 9.53 | 12.7 | 9.53 | 22.23 | 12.7 | 28.58 | 34.93 | 41.28 | 47.63 | 53.98 | ||
| 600 | 24" | 609.6 | 6.35 | 9.53 | 14.27 | 9.53 | 17.48 | 24.61 | 12.7 | 30.96 | 38.89 | 46.02 | 52.37 | 59.54 | |
| 650 | 26" | 660.4 | 7.92 | 12.7 | 9.53 | 12.7 | |||||||||
| 700 | 28" | 711.2 | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | 9.53 | 12.7 | ||||||||
| 750 | 30" | 762 | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | 9.53 | 12.7 | ||||||||
| 800 | 32" | 812.8 | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | 9.53 | 17.48 | 12.7 | |||||||
| 850 | 34" | 863.6 | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | 9.53 | 17.48 | 12.7 | |||||||
| 900 | 36" | 914.4 | 7.92 | 12.7 | 15.88 | 9.53 | 19.05 | 12.7 | |||||||
Seamless Pipes
Seamless pipes, available in various wall thicknesses, are designed for precise applications, with cold-rolled thin-walled pipes achieving thicknesses as low as 0.25 mm or less.
The outer diameter of hot-rolled seamless pipe is generally greater than 32mm, the wall thickness is 2.5-200mm, the outer diameter of cold-rolled seamless steel pipe can be 6mm, the wall thickness can be 0.25mm, the outer diameter of thin-walled pipe can be 5mm, and the wall thickness is less than 0.25mm, cold rolling
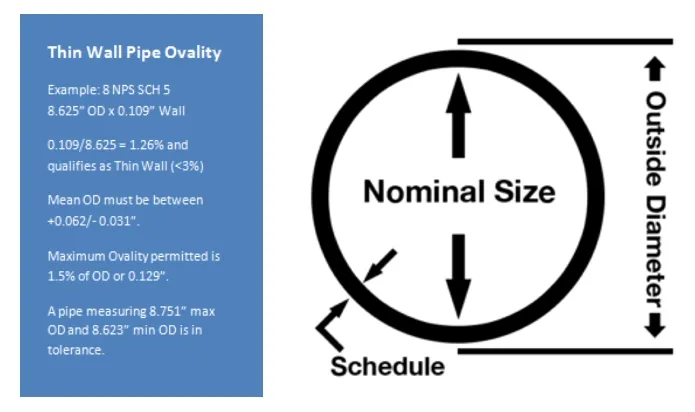
The ability to produce seamless pipes with ultra-thin walls and controlled ovality makes them critical for industries like automotive, hydraulics, and petrochemicals, ensuring reliability and performance.
| NPS/ DN/ OD | Permissible Variations in Outside Diameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Over | Under | |||
| in. | mm | in. | mm | |
| NPS 1/8 to 1½, incl DN 6 to 40 OD 10.3 to 48.3, mm |
1/64 | 0.4 | 1/64 | 0.4 |
| Over 1½ to 4, incl DN 40 to 100 OD 48.3 to 114.3, mm |
1/32 | 0.8 | 1/32 | 0.8 |
| Over 4 to 8, incl DN 100 to 200 OD 114.3 to 219.1, mm |
1/16 | 1.6 | 1/32 | 0.8 |
| Over 8 to 18, incl DN 200 to 450 OD 219.1 to 457, mm |
3/32 | 2.4 | 1/32 | 0.8 |
| Over 18 to 26, incl DN 450 to 650 OD 457 to 660, mm |
1/8 | 3.2 | 1/32 | 0.8 |
According to the production method, seamless tubes are divided into hot - rolled tubes, cold - rolled tubes, cold - drawn tubes, extruded tubes, jacking tubes, etc. The maximum diameter is 650 mm and the minimum diameter is 0.3 mm. Depending on the application, there are thick - walled tubes and thin - walled tubes. Seamless steel tubes are mainly used as petroleum geological drilling tubes, cracking tubes for petrochemical industry, boiler tubes, bearing tubes and high - precision structural steel tubes for automobiles, tractors and aviation. In the plate, Q345B seamless steel pipe belongs to the low - alloy series.
Among the low - alloy materials, this kind of material is the most common. The outside diameter of hot - rolled seamless pipe is usually more than 32mm, the wall thickness is 2.5 - 200mm, the outside diameter of cold - rolled seamless steel pipe can be 6mm, the wall thickness can be 0.25mm, the outside diameter of thin - walled pipe can be 5mm, and the wall thickness is less than 0.25mm, cold rolling has higher dimensional accuracy than hot rolling.
A consolidated overview of international seamless pipe standards, their materials, and applications.
| Standard System | Standard Code | Material Type | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM / ASME (USA) |
ASTM A53 | Carbon Steel | General-purpose piping, structural |
| ASTM A106 | Carbon Steel | High-temperature service | |
| ASTM A179 | Low Carbon Steel | Heat exchangers, condensers | |
| ASTM A333 | Carbon/Alloy Steel | Low-temperature service | |
| ASTM A335 | Alloy Steel | High-temperature, pressure piping | |
| ASTM A213 / A209 | Alloy/Stainless Steel | Boilers, superheaters | |
| ASTM A312 | Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant piping | |
| ASTM A519 | Carbon/Alloy Steel | Mechanical tubing (e.g., SAE 1026) | |
| ASTM A790 | Duplex Stainless Steel | High-strength, corrosion-resistant service | |
| API (Oil & Gas) |
API 5L | Carbon Steel | Oil & gas pipelines |
| API 5CT | Carbon Steel | Casing & tubing for wells | |
| JIS (Japan) |
JIS G3454/G3455/G3456 | Carbon Steel | Pressure piping service |
| JIS G3460 | Carbon Steel | Boilers, heat exchangers | |
| JIS G3429 | High-strength Steel | High-pressure gas cylinders | |
| GB (China) |
GB 3087 | Carbon Steel | Low & medium pressure boilers |
| GB 5310 | Carbon Steel | High-pressure boiler pipes | |
| GB/T 8163 | Carbon Steel | Fluid and structural use |

Seamless pipes are critical in various industries thanks to their excellent strength, temperature resistance, and structural uniformity. They ensure safe and efficient performance in demanding environments.
Used in steam pipelines, boiler tubes, superheaters, and heat exchangers for high-temperature and high-pressure conditions in power plants.
Transports crude oil, natural gas, and petroleum products in pipelines and refinery units, handling high-pressure and corrosion.
Handles chemicals, gases, and hazardous substances in reactors and heat exchangers, ensuring safe processing.
Applied in automotive systems and machinery for fluid conveyance and precision components requiring strength and accuracy.
Used in structural support, water and sewage systems, and building frameworks for strength and corrosion resistance.
Utilized in hydraulic and engine systems onboard, resisting corrosion in marine environments.
Employed in aircraft and military equipment for hydraulic systems and structural components.
Stainless pipes for hygienic transport of food and pharmaceutical products, maintaining sterility.
Designed for transporting slurries and chemicals in mining, withstanding abrasion and harsh conditions.

Other structural pipes provide high strength and v...
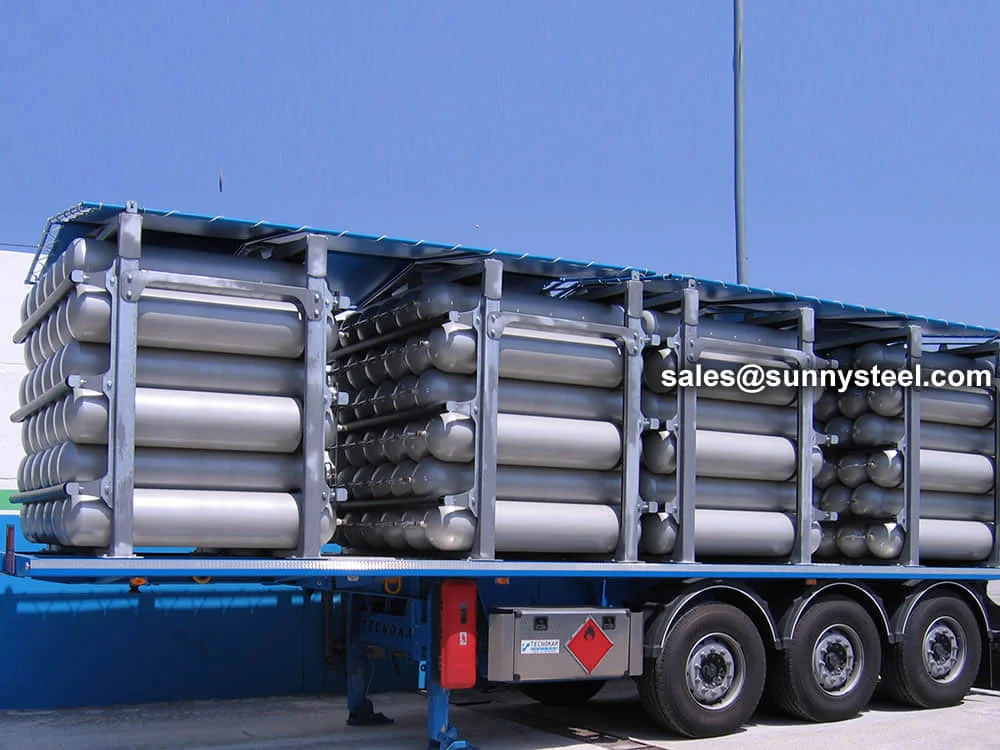

Steel pipe for gas cylinder offers high-strength, ...
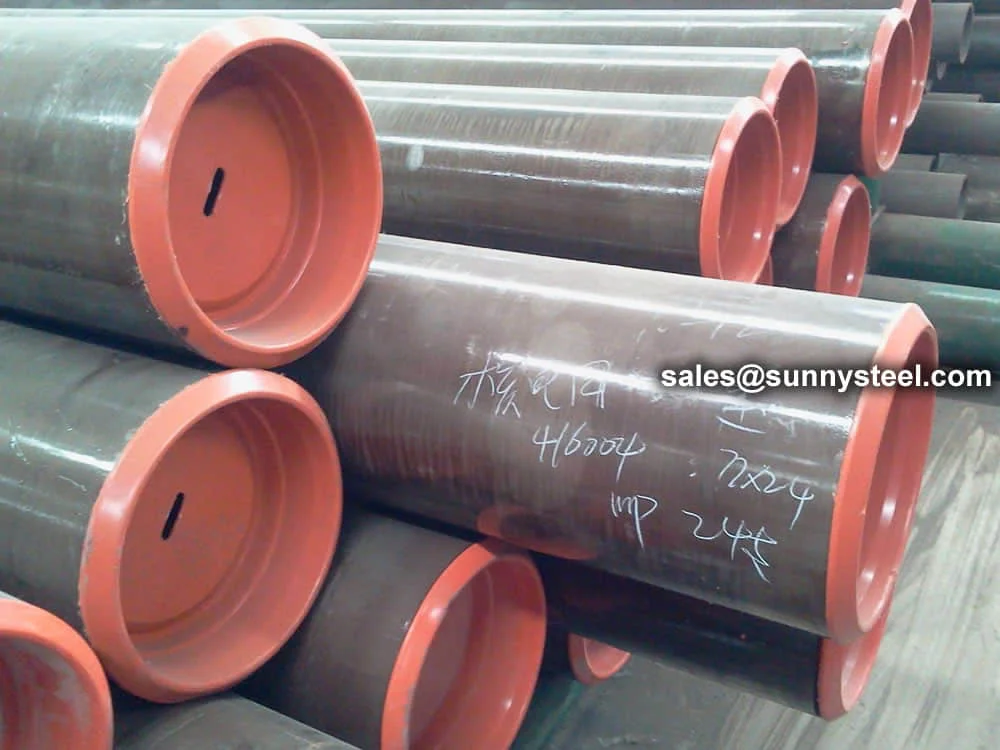

Seamless pipes for high-temperature applications o...
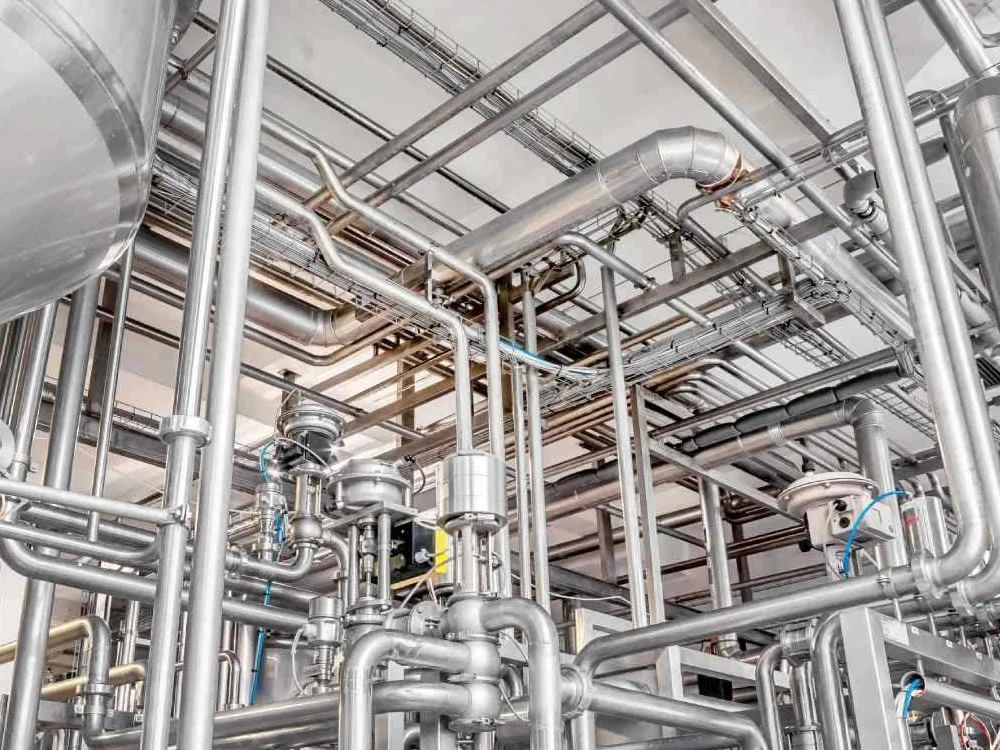

Pipes for chemical equipment provide exceptional c...