| Oil and Gas |
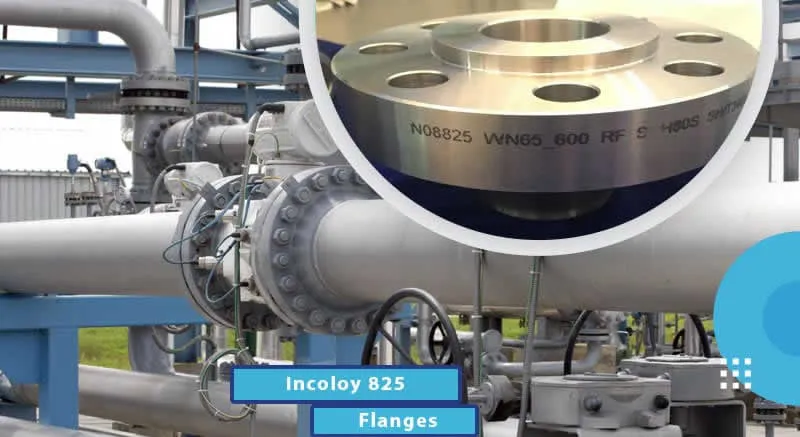
• Pipelines (Crude Oil/Gas Transmission): Stainless steel
Nipoflanges (e.g., ASTM A182 F316) are used for onshore/offshore pipelines,
resisting corrosion from saline environments and hydrocarbon impurities.
• Wellhead & Processing Facilities: High-pressure Nipoflanges (ASME
B16.5 Class 300/600) adapt to wellhead pressure fluctuations and high-temperature
fluid processing.
|
| Chemical Industry |
• Corrosive Fluid Handling: Duplex/super duplex steel Nipoflanges
(e.g., ASTM A182 F51) or nickel-alloy (Hastelloy) Nipoflanges are used for acids
(sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid) and solvent pipelines, preventing material
degradation.
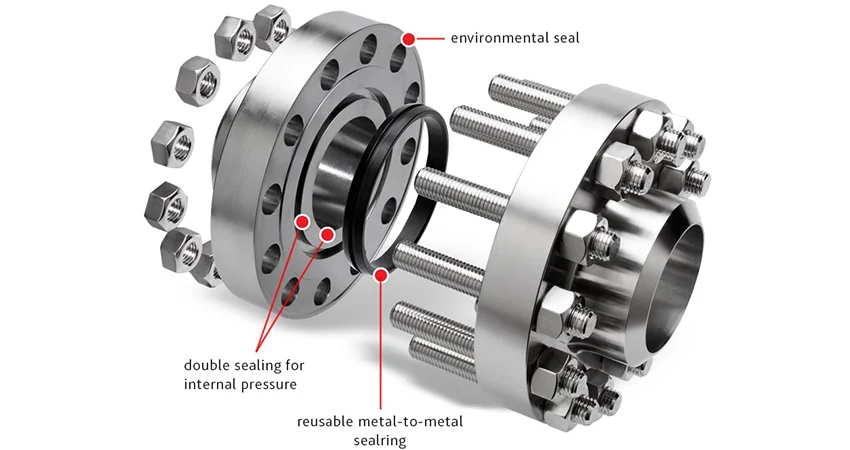
• Reactor & Tank Connections: Nipoflanges with tight-seal designs
(raised face/RF) ensure no leakage of toxic or flammable chemicals, complying with
safety standards (e.g., API 598).
|
| Plumbing (Commercial/Civil) |
• Building Water/Gas Piping: Alloy steel Nipoflanges (e.g., ASTM
A350 LF2) or carbon steel (ASTM A105) Nipoflanges are used for indoor plumbing,
balancing cost-effectiveness and resistance to tap water corrosion.
• HVAC Systems: Low-pressure Nipoflanges (Class 150) connect
heating/cooling water pipelines, ensuring stable fluid circulation.
|
| Heating Systems |
• District Heating Networks: Carbon steel Nipoflanges (ASTM A105)
with anti-corrosion coatings (epoxy) are used for high-temperature hot water
(≤120°C) transmission pipelines, resisting scale buildup and thermal stress.
• Residential Boilers: Small-diameter Nipoflanges (NPS 2-4) connect
boiler outlets to heating pipes, ensuring tight sealing to prevent steam leakage.
|
| Water Supply Systems |
• Municipal Water Treatment: Carbon steel Nipoflanges (ASTM A105) or
304 stainless steel Nipoflanges are used for raw water, treated water, and sewage
pipelines, adapting to chlorine disinfection environments.
• Desalination Plants: Stainless steel Nipoflanges (F316L) resist
seawater corrosion in reverse osmosis (RO) water supply lines.
|
| Power Plants (Thermal/Nuclear) |
• Thermal Power: High-temperature alloy Nipoflanges (e.g., ASTM A182
F22) are used for boiler steam pipelines (≤550°C) and turbine connections, complying
with ASME B16.5 for dimensional accuracy.
• Nuclear Power: Nickel-alloy (Inconel) or titanium Nipoflanges are
used in reactor cooling systems, resisting radiation-induced material fatigue and
high-pressure coolant (water/helium) erosion.
|
| Paper and Pulp Industry |
• Pulp Processing Lines: Nipoflanges with wear-resistant materials
(e.g., alloy steel with hard chrome plating) are used for wood pulp, black liquor,
and bleaching agent (chlorine dioxide) pipelines, preventing abrasion from pulp
fibers.
• Drying Section: High-temperature Nipoflanges (Class 150/300)
connect steam-heated drying cylinders, ensuring stable heat transfer for paper
production.
|
| Food Processing Industry |
• Hygienic Piping (Dairy/Beverages): 304/316L stainless steel
Nipoflanges (ASTM A182) with smooth surfaces (polished to Ra ≤ 0.8 μm) are used,
complying with FDA/USDA standards to avoid food residue and bacterial growth.
• Canning & Brewing: Nipoflanges with sanitary gaskets
(silicone/EPDM) connect fruit juice, beer, or canned food processing lines, ensuring
no contamination of edible products.
|
| Manufacturing Industry |
• Automotive/Aerospace: Small-diameter Nipoflanges (NPS 1/2-2)
connect hydraulic oil, coolant, or fuel pipelines in production equipment, ensuring
precise fluid control for machining processes.
• Heavy Machinery: Carbon steel Nipoflanges (ASTM A105) are used for
construction machinery (excavators, cranes) hydraulic systems, withstanding
vibration and mechanical stress.
|
| Structural Pipes |
• Industrial Buildings/Steel Structures: Carbon steel Nipoflanges
(ASTM A105) connect structural support pipes (e.g., for scaffolding, equipment
frames) or fire-fighting pipelines, balancing load-bearing capacity and corrosion
resistance (with galvanized coatings).
• Offshore Platforms: Corrosion-resistant Nipoflanges (stainless
steel or coated carbon steel) connect structural pipes, adapting to marine salt
spray environments.
|
| General Purpose Applications |
• Low-Pressure Fluid Transfer: Carbon steel Nipoflanges (Class 150)
are used for non-corrosive fluids (air, freshwater) in workshops, warehouses, or
small-scale processing facilities, prioritizing cost-effectiveness.
• Equipment Maintenance: Standardized Nipoflanges (ASME B16.5) serve
as replacement parts for aging pipelines or machinery, ensuring compatibility with
existing systems.
|