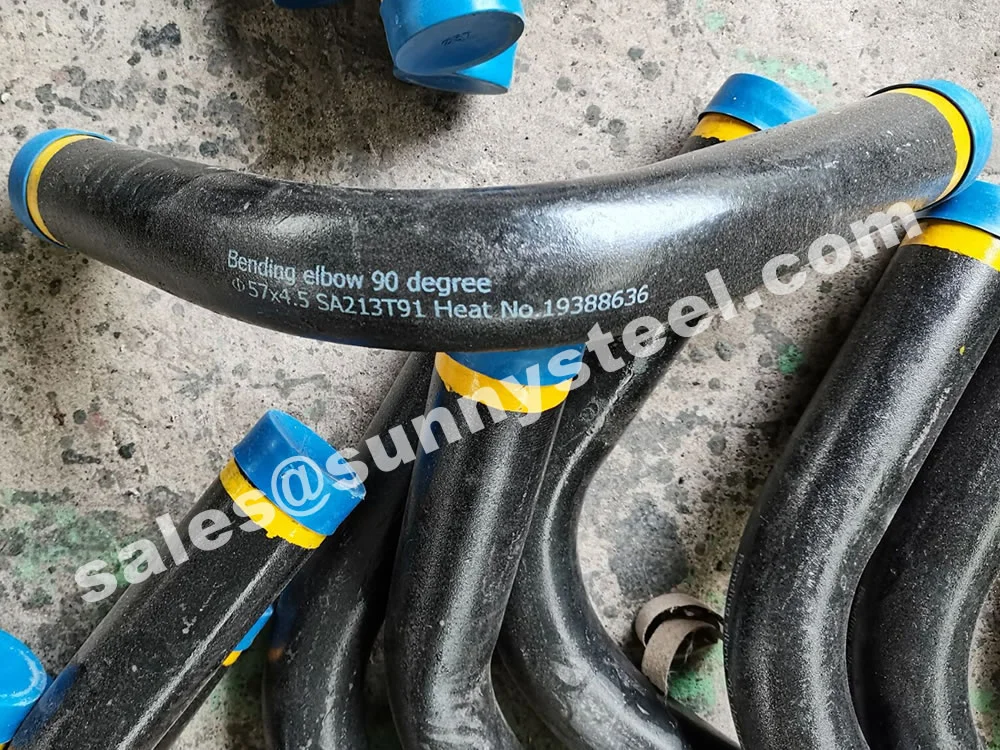
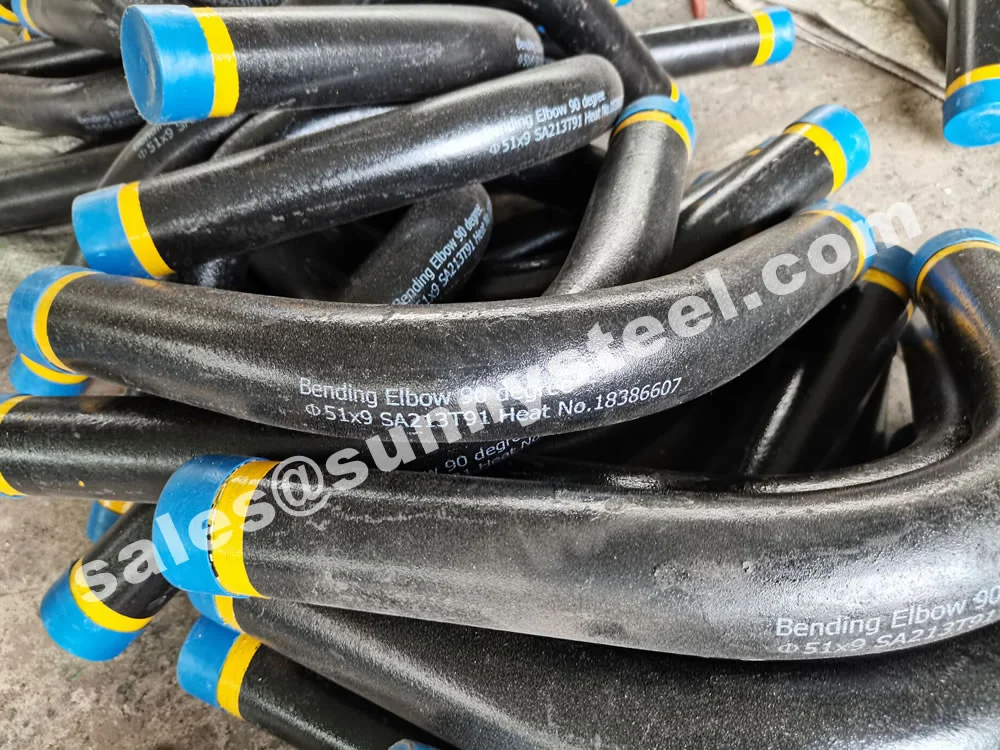
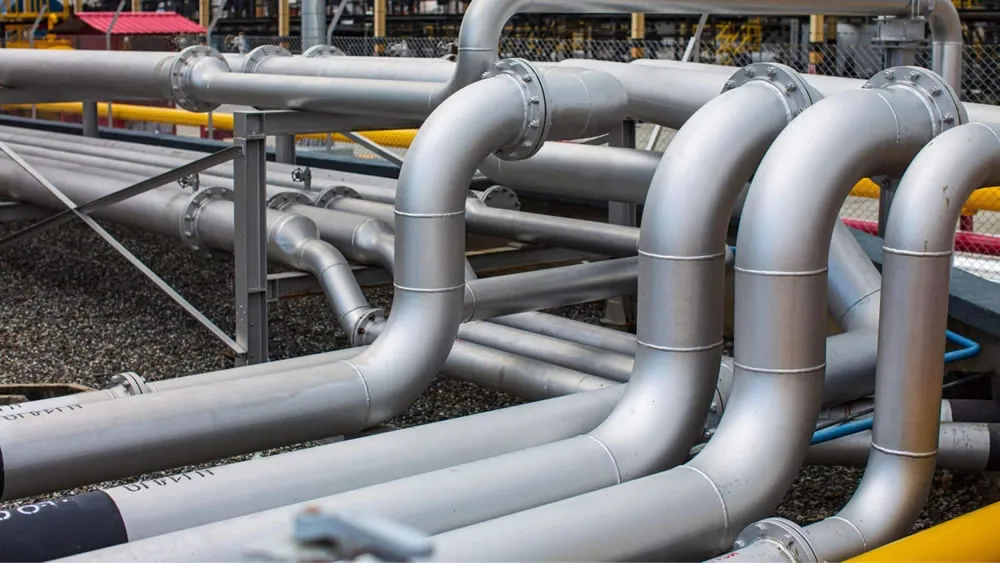
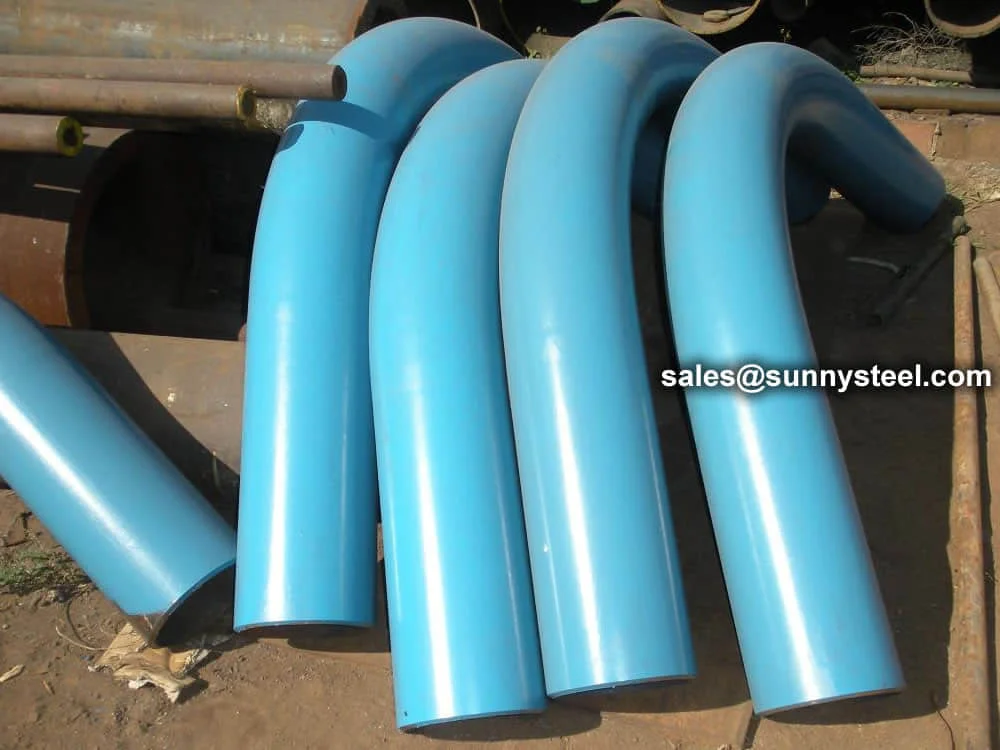
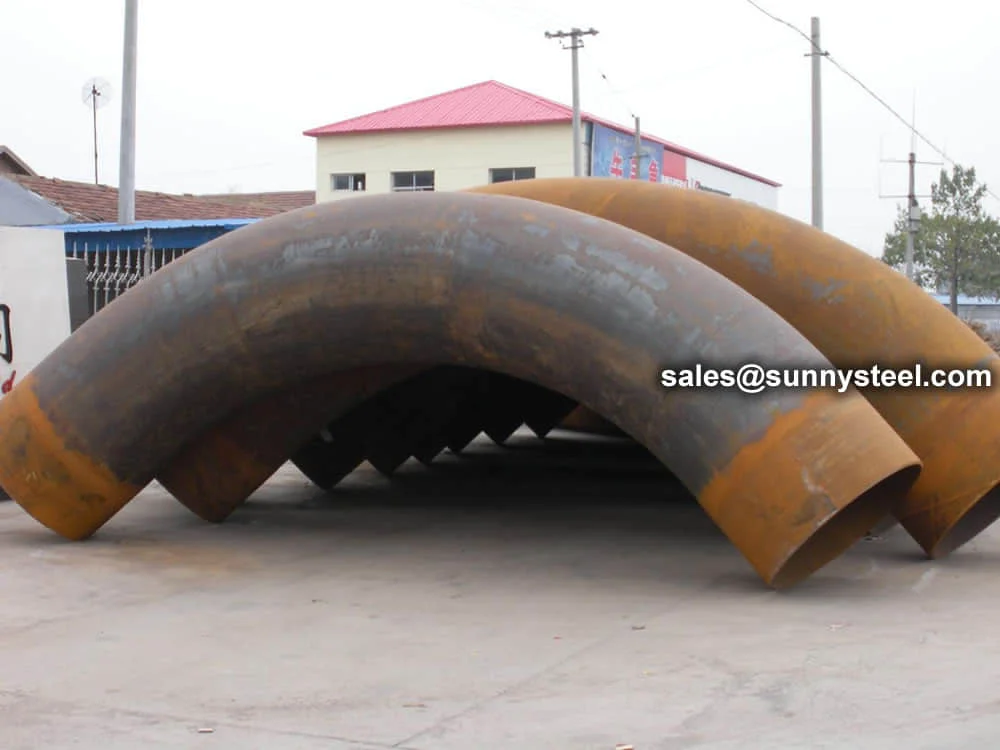
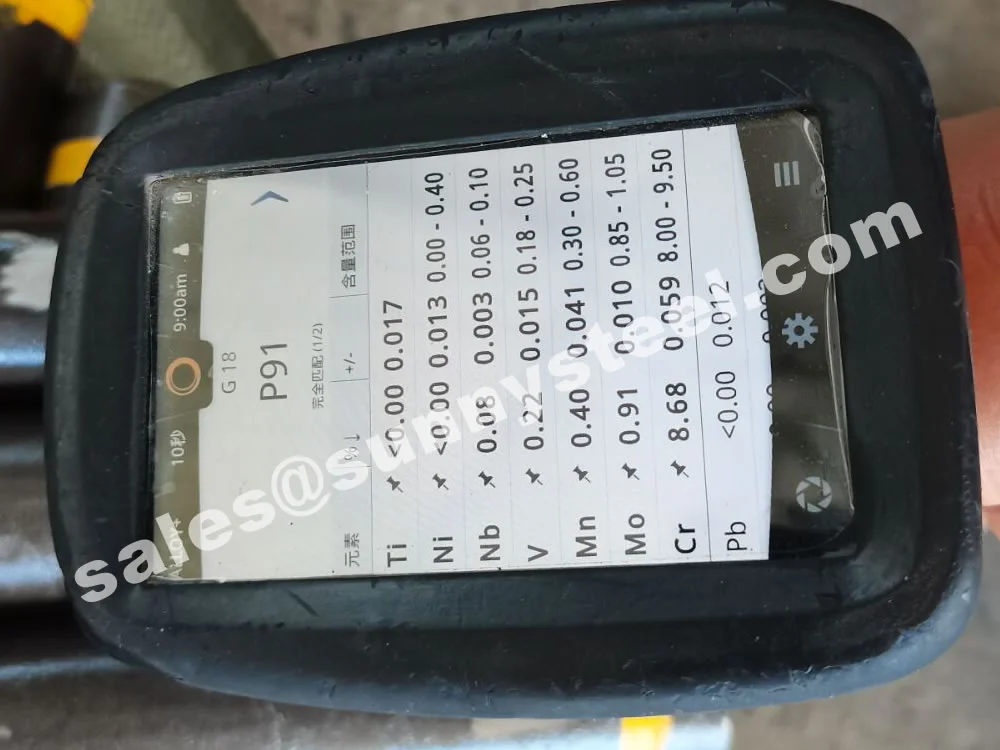
ASTM A213 T91 Pipe Bending involves forming seamless alloy steel tubes into bends (e.g., 3D, 5D, 7D, or 180° U-bends) for high-pressure, high-temperature applications. ASTM A213 T91, a creep strength-enhanced ferritic (CSEF) steel (UNS K90901), contains 8.0–9.5% chromium, 0.85–1.05% molybdenum, and micro-alloying elements like vanadium, niobium, and nitrogen. It offers superior high-temperature strength (up to 600°C), creep resistance, and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for boiler pipeline protection in power generation, petrochemical, and chemical processing industries.
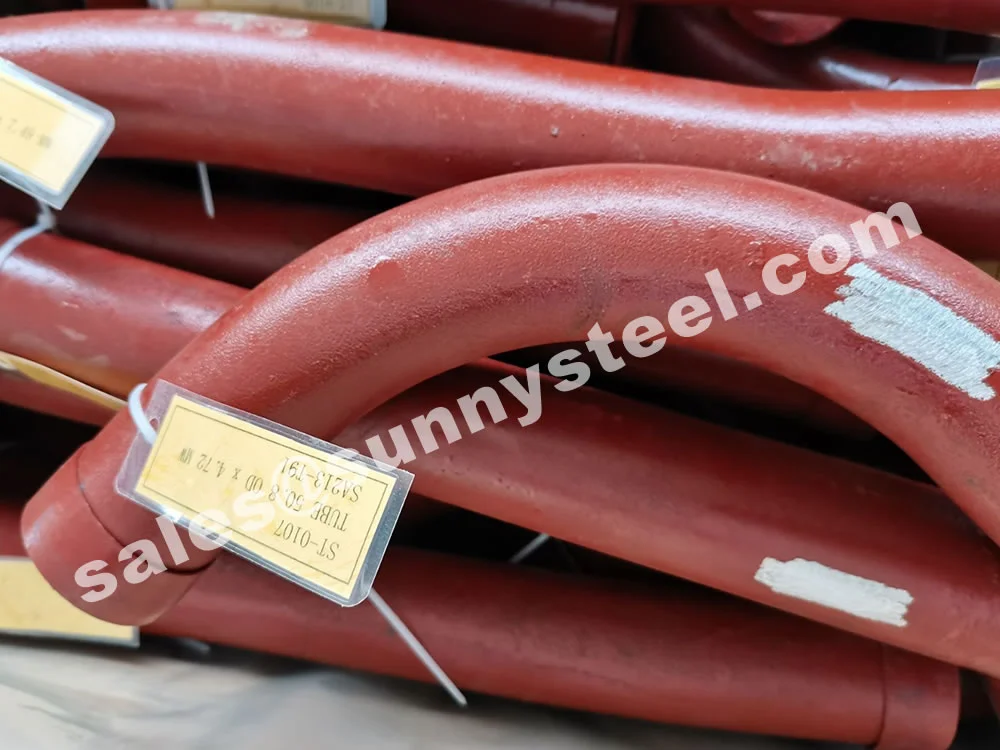
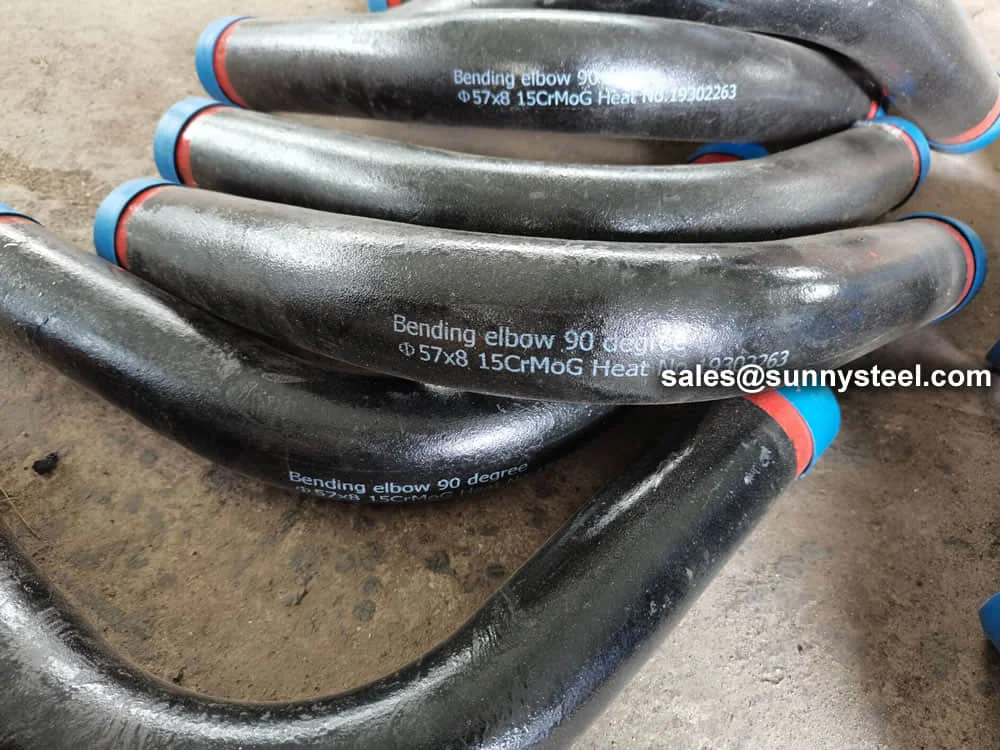
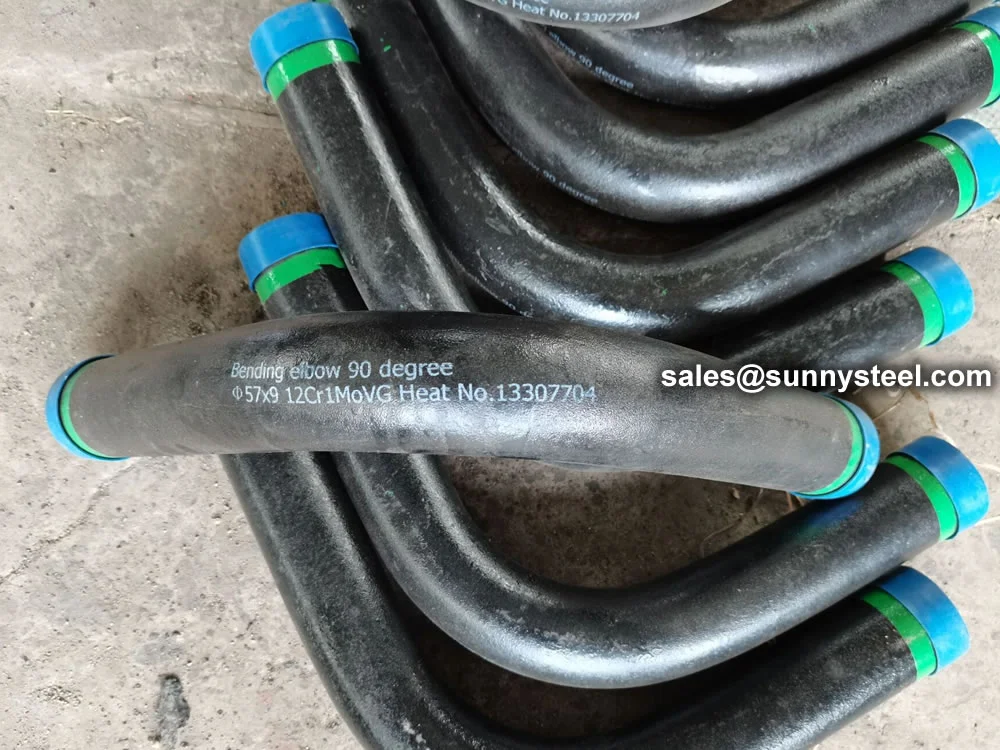
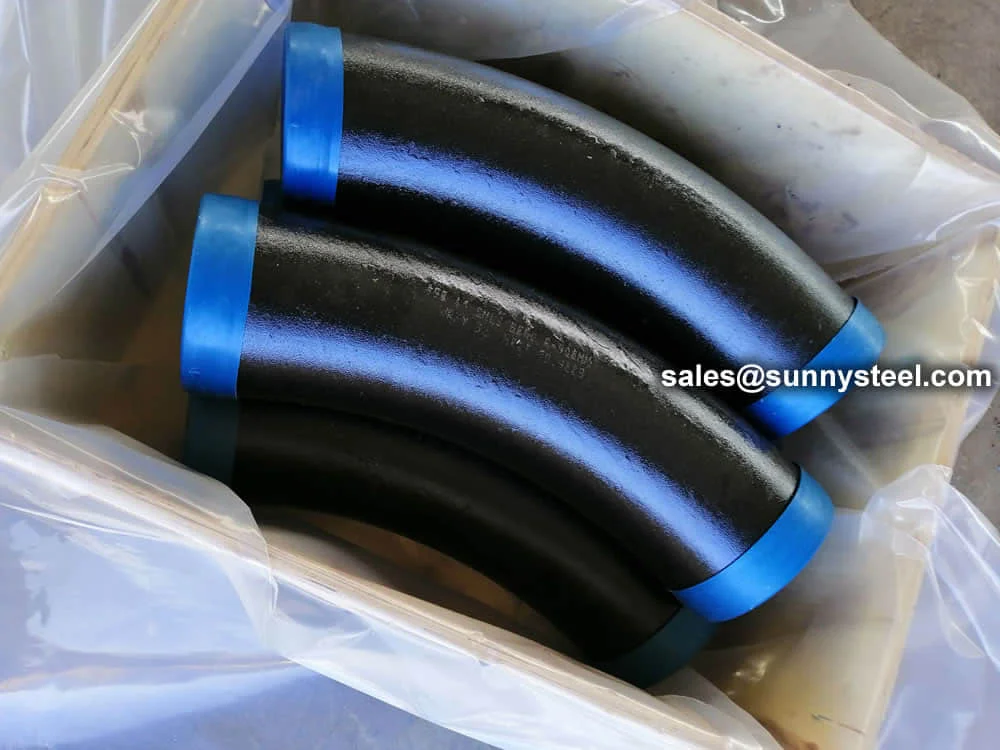
Manufactured via hot induction bending or cold drawing with heat treatment (normalized ≥1040°C, tempered ≥730°C), T91 pipe bends are available in sizes from 3/4" (19.05mm) to 5" (127mm) outer diameter, with wall thicknesses from 0.4mm to 12.7mm, and bend radii of 3D, 5D, 7D, or custom. They exhibit tensile strength (≥585 MPa), yield strength (≥415 MPa), elongation (≥20%), and hardness (≤250 HB), ensuring durability in ultra-supercritical (USC) boiler systems.
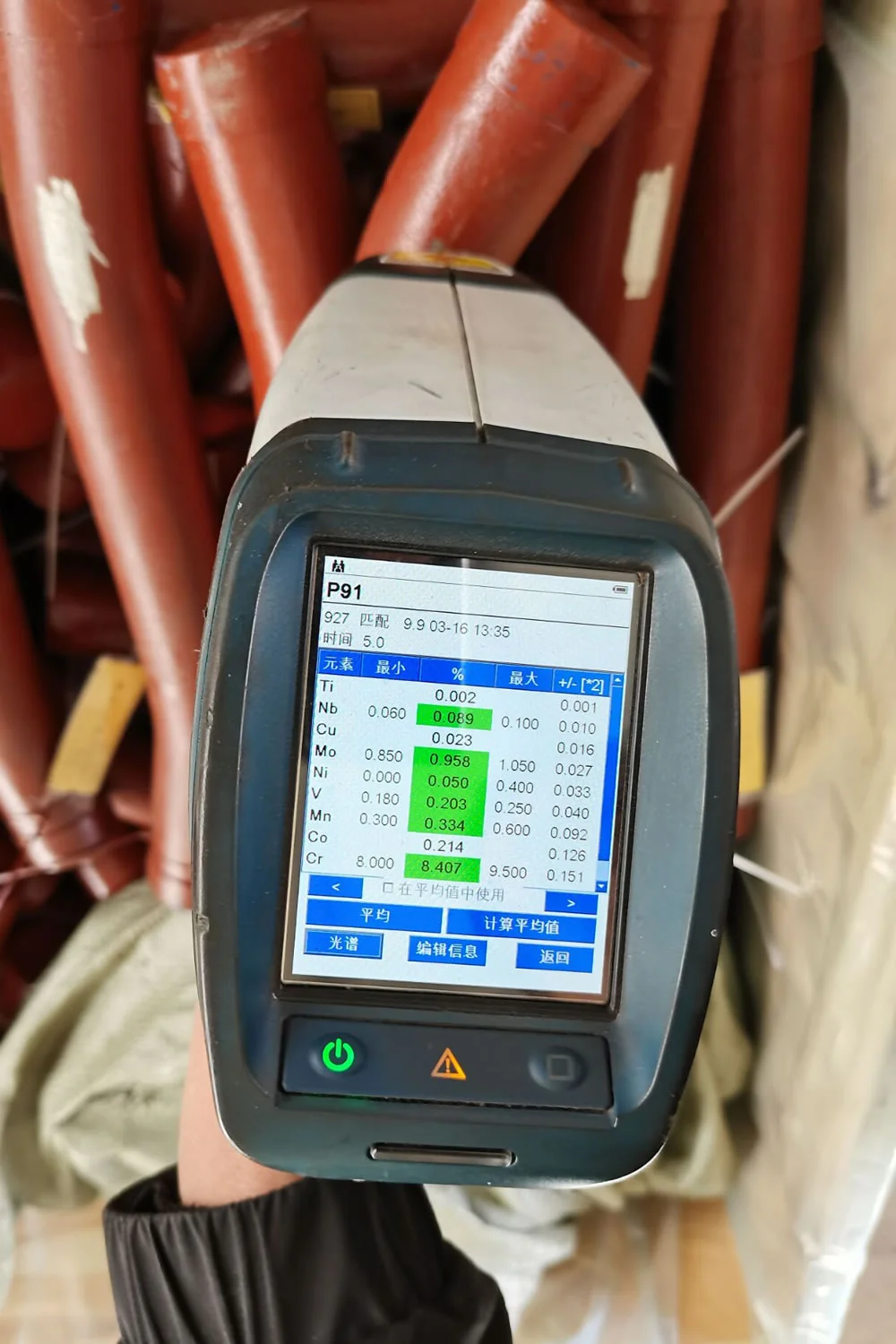
T91 pipe bends require careful welding due to their complex metallurgy, with preheating and post-weld heat treatment to prevent cracking. Rigorous testing, including chemical analysis, tensile testing, flattening tests, and nondestructive methods (radiographic, ultrasonic, PMI), ensures quality. The high chromium content forms a protective oxide layer, enhancing corrosion resistance, while coatings like FBE further protect against rust and chemical exposure.
With a density of approximately 7.85 g/cm³ and excellent thermal stability, T91 pipe bends are ideal for high-pressure boilers (pressure ≥9.8 MPa, temperature 450°C–600°C), superheaters, reheaters, and heat exchangers. Their smooth interior surfaces reduce flow resistance, making them suitable for boiler pipeline protection, refinery piping, and structural applications like cooling coils and frames.
For engineers seeking robust high-temperature piping solutions, ASTM A213 T91 pipe bends offer unmatched strength, erosion resistance, and longevity, addressing challenges like pipeline corrosion and creep in demanding industrial environments.