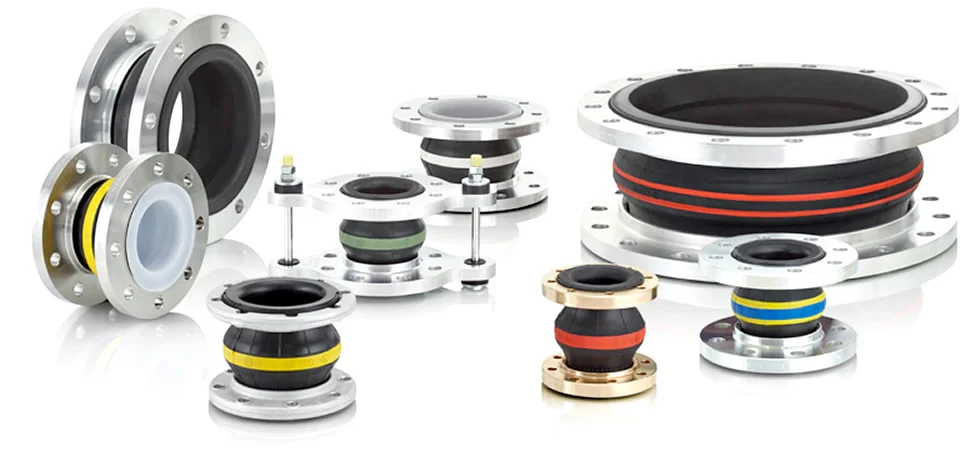
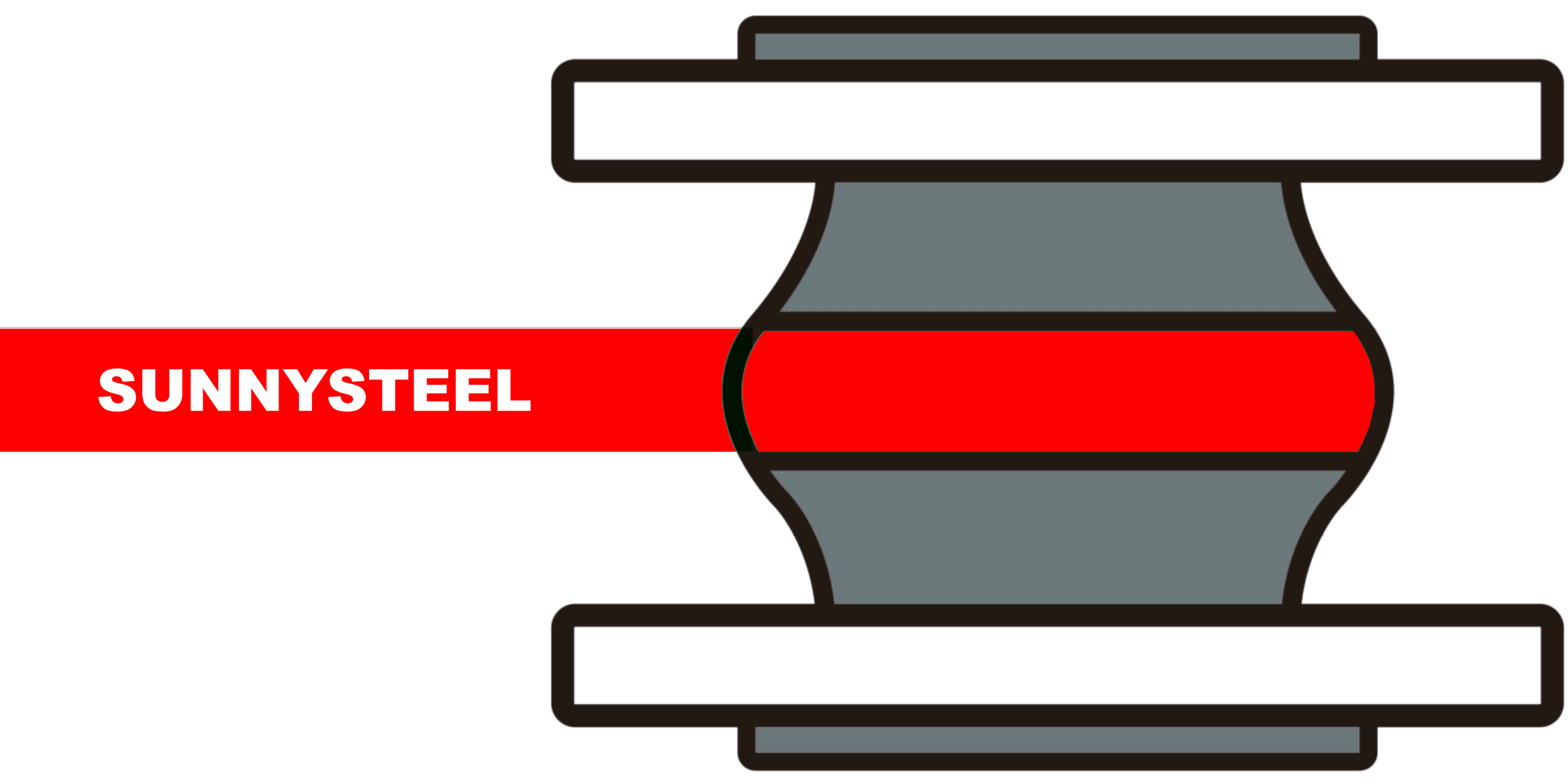
What is a Rubber Expansion Joint?
High Flexibility
Absorb axial, lateral, and angular movements in piping systems with
exceptional elasticity.
Vibration & Noise Control
Superior isolation and dampening of vibrations from pumps, compressors, and
machinery.
Chemical Resistance
Resistant to wide range of chemicals, acids, and abrasive substances.
Rubber Expansion Joint, also known as a flexible rubber joint or compensator,
is a critical component in industrial piping systems designed to absorb vibration, reduce
noise, and compensate for thermal expansion and contraction. Compliant with standards like DIN, ANSI, and
JIS, these joints are made from durable elastomers such as EPDM, NBR, Neoprene, or Viton, reinforced with
synthetic fibers or steel flanges, ensuring excellent corrosion resistance and flexibility.
They are widely used in HVAC, water treatment, power plants, chemical industries, and marine systems for
boiler pipeline protection.
The rubber expansion joint features a flexible bellows design that accommodates axial,
lateral, and angular movements, reducing stress on pipelines caused by temperature fluctuations, mechanical
vibrations, or misalignment. Available in sizes from 1” to 80” (DN25 to DN2000) with pressure ratings up to
25 bar, these joints can operate in temperatures from -20°C to 120°C, depending on the rubber compound.
Protective coatings or PTFE linings further enhance corrosion resistance, making them ideal
for handling corrosive fluids like seawater, acids, or alkalis in pipeline wear solutions.
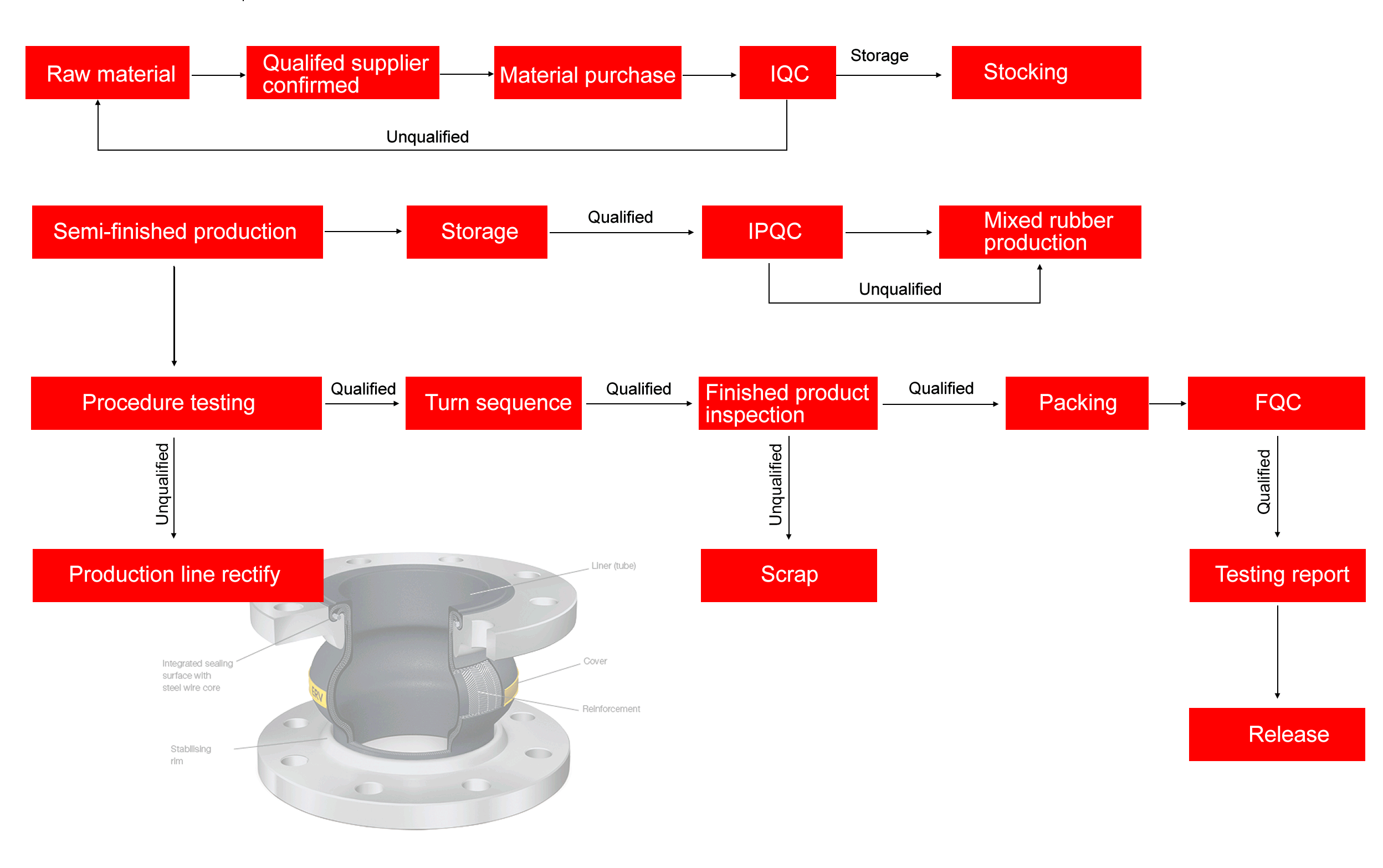
Manufactured through high-pressure molding and vulcanization, rubber expansion joints
undergo rigorous testing, including burst, pressure, and fatigue tests, to ensure compliance with industry
standards. Their high elasticity and damping properties reduce noise by up to 25 decibels and mitigate
pipeline wear, extending system lifespan. The joints support flanged, threaded, or union connections,
offering versatility for complex piping layouts in applications like pumps, chillers, and cooling towers.
Compared to metallic expansion joints, rubber expansion joints offer superior flexibility
and noise reduction but are less suited for extreme high-temperature or high-pressure applications. Their
lightweight design and ease of installation minimize labor costs, while materials like EPDM provide
excellent resistance to weathering and chemical erosion. These joints are particularly effective in systems
requiring boiler pipeline protection, where thermal cycling and vibration are common
challenges.
Rubber expansion joints address critical issues like pipeline stress, corrosion, and noise
in dynamic industrial systems. Their flexible, corrosion-resistant design makes them a reliable choice for
engineers seeking cost-effective industrial piping solutions for demanding environments,
ensuring safety and operational efficiency.
Why choose a rubber expansion joint?
Rubber expansion joints and connectors are the ideal choice for many piping situations, and they have several uses.
- Rubber expansion joints are most often used as a flexible connector between a vibrating piece of mechanical equipment and the pipeline. These rubber connectors are generally the best solution for isolating noise and vibration and to keep these unwanted dynamics from being transmitted down the pipeline to occupied areas. Single and double spheres are quite common for this application in conveying water in HVAC systems.
- They can also be used to absorb pipe movements. Spherical connectors are available in either single sphere and double sphere to absorb greater pipe motions. Spool type expansion joints can be built with multiple arches to take up greater movements.
- Rubber connectors will also provide for a reasonable amount of pipe offset caused by equipment settling.
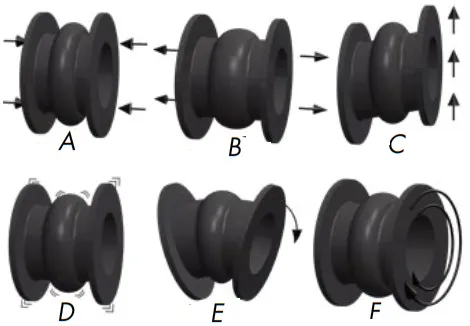
The function of a rubber expansion joint and the absorption of various movements:
A-axial compression, B-axial elongation, C-lateral or transverse movement, D-vibration, E-angular movement, F-torsional movement.
Function & Performance
As illustrated in the picture, rubber expansion joints are primarily designed to absorb and compensate for various movements and vibration in a piping systems:
- Axial Compression – The dimensional reduction or shortening of in face-to-face parallel length of the joint measured along the longitudinal axis.
- Axial Elongation – The dimensional increase or lengthening of face-to-face parallel length of the joint measured along the longitudinal axis.
- Lateral Movement – The movement of relating displacement of the two ends of the joint perpendicular to its longitudinal axis.
- Vibration – Mechanical oscillations in the piping system, usually in high frequency.
- Angular Movement – The angular displacement of the longitudinal axis of the joint from its initial straight line position, measured in angle degrees. One half of the joint has axial elongation and the other has axial compression.
- Torsional Movement – One end of the expansion joint is twisted around the longitudinal axis while the other end is held fixed.
Characteristics of rubber expansion joint
- Small size, light weight, good elasticity, easy installation and maintenance.
- Horizontal, vertical and angular displacements can be generated during installation, which is not limited by eccentric and non-parallel flanges of user pipes.
- Vibration and noise reduction function
- Strong corrosion resistance and long service life.
Advantages of rubber expansion joint
- Guaranteed quality of all the products we supplied.
- Reasonable prices.
- Ensured delivery schedule.
- Perfect service system.
Rubber expansion joints for piping systems
Rubber Expansion Joints for Piping Systems provide time-tested ways to accommodate pressure loads, relieve movement stresses, reduce noise, isolate vibration, compensate for misalignment after plants go on stream, and prolong the life of motive equipment. Rubber expansion joints are available in a variety of styles and are used to convey fluid under vacuum pressure conditions in piping systems. Flanged rubber expansion joints are most common and are available in single – and multi-arch designs. They can be custom-engineered to fit your application requirements. Our rubber expansion joints are particularly beneficial due to their flexible nature, which makes them suitable for many functions, including the absorption of sound, thermal energy and shock. They are specifically designed to reduce the need for maintenance, repair and manual assistance.
Benefits of flexible rubber expansion joints
Flexible rubber expansion joints offer several benefits in piping systems, contributing to the overall performance, reliability, and longevity of the system. Here are some key advantages:
- Economy of minimal face-to-face dimensions
- Lightweight construction requires no special handling equipment
- Insulates against the transfer of noise and vibration
- Compensates for misalignment
- No electrolysis
- Greater recovery from movement
- Ease of Installation
- Small space requirements
- Low movement forces required
- Reduced fatigue factor
- Reduced heat loss
- Corrosion and erosion resistant
- No gaskets required
Changes in temperature and pressure in piping systems connected to pumps lead to thermal expansion and contraction within the pipes. Rubber expansion joints and connectors are the ideal choice for many piping situations, and they have several uses. Rubber expansion joints are most often used as a flexible connector between a vibrating piece of mechanical equipment and the pipeline. They can also be used to absorb pipe movements. Rubber connectors will also provide for a reasonable amount of pipe offset caused by equipment settling.
Available options include PTFE-lined, eccentric reducing, concentric reducing, filled arch, lightweight and off-set configurations. They can be designed to operate up to 200 psi and withstand temperatures up to 500º F. Sizes available from 1/2″ to 144″.
Careful selection of the expansion joint design and material for a given application, as well as properly engineered installation are important factors in determining performance. These factors should be fully evaluated by each person selecting and applying expansion joints for any application.
Construction Terms for Rubber Expansion Joints
A rubber expansion joint generally consists of inner tube, cover and carcass. The inner tube shall be made of natural rubber, synthetic rubber, or blend of synthetic rubber. It is a seamless protective, leak-proof lining that extends through the bore to the outside edges of the joint. Since the inner tube is in direct contact with the flowing media, it shall be designed to cover service conditions for chemical, petroleum, sewage, gaseous and abrasive materials. The purpose of the tube is to eliminate the possibility of the materials being handled penetrating the carcass and weakening the fabric. The cover is the exterior surface of the joint that is formed from natural or synthetic rubber. The prime function of the cover is to protect the carcass from outside damage caused by atmospheric chemicals, oils, air, sunlight, vapor, etc. The carcass or body of the rubber expansion joint is the flexible and supporting member between the tube and cover. It is the structural framework of the joint and is made from multiple plies woven fabric or tire cord impregnated with synthetic rubber. Steel wires or solid metal rings are often embedded in the carcass to provide additional reinforcement to the body fabric.
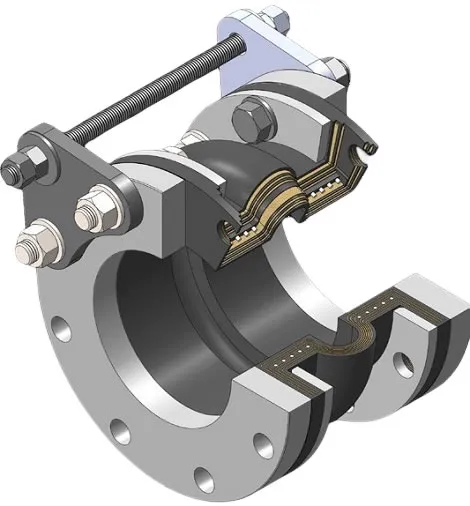
3-dimensional model of a spool arch type rubber expansion joint
Miscellaneous design patterns of rubber expansion joints are available:
(1) Integral Rubber Flanges – The end connection flanges of the joint are integrally formed as a part of the elastomeric bellows. It is also called “spool arch type rubber expansion joint”.
(2) Floating Metallic Flanges – The metal flanges shall have a groove to accept the molded bead in the body at each end of the expansion joint bellows.
(3) Spherical Type – Long radius arch, either single sphere or twin sphere, to provide better movement capability and strength.
(4) Control Units – Tie rods or control rods are provided to minimize possible damage to the expansion joint caused by excessive motion of the piping system.
(5) Custom Designs – rectangular flange connection, threaded union connection, tapered reducer type, no-arch U type, hinged type, gimbal type, sleeve type, PTFE lined type.
Carcass
The body of the expansion joint consisting of fabric and / or interior metal reinforcement.
Cover
The natural or synthetic rubber exterior of the joint which protects the carcass from damage.
Fabric Reinforcement
A synthetic or natural fabric between the tube and cover that flexibly supports the expansion joint for movement or pressure.
Metal Reinforcement
Solid rings or wire embedded in the carcass which strengthen the expansion joint to withstand high pressure or vacuum.
Tube
A protective, leak-proof lining tube that extends through the bore to the outside edges of the flanges to eliminate the possibility of the fluids penetrating the carcass and weakening the fabric.
Pipe Expansion Joint Product Types & Service Items
| Single Sphere |
Twin Sphere |
Union Spherical |
| Spool Arch |
Tie Rods |
Special Design |
| Flange Drilling |
Installation & Maintenance |
Testing & Inspection |
Flex Connector vs. Expansion Joint
A rubber expansion joint can be used as a flex connector, to absorb noise and vibration from adjacent equipment. In this application, there are usually not anchors in the piping systems and the rubber expansion joint should employ control units to keep the product from expanding under pressure. Control unit nuts should be snug (using 1/4″ thick rubber washers. Alternately, these connectors can be used as a piping expansion joint to absorb thermal pipe growth or temporary pipe movements. Like metal bellows expansion joint systems, in these cases, this rubber product becomes part of the expansion joint system which includes main anchors and pipe alignment guides. Rubber expansion joints can also be used as both flex connectors and expansion joints in the same system. When using rubber connectors as an expansion joint in the piping system, they may or may not be located next to vibrating equipment. Control units can be used as a back-up safety device in the case of an main anchor failure, but nuts and washers should be loosened to allow for the full extension or contraction of the expansion joint.

(Above) Rubber connector used as an expansion joint to take up thermal growth and other pipe movements. There are anchors located on either side of the expansion joint, the joint is located as close to an anchor as possible, and pipe alignment guides are spaced out on the piping to prevent pipe bucking under column loads.
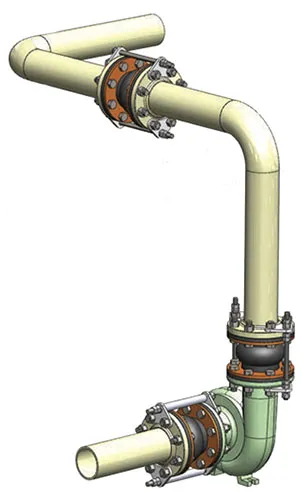
(Above) Rubber connectors used as flex connectors for noise and vibration. There are no piping anchors present and control units are installed on the rubber connectors.