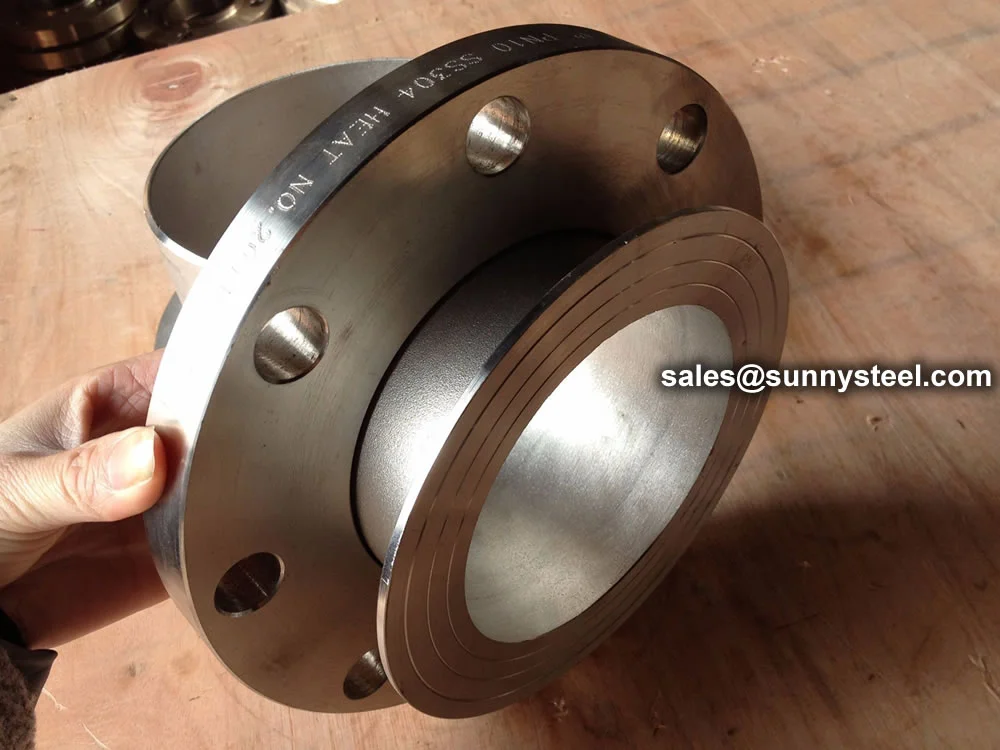

Lap Joint Stub End Dimensions
Asme b16.
Lap Joint Stub End Dimensions
Asme b16.9 stub ends are used with lap joint flanges, providing a cost-effective and flexible piping connection solution in various industries.
ASME B16.9 Stub Ends are high-quality pipe fittings designed to connect pipes with lap joint flanges, providing exceptional corrosion resistance and reliability for industrial piping systems. Manufactured to meet the stringent requirements of ASME B16.9 standards, these stub ends are engineered for seamless integration in demanding applications such as boiler pipeline protection, oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing, and food production. Their design facilitates easy assembly, disassembly, and alignment, making them ideal for systems requiring frequent maintenance or retrofitting.
ASME B16.9 stub ends are crafted from materials like carbon steel (ASTM A234 WPB), stainless steel (ASTM A403 WP304/316L), or alloy steel, using seamless or welded processes to ensure robust, leak-free connections. The flared end, compatible with lap joint flanges, allows rotational alignment for precise bolt hole positioning, reducing installation complexity. Available in short (MSS SP-43) and long (ASA) patterns, these fittings come in sizes from 1/2” to 36” (DN15 to DN900) and wall thicknesses from SCH 5S to XXS, meeting diverse project specifications. Surface treatments such as galvanizing, 3LPE, or passivation enhance corrosion resistance, ensuring durability in harsh environments.
Welded stub ends undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, ultrasonic, and dye penetrant inspections, to ensure compliance with ASME B16.9 and other relevant standards like ASTM and API. With tensile strengths ranging from 415 MPa (carbon steel) to 515 MPa (stainless steel), these fittings excel in resisting corrosion, thermal stress, and pipeline wear. Their design supports applications involving corrosive fluids, high-pressure gases, or abrasive materials, making them a reliable choice for industrial piping systems in refineries, power plants, and chemical facilities.
The versatility of ASME B16.9 stub ends lies in their compatibility with lap joint flanges, which allows the use of lower-cost backing flanges, reducing overall system costs. Compared to other fittings like tees or reducers, stub ends offer a cost-effective solution for systems requiring frequent disassembly, such as in food processing or water treatment. Their ability to accommodate thermal expansion and misalignment makes them ideal for complex piping layouts, particularly in boiler pipeline protection and petrochemical applications.
ASME B16.9 stub ends address critical challenges like corrosion, pipeline wear, and maintenance complexity in high-throughput industrial systems. Their robust construction, adherence to strict standards, and material versatility make them a preferred choice for engineers seeking durable pipe fittings for extreme environments. Whether used in high-temperature boiler systems or corrosive chemical processing plants, these stub ends deliver unmatched performance, safety, and longevity.
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.30 max (WPB), 0.08 max (WP304) |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.29-1.06 (WPB), 2.00 max (WP304) |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.05 max (WPB), 0.045 max (WP304) |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.058 max (WPB), 0.03 max (WP304) |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.10 min (WPB), 0.75 max (WP304) |
| Chromium (Cr) | - (WPB), 18.0-20.0 (WP304) |
| Nickel (Ni) | - (WPB), 8.0-11.0 (WP304) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) | 415 (WPB), 515 (WP304) |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) | 240 (WPB), 205 (WP304) |
| Elongation, min (%) | 22 (WPB), 40 (WP304) |
| Hardness, max (HBW) | 197 (WPB), 201 (WP304) |
| Feature | ASME B16.9 Stub End | ASME B16.9 Tee | ASME B16.9 Reducer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon/Stainless Steel | Carbon/Stainless Steel | Carbon/Stainless Steel |
| Connection Type | Welded with Lap Joint | Welded/Threaded | Welded |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Material-dependent) | Excellent (Material-dependent) | Excellent (Material-dependent) |
| Applications | Flange connections, maintenance | Branching, flow distribution | Size transition |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 415-515 (min) | 415-515 (min) | 415-515 (min) |
| Installation Complexity | Low (Flange alignment) | Moderate (Pipe cutting) | Low (Welded) |
| Key Advantage | Easy maintenance, cost-effective | Balanced flow distribution | Seamless size transition |
A curated list of long-tail keywords for ASME B16.9 stub ends, covering specifications, applications, and material properties, presented in a two-column layout.
Note: ASME B16.9 stub ends comply with ASME B16.9 and ASTM standards. For detailed specifications, refer to the relevant standards or contact a certified supplier.

Quick removal of piping sections without disturbing the entire system for maintenance and inspection.
Use expensive materials only where needed, with cheaper backing flanges reducing overall cost.
Rotating backing flange allows easy alignment of bolt holes during installation.
Properly welded and assembled stub ends provide secure and leak-proof joints.
Compatible with various flange types and available in wide range of materials and sizes.
Manufactured to strict international standards with comprehensive testing and inspection.
Description: Produced and machined specifically to fit lap joint flanges.
Description: Suited for standard slip-on flanges acting as lap-joint flanges.
Description: Versatile for both lap joint and slip-on backing flanges.
Description: Similar to Type "C" with concentric serrations on lap face.
Longer length for easier alignment and welding. Suitable for frequent disassembly applications.
Standard Lap Joint FlangesSimilar length to pipe. Ideal for space-limited applications where flange needs to be close to pipe end.
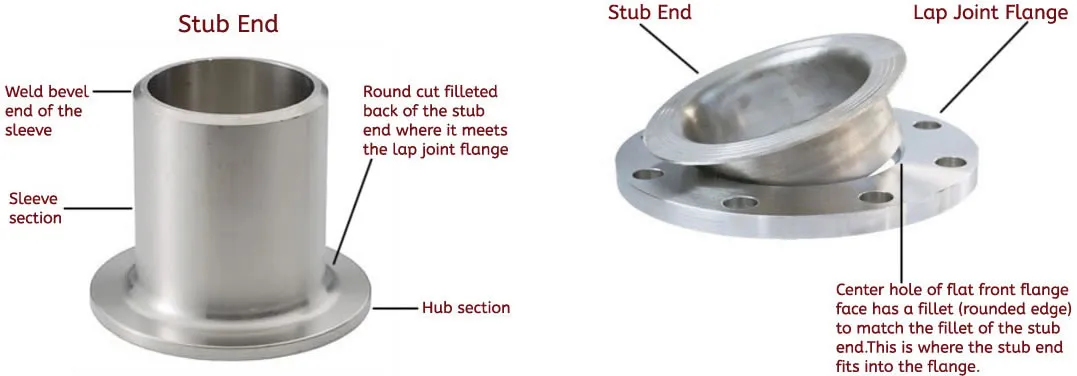
Slip-On FlangesIn piping systems, a stub end is a crucial component used for connecting pipes of different materials and sizes. It provides a convenient and cost-effective solution for achieving a leak-free joint without the need for welding. In this article, we will explore the geometry, types, and applications of stub ends, shedding light on their significance in various industries and projects.
| N.D. | Out diameter | Hight(F) | Stub end O.D.(G) | Beveld radio(R) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPS | DN | OD | Mss | ANSI | Nominal&max | Nominal&min | A Max | B Max |
| 1/2 | 15 | 21.3 | 50.8 | 76.2 | 35 | 34 | 3 | 0.8 |
| 3/4 | 20 | 26.7 | 50.8 | 76.2 | 43 | 42 | 3 | 0.8 |
| 1 | 25 | 33.4 | 50.8 | 101.6 | 51 | 50 | 3 | 0.8 |
| 1 1/4 | 32 | 42.4 | 50.8 | 101.6 | 64 | 63 | 4.8 | 0.8 |
| 1 1/2 | 40 | 48.3 | 50.8 | 101.6 | 73 | 72 | 6.4 | 0.8 |
| 2 | 50 | 60.3 | 63.5 | 152.4 | 92 | 91 | 7.9 | 0.8 |
| 2 1/2 | 65 | 73 | 63.5 | 152.4 | 105 | 104 | 7.9 | 0.8 |
| 3 | 80 | 88.9 | 63.5 | 152.4 | 127 | 126 | 9.6 | 0.8 |
| 3 1/2 | 90 | 101.6 | 76.2 | 152.4 | 140 | 139 | 9.6 | 0.8 |
| 4 | 100 | 114.3 | 76.2 | 152.4 | 157 | 156 | 11.2 | 0.8 |
| 5 | 125 | 141.3 | 76.2 | 203.2 | 186 | 185 | 11.2 | 1.6 |
| 6 | 150 | 168.3 | 88.9 | 203.2 | 216 | 215 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 8 | 200 | 219.1 | 101.6 | 203.2 | 270 | 269 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 10 | 250 | 273.1 | 127 | 254 | 324 | 322 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 12 | 300 | 323.9 | 152.4 | 254 | 381 | 379 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 14 | 350 | 355.6 | 152.4 | 304.8 | 413 | 411 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 16 | 400 | 406.4 | 152.4 | 304.8 | 470 | 468 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 18 | 450 | 457.2 | 152.4 | 304.8 | 533 | 531 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 20 | 500 | 508 | 152.4 | 304.8 | 584 | 582 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 22 | 550 | 559 | 152.4 | 304.8 | 641 | 639 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
| 24 | 600 | 610 | 152.4 | 304.8 | 692 | 690 | 12.7 | 1.6 |
The following information shall be provided to order a stub end:
Stub ends can be ordered with different ends finishing:
| Material Type | Standards & Grades | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A234 WPB, A420 WPL6 | High strength, cost-effective, good weldability | General industrial piping, oil & gas, power generation |
| Stainless Steel | ASTM A403 WP304/304L, WP316/316L | Excellent corrosion resistance, hygienic properties | Chemical processing, food & beverage, pharmaceutical |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A234 WP1, WP5, WP9, WP11, WP22, WP91 | Enhanced strength, high-temperature resistance | High-temperature and high-pressure services |
Butt Weld Fittings
Stainless Steel Fittings
Buttwelding Ends
Japanese Standards
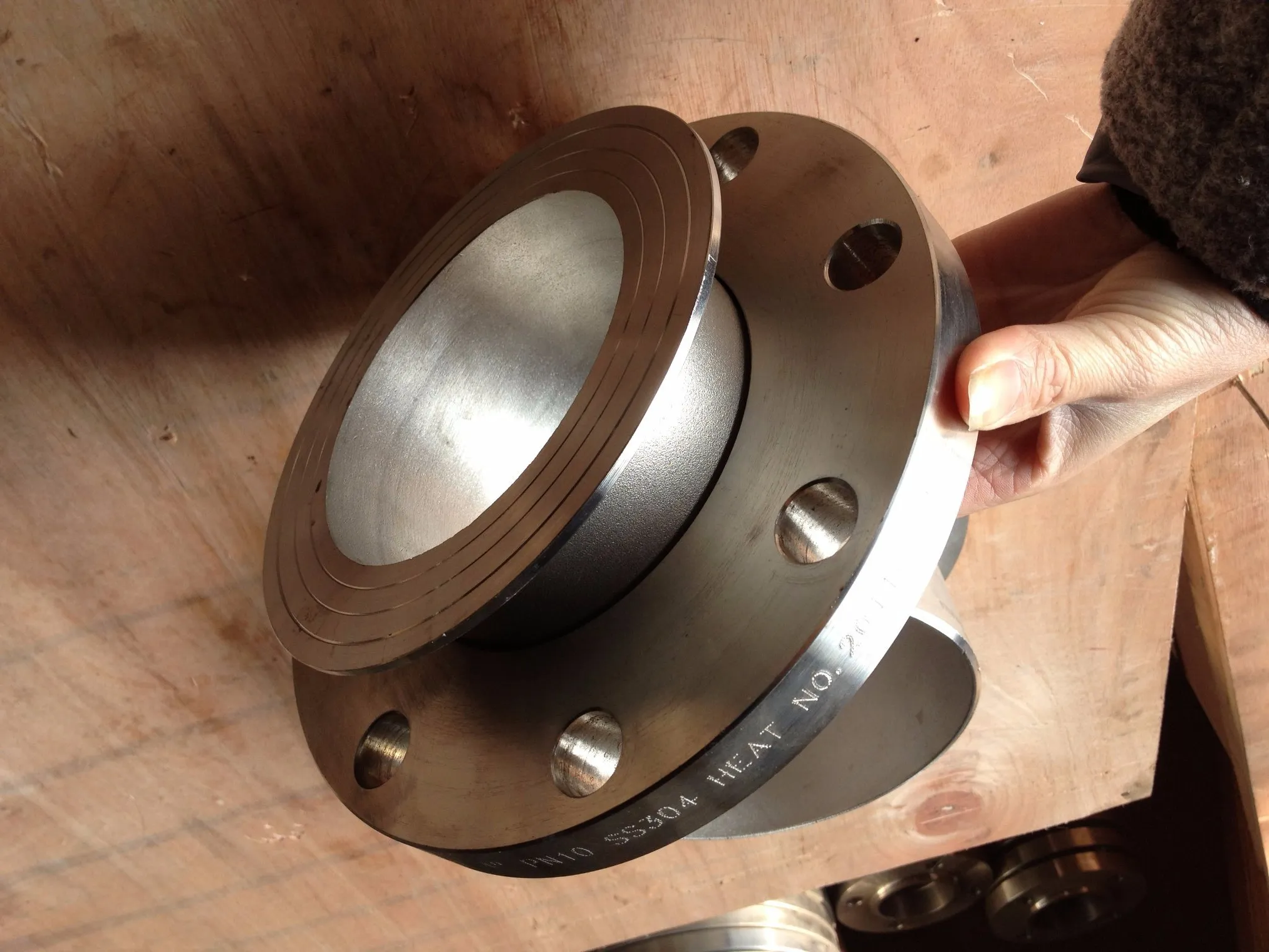

The ASME B16.9 Stub End allows sections pipe to be opened for inspection, cleaning or replacement without the need for additional welding.

Carbon steel stub ends provide durable, corrosion-...
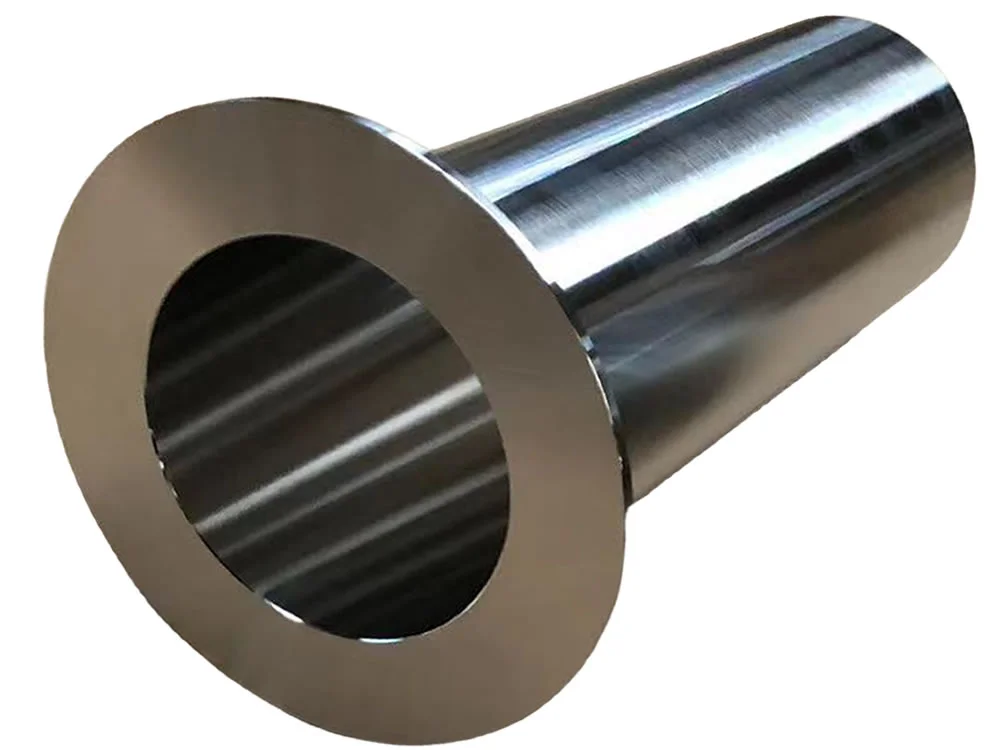

Stainless steel stub ends provide superior corrosi...
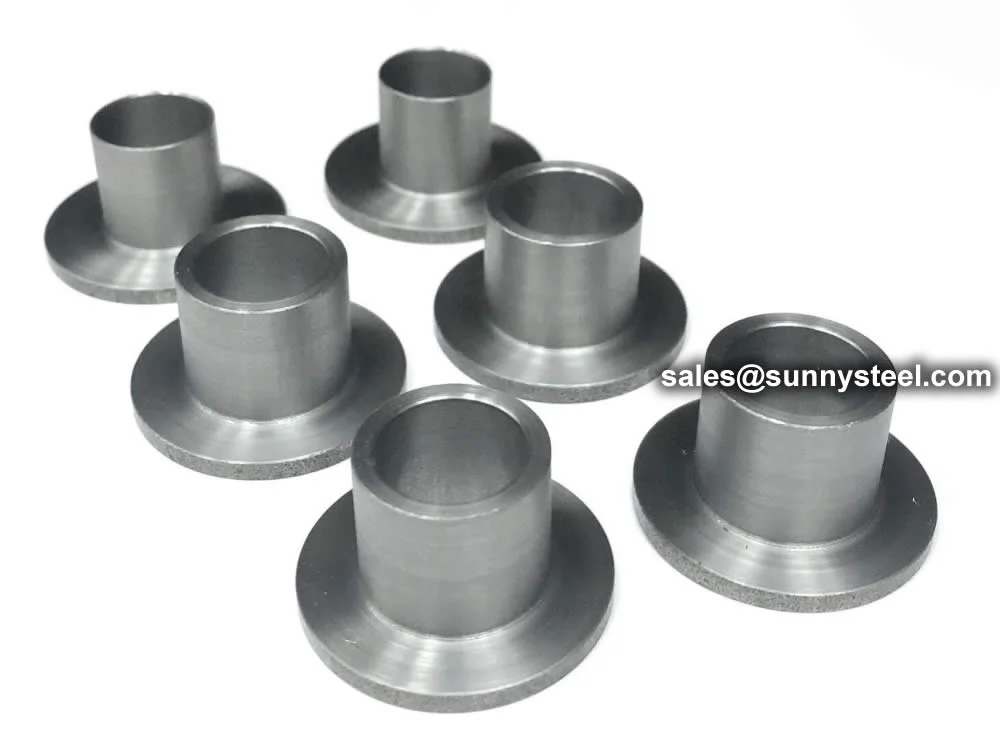

Lap joint stub ends provide flexibility, corrosion...

The a403 wps304l stainless stub end is a pipe fitt...
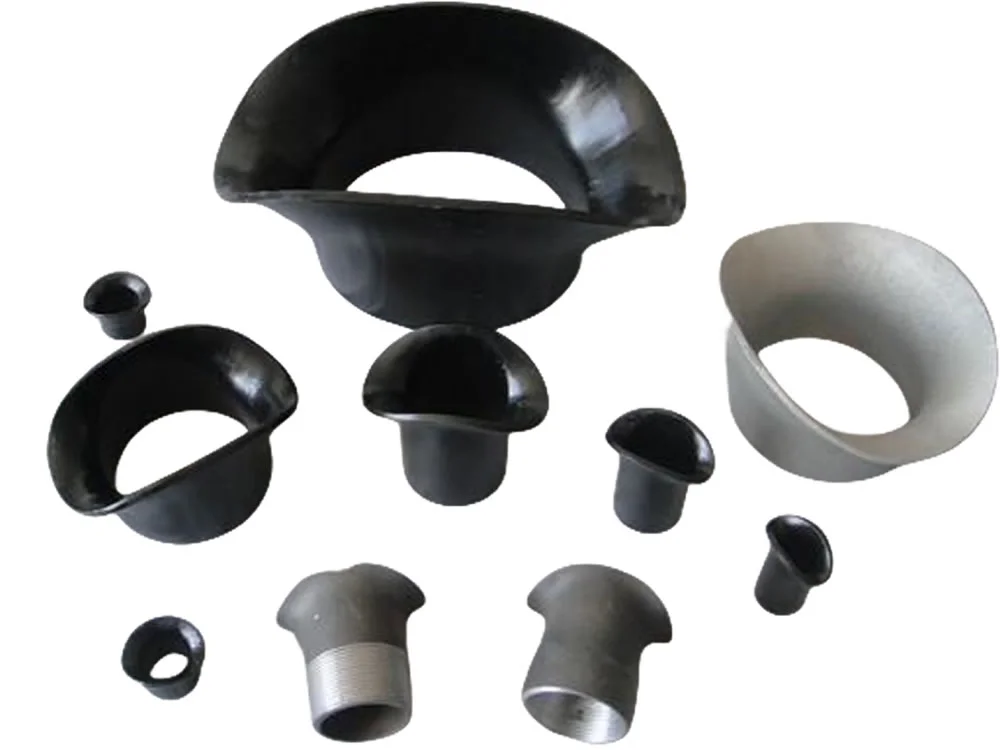

Pipe saddle fittings provide safe and economical s...
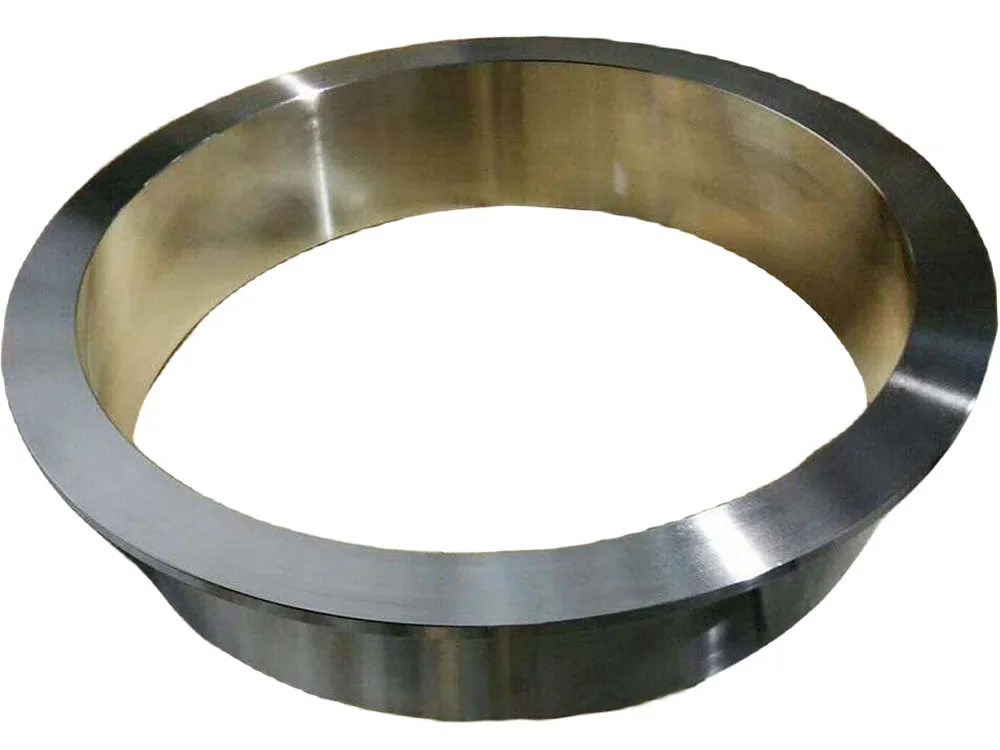

Pipe collar is a pipe fitting used in industrial p...