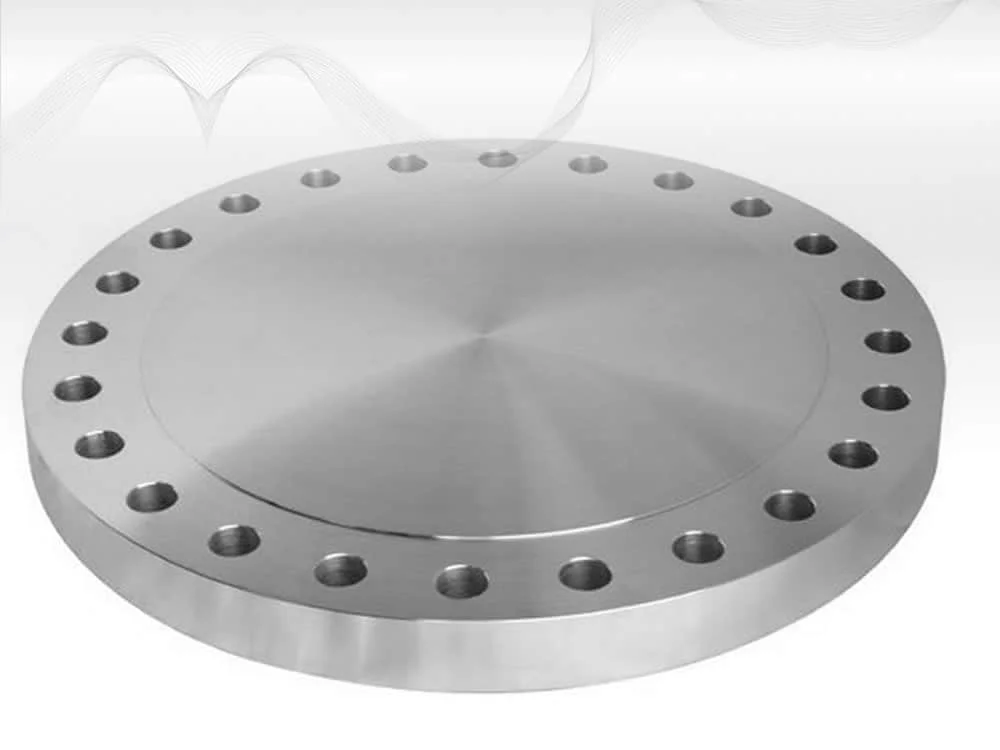
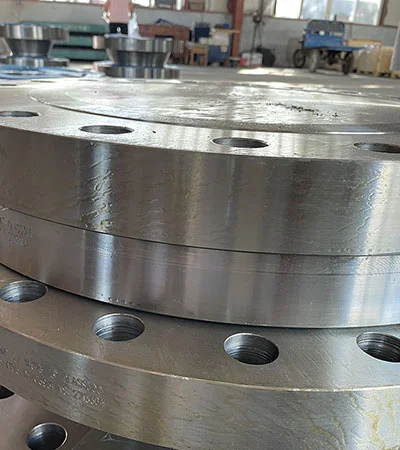
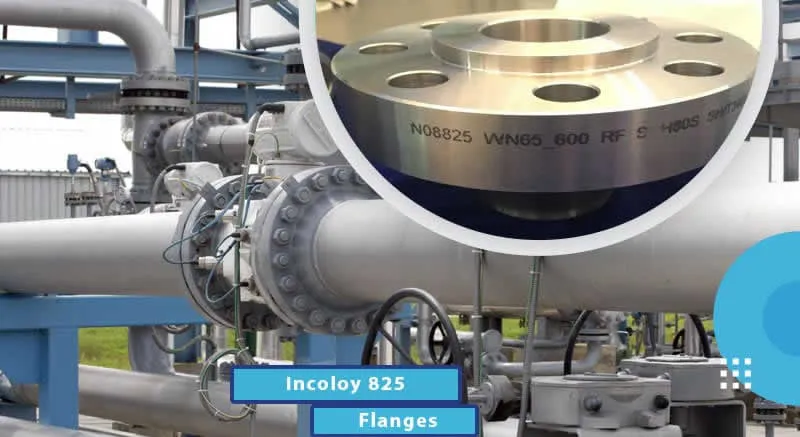
Blind Flange is a solid disc used to seal the end of a piping system, preventing flow and
providing pressure containment. Conforming to ASME B16.5, ASME B16.47, and DIN standards, it is crafted from
materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys for durability in harsh conditions.
The Sealing Flange Solution features a flat or raised face with bolt holes for secure
attachment, available in sizes from 1/2” to 60” and pressure ratings up to 2500 PSI. Its design allows for
easy inspection or future expansion by removing the flange, making it ideal for temporary or permanent
closures.
Blind Flange undergoes hydrostatic and ultrasonic testing to ensure leak-proof performance.
Coated with galvanizing or FBE for corrosion resistance, it withstands temperatures from -20°C to 600°C,
depending on the material, and is suitable for high-pressure applications in oilfields and refineries.
Compared to pipe caps, Blind Flange offers greater accessibility and reusability, enabling
system modifications without cutting pipes. Proper bolt torque and gasket selection are key to maintaining
its seal integrity. With a service life of 20–40 years, it is a cost-effective closure option.
Blind Flange addresses challenges like pressure leaks and corrosion in industrial piping,
providing a reliable, durable, and adaptable solution for sealing oil, gas, and chemical pipelines.

DIN16 Blind Flange
What is a Blind Flange?
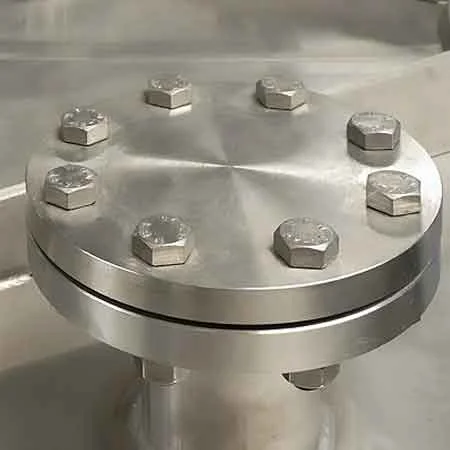
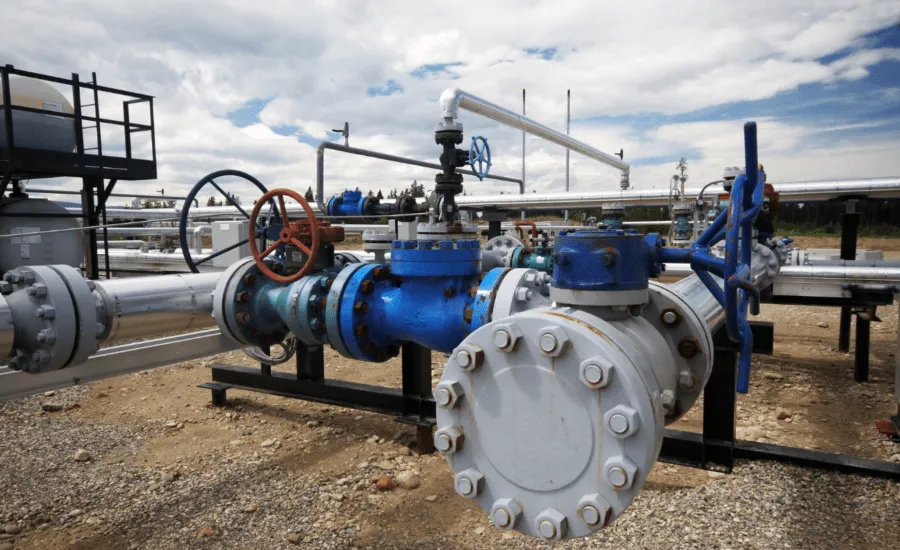
Blind flanges are providing a means to seal off the end of a pipe or vessel.
These flanges are typically solid discs bolted onto the pipe’s end, typically with a defined
facing for sealing. Blind Flanges are used for many applications, including:
- Isolation of pipe sections for maintenance or repai
- Termination of pipelines
- Pressure testing
- Access points for cleaning or inspection
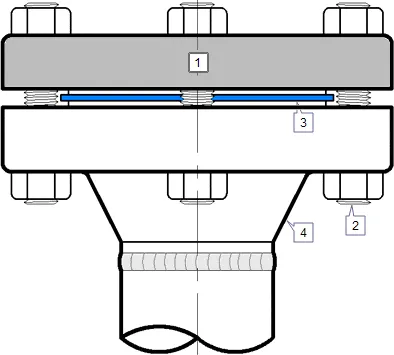
1. Blind flange 2. Stud Bolt 3. Gasket 4. Other flange
Major Function - Where to use
The blind flange is used to close ends of piping systems.
It is a kind of round plate with no center hold but with all the proper bolt holes. This
blind flange is available in various sizes and materials and is used to provide positive
closer on the ends of pipes, valves or equipment nozzles. This flange helps in easy access
to a line once it has been sealed. The blind flange is sometimes custom made or machined to
accept a nominal sized pipe to which reduction is being made.
A blind flange is useful for making repairs to a pipeline further up the line. In fact,
during construction of a pipeline, a blind flange may be built into the final length of
pipe. This allows for expansion or continuation of the pipeline simply by adding onto the
final flange.