Pipe Elbow for Corrosion-Resistant Piping Solutions?
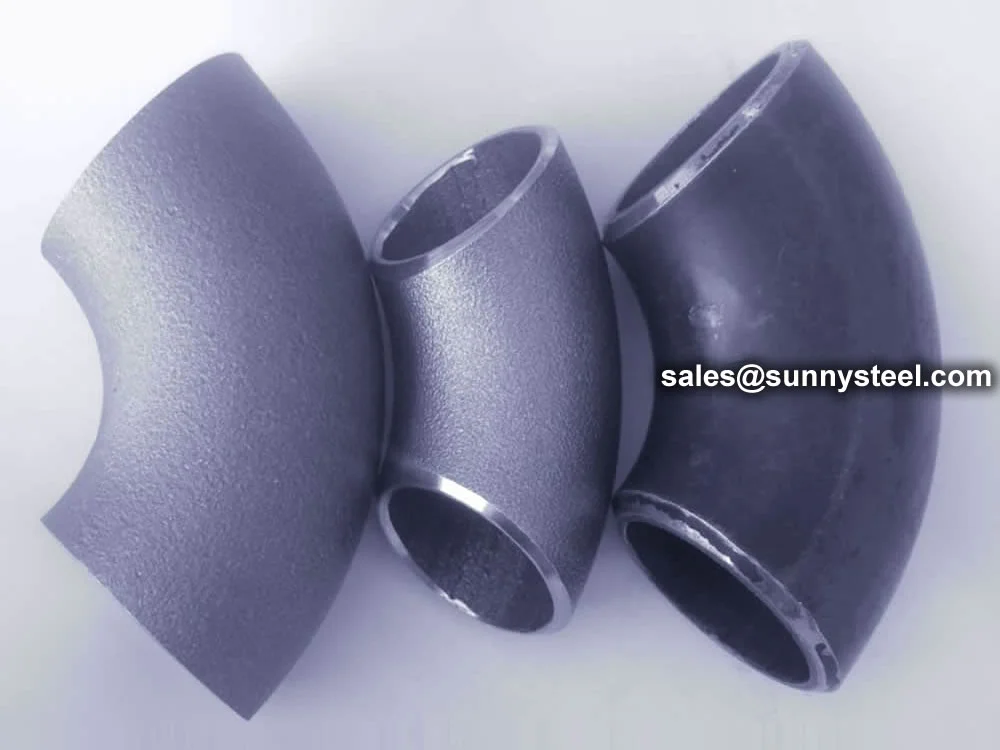
Pipe Elbow fittings are critical components in industrial piping systems, designed to redirect flow with exceptional corrosion resistance and erosion resistance. Our seamless alloy steel elbows, compliant with ASME B16.9 standards, are engineered for high-pressure and high-temperature environments, making them ideal for boiler pipeline protection in refineries, petrochemical plants, and power generation facilities.
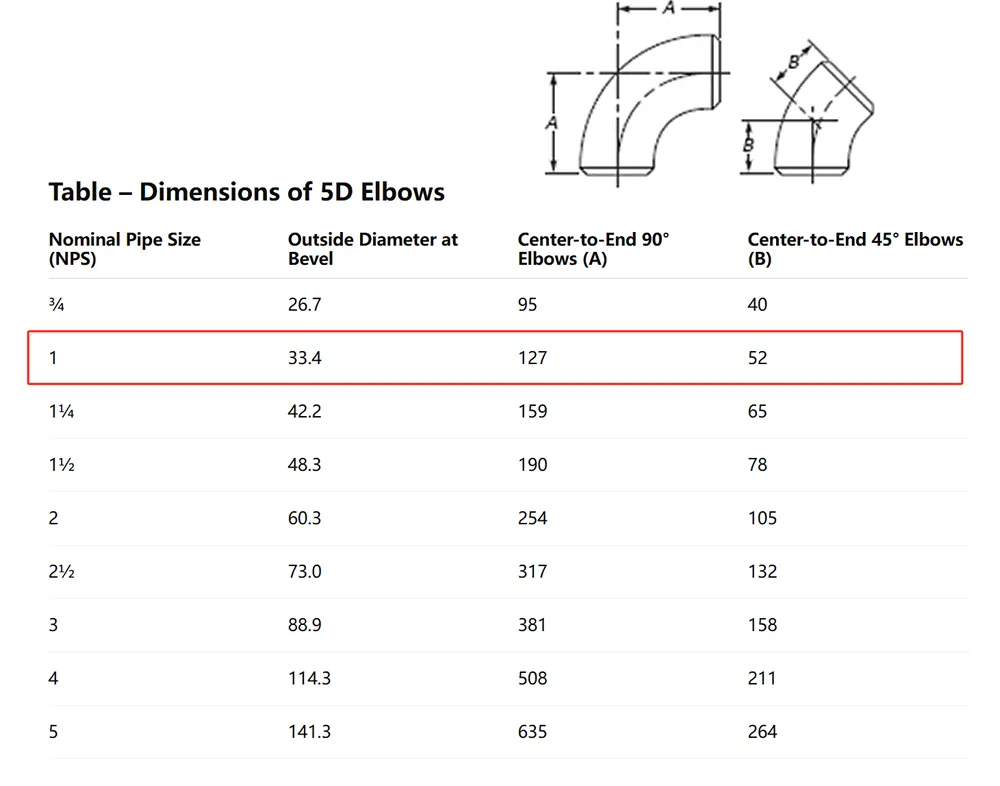
Manufactured using hot-rolling or cold-drawing processes, these seamless alloy elbows undergo precise heat treatment to optimize mechanical properties. The alloy composition, featuring high chromium and molybdenum content, enhances oxidation resistance, creep strength, and durability against abrasive materials. This makes them perfect for handling corrosive fluids, gases, and abrasive slurries in industrial piping systems. Available in angles like 90°, 45°, and 22.5°, with long-radius (1.5D) and short-radius (1D) options, our elbows cater to diverse pipeline configurations.
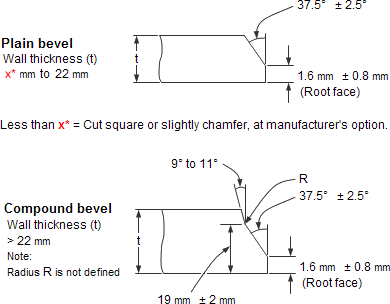
Our pipe elbows support bending, flanging, and welding, with recommended preheating (150-200°C) and post-weld heat treatment (650-700°C) to ensure weld integrity. Available in sizes from 1/2” to 24” (DN15 to DN600) and wall thicknesses from SCH 40 to SCH 160, they meet the demands of complex piping systems. Rigorous testing, including tensile, flattening, and hydrostatic tests, ensures compliance with industry standards, guaranteeing reliability in extreme conditions up to 650°C.
With surface treatments like 3LPE or FBE coatings, these elbows offer enhanced corrosion resistance, making them suitable for oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing, and pneumatic conveying systems. Compared to standard carbon steel elbows, our alloy steel elbows provide superior resistance to hydrogen sulfide corrosion and stress cracking, ensuring long-term performance in harsh environments.
For engineers seeking reliable boiler pipeline protection and durable industrial piping solutions, our seamless alloy elbows deliver unmatched strength, safety, and longevity, addressing challenges like pipeline wear, corrosion, and thermal stress in high-throughput systems.
Comparison of Seamless Alloy Elbow with Other Pipe Fittings
| Feature |
Seamless Alloy Elbow |
Carbon Steel Elbow |
Stainless Steel Elbow |
| Material Type |
Ferritic Alloy Steel |
Carbon Steel |
Stainless Steel |
| Temperature Range |
High (up to 650°C) |
Moderate (up to 427°C) |
High (up to 870°C) |
| Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent (High Cr/Mo) |
Moderate (With coatings) |
Superior (Austenitic) |
| Erosion Resistance |
Excellent |
Good |
Moderate |
| Applications |
Boilers, Petrochemical, Refineries |
General Piping, Oil/Gas |
Food Processing, Marine |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) |
415 (min) |
415 (min) |
515 (min) |
| Yield Strength (MPa) |
205 (min) |
240 (min) |
205 (min) |
| Key Advantage |
High-temp corrosion resistance |
Cost-effective for general use |
Superior corrosion resistance |
Key Benefits
Corrosion Resistance
High chromium content ensures protection against rust and corrosive fluids.
Erosion Resistance
Durable alloy steel withstands wear from abrasive slurries.
Boiler Pipeline Protection
Ideal for high-temperature boiler systems and industrial applications.
Weldability
Supports welding and bending for flexible pipeline configurations.
Cost-Effective
Long lifespan reduces maintenance and replacement costs.
High Strength
Superior tensile strength for demanding industrial piping systems.