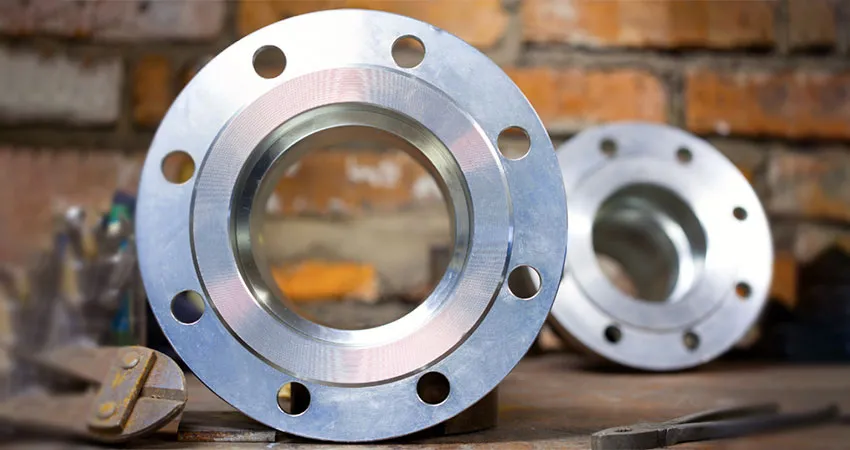
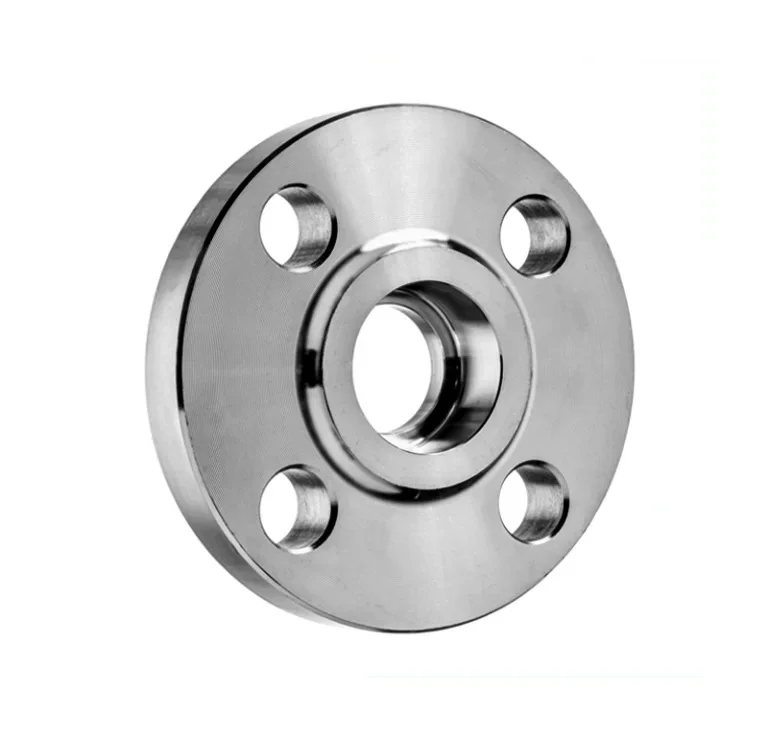
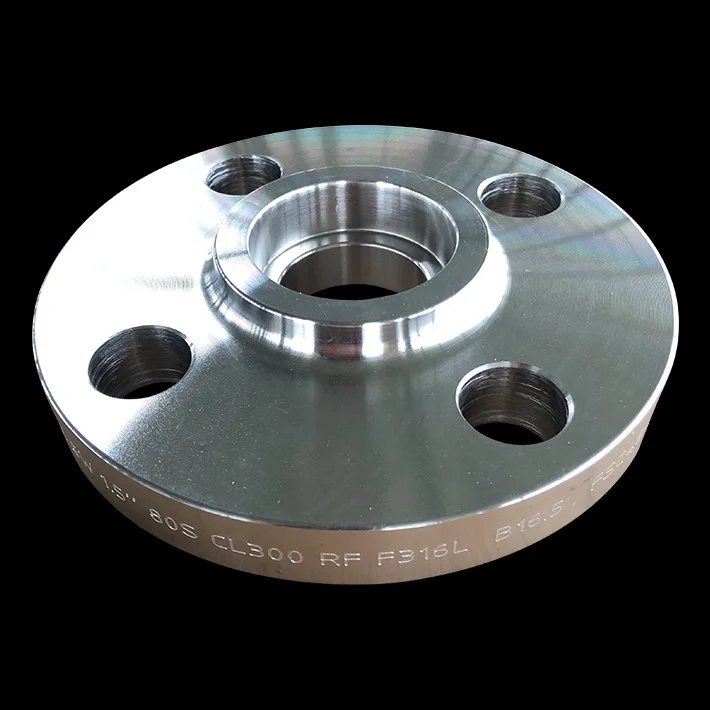
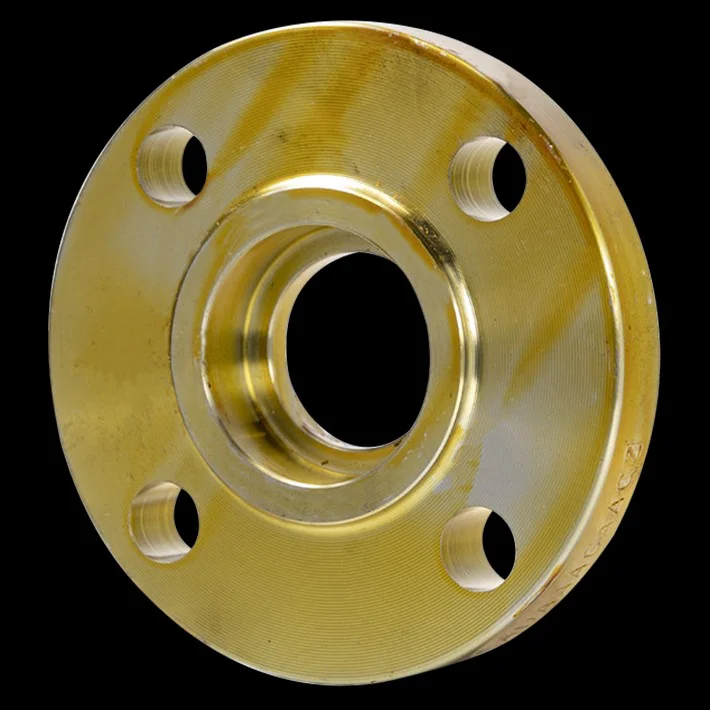
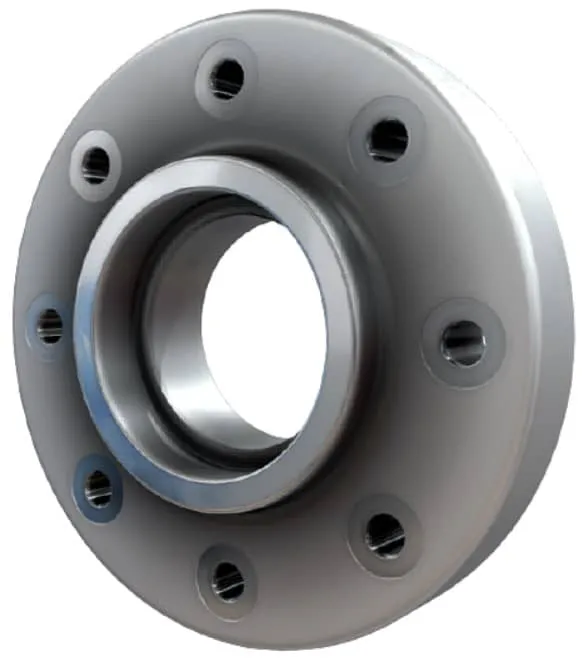
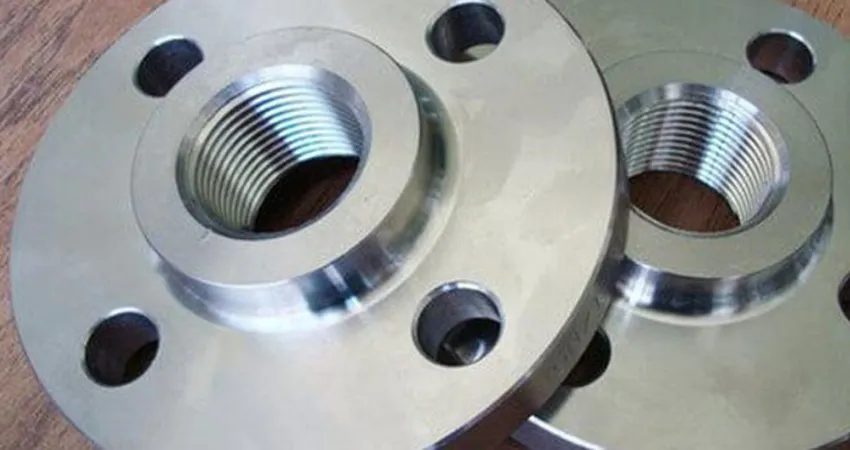
Socket Weld Flange is a forged fitting with a socket to insert the pipe, welded for a strong, leak-proof connection. Compliant with ASME B16.5, it uses carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloys for durability. As of August 19, 2025, it remains a preferred choice.
The High-Pressure Flange features a recessed area for pipe insertion, welded around the socket, offering pressure ratings up to 3000 PSI for Class 1500. Available in sizes from 1/2” to 4”, it suits high-pressure and high-temperature systems.
Socket Weld Flange undergoes ultrasonic and hydrostatic testing for reliability. Coated with galvanizing or FBE, it resists corrosion and operates from -20°C to 600°C, making it ideal for oil and gas and chemical processing as of August 2025.
Compared to slip-on flanges, Socket Weld Flange provides superior strength and fatigue resistance for high-pressure applications. Proper welding techniques ensure a secure joint, with a service life of 20–40 years.
Socket Weld Flange addresses challenges like leaks and pressure loss in industrial piping, offering a robust solution for oil, gas, and chemical systems as of August 19, 2025.
What is a socket weld flange?
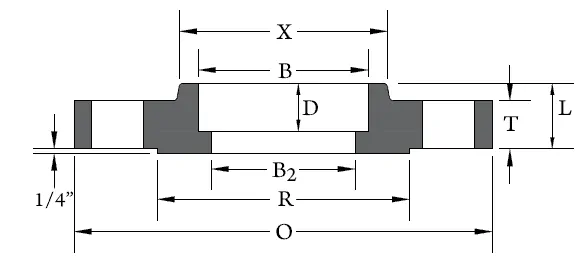
Socket weld flanges have a socket in which a pipe is inserted; the pipe is secured by one fillet weld located on the exterior of the flange hub.
A significant disadvantage with this type of flange is that it is not considered a high-integrity joint because the weld is difficult to prove; thus socket weld flanges are only suitable for low to medium classes (≤ ASME 600). Due to their lower integrity and unsuitability for use at higher pressures, socket weld flanges almost always have flat or raised faces.
The advantage of socket weld flanges is their simple design, they are well suited for small pipe size applications e.g. 2 inches (5cm) and below, and for non-critical applications e.g. non-hazardous systems; they are not suitable for highly erosive or corrosive systems.
Socket weld flange datasheets
For larger nominal sizes, it is safe to assume that a socket weld flange would be made to order for your application, due to the fact that larger pipe size assemblies will typically call for a slip on or weld neck connection.
ANSI Class Specifications for Raised Face Socket Flanges
| Class |
Raised Face |
| ANSI 150 |
Socket, ANSI Class 150 (in) |
| ANSI 300 |
Socket, ANSI Class 300 (in) |
| ANSI 400 |
Socket, ANSI Class 400 (in) |
| ANSI 600 |
Socket, ANSI Class 600 (in) |
| ANSI 900 |
Socket, ANSI Class 900 (in) |
| ANSI 1500 |
Socket, ANSI Class 1500 (in) |
| ANSI 2500 |
Socket, ANSI Class 2500 (in) |