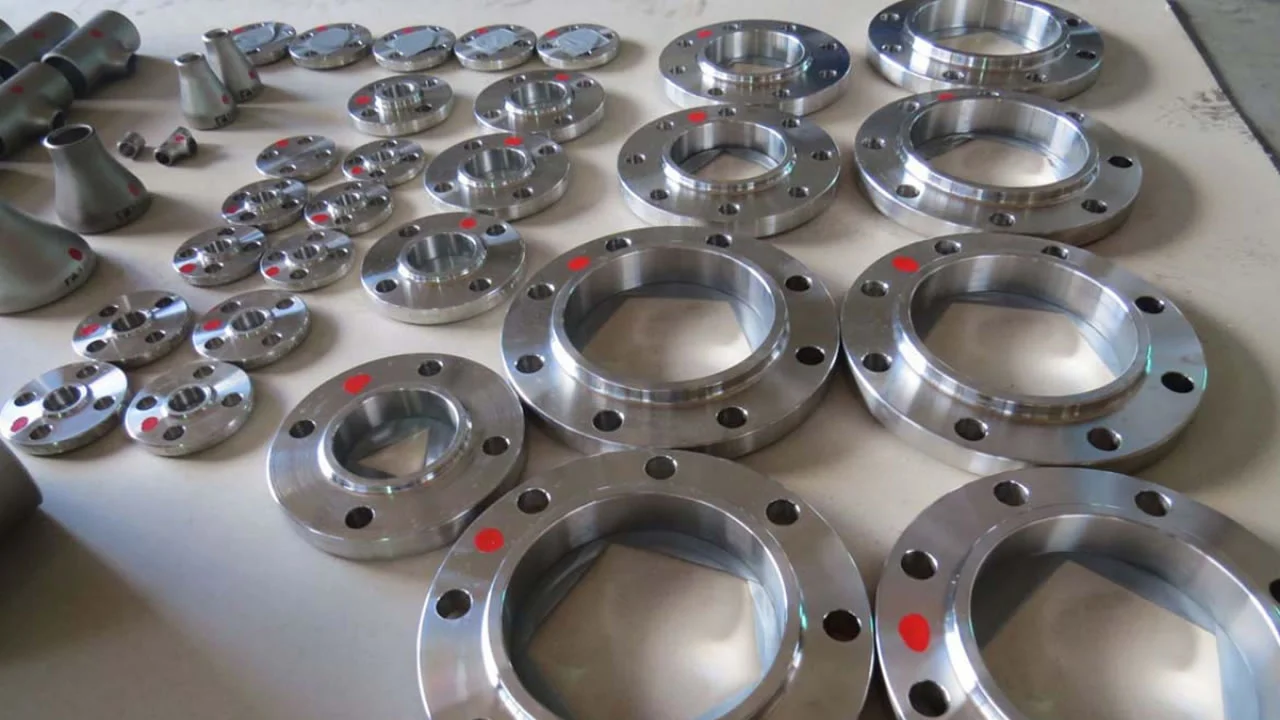
Stainless Steel 304 Flanges are corrosion-resistant flanges crafted from grade 304 stainless steel, adhering to ASTM A182 and ASME B16.5 standards as of August 25, 2025, 02:47 AM PDT. These Corrosion-Resistant Flanges excel in durability.
Available in sizes from 1/2” to 48” with pressure ratings up to Class 2500, Stainless Steel 304 Flanges withstand temperatures up to 870°C, making them ideal for demanding environments.
Forged or machined with a high chromium-nickel composition, these flanges offer excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion, enhanced by surface treatments like passivation as of August 2025. Reliability stands out.
Compared to carbon steel flanges, Stainless Steel 304 Flanges provide superior corrosion resistance, with a service life of 20–40 years with proper maintenance and care.
Stainless Steel 304 Flanges address challenges like rust and chemical exposure, delivering robust stainless steel piping flanges as of August 25, 2025.
Chemical Composition of Grade 304 Stainless Steel| Element | Percentage (%) | Function |
|---|
| Carbon (max) | 0.08 | Enhances strength and hardness |
| Manganese (max) | 2.00 | Improves toughness |
| Phosphorus (max) | 0.045 | Reduces brittleness |
| Sulfur (max) | 0.030 | Enhances machinability |
| Silicon (max) | 1.00 | Increases strength |
| Chromium | 18.0–20.0 | Provides corrosion resistance |
| Nickel | 8.0–10.5 | Enhances ductility and resistance |
| Nitrogen (max) | 0.10 | Improves strength |
The composition of Stainless Steel 304 Flanges ensures exceptional corrosion resistance and mechanical stability.
Mechanical Properties of Grade 304 Stainless Steel (ASTM A182)| Property | Value | Test Standard |
|---|
| Tensile Strength (min) | 515 MPa | ASTM A370 |
| Yield Strength (min) | 205 MPa | ASTM A370 |
| Elongation (min) | 40% | ASTM E8 |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 123–183 HB | ASTM E10 |
| Impact Toughness (min) | 50 J at -196°C | ASTM E23 |
| Temperature Range | -196°C to 870°C | N/A |
These properties make Stainless Steel 304 Flanges ideal for high-temperature and corrosive environments.
Comparison of Stainless Steel 304 Flanges with Other Standards| Standard/Type | Material | Size Range | Pressure Rating | Key Advantage |
|---|
| Stainless Steel 304 Flanges | Grade 304 Stainless Steel | 1/2”–48” | Up to Class 2500 | Superior Corrosion Resistance |
| ASME B16.5 | Forged Steel | 1/2”–24” | Class 150–2500 | Standardized Versatility |
| ASTM A105 | Carbon Steel | 1/2”–48” | Class 150–2500 | Cost-Effective Strength |
| Stainless Steel 316 Flanges | Grade 316 Stainless Steel | 1/2”–48” | Up to Class 2500 | Enhanced Corrosion Resistance |
Stainless Steel 304 Flanges offer excellent corrosion resistance, while ASME B16.5 provides versatility, ASTM A105 is cost-effective, and 316 Flanges enhance resistance further as of August 25, 2025.