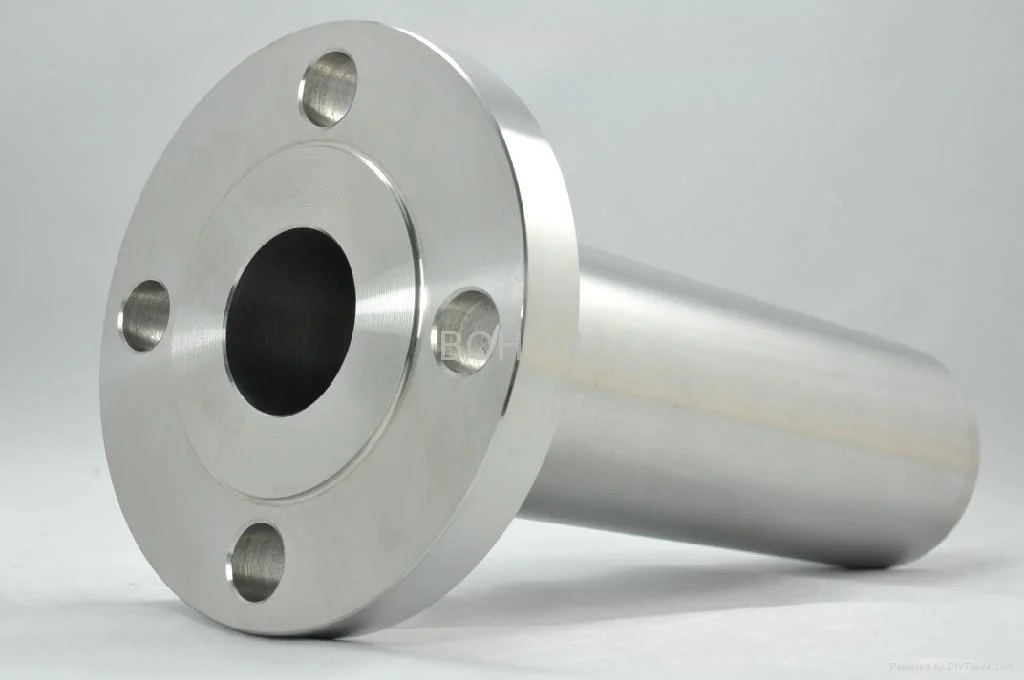
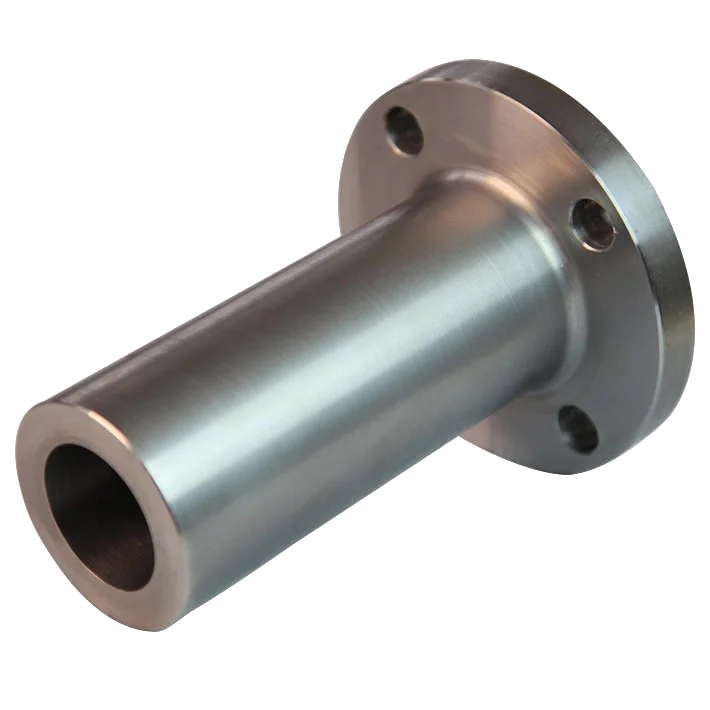
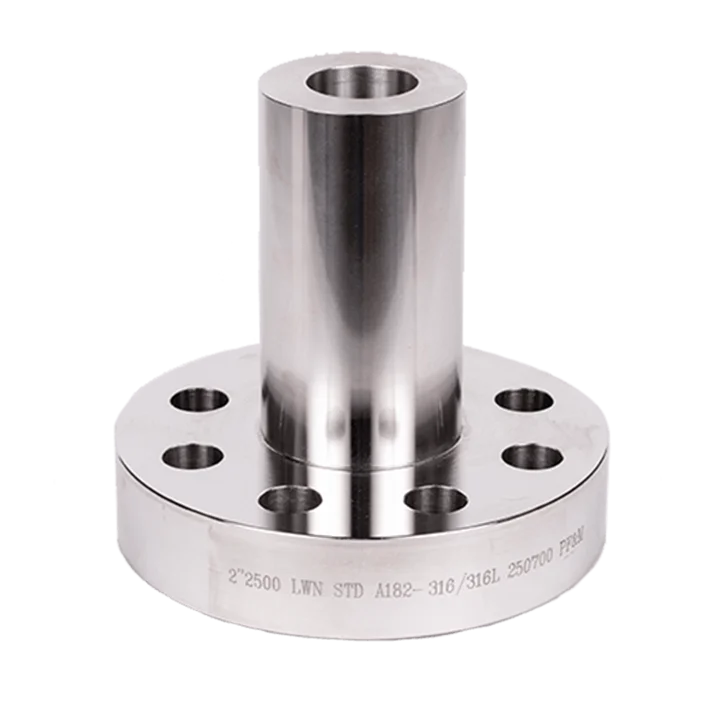
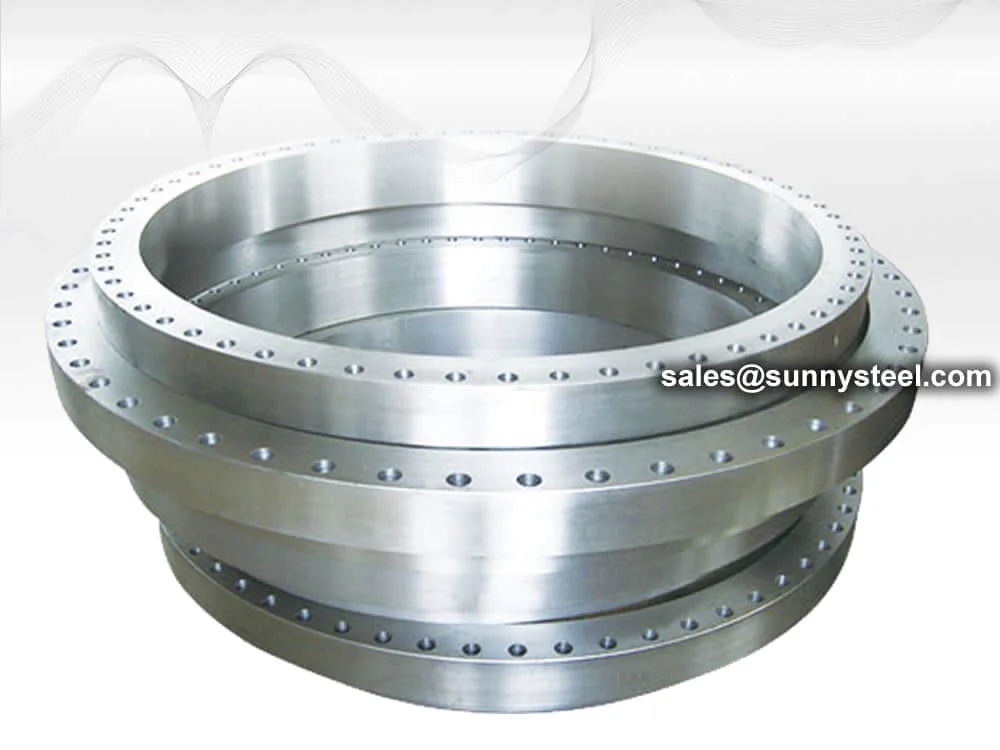
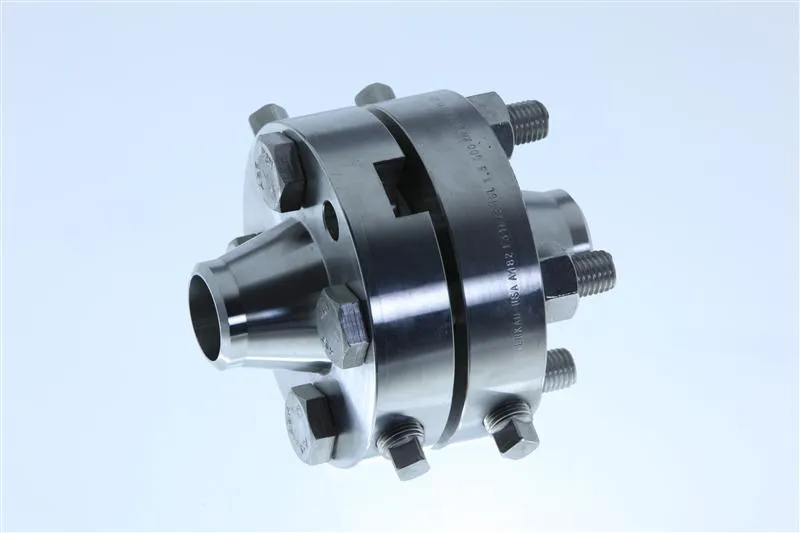
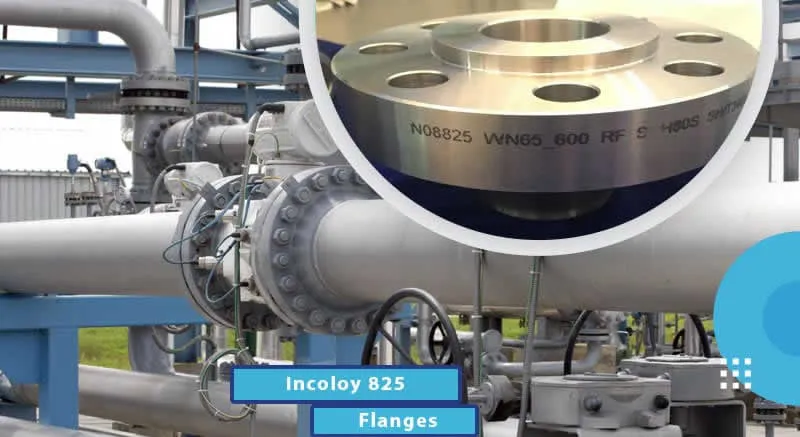
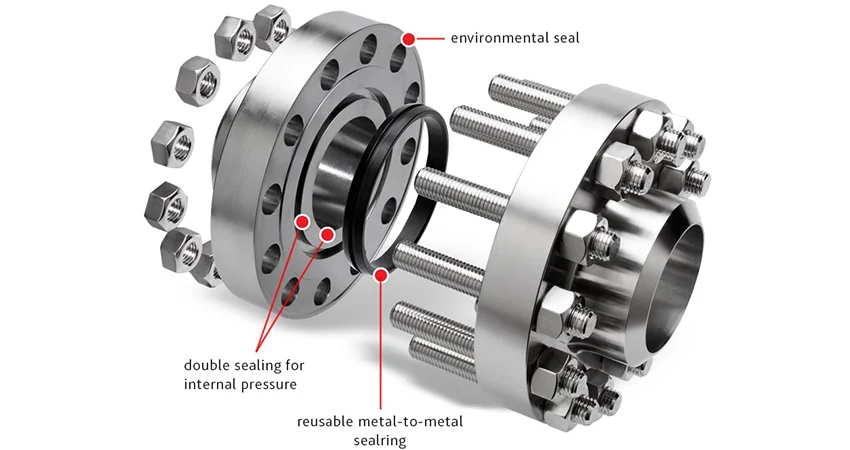
Long Weld Neck Flange is an integral self-reinforcing flange designed for
high-pressure and high-temperature applications in industrial piping systems, particularly in
pressure vessels and boiler pipeline protection. Conforming to ASME B16.5 and ASME B16.47
standards, these flanges feature an extended neck that acts as a nozzle, eliminating the need for additional pipe
sections. Made from materials like carbon steel (ASTM A105), stainless steel (ASTM A182 F304/316), or alloy steel,
they offer exceptional corrosion resistance and structural integrity, ideal for oil and gas,
petrochemical, and power generation industries.
The long weld neck flange is manufactured through forging or casting, ensuring a one-piece
construction that enhances strength and eliminates weld seams. Available in sizes from 1/2” to 24” (ASME B16.5) and
26” to 60” (ASME B16.47), with pressure ratings from Class 150 to 2500, these flanges come with raised face (RF),
flat face (FF), or ring-type joint (RTJ) configurations. The extended neck, typically 9”, 12”, or 16” long, provides
reinforcement, reducing stress concentration at the pipe connection. Surface treatments like 3LPE, galvanizing, or
passivation enhance corrosion resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments handling
corrosive fluids or gases.
These welded nozzle flanges undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, ultrasonic, and
radiographic inspections, to ensure compliance with ASME standards. With tensile strengths ranging from 485 MPa
(A105) to 515 MPa (F304), they excel in high-pressure systems up to 2500 psi and temperatures up to 870°C. The long
neck ensures smooth flow transitions, minimizing turbulence and erosion, which is critical for boiler
pipeline protection in power plants or refineries. The butt-weld connection, typically a V-weld,
provides a strong, leak-free joint, ideal for critical applications like LNG terminals or chemical processing.
Compared to standard weld neck flanges, long weld neck flanges offer superior reinforcement due to
their extended neck, making them ideal for pressure vessels and nozzles requiring precise alignment or heavy loads.
They are commonly used as alternatives to a weld neck flange and pipe combination, reducing fabrication costs and
installation time. Their versatility extends to applications like subsea pipelines, nuclear power plants, and marine
systems, where durable pipe fittings are essential for safety and longevity.
Long weld neck flanges address challenges like pipeline wear, thermal stress, and corrosion in
demanding industrial systems. Their robust design, compliance with strict standards, and material versatility make
them a preferred choice for engineers seeking reliable solutions for industrial piping. Whether
used in high-pressure oil and gas pipelines or corrosive petrochemical environments, these flanges deliver unmatched
performance, safety, and durability.
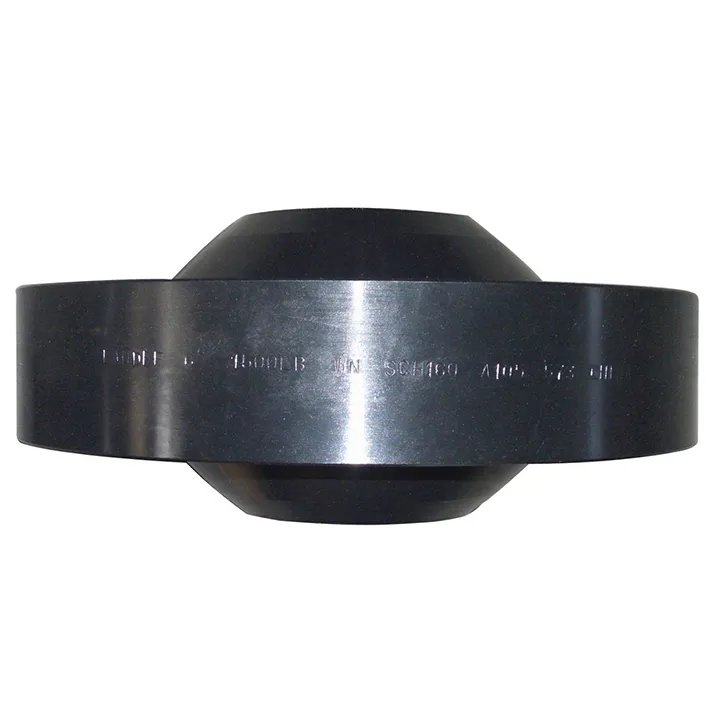
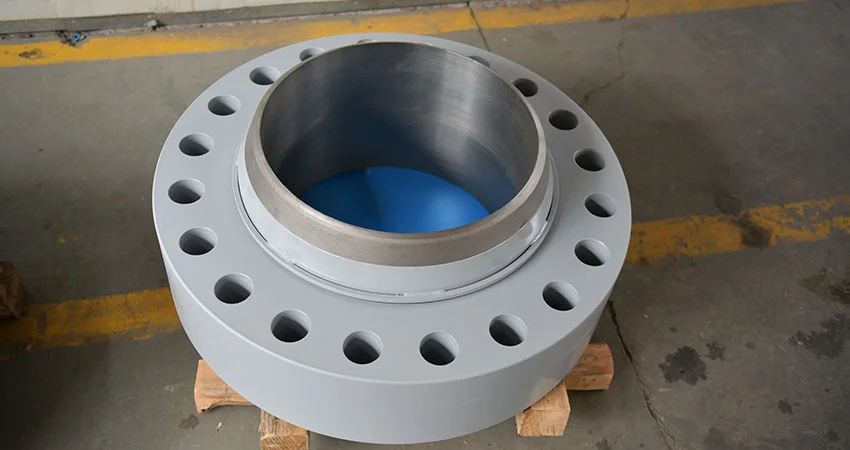
Simplified called as LWN flange, the neck part seems like a elongated pipe and connected to a flange. So in most cases it works as a nozzle for a column or a barrel.
- Design: These flanges have an extended neck, which acts as a continuation of the pipe and is longer than that of a standard weld neck flange.
- Purpose: Provide additional reinforcement and facilitate precise nozzle placement or custom equipment connections.
- Applications: Commonly used in pressure vessels, columns, heat exchangers, and high-temperature/high-pressure systems.
- Recognition: Easily identified by their extended neck length, designed for specialized applications.
You can choose for a normal thickness long welding neck flange or a heavy LWN flange that with bigger thickness and a differently shape.
Chemical Composition of Long Weld Neck Flange
| Element |
ASTM A105 (%) |
ASTM A182 F304 (%) |
| Carbon (C) |
0.35 max |
0.08 max |
| Manganese (Mn) |
0.60-1.05 |
2.00 max |
| Phosphorus (P) |
0.035 max |
0.045 max |
| Sulfur (S) |
0.040 max |
0.03 max |
| Silicon (Si) |
0.10-0.35 |
0.75 max |
| Chromium (Cr) |
0.30 max |
18.0-20.0 |
| Nickel (Ni) |
0.40 max |
8.0-11.0 |
Mechanical Properties of Long Weld Neck Flange
| Property |
ASTM A105 |
ASTM A182 F304 |
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) |
485 |
515 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) |
250 |
205 |
| Elongation, min (%) |
22 |
40 |
| Hardness, max (HBW) |
187 |
201 |
Comparison of Long Weld Neck Flange with Other Flanges
| Feature |
Long Weld Neck Flange |
Standard Weld Neck Flange |
Slip-On Flange |
| Material Type |
Carbon/Stainless Steel |
Carbon/Stainless Steel |
Carbon/Stainless Steel |
| Connection Type |
Butt Weld (Extended Neck) |
Butt Weld |
Fillet Weld |
| Corrosion Resistance |
Excellent (Material-dependent) |
Excellent (Material-dependent) |
Moderate (Coatings needed) |
| Applications |
Pressure vessels, nozzles |
High-pressure pipelines |
Low-pressure systems |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) |
485-515 (min) |
485-515 (min) |
415-485 (min) |
| Installation Complexity |
Moderate (Welding required) |
Moderate (Welding required) |
Low (Simpler welding) |
| Key Advantage |
Reinforced nozzle, no extra pipe |
Smooth stress distribution |
Cost-effective, easy install |