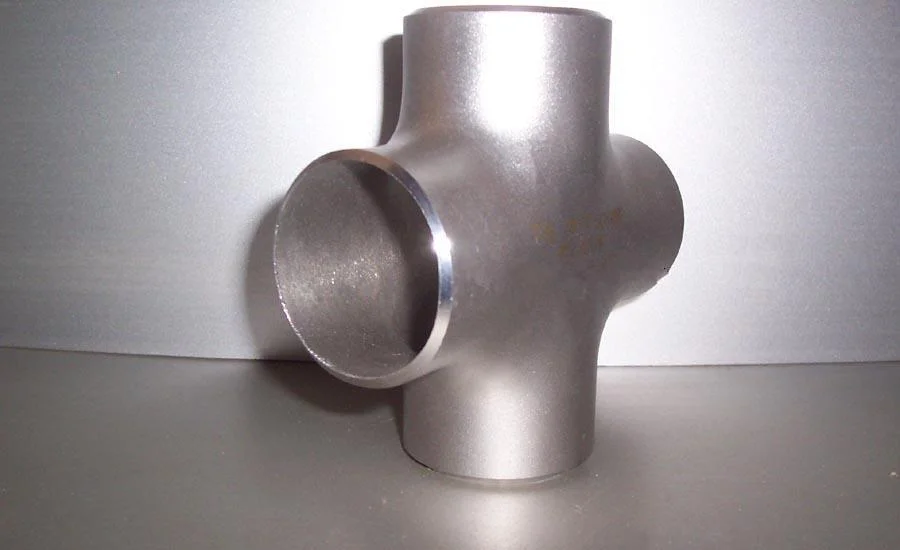

Corrosion-resistant Cross Fittings For Seamless Pipeline Branching
Butt weld cross fittings ensure robust, corrosion-resistant connections for industrial piping systems.
Corrosion-resistant Cross Fittings For Seamless Pipeline Branching
Butt weld cross fittings ensure robust, corrosion-resistant connections for industrial piping systems. ideal for boiler pipeline protection and oil/gas applications, they deliver reliable, leak-free performance.
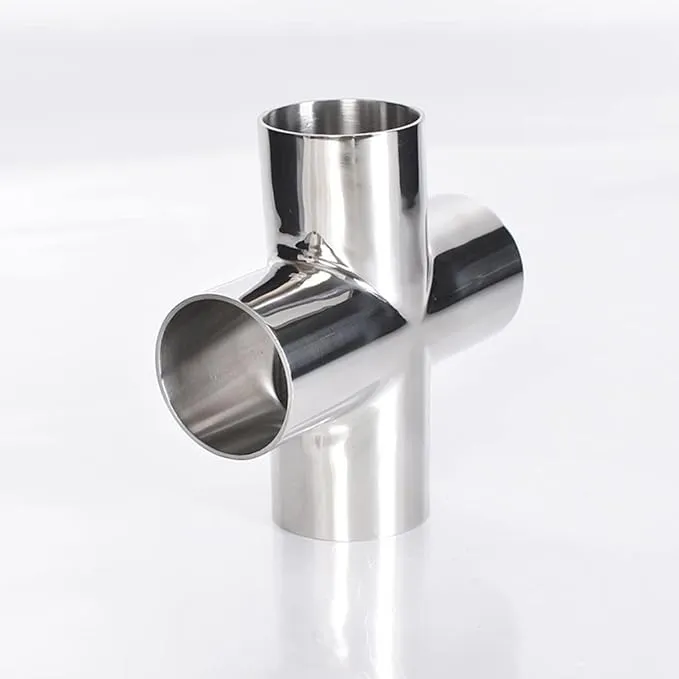
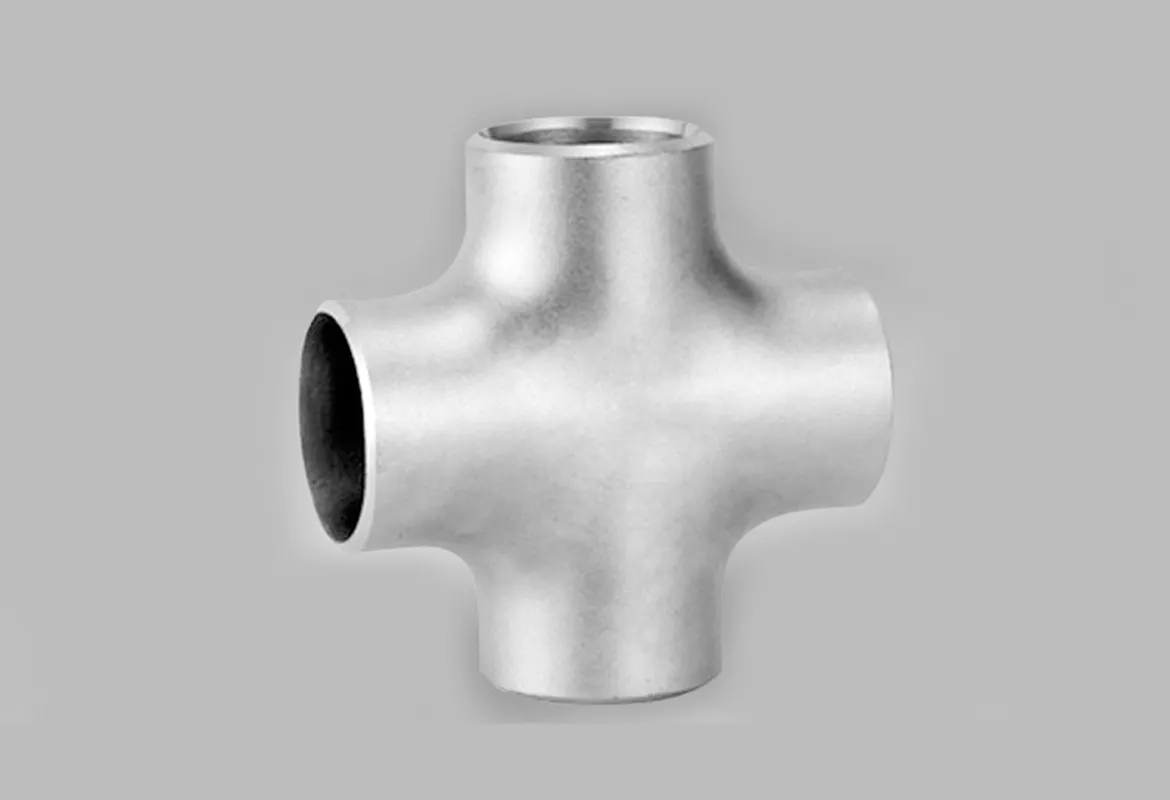
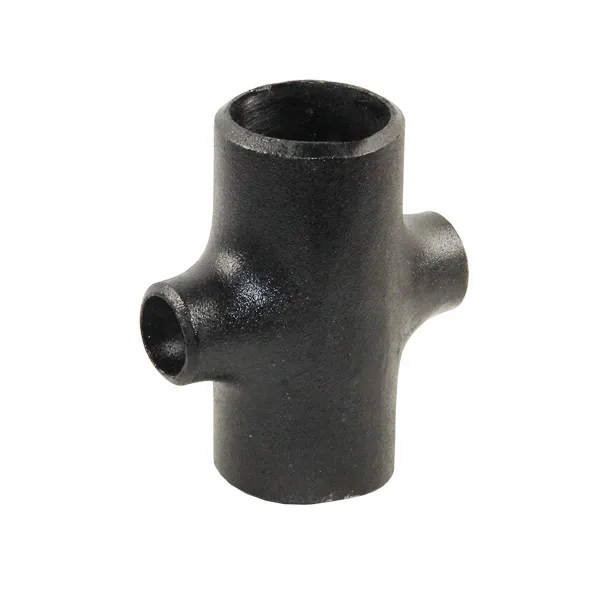
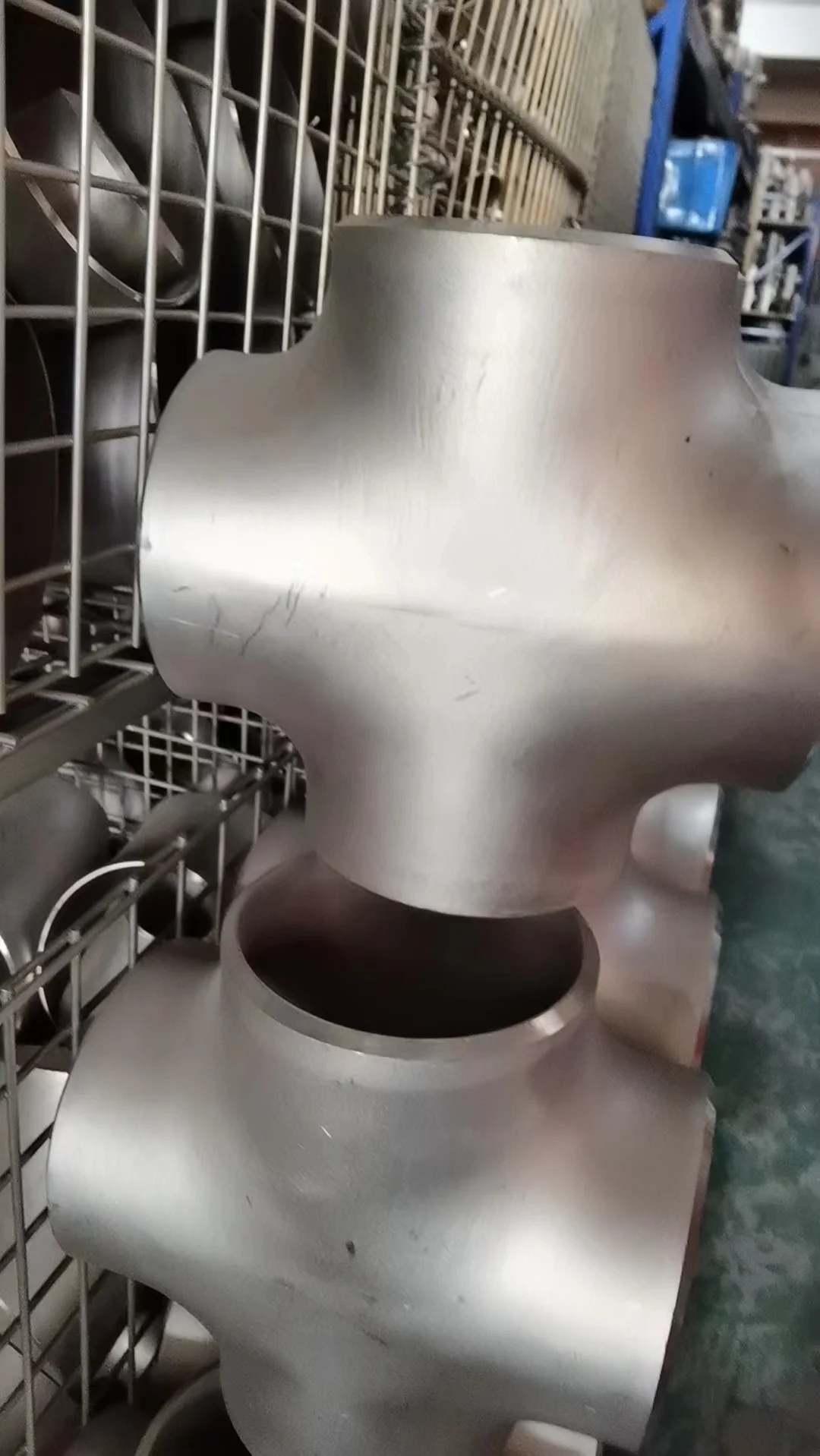
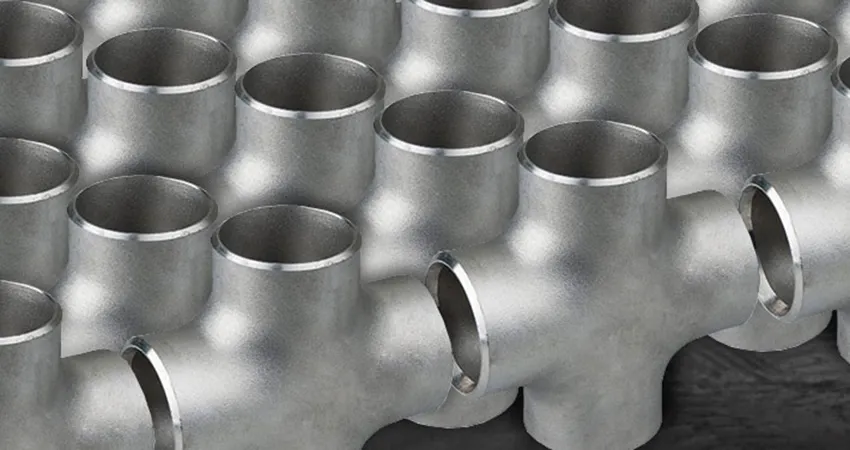





A butt weld cross is a four-port pipe fitting that allows for the connection of four pipes, enabling the distribution or convergence of fluids or gases in a pipeline system. The "butt weld" refers to the method of connection, where the edges of the fitting and pipe are joined together with a full, welded seam for a strong and leak-proof connection, as opposed to threaded or socket-weld fittings.

Butt Weld Cross fittings are critical components designed to create four-way branch connections in industrial piping systems, ensuring robust, leak-free performance. Conforming to standards such as ASME B16.9, ASTM A234, and ASTM A403, these fittings are engineered for demanding applications, including boiler pipeline protection, oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing, and power generation. Their seamless or welded construction provides exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature environments requiring reliable branching solutions.
Manufactured from materials like carbon steel (ASTM A234 WPB), stainless steel (ASTM A403 WP304/316L), or alloy steel, butt weld cross fittings are produced through forging, hot-forming, or welding processes to ensure high structural integrity. Available in equal and reducing configurations, these fittings come in sizes from 1/2” to 48” (DN15 to DN1200) and wall thicknesses from SCH 5S to XXS, meeting diverse project requirements. Surface treatments such as galvanizing, 3LPE, or passivation enhance corrosion resistance, ensuring suitability for harsh conditions in industries like petrochemicals, marine, and food processing.
Welded cross fittings undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, ultrasonic, and radiographic inspections, to ensure weld quality and compliance with ASME B16.9 and other standards. With tensile strengths ranging from 415 MPa (carbon steel) to 515 MPa (stainless steel), these fittings excel in systems handling high-pressure fluids, corrosive gases, or abrasive materials. Their design ensures smooth flow distribution across all four directions, minimizing turbulence and pressure loss, making them ideal for industrial piping systems where efficiency and reliability are paramount.
The key advantage of butt weld cross fittings lies in their ability to create complex, multi-directional branch connections with high strength and minimal welding, reducing installation time compared to fabricated alternatives. They are particularly suited for applications requiring balanced flow distribution, such as in boiler pipeline protection or refinery piping systems. Compared to other fittings like tees or weldolets, butt weld crosses offer greater versatility for four-way branching, making them ideal for intricate piping layouts in chemical plants, power generation facilities, and oil and gas refineries.
Butt weld cross fittings address critical challenges like pipeline corrosion, pressure loss, and complex branching in industrial systems. Their robust construction, adherence to strict standards, and material versatility make them a preferred choice for engineers seeking durable pipe fittings. Whether used in high-temperature boiler systems, corrosive petrochemical environments, or hygienic food processing lines, these fittings deliver unmatched performance, safety, and longevity.
| Element | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.30 max (WPB), 0.08 max (WP304) |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.29-1.06 (WPB), 2.00 max (WP304) |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.05 max (WPB), 0.045 max (WP304) |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.058 max (WPB), 0.03 max (WP304) |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.10 min (WPB), 0.75 max (WP304) |
| Chromium (Cr) | - (WPB), 18.0-20.0 (WP304) |
| Nickel (Ni) | - (WPB), 8.0-11.0 (WP304) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) | 415 (WPB), 515 (WP304) |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) | 240 (WPB), 205 (WP304) |
| Elongation, min (%) | 22 (WPB), 40 (WP304) |
| Hardness, max (HBW) | 197 (WPB), 201 (WP304) |
| Feature | Butt Weld Cross | Butt Weld Tee | Weldolet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon/Stainless Steel | Carbon/Stainless Steel | Carbon/Stainless Steel |
| Connection Type | Welded (Four-way) | Welded (Three-way) | Welded (Branch) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Material-dependent) | Excellent (Material-dependent) | Excellent (Material-dependent) |
| Applications | Multi-directional branching | Three-way branching | Single branch connections |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 415-515 (min) | 415-515 (min) | 485-515 (min) |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate (Welding required) | Moderate (Welding required) | Low (Minimal welding) |
| Key Advantage | Four-way flow distribution | Balanced three-way branching | Compact, high-strength branch |
Enhanced by coatings or stainless steel for harsh environments.
Welded design ensures robust, leak-free connections.
Ideal for boilers, oil/gas, and chemical systems.
Supports four-way branching for complex systems.
Resists thermal expansion and pipeline wear.
Available in equal or reducing types for specific needs.

A piping fitting cross is a type of piping fitting that is used to connect four pipes or tubes at right angles to each other. It is commonly used in plumbing, HVAC, and industrial applications where a cross-shaped pipe or tube configuration is required.
Piping fitting crosses are available in different sizes and materials, such as carbon steel and stainless steel, depending on the application. They typically have four connection points, with each point designed to accommodate a pipe or tube of the same size and material.
Piping fitting crosses are designed to provide a strong and secure connection between four pipes or tubes, which allows for the efficient and effective flow of fluid or gas through the system. They are also available in different styles, such as reducing crosses, which allow for greater flexibility and customization in piping system design. The installation of piping fitting crosses requires careful consideration of the pipe size, material, pressure, temperature, and fluid being conveyed to ensure proper fit and performance.
Cross Pipe Fittings, also known as four-way fittings, have one inlet and three outlets and often feature solvent-welded sockets, or female-threaded ends. The ends are positioned at 90-degree angles and the threads are designed to create a stable grip and secure connection to male pipe fittings.
| Material Type | Standards & Grades | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | ASTM A105, A350 LF2, A694 F52/F60/F65 | High strength, good weldability, cost-effective | General industrial piping, oil & gas, power generation |
| Stainless Steel | ASTM A182 F304/304L, F316/316L, F321, F347 | Excellent corrosion resistance, hygienic properties | Chemical processing, food & beverage, pharmaceutical |
| Alloy Steel | ASTM A182 F1, F5, F9, F11, F22, F91 | Enhanced strength, high-temperature resistance | High-temperature and high-pressure services |
Integrally Reinforced Forged Branch Outlet Fittings
Forged Fittings, Socket-Welding and Threaded
Butt-welding Fittings
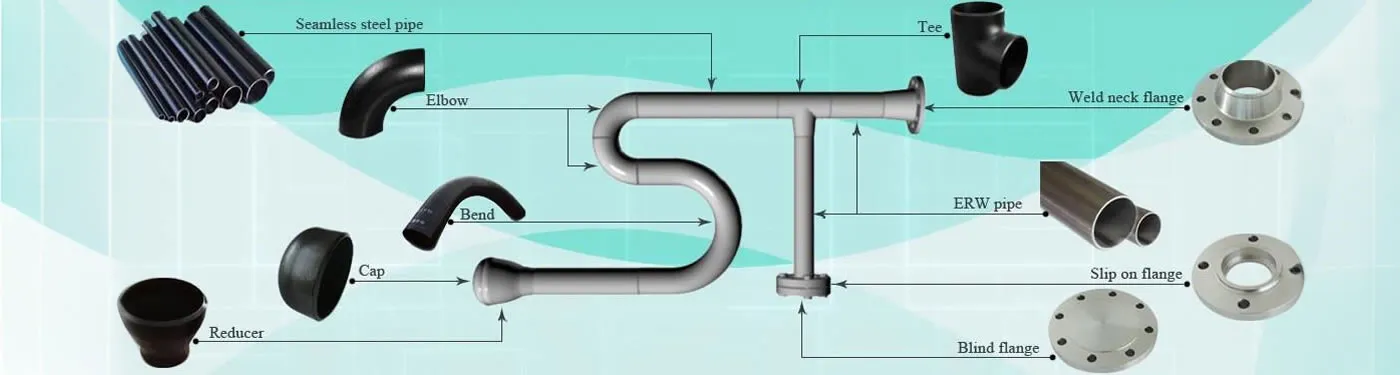
Industries Using
Butt Weld Cross components that are used to connect, join, or adapt different parts of a system, such as pipes, tubes, or hoses. They serve multiple purposes, including:
The choice of fittings depends on the specific requirements of the system, including factors like the type of fluid or gas, pressure, temperature, and the layout of the piping or tubing system.
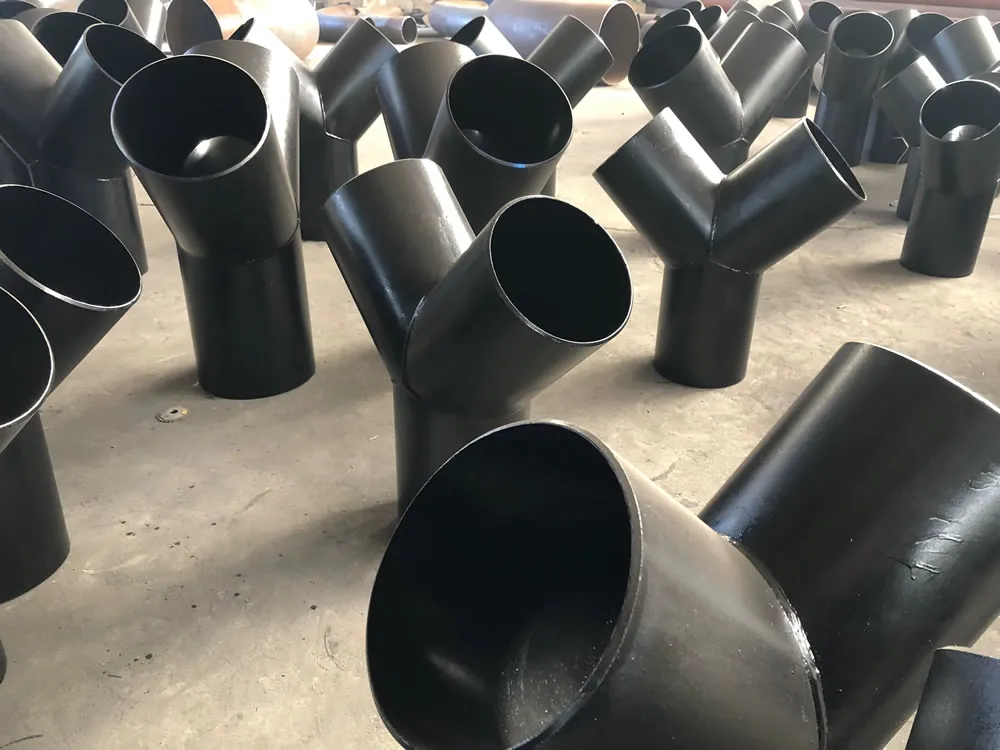

Y tees ensure corrosion-resistant, smooth fluid fl...
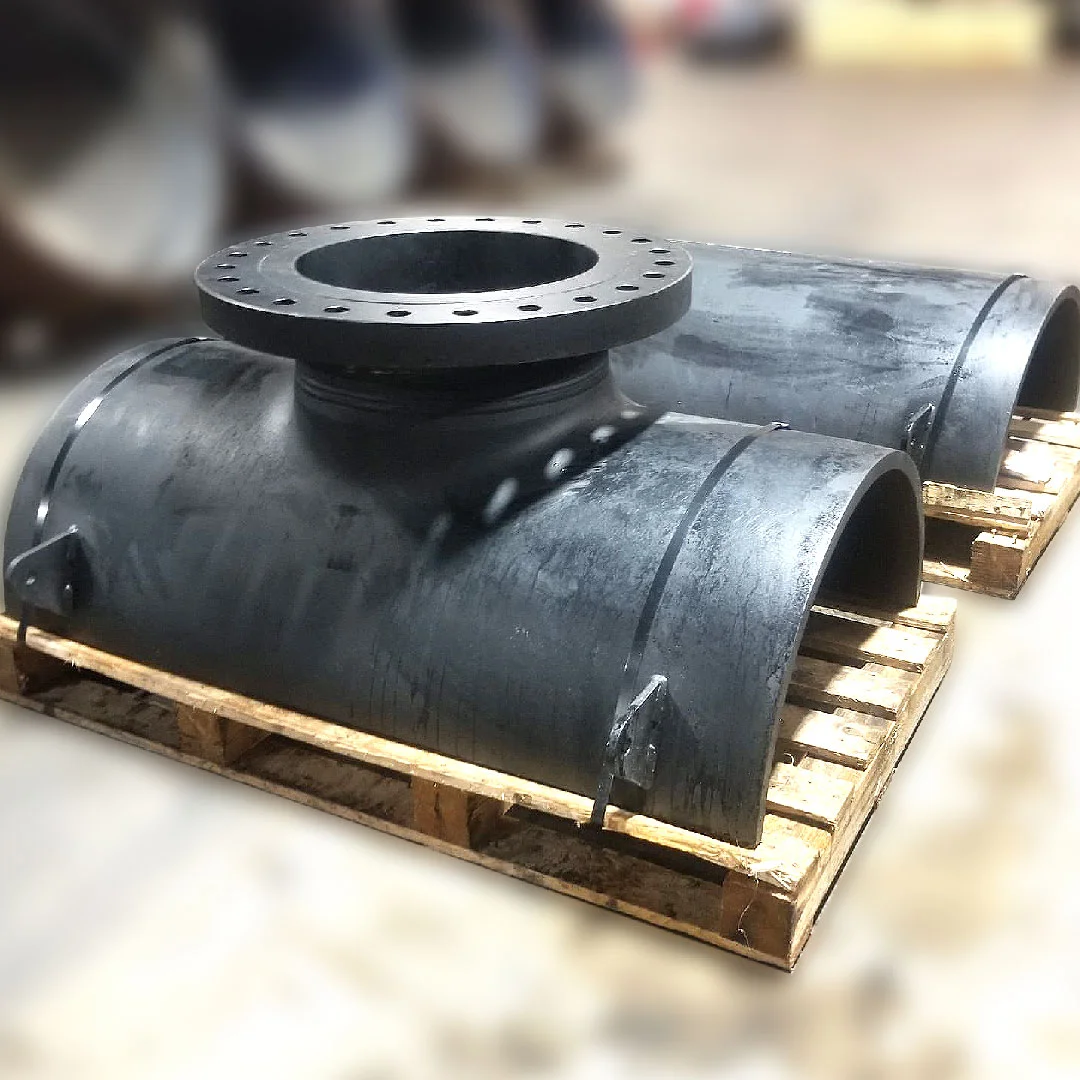

Split tees provide robust, corrosion-resistant bra...
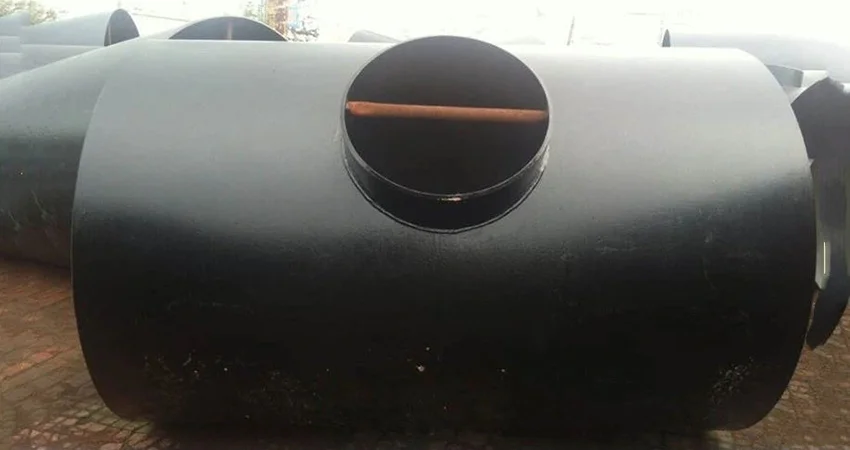

Large diameter elbows provide durable, corrosion-r...
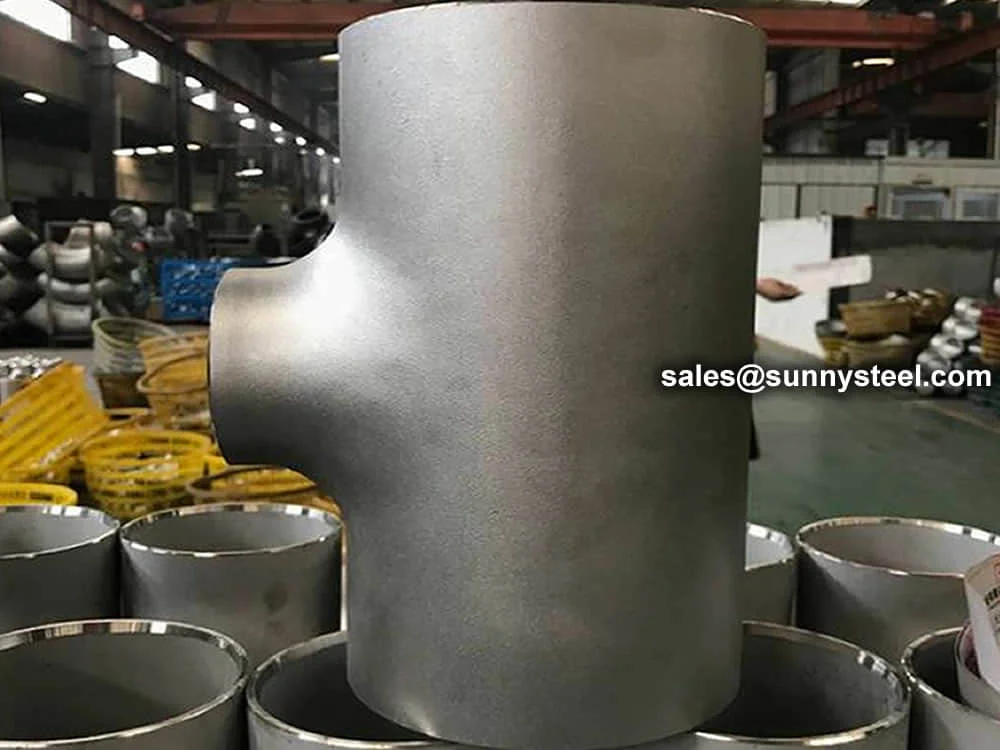

Stainless steel tees are butt-weld pipe fittings d...
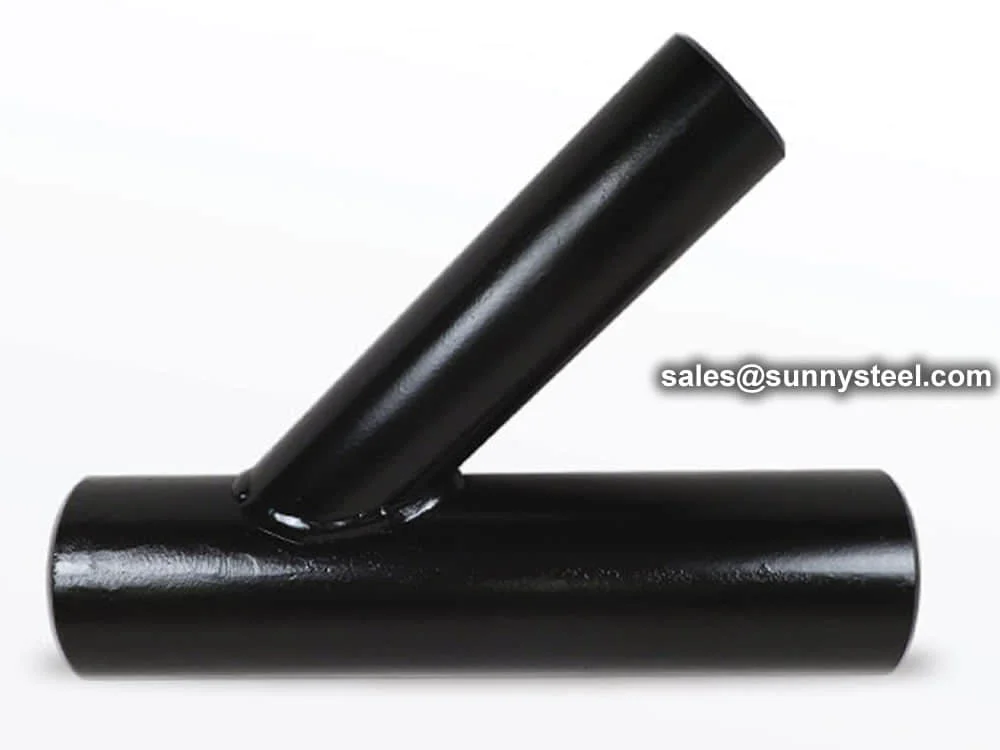

A lateral pipe tee means a pipe fitting which is s...
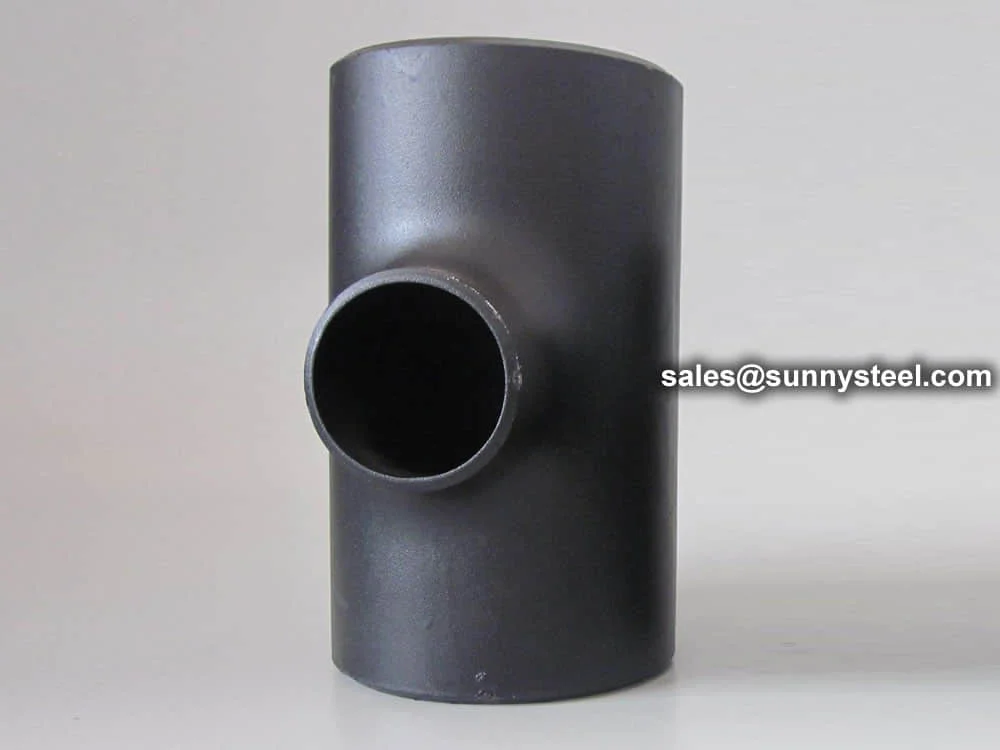

Reducing tee, like all pipe tees, is in the shape ...