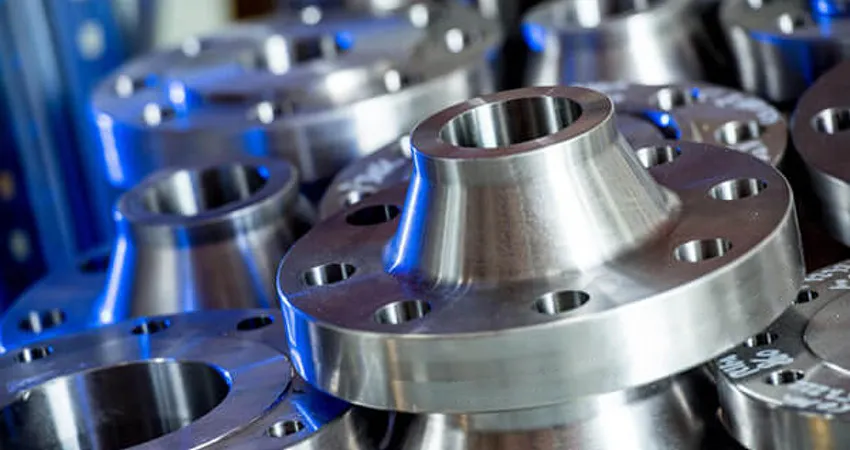
Reducing Flanges are versatile steel flanges engineered to connect pipes of varying
diameters, adhering to ASME B16.5 standards as of August 23, 2025, 05:48 PM PDT. These Pipe Size
Transition Flanges facilitate seamless flow transitions in industrial systems.
Available in sizes from 1/2” to 48”, Reducing Flanges support pressure ratings from Class
150 to 2500 and temperature tolerances up to 600°C, depending on the material, making them suitable for
diverse applications.
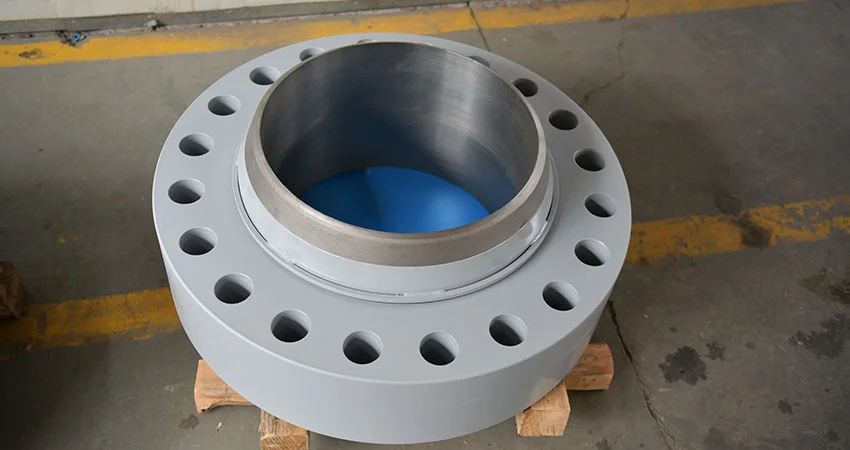
Reducing flanges are a specialty flange that are most often used on projects that require the fitting
together of different sized pipes.
Our range of plate flanges can be availed in different dimensional specifications depending upon the
requirements and their applications.
Crafted through forging or machining, these flanges ensure durable transitions, with coatings like 3LPE or
galvanizing enhancing corrosion resistance as of August 2025. Their design optimizes
industrial piping efficiency.
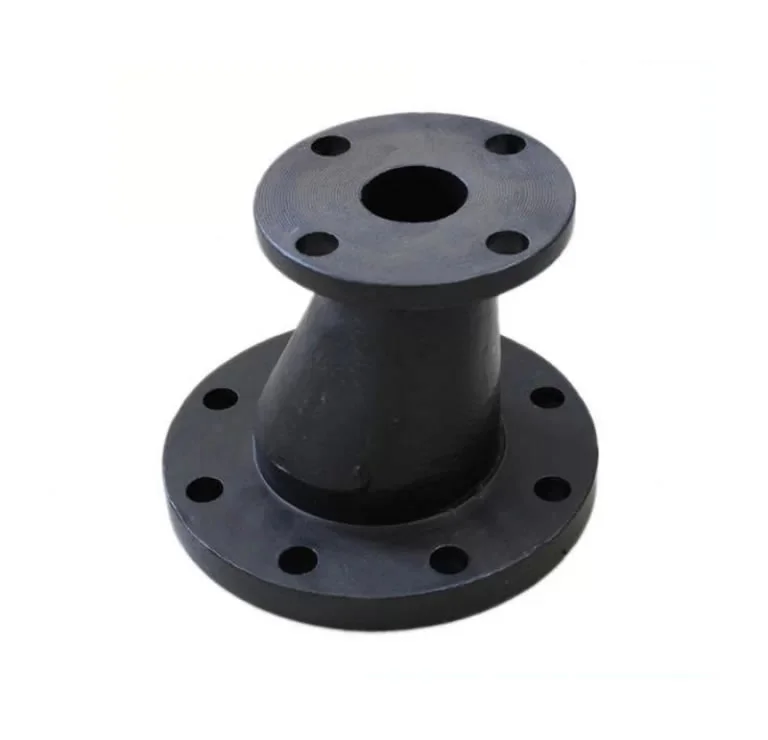
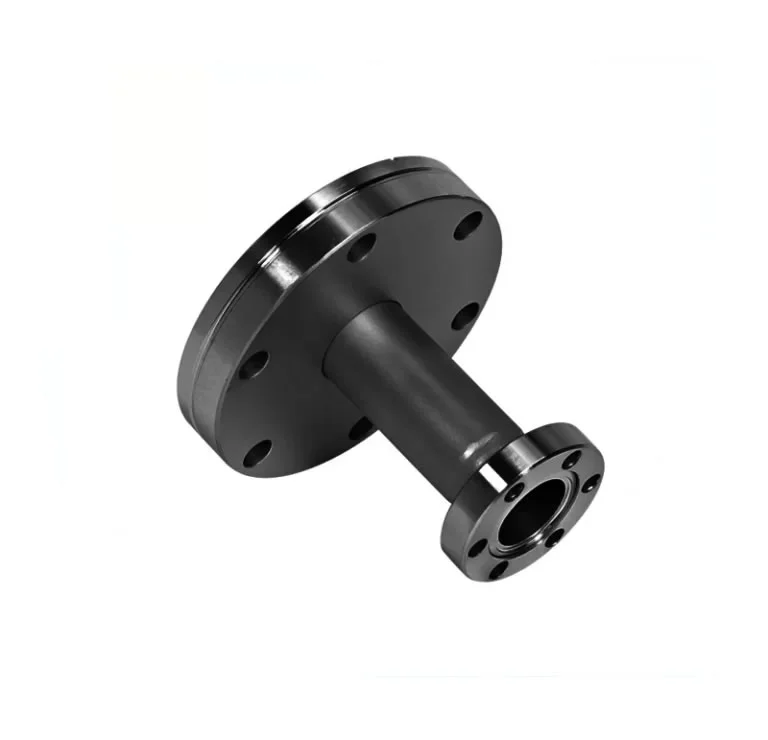
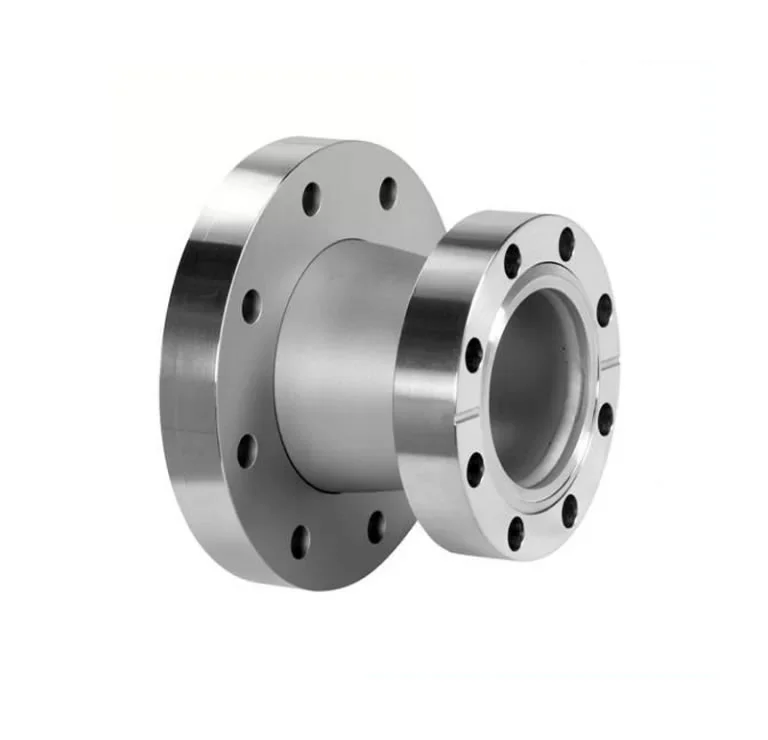
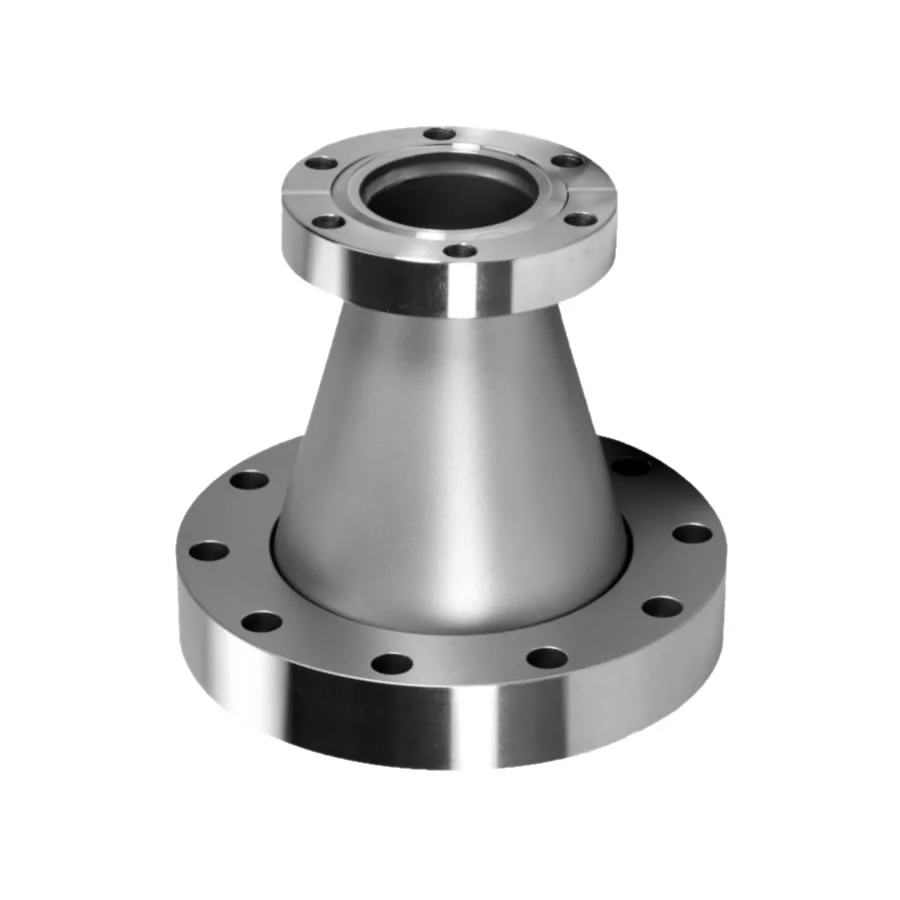
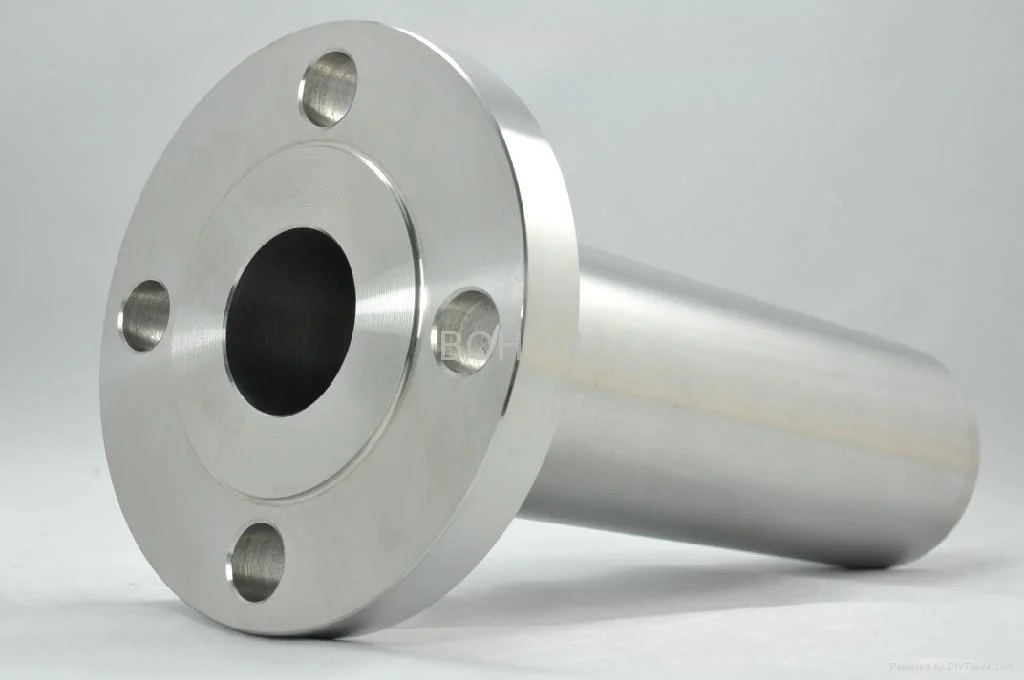
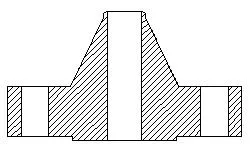
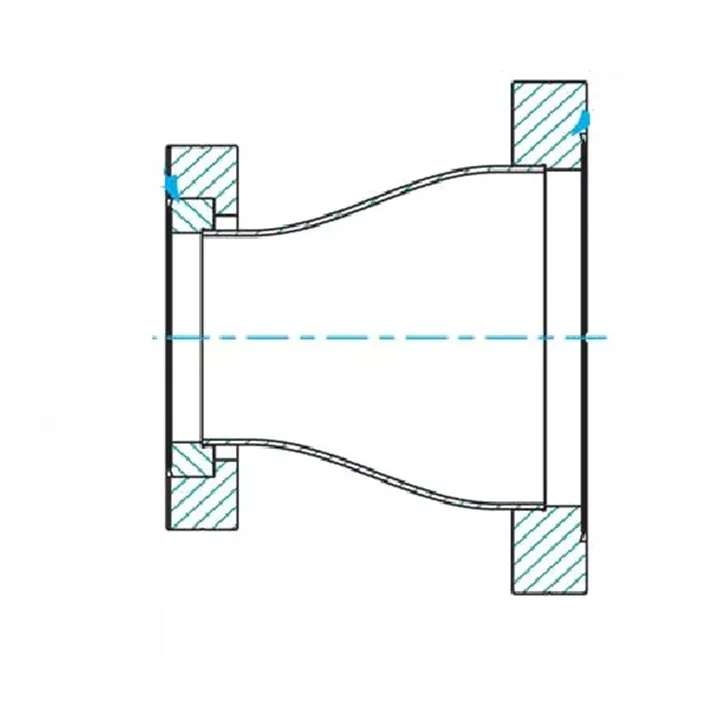
A reducing flange consists of a flange with one specified diameter having a bore of a different and smaller,
diameter. Except for the bore and hub dimensions, the flange will have dimensions of the larger pipe size.
Compared to standard flanges, Reducing Flanges offer greater flexibility for diameter
adjustments, boasting a service life of 15–35 years with proper maintenance and protective coatings.
Reducing Flanges effectively tackle challenges such as mismatched pipe sizes and flow
inefficiencies, providing reliable industrial piping solutions as of August 23, 2025.
ASME B16.5 Reducing Flanges
Special Flanges
What is a Reducing Flange?
Reducing flanges are designed for when there is a change in the pipe size.
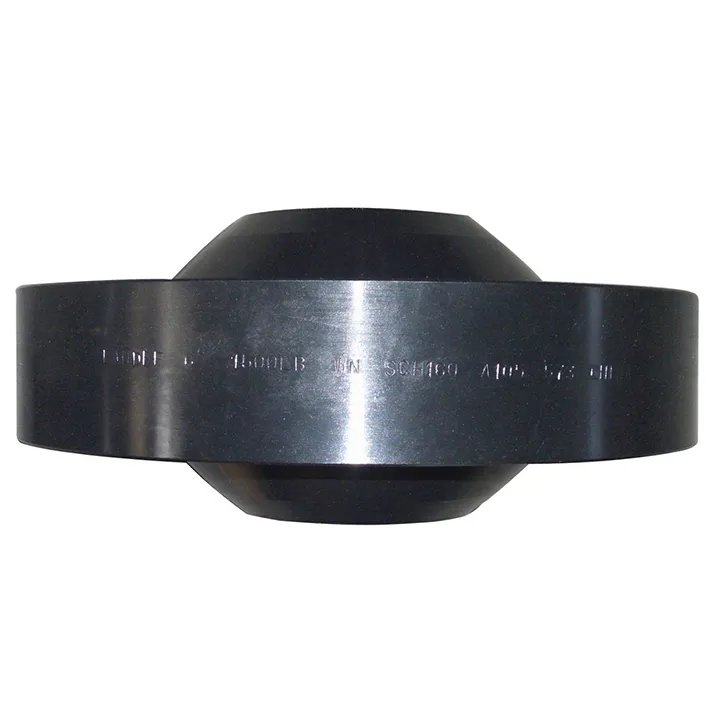
The predominate flange (dimensions) matching the larger pipe size (NPT) but having a smaller bore matching the smaller pipe size (NPT). These flanges normally come in blind, slip-on, threaded and weld neck flanges.
They are available in all pressure classes and provide a good alternative to connecting two different sizes of pipe. This type of flange should not be used if an abrupt transition would create unwanted turbulence, such as at a pump.