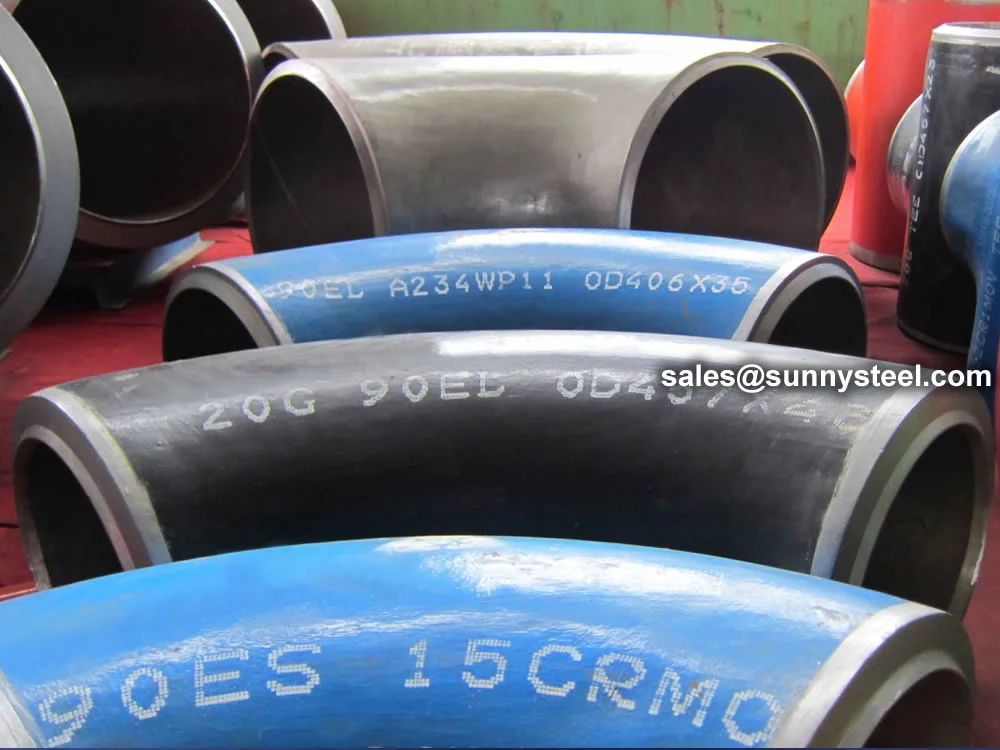
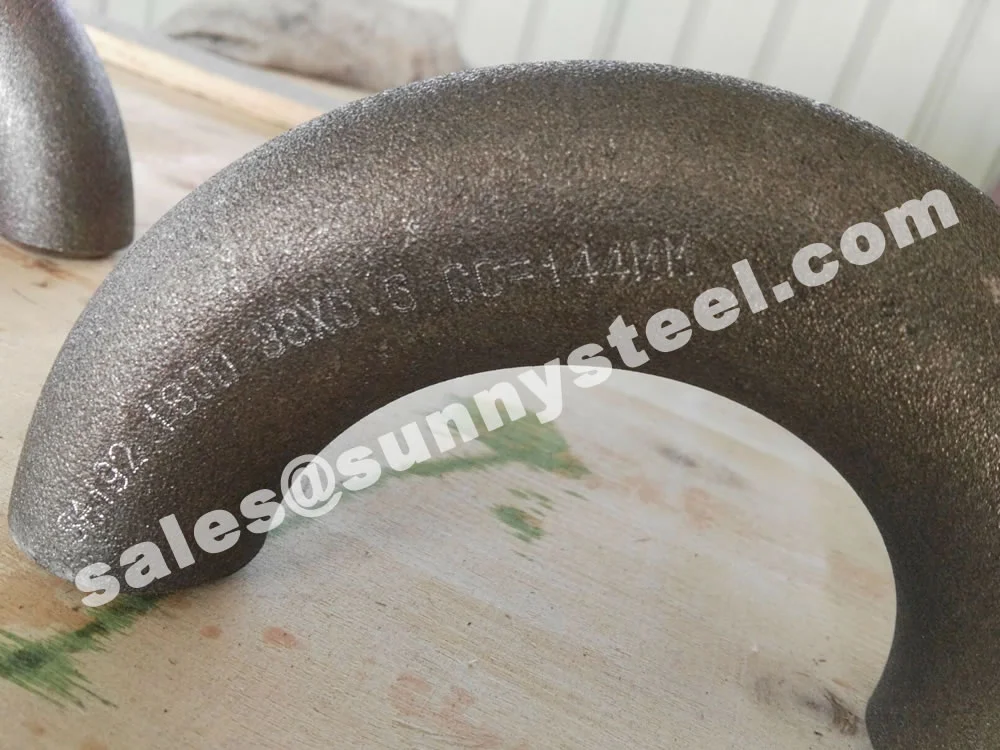
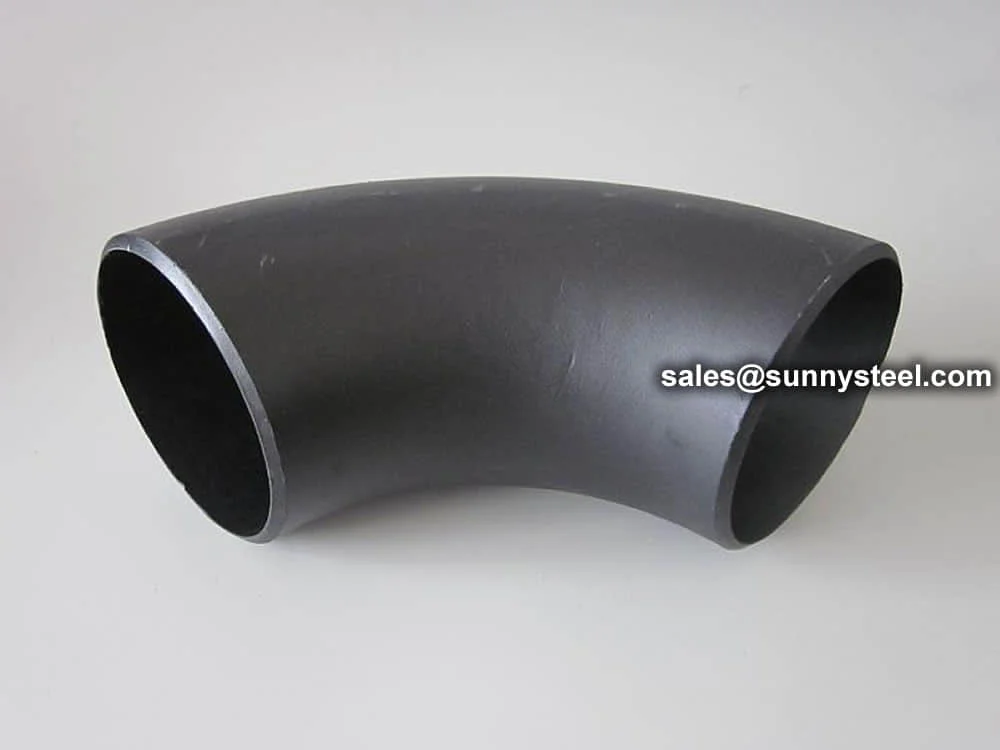
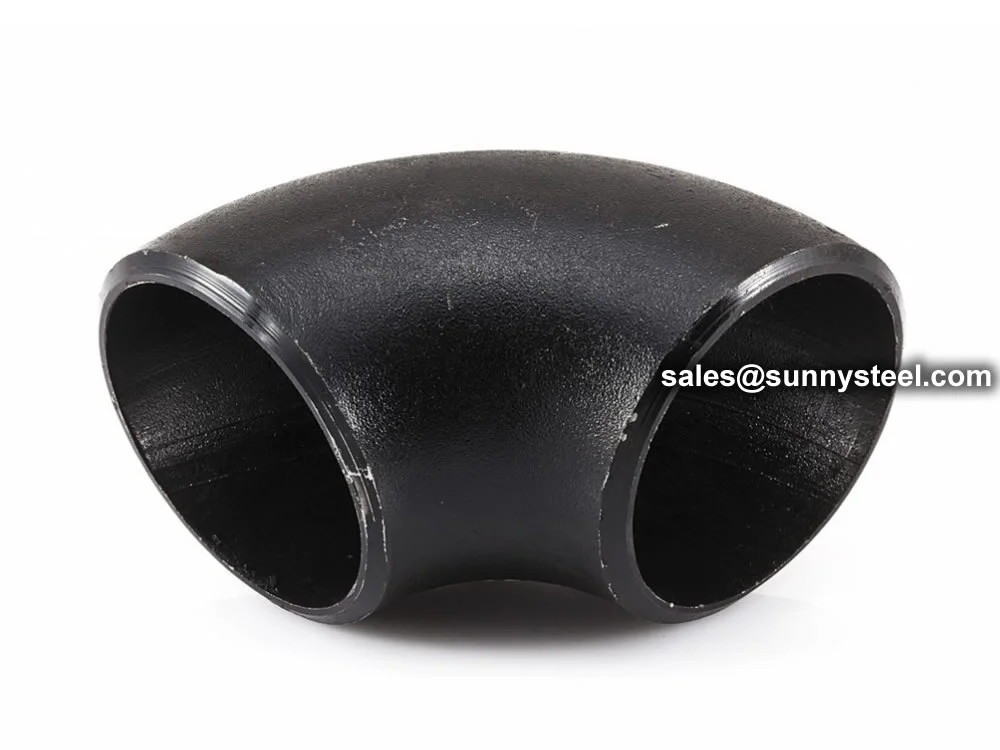
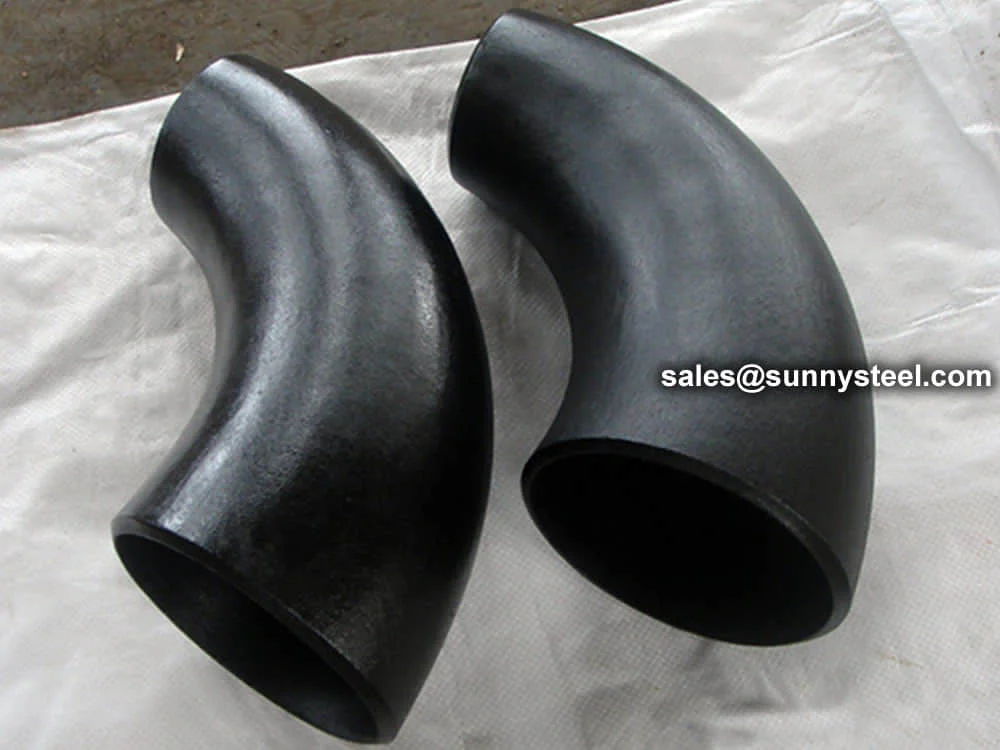
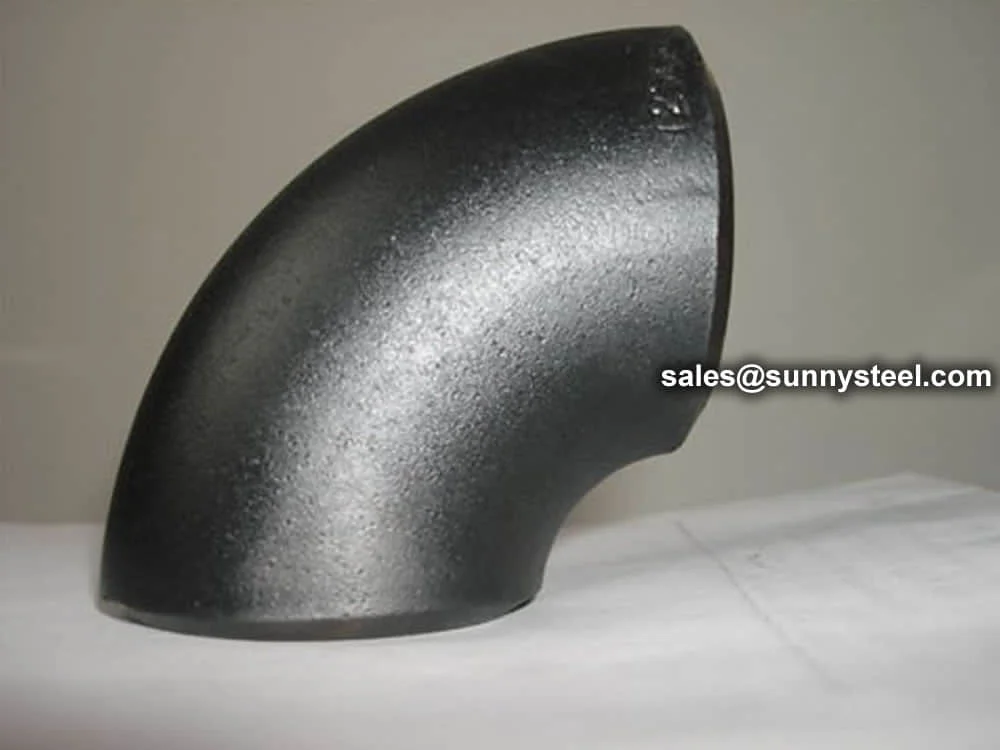
ASTM A234 WP11 Elbows are high-quality alloy steel pipe fittings designed for
high-temperature piping systems, compliant with ASME B16.9 standards. These seamless or
welded elbows provide excellent corrosion resistance and erosion
resistance, making them ideal for boiler pipeline protection in
refineries, petrochemical plants, and power generation facilities.
ASTM A234 WP11 elbows are manufactured through hot-forming or cold-forming processes, followed by
normalizing and tempering heat treatments to enhance strength and toughness at temperatures up to 620°C.
With chromium (1.00-1.50%) and molybdenum (0.44-0.65%) content, they offer robust resistance to
oxidation, creep, and wear from corrosive fluids and abrasive slurries. Available in long-radius (LR,
R=1.5D), short-radius (SR, R=1D), and reducing configurations, these elbows support angles of 90°, 45°,
and 22.5° for versatile industrial piping designs.
These elbows support welding, bending, and flanging, with recommended preheating (150-200°C) and
post-weld heat treatment (620-675°C) to ensure weld integrity. Available in sizes from 1/2” to 24” (DN15
to DN600) and wall thicknesses from SCH 40 to SCH 160, they meet diverse pipeline requirements. Rigorous
testing, including tensile, flattening, and hydrostatic tests, ensures compliance with ASTM A234
standards for high-temperature service.
Enhanced with coatings like 3LPE, FBE, or galvanizing, ASTM A234 WP11 elbows provide superior
corrosion resistance, protecting against rust and chemical degradation in
high-temperature environments. Their creep strength makes them ideal for boiler pipeline
protection in power plants, superheaters, and petrochemical processing.
For engineers seeking reliable high-temperature piping solutions, ASTM A234 WP11 elbows
deliver exceptional durability, safety, and longevity, addressing challenges like pipeline corrosion,
thermal stress, and high-pressure demands.