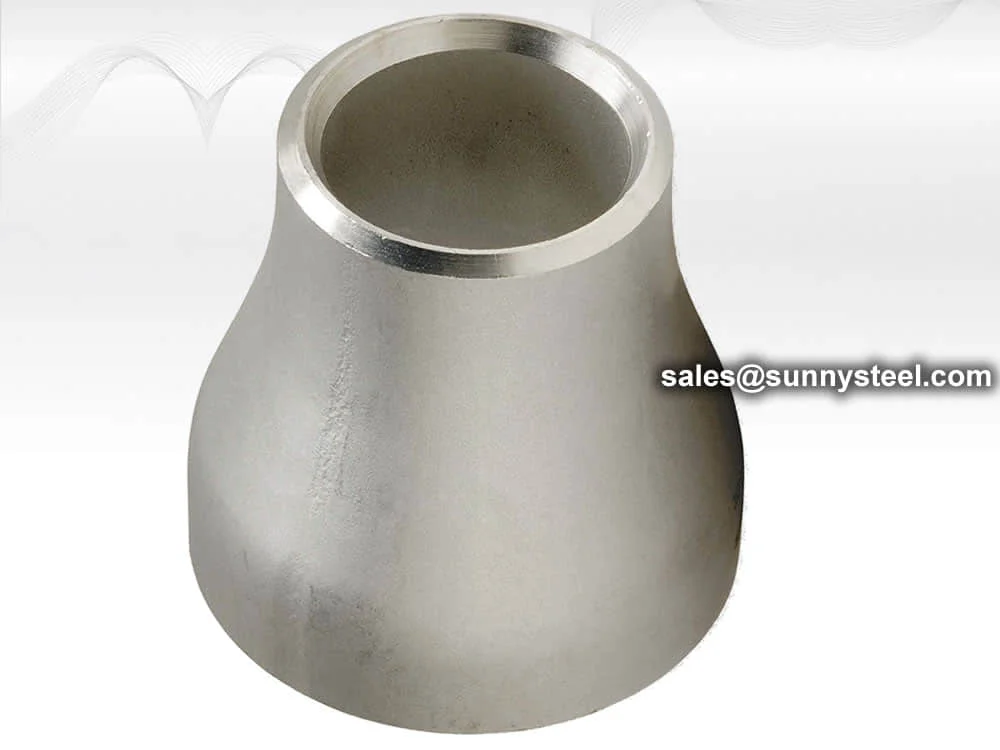

Seamless And Welded Stainless Steel Reducers For Boiler And Petrochemical Applications
A stainless steel reducer is a pipe fitting used to connect pipes of different diameters, enabling a smooth transition in flow within a piping system.
Seamless And Welded Stainless Steel Reducers For Boiler And Petrochemical Applications
A stainless steel reducer is a pipe fitting used to connect pipes of different diameters, enabling a smooth transition in flow within a piping system. they are made from stainless steel for durability and corrosion resistance and are essential in various industries like chemicals, oil and gas, and food and beverage.
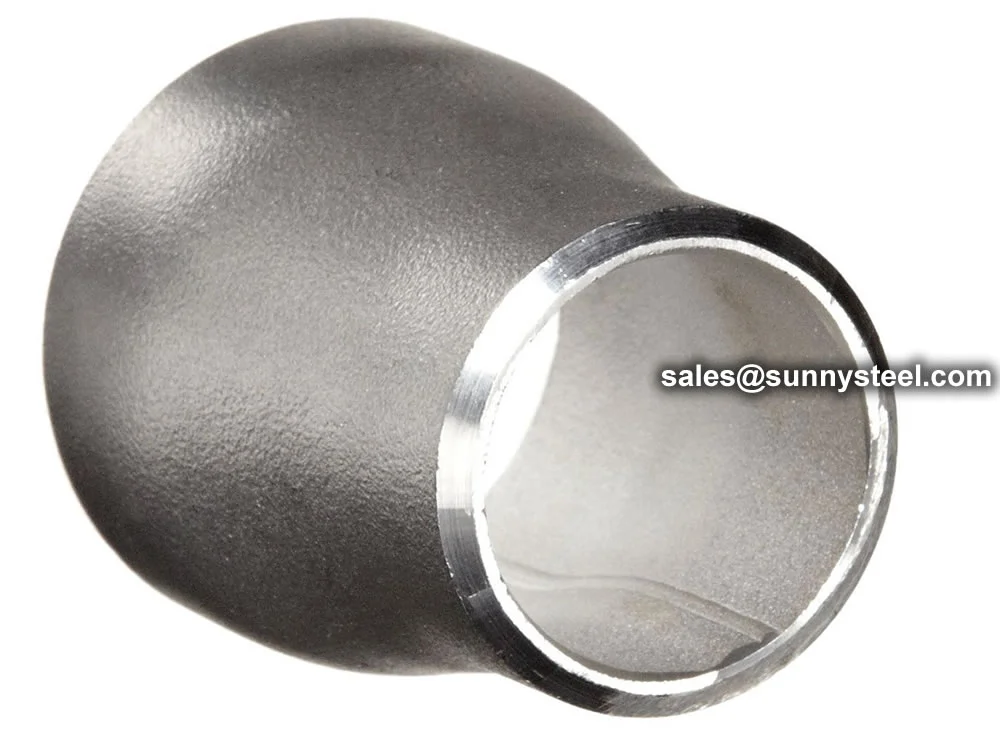
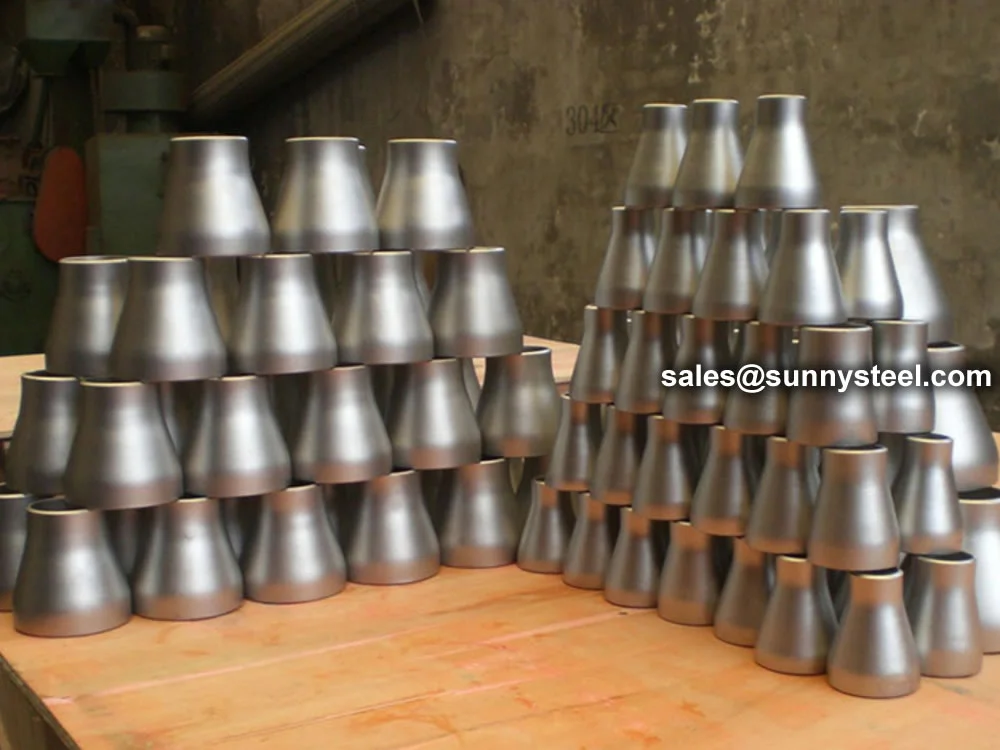
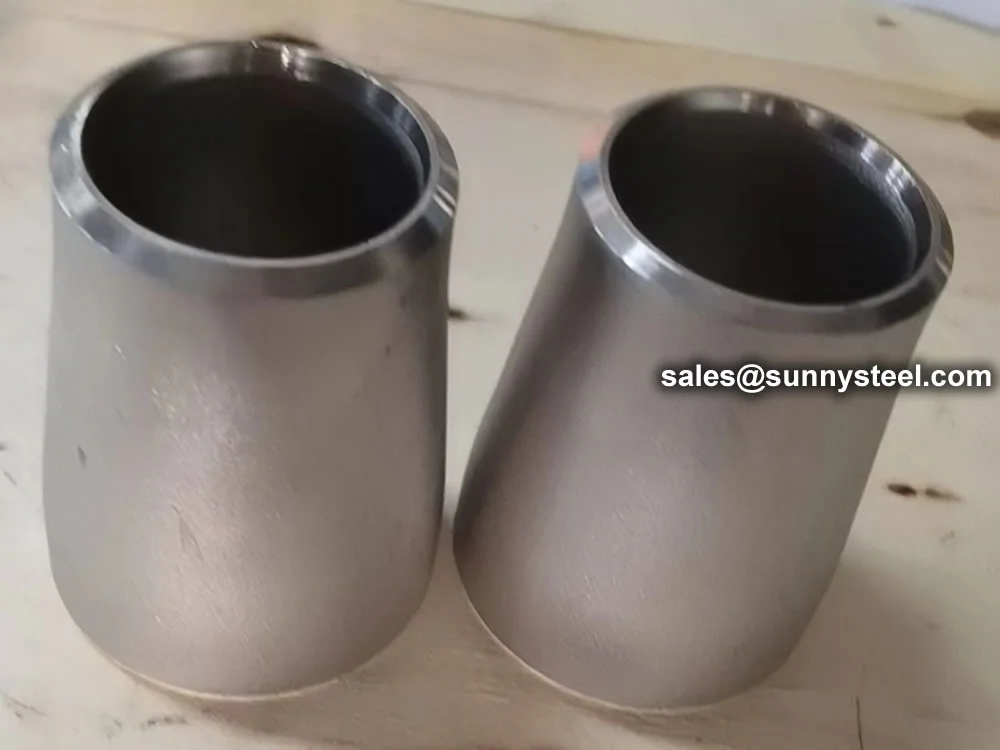





Smooth transition from large to small bore
Minimizes noise and vibration
Prevents air bubble accumulation
Maintains pipeline integrity
Stainless steel pipe reducers are critical fittings that connect pipes of different diameters, ensuring seamless flow transitions in high-pressure and corrosive environments. Available as concentric reducers (aligned centerlines for uniform flow) and eccentric reducers (offset centerlines to prevent liquid or air trapping), they are ideal for boiler pipeline protection and corrosion resistance in industries like power generation, petrochemical, and chemical processing.
Manufactured from austenitic stainless steel grades like ASTM A403 WP304, WP316L, and WP347H, these reducers offer excellent corrosion resistance due to high chromium (16–19%) and nickel (8–13%) content, forming a passive oxide layer. They are available in sizes from 1/2" (12.7mm) to 48" (1219mm) nominal diameter, with wall thicknesses from 0.5mm to 50mm, and comply with ASME B16.9 and ASTM A403 standards. Additional coatings like passivation or FBE enhance corrosion resistance in harsh chemical environments.
Stainless steel reducers undergo rigorous testing, including chemical analysis, tensile testing (e.g., ≥515 MPa for WP347H), hydrostatic testing, and nondestructive methods (radiographic, ultrasonic, PMI). With a density of ~7.96 g/cm³ and thermal conductivity of ~16 W/(m·K) at 20°C, they perform reliably in high-temperature systems (up to 870°C for WP347H) and high-pressure applications (≥9.8 MPa), such as boilers, superheaters, heat exchangers, and refinery pipelines.
Concentric reducers are used in vertical pipelines for uniform flow, while eccentric reducers suit horizontal systems to prevent sediment buildup. Both types minimize turbulence, enhancing erosion resistance and ensuring efficient fluid dynamics. Applications include cooling systems, structural piping, and high-pressure boiler setups, where stainless steel reducers address challenges like pipeline corrosion and thermal stress.
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Standards | ASME B16.9, ASTM A403, EN 10253-4 |
| Types | Concentric Reducer, Eccentric Reducer |
| Materials | Stainless Steel (e.g., ASTM A403 WP304, WP316L, WP347H) |
| Sizes | 1/2" (12.7mm) to 48" (1219mm) Nominal Diameter |
| Wall Thickness | 0.5mm to 50mm |
| Manufacturing | Seamless Forming, Welded Fabrication, Forging, Press Forming |
| Coatings | Passivation, FBE |
| Testing | Chemical Analysis, Tensile (e.g., ≥515 MPa for WP347H), Hydrostatic, Radiographic, Ultrasonic, PMI |
| Operating Conditions | Pressure: ≥9.8 MPa, Temperature: Up to 870°C (grade-dependent) |
Chromium-nickel passivation and FBE coatings protect against chemicals.
Smooth transitions minimize turbulence and wear.
Concentric and eccentric designs ensure efficient fluid dynamics.
Reliable up to 870°C for WP347H in boilers.
Stabilized grades like WP347H prevent intergranular corrosion.
Long-lasting in corrosive and high-pressure environments.
| Feature | Stainless Steel (e.g., WP347H) | Carbon Steel (e.g., A106 Gr.B) | Alloy Steel (e.g., 12Cr1MoVG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Cr-Ni passivation) | Moderate (requires coatings) | Good (Cr, V oxide layer) |
| Temperature Range | Up to 870°C | Up to 425°C | 450°C–580°C |
| Tensile Strength | ≥515 MPa | ≥415 MPa | ≥470 MPa |
| Weldability | Excellent (no sensitization in WP347H) | Good (preheating for thick walls) | Good (care for thick walls) |
| Applications | Boilers, petrochemical, chemical | Boilers, general piping | Boilers, petrochemical |
| Cost | Higher | Lower | Moderate |
| Key Advantage | Superior corrosion resistance | Cost-effective | Balanced strength and corrosion |
A curated list of long-tail keywords for stainless steel pipe reducers, covering types, grades, and industrial applications.
Note: Stainless steel pipe reducers are engineered for corrosion-resistant piping in critical industrial applications. Contact a certified supplier for detailed specifications.

Description: Symmetrical in shape, with both ends aligned along the center. Resembles a cone.
Application: Widely used in vertical pipelines or when centerline maintenance is required.
Description: Not symmetrical, with one side flat and ends off-center from one another.
Application: Primarily used in horizontal pipelines for air bubble prevention or drainage.
Standards: ASME B16.9 and ASME B16.25
Description: Ends are plain or beveled, designed for butt welding to pipes.
Standards: ASME B16.11
Description: Also known as socket weld insert, available in three types (1, 2, and 3).
| Grade | C (% max) | Mn (% max) | Si (% max) | P (% max) | S (% max) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Mo (%) | N (% max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | - | 0.10 |
| 304L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-12.0 | - | 0.10 |
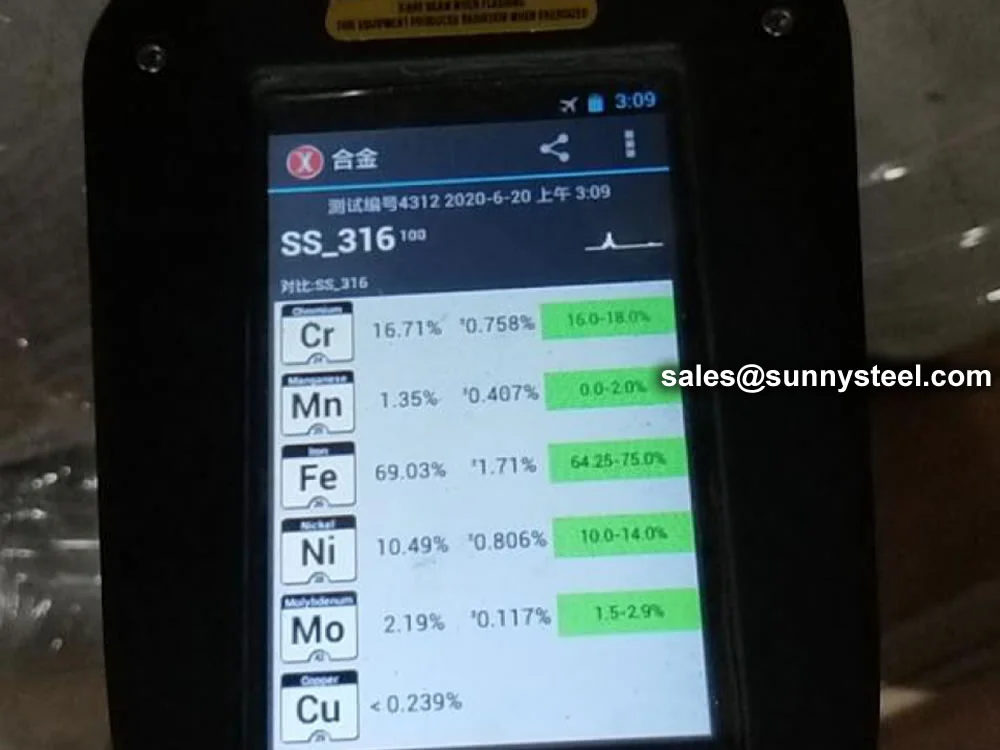
| 316 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
| 316L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
The low carbon content in 304L and 316L enhances weldability, while molybdenum in 316 and 316L improves resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making Stainless steel reducer ideal for harsh environments.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (min, MPa) | Yield Strength (min, MPa) | Elongation (min, %) | Hardness (max, HB) | Hardness (max, HRB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 304L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
These mechanical properties make Stainless steel reducer suitable for applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as architectural structures, marine environments, and chemical processing.
In order to solve the cumbersome and difficult to remember stainless steel grades, improve the practicability of the brand representation, and the contrast with the international standard grades, China has formulated the "Universal Code System for Steel and Alloy Grades", such as 06Cr19Ni10, corresponding to 304. Different grades of stainless steel have different ingredients, but they all have a national standard. The standards of each country are also different.
| No | China (GB) | Japan (JIS) | American | Korea (KS) | EU (BS EN) | India (IS) | Australia (AS) | Taiwan (CNS) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old | New (07.10) | SUS | ASTM | UNS | STS | EN | IS | AS | CNS | |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1Cr17Mn6Ni5N | 12Cr17Mn6Ni5N | SUS201 | 201 | S20100 | STS201 | 1.4372 | 10Cr17Mn6Ni4N20 | 201-2 | 201 |
| 2 | 1Cr18Mn8Ni5N | 12Cr18Mn9Ni5N | SUS202 | 202 | S20200 | STS202 | 1.4373 | — | — | 202 |
| 3 | 1Cr17Ni7 | 12Cr17Ni7 | SUS301 | 301 | S30100 | STS301 | 1.4319 | 10Cr17Ni7 | 301 | 301 |
| 4 | 0Cr18Ni9 | 06Cr19Ni10 | SUS304 | 304 | S30400 | STS304 | 1.4301 | 07Cr18Ni9 | 304 | 304 |
| 5 | 00Cr19Ni10 | 022Cr19Ni10 | SUS304L | 304L | S30403 | STS304L | 1.4306 | 02Cr18Ni11 | 304L | 304L |
| 6 | 0Cr19Ni9N | 06Cr19Ni10N | SUS304N1 | 304N | S30451 | STS304N1 | 1.4315 | — | 304N1 | 304N1 |
| 7 | 0Cr19Ni10NbN | 06Cr19Ni9NbN | SUS304N2 | XM21 | S30452 | STS304N2 | — | — | 304N2 | 304N2 |
| 8 | 00Cr18Ni10N | 022Cr19Ni10N | SUS304LN | 304LN | S30453 | STS304LN | — | — | 304LN | 304LN |
| 9 | 1Cr18Ni12 | 10Cr18Ni12 | SUS305 | 305 | S30500 | STS305 | 1.4303 | — | 305 | 305 |
| 10 | 0Cr23Ni13 | 06Cr23Ni13 | SUS309S | 309S | S30908 | STS309S | 1.4833 | — | 309S | 309S |
| 11 | 0Cr25Ni20 | 06Cr25Ni20 | SUS310S | 310S | S31008 | STS310S | 1.4845 | — | 310S | 310S |
| 12 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2 | SUS316 | 316 | S31600 | STS316 | 1.4401 | 04Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 316 | 316 |
| 13 | 0Cr18Ni12Mo3Ti | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2Ti | SUS316Ti | 316Ti | S31635 | — | 1.4571 | 04Cr17Ni12MoTi20 | 316Ti | 316Ti |
| 14 | 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 | 022Cr17Ni12Mo2 | SUS316L | 316L | S31603 | STS316L | 1.4404 | 02Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 316L | 316L |
| 15 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2N | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2N | SUS316N | 316N | S31651 | STS316N | — | — | 316N | 316N |
| 16 | 00Cr17Ni13Mo2N | 022Cr17Ni13Mo2N | SUS316LN | 316LN | S31653 | STS316LN | 1.4429 | — | 316LN | 316LN |
| 17 | 0Cr18Ni12Mo2Cu2 | 06Cr18Ni12Mo2Cu2 | SUS316J1 | — | — | STS316J1 | — | — | 316J1 | 316J1 |
| 18 | 00Cr18Ni14Mo2Cu2 | 022Cr18Ni14Mo2Cu2 | SUS316J1L | — | — | STS316J1L | — | — | — | 316J1L |
| 19 | 0Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 06Cr19Ni13Mo3 | SUS317 | 317 | S31700 | STS317 | — | — | 317 | 317 |
| 20 | 00Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 022Cr19Ni13Mo3 | SUS317L | 317L | S31703 | STS317L | 1.4438 | — | 317L | 317L |
| 21 | 0Cr18Ni10Ti | 06Cr18Ni11Ti | SUS321 | 321 | S32100 | STS321 | 1.4541 | 04Cr18Ni10Ti20 | 321 | 321 |
| 22 | 0Cr18Ni11Nb | 06Cr18Ni11Nb | SUS347 | 347 | S34700 | STS347 | 1.4550 | 04Cr18Ni10Nb40 | 347 | 347 |
| Austenitic-Ferritic Stainless Steel (Duplex) | ||||||||||
| 23 | 0Cr26Ni5Mo2 | — | SUS329J1 | 329 | S32900 | STS329J1 | 1.4477 | — | 329J1 | 329J1 |
| 24 | 00Cr18Ni5Mo3Si2 | 022Cr19Ni5Mo3Si2N | SUS329J3L | — | S31803 | STS329J3L | 1.4462 | — | 329J3L | 329J3L |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 25 | 0Cr13Al | 06Cr13Al | SUS405 | 405 | S40500 | STS405 | 1.4002 | 04Cr13 | 405 | 405 |
| 26 | — | 022Cr11Ti | SUH409 | 409 | S40900 | STS409 | 1.4512 | — | 409L | 409L |
| 27 | 00Cr12 | 022Cr12 | SUS410L | — | — | STS410L | — | — | 410L | 410L |
| 28 | 1Cr17 | 10Cr17 | SUS430 | 430 | S43000 | STS430 | 1.4016 | 05Cr17 | 430 | 430 |
| 29 | 1Cr17Mo | 10Cr17Mo | SUS434 | 434 | S43400 | STS434 | 1.4113 | — | 434 | 434 |
| 30 | — | 022Cr18NbTi | — | — | S43940 | — | 1.4509 | — | 439 | 439 |
| 31 | 00Cr18Mo2 | 019Cr19Mo2NbTi | SUS444 | 444 | S44400 | STS444 | 1.4521 | — | 444 | 444 |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 32 | 1Cr12 | 12Cr12 | SUS403 | 403 | S40300 | STS403 | — | — | 403 | 403 |
| 33 | 1Cr13 | 12Cr13 | SUS410 | 410 | S41000 | STS410 | 1.4006 | 12Cr13 | 410 | 410 |
| 34 | 2Cr13 | 20Cr13 | SUS420J1 | 420 | S42000 | STS420J1 | 1.4021 | 20Cr13 | 420 | 420J1 |
| 35 | 3Cr13 | 30Cr13 | SUS420J2 | — | — | STS420J2 | 1.4028 | 30Cr13 | 420J2 | 420J2 |
| 36 | 7Cr17 | 68Cr17 | SUS440A | 440A | S44002 | STS440A | — | — | 440A | 440A |
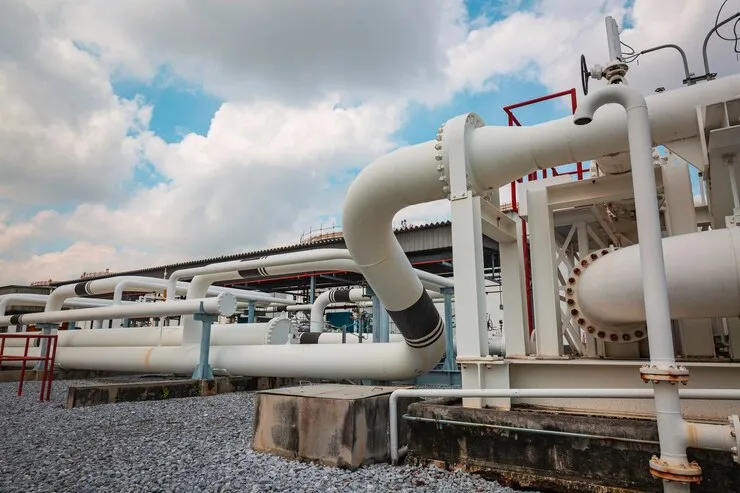

Pipelines, refineries, and petrochemical plants
Power plants for steam, water, and fuel lines
Chemical plants for process piping systems
Municipal and industrial water supply systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems
Hygienic piping systems with stainless steel reducers
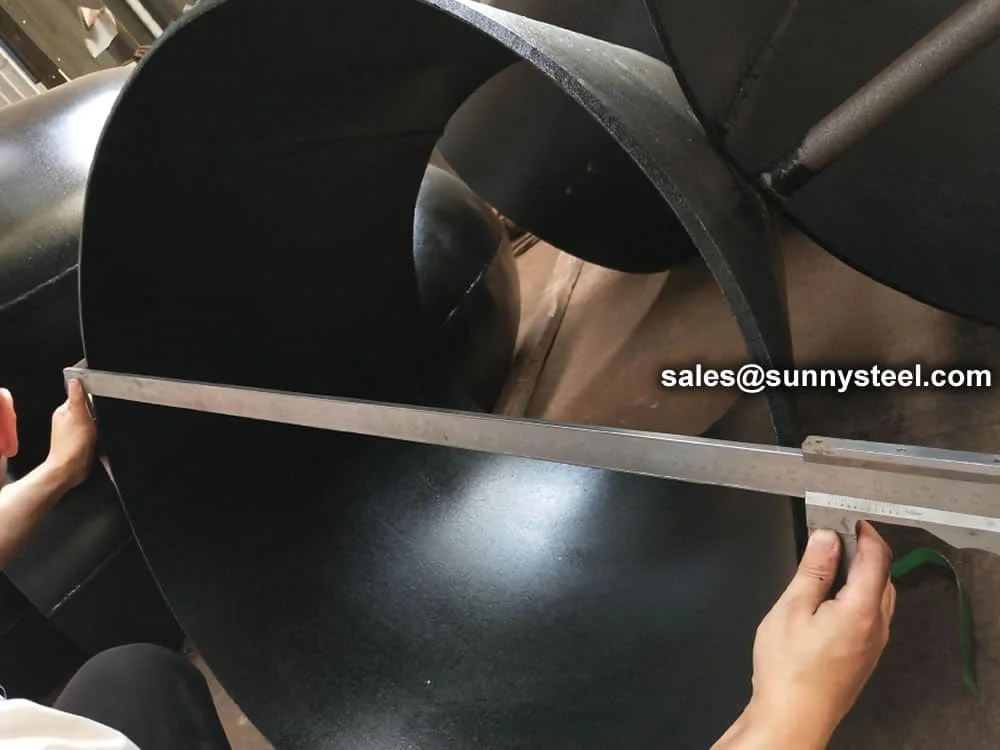

Large-size eccentric reducers (≥24" or 610mm)...
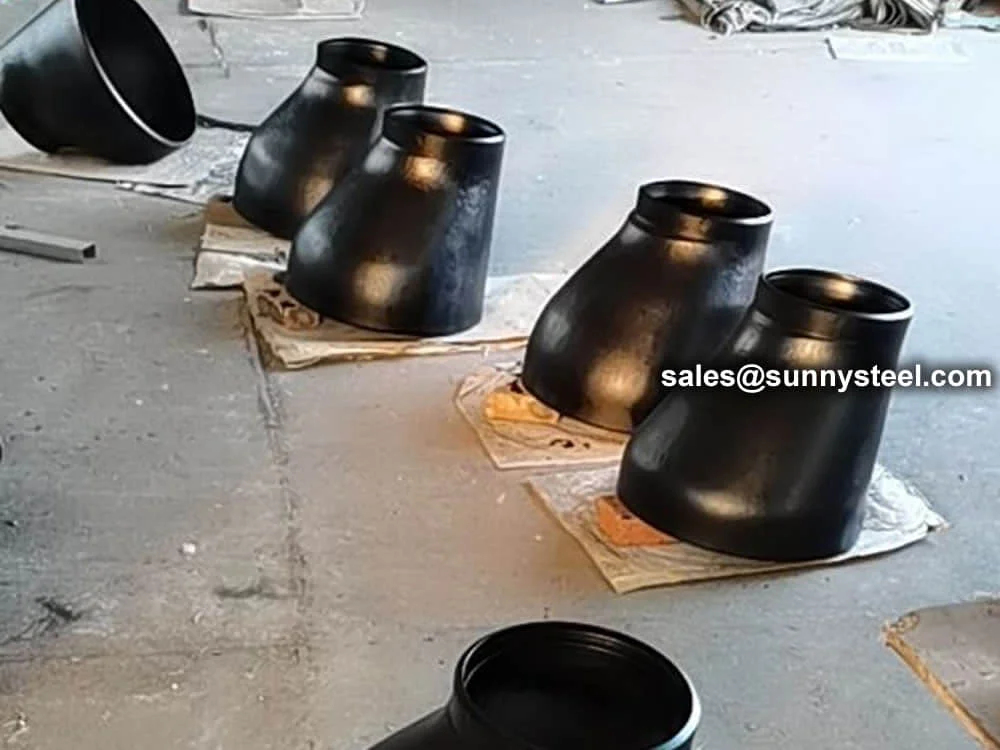

Astm a234 wpb eccentric reducers are high-quality ...
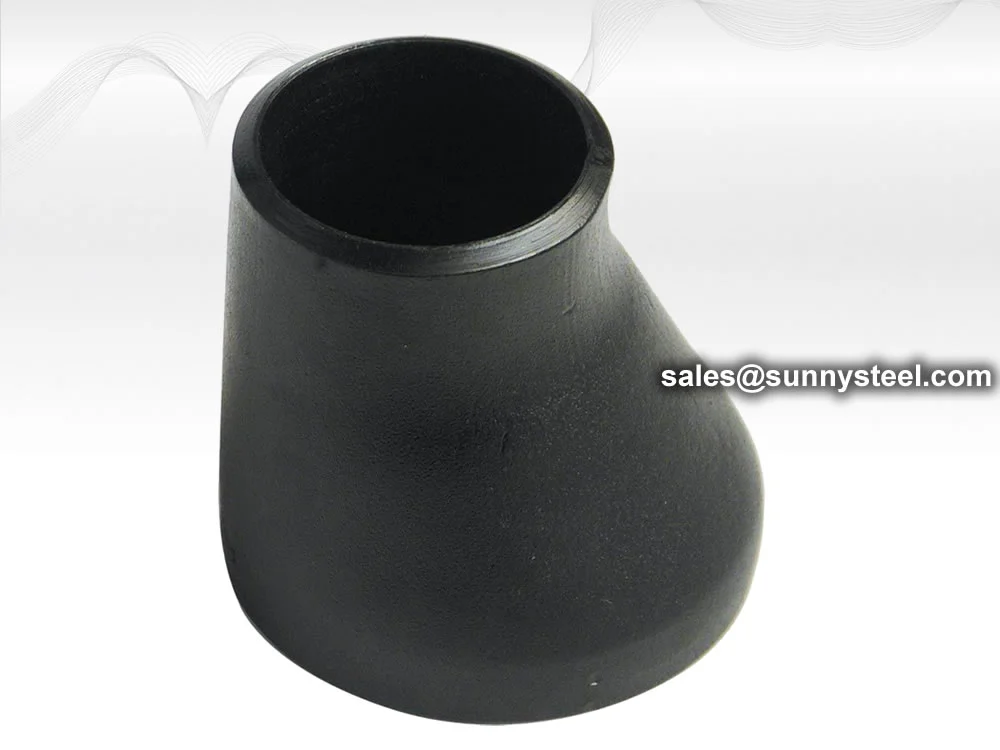

Eccentric reducers are fittings used to connect pi...
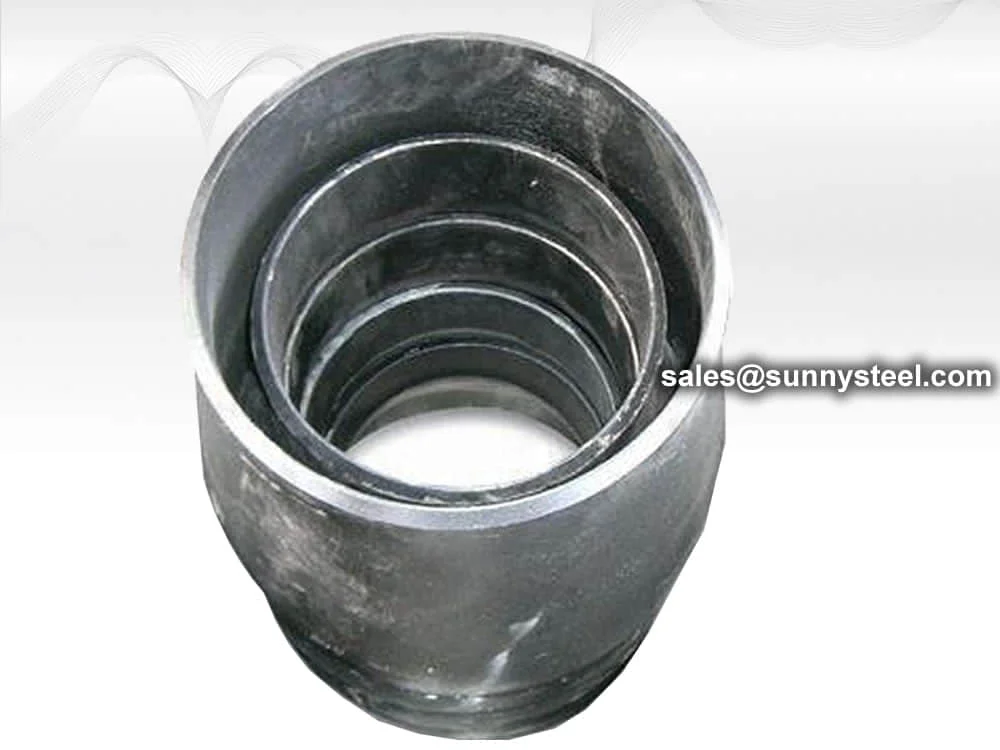

Astm a234 wpb concentric reducers are high-quality...
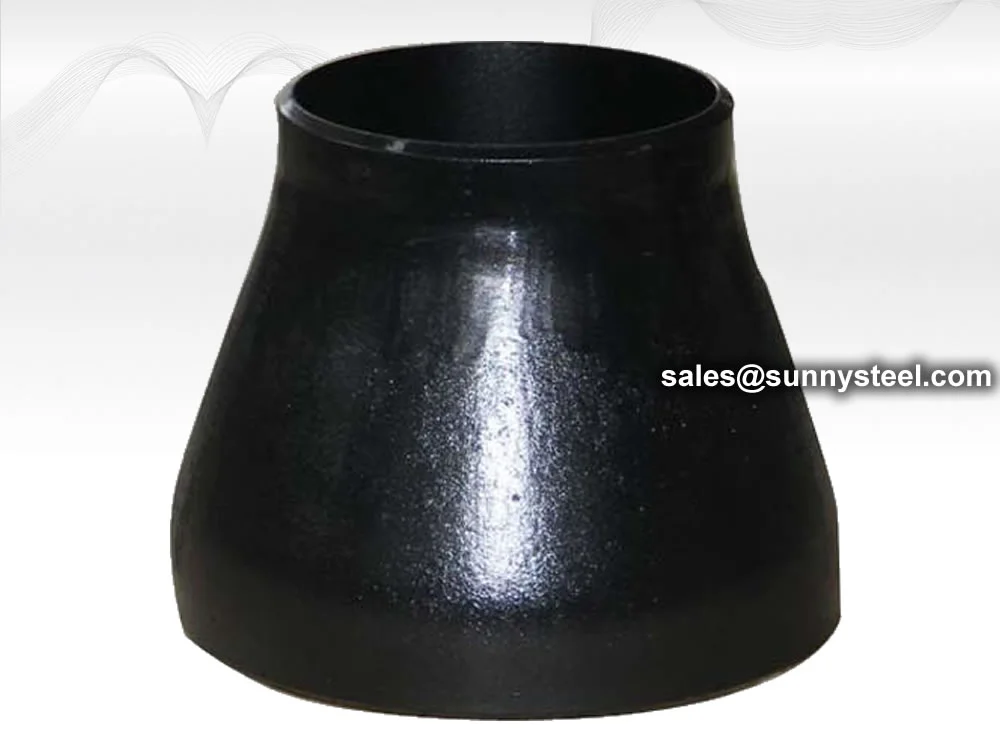

Concentric reducers are essential pipe fittings th...
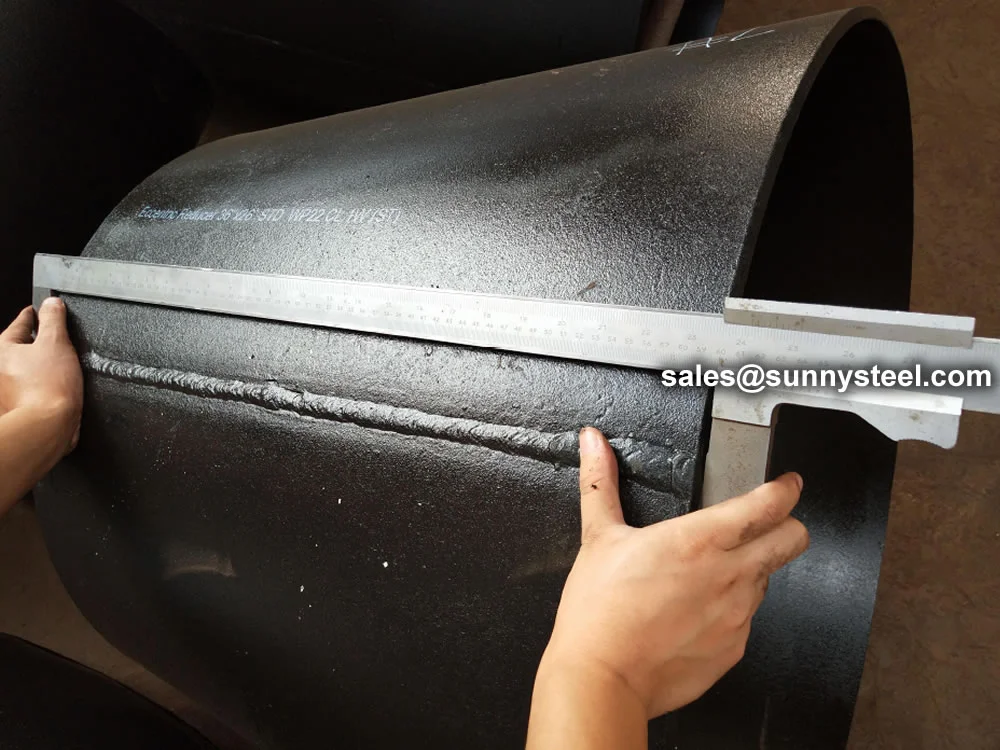

Astm a234 wp22 reducers are high-performance low-a...