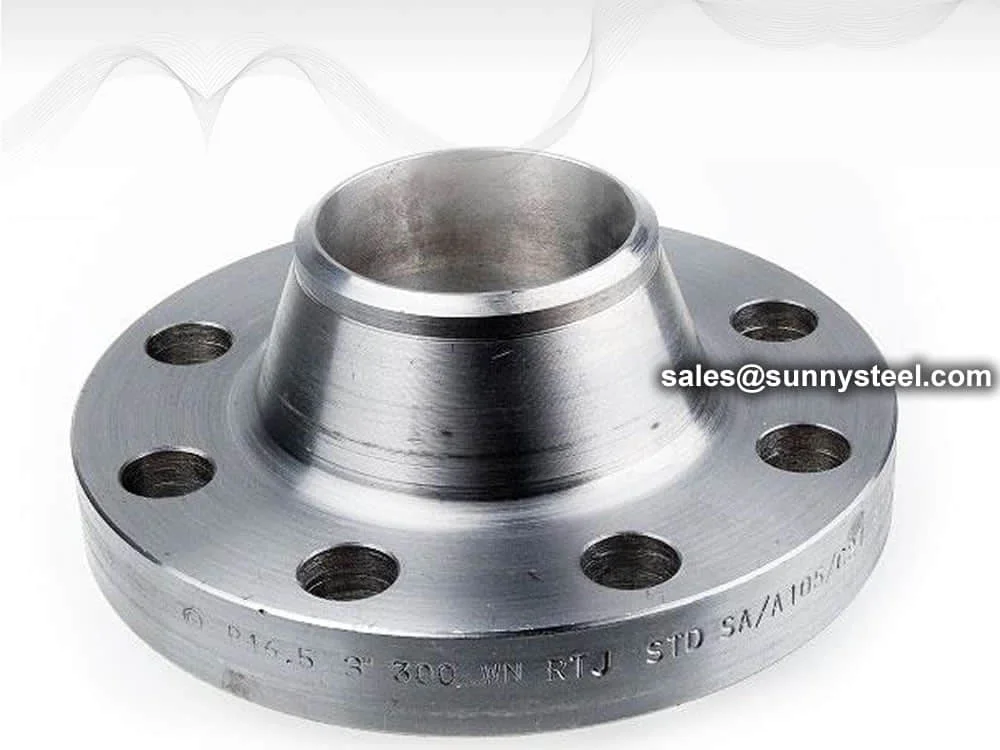
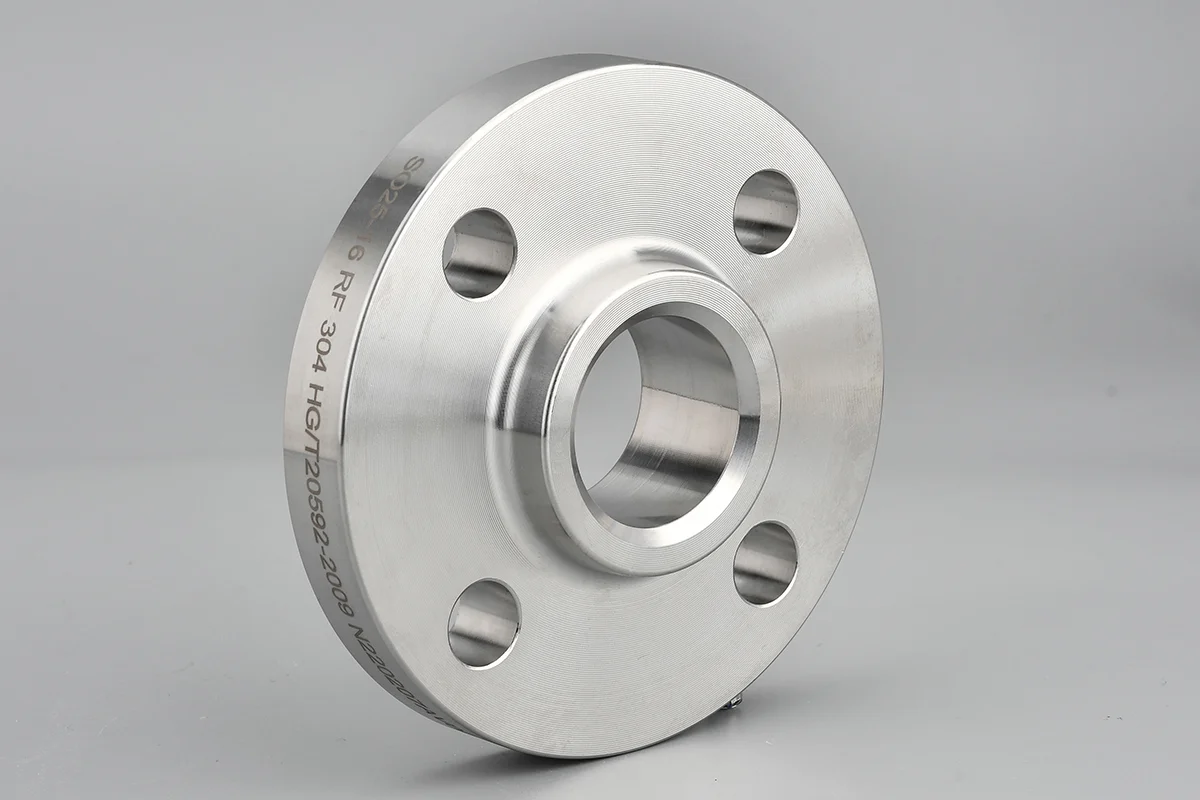
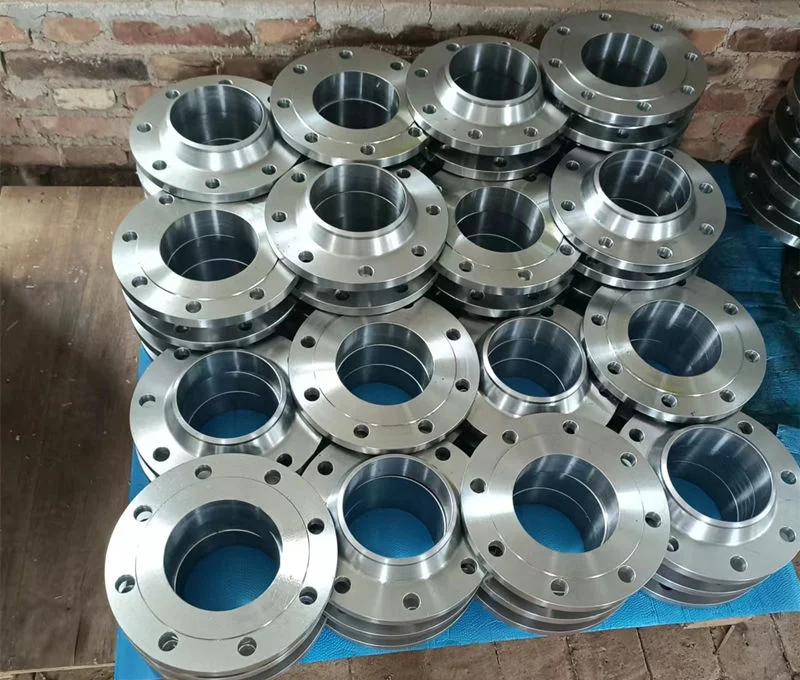
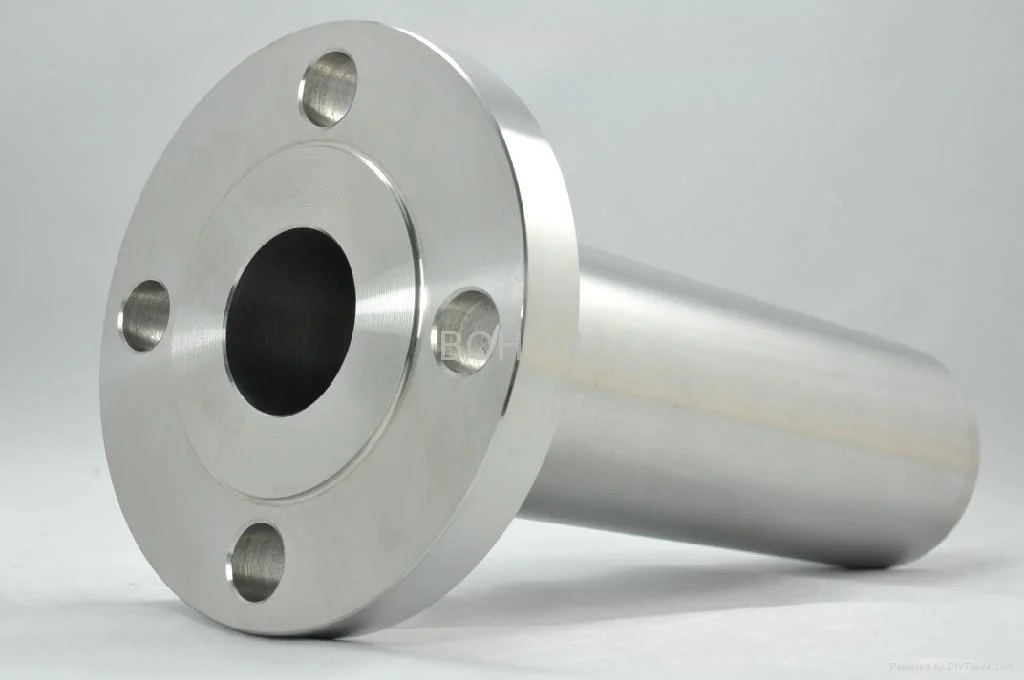
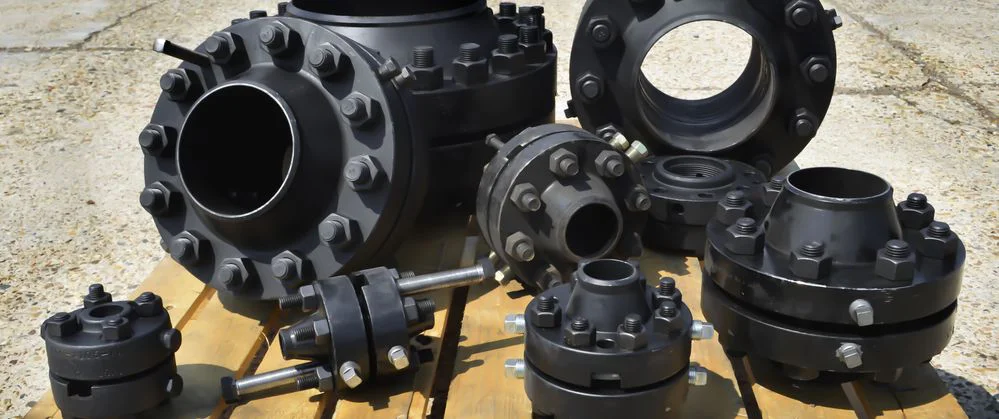
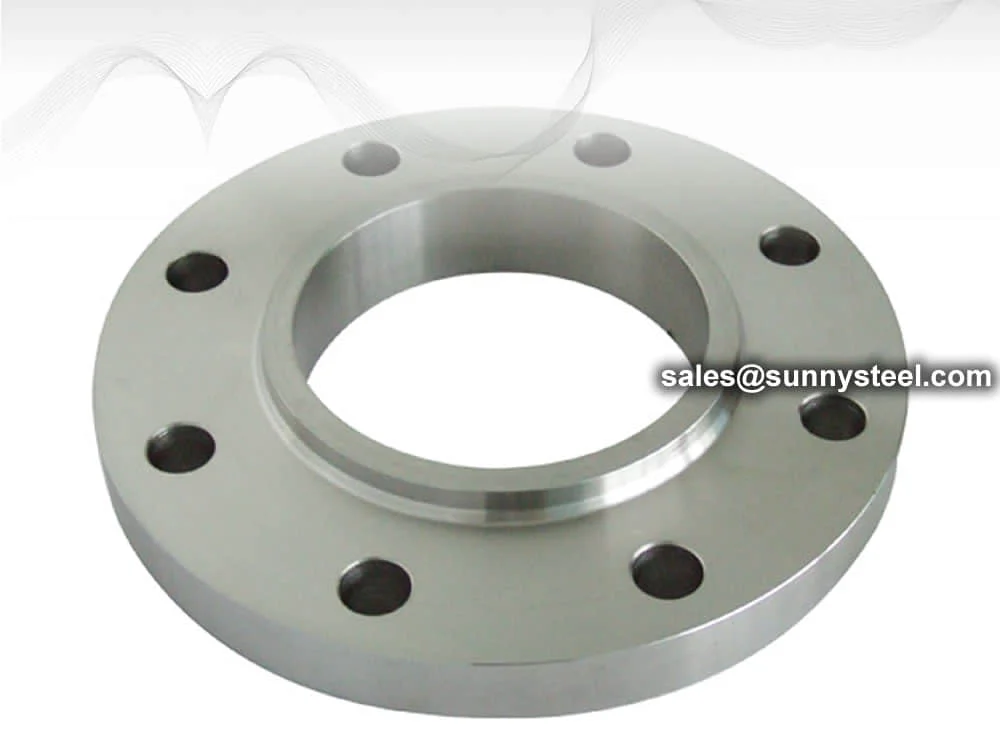
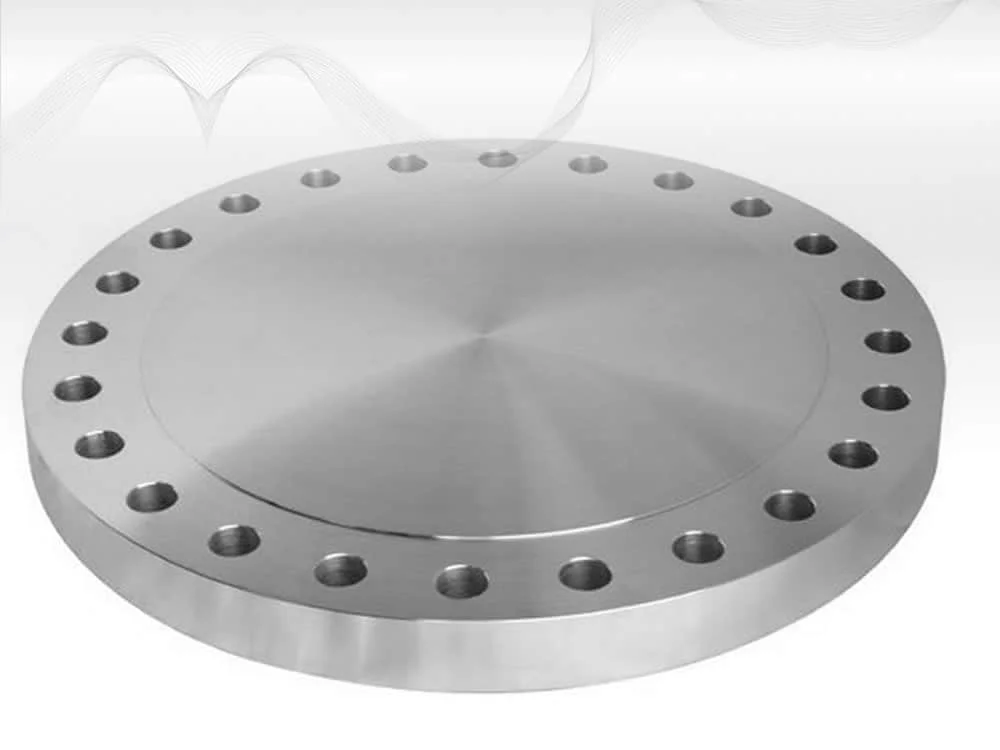
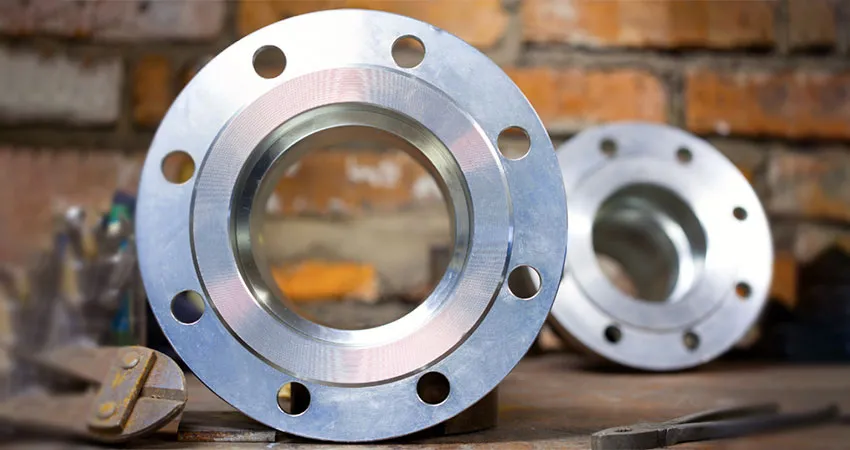
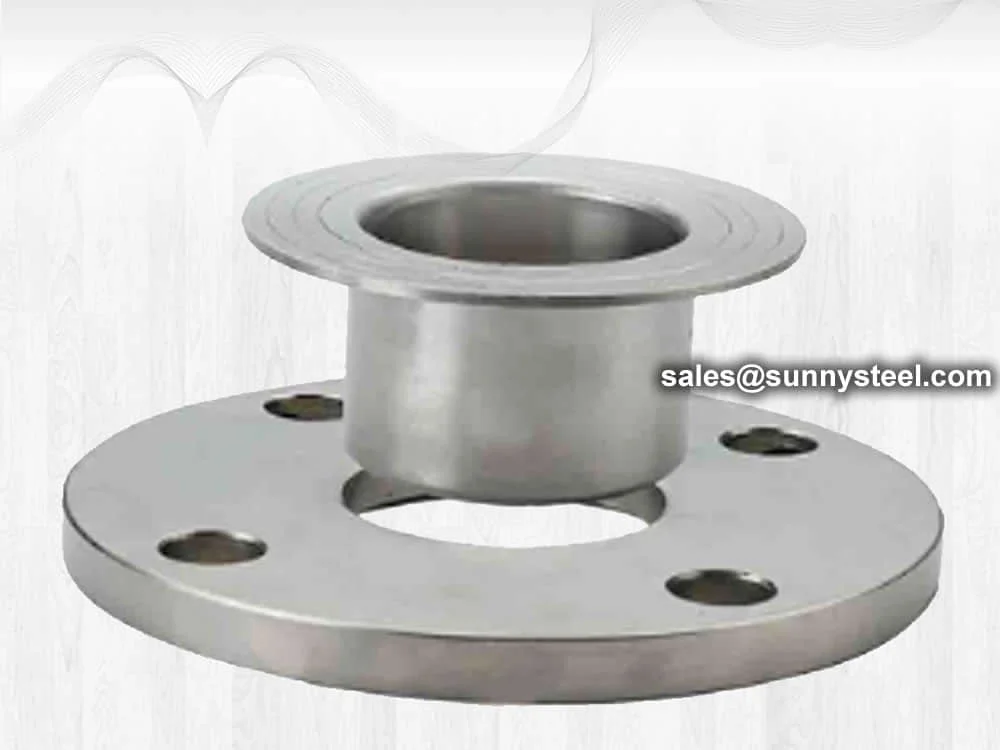
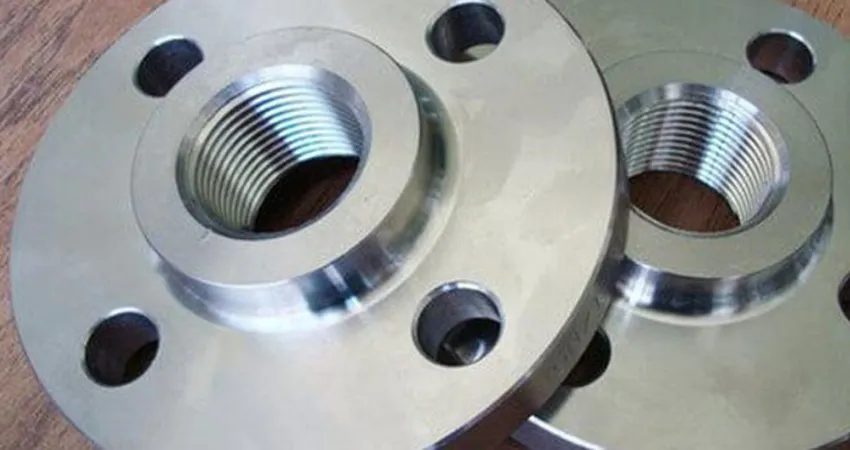
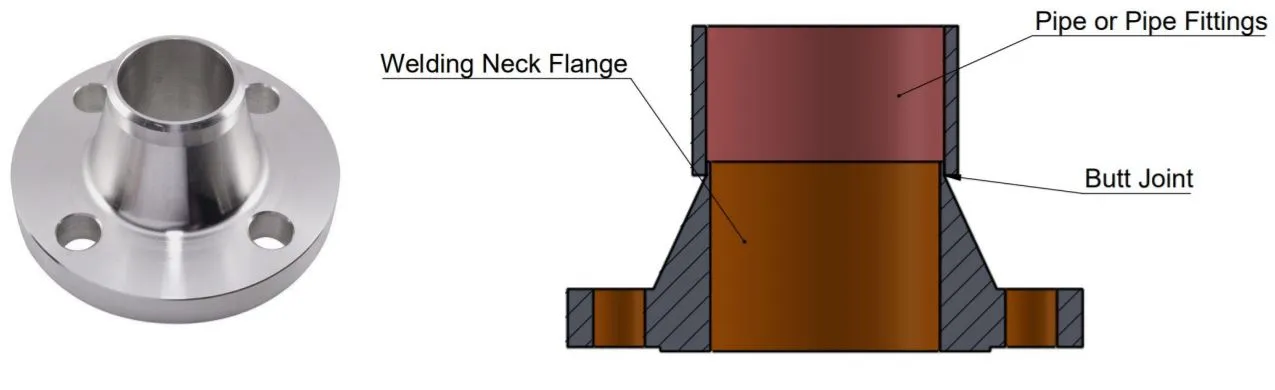
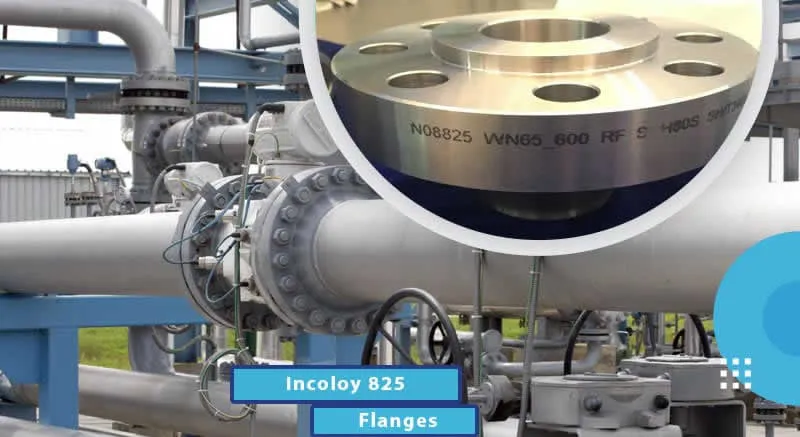
Welding Neck Flange
High-strength And High-pressure Piping Solution
Welding neck flanges provide high-strength, high-pressure piping connections with excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for oil, gas, and power systems.
Welding Neck Flange
High-strength And High-pressure Piping Solution
Welding neck flanges provide high-strength, high-pressure piping connections with excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for oil, gas, and power systems.