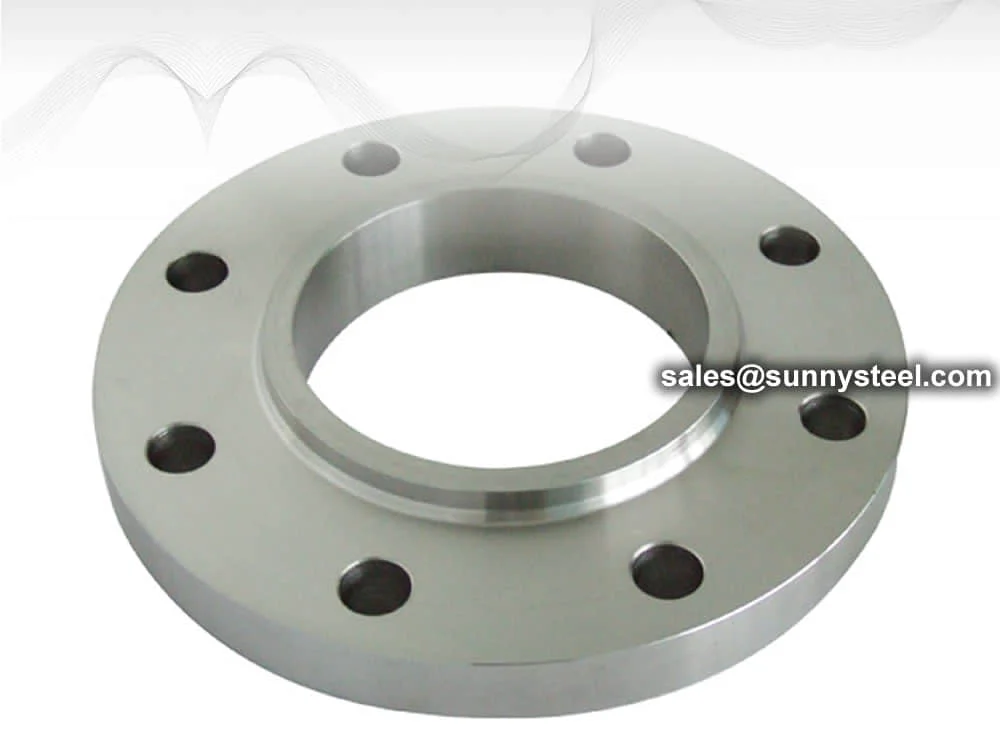
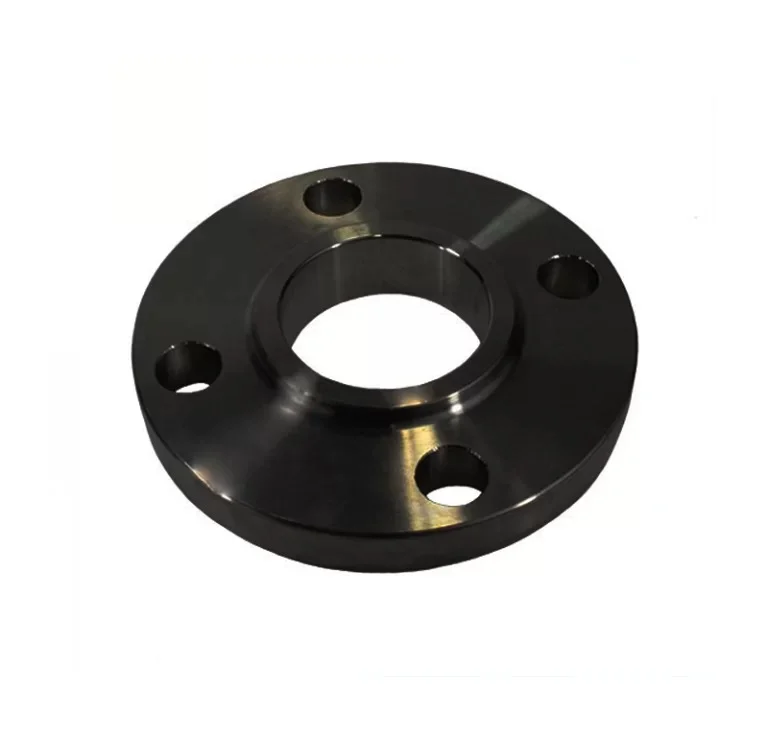
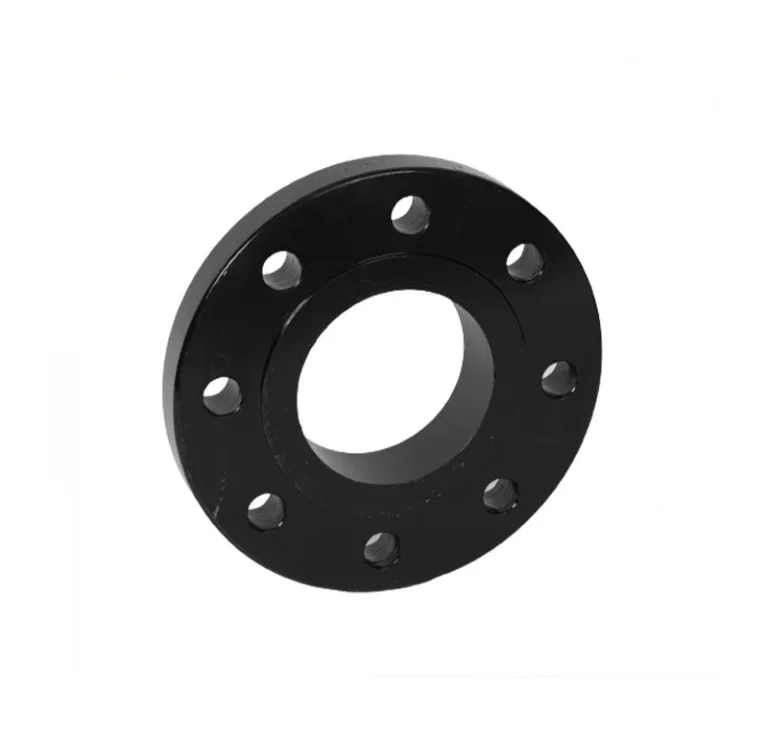
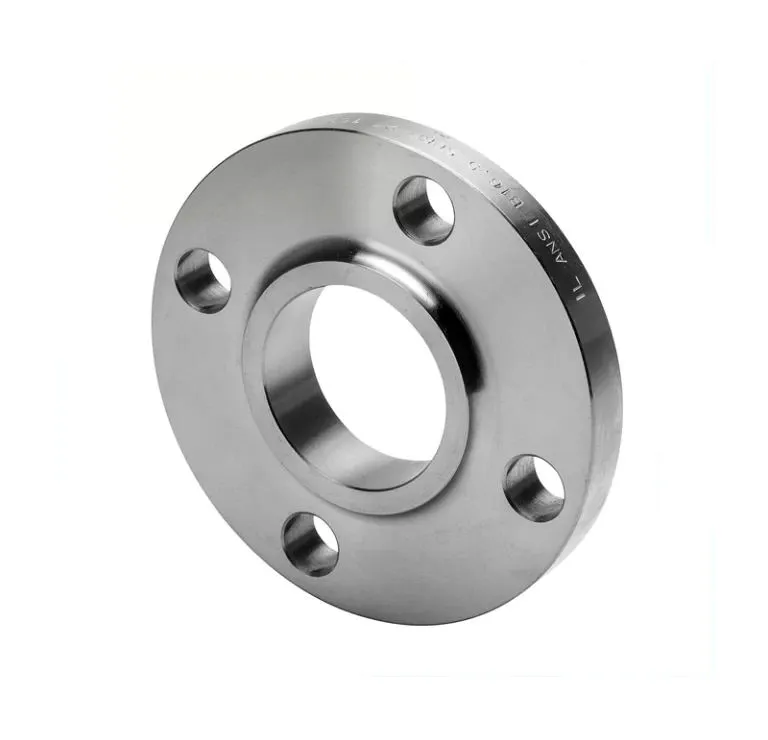
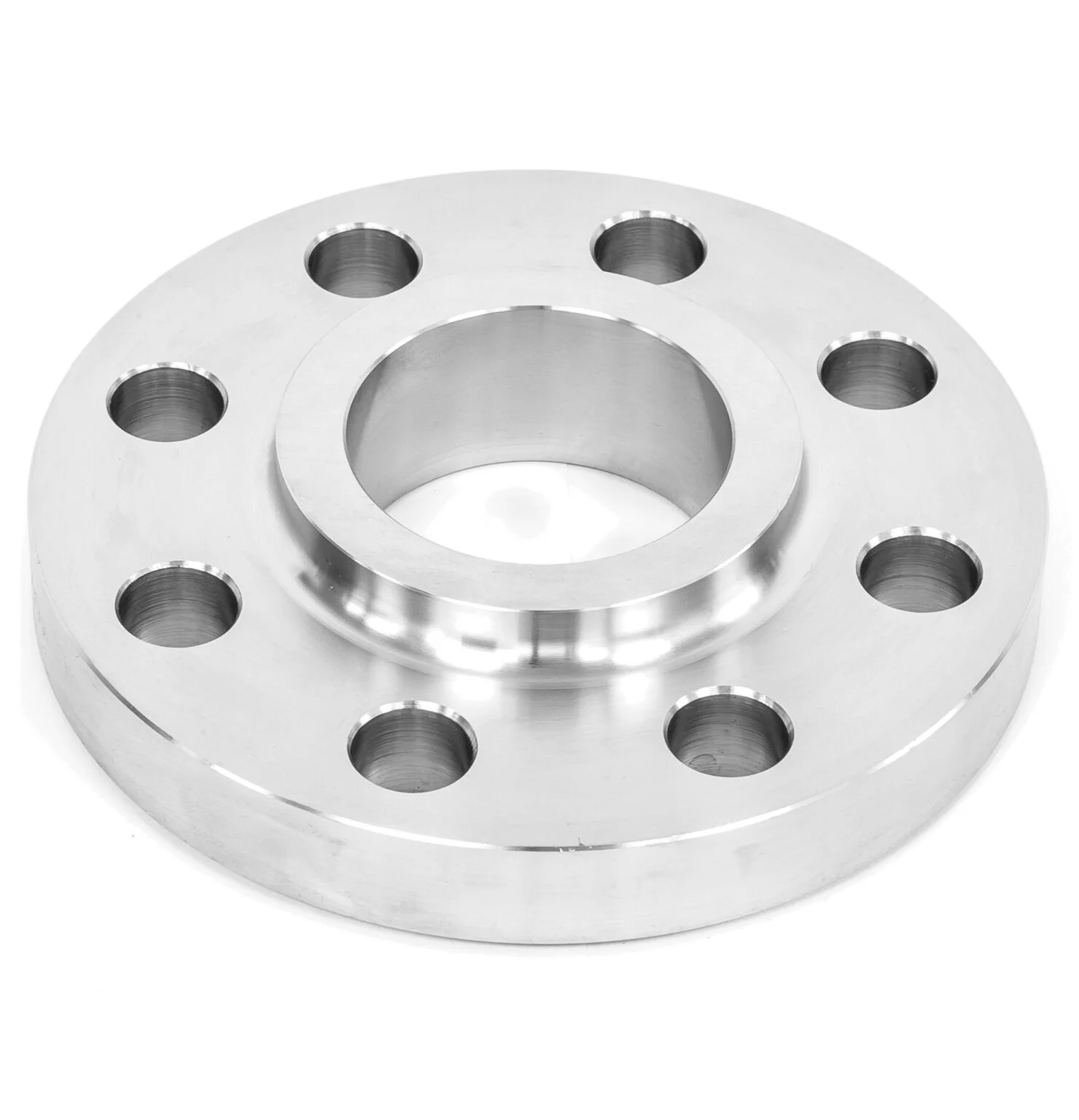
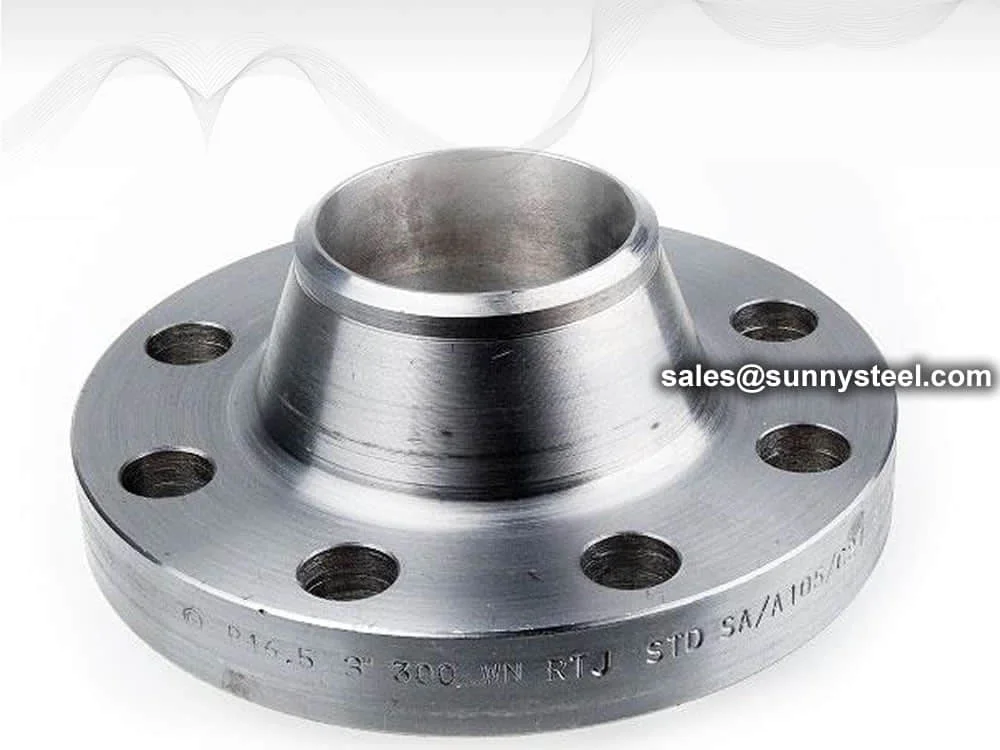
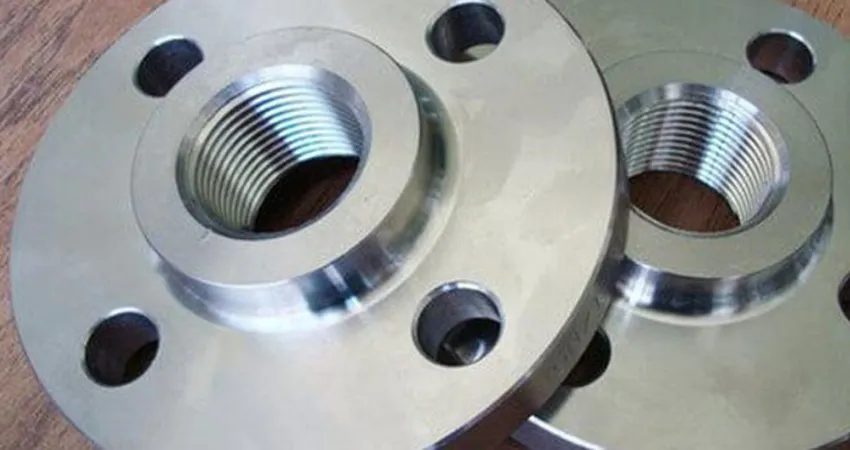
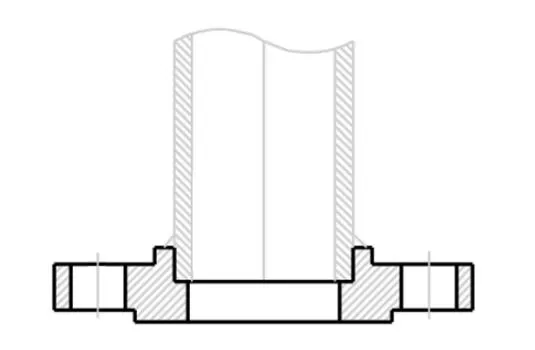
Slip-On Flange is a ring-shaped fitting slipped over the pipe end and welded on both sides,
offering a simple and economical connection. Compliant with ASME B16.5 and DIN standards, it is crafted from
carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys for durability. As of August 19, 2025, it remains a top choice for
efficient piping.
The Easy Pipe Flange features a slightly larger bore than the pipe, allowing easy
installation and alignment, with pressure ratings up to 300 PSI for Class 150 and 600 PSI for Class 300.
Available in sizes from 1/2” to 24”, it suits low to moderate-pressure systems.
Slip-On Flange undergoes hydrostatic and radiographic testing to ensure leak-proof
performance. Coated with galvanizing or FBE for corrosion resistance, it operates effectively from -20°C to
400°C, depending on material, making it ideal for oil and gas pipelines.
Compared to weld neck flanges, Slip-On Flange reduces installation time and costs, though
it offers less strength for high-pressure applications. Proper welding and alignment are essential for a
secure joint. It provides a service life of 15–30 years.
Slip-On Flange addresses challenges like high installation costs and misalignment in
industrial piping, delivering an efficient, durable solution for oil, gas, and water treatment systems as of
August 2025.
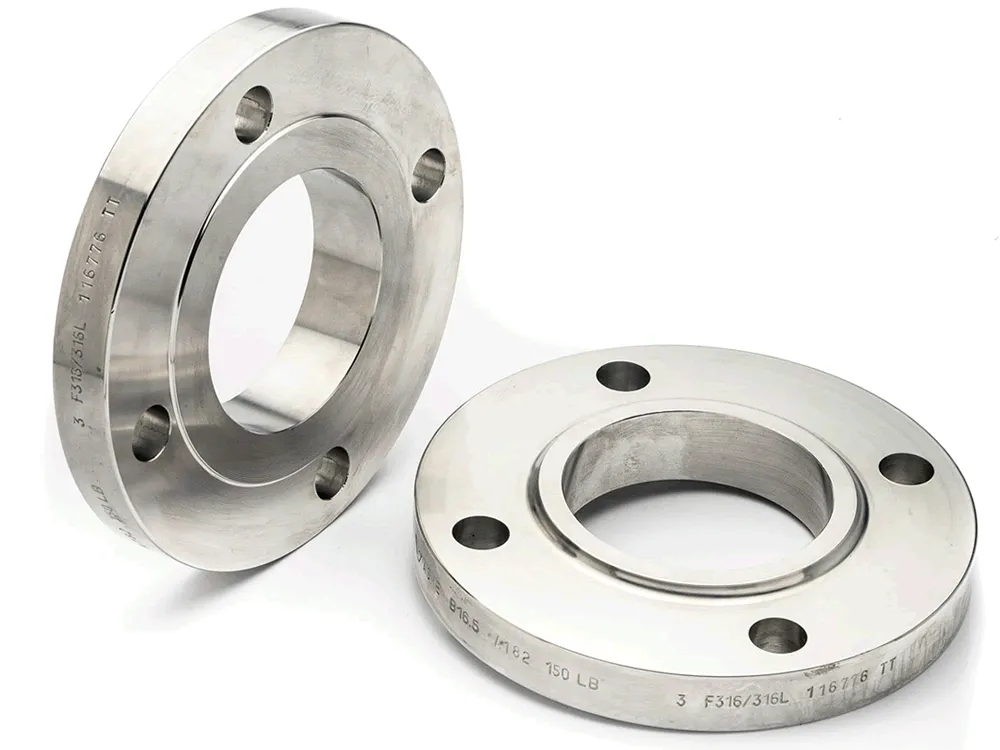

Stainless 316L Slip-on Flange
What Is a Slip-On Flange?
Slip-on flanges are versatile pipe fittings designed for easy welding and length
adjustment, ideal for lower pressure applications.
Lap Joint flanges are sometimes referred to by other names, including:
- Simple structure & easy installation
- Connected with fillet welds (top &
bottom)
- Cost-effective solution
- Suitable for low-pressure
applications
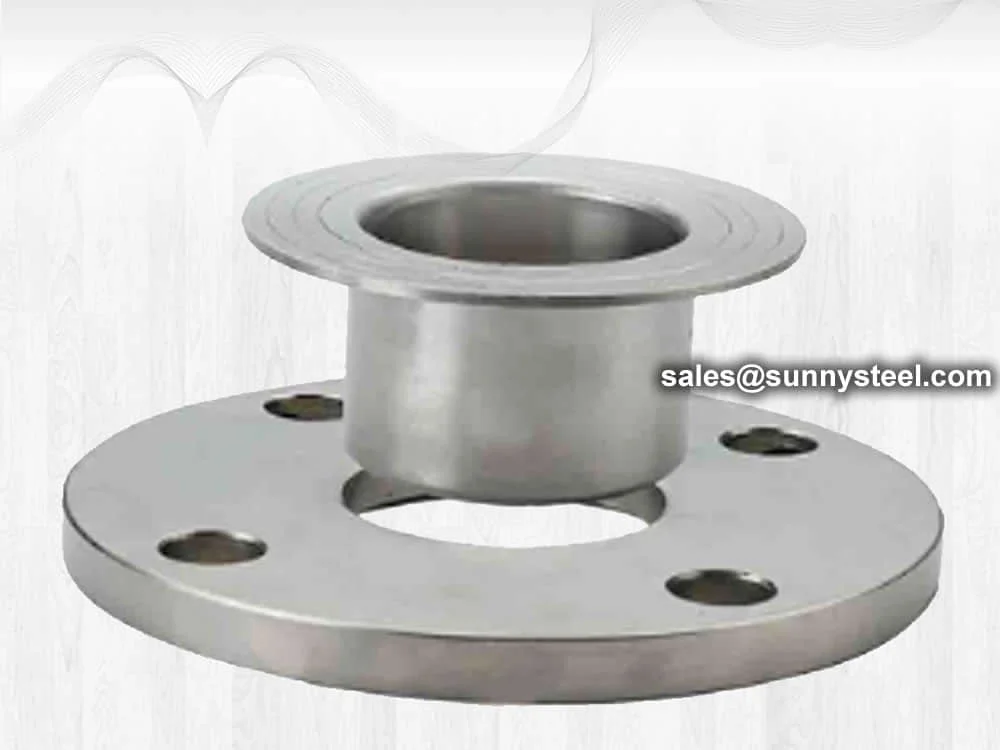
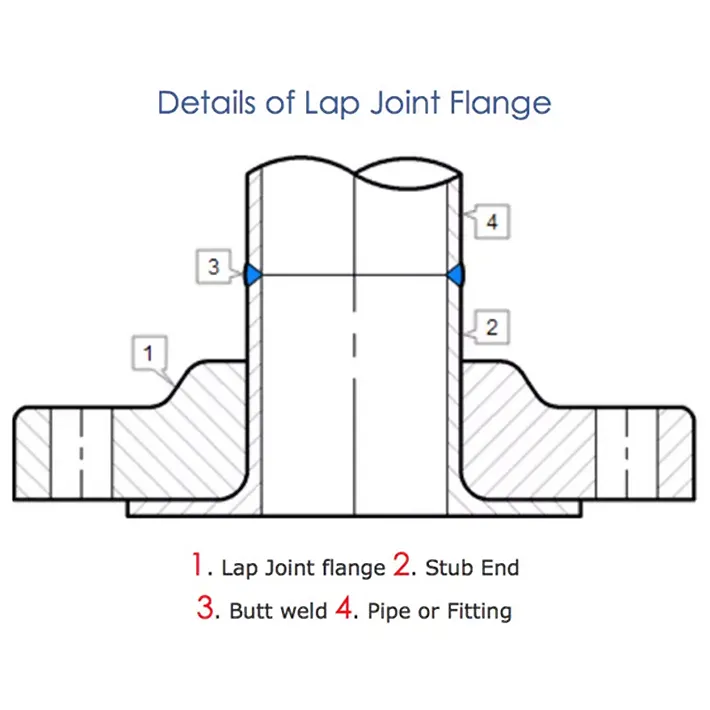
Lap joint flange is used with a lap joint stub end fitting. Lap joint flange is similar to a slip-on flange,
but with two differences. The radius and the flat face, both allow the flange to secure against the stub end
fitting. This is useful where alignment of bolt holes is difficult, such as with spools to be attached to
flanged nozzles of vessels. A lap joint is used in low pressure applications and not suitable where high
external of heavy loads are present.
These flanges are always used with either a stub end or taft which is butt welded to the pipe with the flange
loose behind it. This means the stub end or taft always makes the face. The lap joint is favoured in low
pressure applications because it is easily assembled and aligned. To reduce cost these flanges can be
supplied without a hub and/or in treated, coated carbon steel.
Lap joint flanges are usually used in low pressure applications and are not suitable when there are high
loads on the flange pair. Some types of piping require the use of lap joint flanges. For example, metallic
pipe that has been plastic lining may have lap joint flanges.
Using lap joint flanges might be an option for saving costs when the piping is made of exotic materials. By
using a lap joint flange, the wetted materials would consist of the exotic materials and the flange would be
carbon steel. Since the flange doesn’t ever come in contact with the process fluid, it would not be
affected by the fluids.
Dimensions on the lap joint flange are similar to weld neck, slip on or socket weld flanges. The backing
flange has the same number of bolt holes, size and thickness of a weld neck or slip on flange.
Lap joint flange (simplified as LTF flange) shape is similar to slip on flange, it has a curved radius at the
bore, which can connect with a stub end fittings and slide over the pipe. In this form, the pipe is usually
welded to this stub end so the lap joint flange can rotate freely around the stub end.
The advantage of this combination that it will be easy with alignment for the bolt hole, easy to install and
uninstall, much more convenient to do examinations and maintenance.
The lap joint stub end is butt welded to the pipe, while the lap joint flange is slid onto the pipe before
the final welding takes place. The flange has a raised flat portion called the lap, which allows it to
overlap with the flanged portion of the stub end, creating a tight seal.
Lap joint flanges are known for their ease of installation and cost-effectiveness. They provide flexibility
and can accommodate slight misalignment or movement between the pipe and the flange. However, they are not
as strong as other types of flanges, such as welding neck or slip-on flanges.
It's important to note that lap joint flanges should not be used in applications with high temperatures or
high pressures, as they may not provide the necessary strength and sealing capabilities. Consulting with a
qualified engineer or referring to relevant standards and guidelines is recommended when selecting the
appropriate flange type for a specific application.
Lap joint flange with stub end
Working Environment
Lap joint flange is typically used for low pressure application.
It is not suitable when the flange pair need to bear high loads. Some pipes required to use
this type flange, like a metal pipe already lined with plastic may have to use lap joint
flanges.
Types of Slip On Flange Welding
The SO flange can be divided into SO welding plate flange and SO welding hubbed steel pipe
flange.
Its mechanical characteristics are between the integral flange and the looping flange. The structure is
simple, and the processing is convenient. So slip on flange welding is widely used in various fluid
pipelines. Depends on different face, there are also ranges raised face type and ring type joint face type.
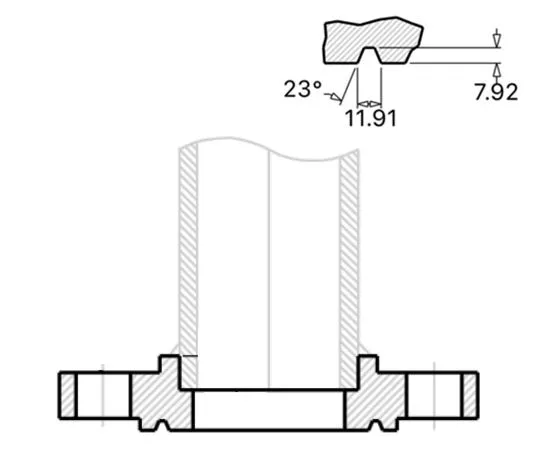
Raised Face Slip On Flanget
There is a small portion extruded from the bottom face of the slip on flange, this type is raised
face slip on flange. The function of this area is to place a gasket seat during installation to
get a better sealing performance.
As the pressure ratings bigger, the height of this raised face will be bigger.
RTJ Slip on Flange
A small grooved is machined on the raised face part, this form is called RTJ type, the function of this groove is to place the gasket ring, also applied for sealing, compared to RF type, RTJ is designed for high pressure use.
Slip on flange use slip welding to connect equipment, so either below of name is describing the same flange:
- Slip on weld flange
- Slip on flange weld
- Weld slip on flange
- Slip on flange welding
- SO flange
Advantages of Slip On Flange
Slip-On flanges or SO flanges are commonly lower in price than weld-neck flanges, and to this effect are a popular choice for our customers.
- Lower installation costs
- More easy to align with other parts during installation
- Better leaking proof
- Inner and outer welding on flange
- Takes less time to cut accurately for the pipelines
- As pipe slides on the flange, it compatible with lower hub on slip on flange
Slip-on flange datasheets
ASME B16.5 Slip-On (SO) Flange Datasheets by Class and Face Type
| Class |
Flat Face (FF) |
Raised Face (RF) |
Ring Type Joint (RTJ) |
| ANSI 150 |
SO Flange ANSI 150 FF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 150 RF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 150 RTJ (in) |
| ANSI 300 |
SO Flange ANSI 300 FF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 300 RF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 300 RTJ (in) |
| ANSI 400 |
SO Flange ANSI 400 FF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 400 RF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 400 RTJ (in) |
| ANSI 600 |
SO Flange ANSI 600 FF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 600 RF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 600 RTJ (in) |
| ANSI 900 |
SO Flange ANSI 900 FF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 900 RF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 900 RTJ (in) |
| ANSI 1500 |
SO Flange ANSI 1500 FF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 1500 RF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 1500 RTJ (in) |
| ANSI 2500 |
SO Flange ANSI 2500 FF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 2500 RF (in) |
SO Flange ANSI 2500 RTJ (in) |
Note: The datasheets shown adhere to ASME B16.5, which covers flange dimensions from
½” to 24”. For sizes larger than 24”, please visit our flange datasheets page.