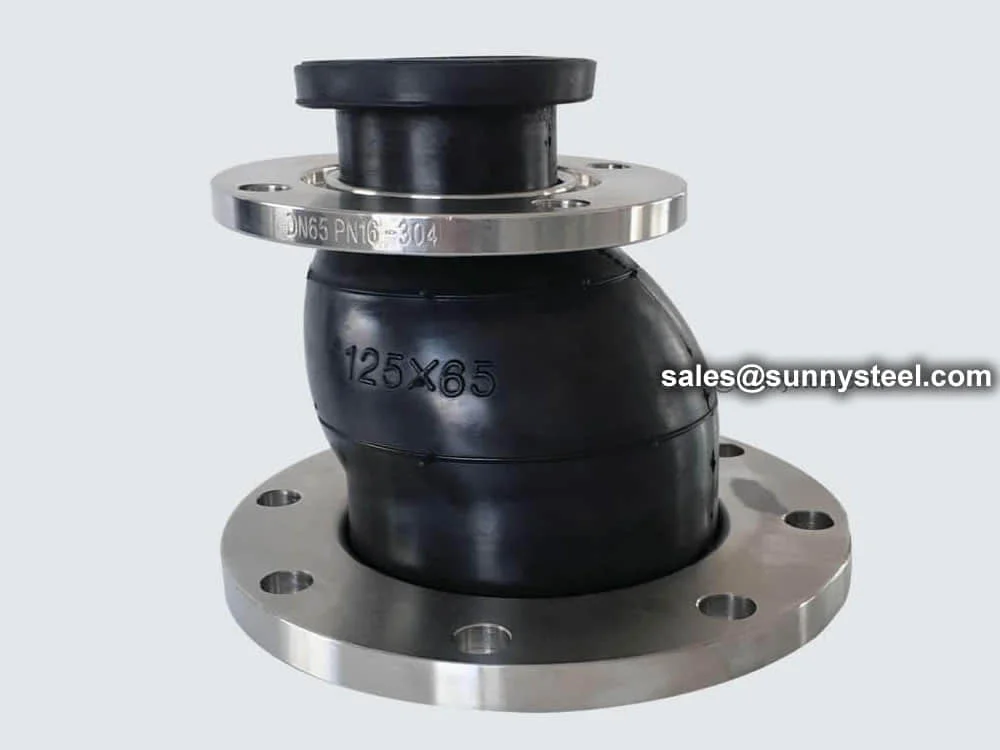

Flexible Connector For Misaligned And Different-diameter Pipes
Eccentric reducer rubber joints connect misaligned pipes of different diameters, absorbing vibration, reducing noise, and offering corrosion resistance for industrial piping.
Flexible Connector For Misaligned And Different-diameter Pipes
Eccentric reducer rubber joints connect misaligned pipes of different diameters, absorbing vibration, reducing noise, and offering corrosion resistance for industrial piping.
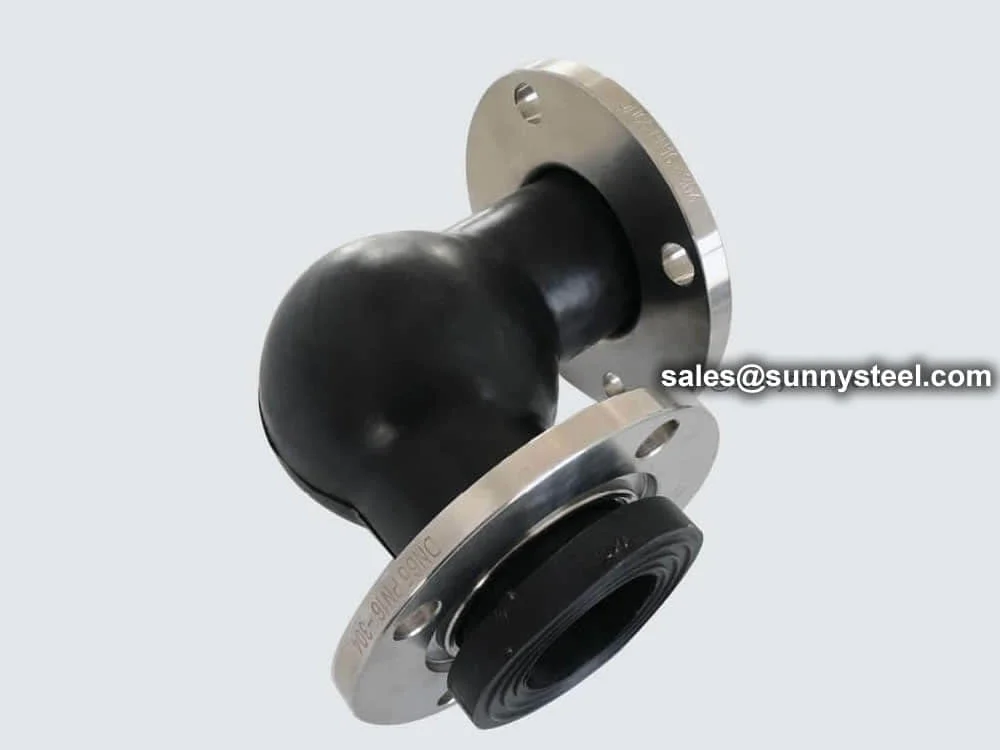
Eccentric Reducer Rubber Joint, also known as an eccentric rubber expansion joint or flexible reducer, is designed to connect pipes of different diameters with offset centerlines, providing pipeline vibration control and corrosion resistance. Constructed from elastomers like EPDM, NBR, or Neoprene, reinforced with nylon cord or steel wire, and fitted with flanged ends (carbon steel, SS304/SS316, or ductile iron), these joints are ideal for industrial piping systems in HVAC, water treatment, chemical processing, and boiler pipeline protection. Their eccentric design accommodates misalignment and ensures smooth flow transitions.
The eccentric reducer rubber joint absorbs axial, lateral, and angular movements, mitigating pipeline stress from thermal expansion, mechanical vibrations, or foundation settlement. Available in sizes from 2” to 24” (DN50 to DN600) with pressure ratings up to 1.6 MPa and temperature ranges from -20°C to 120°C (depending on the elastomer), these joints handle media like water, air, oils, and mild chemicals. Their high-elasticity rubber construction reduces noise by 15-25 decibels and minimizes wear, extending the lifespan of flexible piping solutions. The eccentric configuration, with one side flat, facilitates gas or liquid exhaust, making it suitable for pump inlets or regulating valve installations.
Manufactured through high-pressure vulcanization, eccentric reducer rubber joints undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, vacuum, and fatigue tests, to comply with standards like DIN, ANSI, and JIS. The inner rubber layer resists abrasion and corrosion, while the outer layer protects against environmental damage, ensuring corrosion resistance. These joints are often used with control rods to prevent overextension, particularly in unanchored systems. Materials like NBR provide oil resistance, while EPDM excels in chemical and weathering resistance, making them versatile for boiler pipeline protection and other applications.
Compared to concentric reducer joints, eccentric reducer rubber joints are designed for pipelines with offset centerlines, such as those near walls or floors, saving space and reducing flow resistance. Their non-metallic body prevents electrolysis, enhancing durability in corrosive environments. While less suited for high-pressure or large-movement applications, they excel in systems requiring precise alignment and pipeline vibration control. Their lightweight design and flanged connections simplify installation, reducing costs for flexible piping solutions.
Eccentric reducer rubber joints address challenges like misalignment, vibration, noise, and thermal stress in piping systems. Their corrosion-resistant, flexible design makes them a reliable choice for engineers seeking efficient, durable solutions for industrial piping in HVAC, chemical, and water treatment applications, ensuring operational safety and longevity.
| Material | EPDM | NBR | Neoprene |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range (°C) | -20 to 120 | -20 to 100 | -30 to 110 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 10-20 | 10-15 | 8-17 |
| Elongation at Break (%) | 300-600 | 300-500 | 200-500 |
| Hardness (Shore A) | 60-80 | 60-75 | 50-70 |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acids, alkalis) | Good (oils, fuels) | Moderate (oils, weathering) |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Pressure Rating (bar) | Up to 16 |
| Axial Movement (mm) | ±10 to ±20 |
| Lateral Movement (mm) | ±5 to ±15 |
| Angular Deflection (°) | Up to 10 |
| Noise Reduction (dB) | 15-25 |
Proper installation of a flexible rubber soft joint ensures safety, reliability, and a longer service life for both the pump and the piping system. Follow these guidelines to achieve correct installation:
When installed at pump inlets or outlets, especially under frequent start/stop conditions, use a flange-type stop device on both sides. This prevents excessive stretching or compression of the rubber joint and protects the pump and pipeline.
For large-diameter joints, prepare a short pipe section on one end of the flange. First connect the joint with the short pipe and the other end of the pipeline, then weld the short pipe with the longer pipe section to ease installation and reduce labor intensity.
To avoid misalignment caused by welding deformation, temporarily weld round steel or strong metal supports between both flanges. This keeps the connection rigid during welding. Remove the supports afterwards so the joint stays in a natural, unstressed state.
During temporary welding, always cover the rubber joint with a protective shield to prevent sparks and heat from burning the rubber surface. This ensures welding safety and preserves the integrity of the joint.

Absorb greater movements compared to similar length metal expansion joints, managing lateral, torsional and angular movements effectively.
Dampen disturbances and provide resistance against shock stress from hydraulic surge and water hammer.
Dampen sound transmission with rubber to steel interface, reducing unwanted noise from system imbalances.
Lightweight and easy to handle, simplifying connections and reducing installation time and labor costs.
Significantly extend service life of piping systems and connected equipment, reducing maintenance frequency.
Effectively compensate for minor misalignments during installation or due to structural settling over time.








| Material | Temperature Range | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPDM Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer |
-40°C to +120°C | Water, steam, ozone, weathering resistance | HVAC, water, wastewater systems |
| Nitrile (Buna-N) Acrylonitrile Butadiene |
-30°C to +100°C | Oil, fuel, chemical resistance | Petroleum-based applications |
| Hypalon Chlorosulfonated Polyethylene |
-40°C to +135°C | Ozone, weathering, oxidizing chemicals | Chemical processing, marine |
| Viton (FKM) Fluorocarbon |
-20°C to +200°C | High temperature, aggressive chemicals | Chemical, oil & gas, aerospace |
| Natural Rubber Polyisoprene |
-50°C to +80°C | Elasticity, abrasion resistance | General purpose, low chemical exposure |
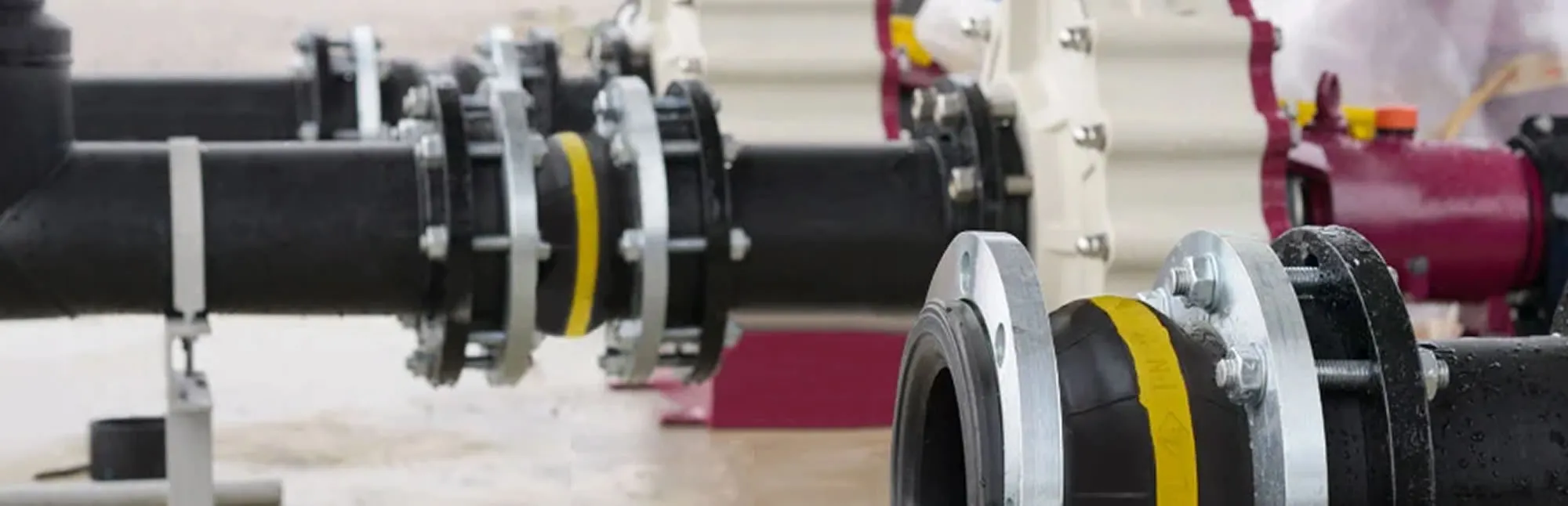
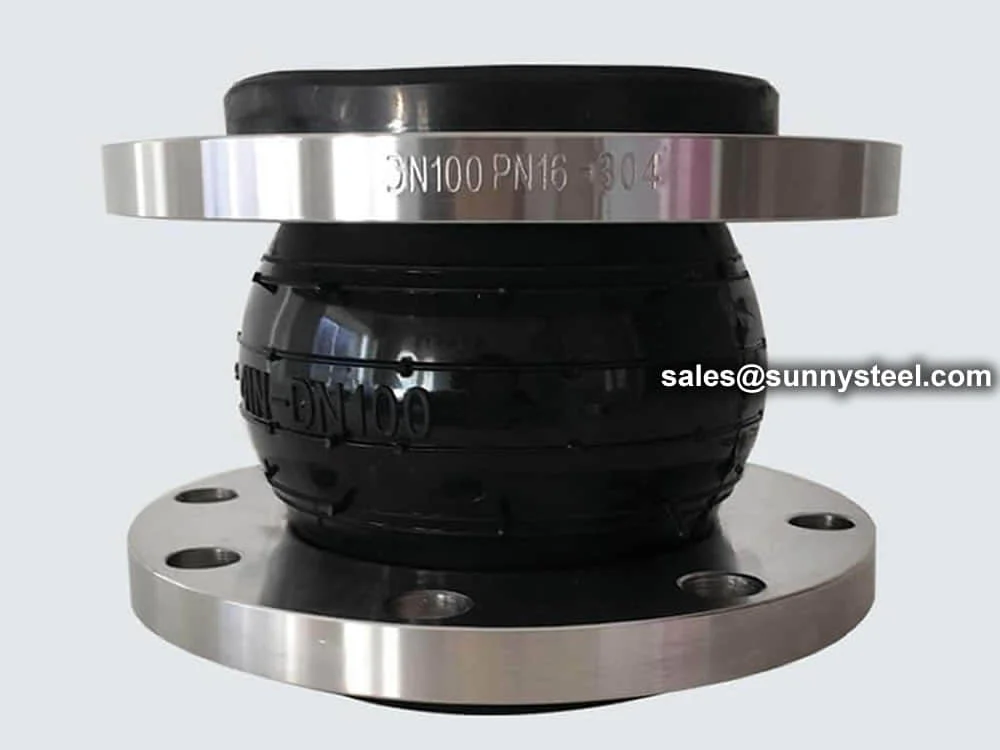
Eccentric Reducer Rubber Joint are essential in industries requiring flexible, corrosion-resistant solutions for thermal expansion and vibration control in piping systems.
Transfers heat between fluids, allowing return flow at 180° in a compact space.
Used in heat exchangers, chemical & petrochemical, food processing, and refrigeration industries.
Seamless stainless U-tubes are essential in nuclear and petrochemical machine building.
Applied in heat exchangers at Oil & Gas, petrochemical plants, refineries, and power plants.
Handles aggressive fluids like sodium hydroxide + sodium hypochlorite safely.
Allows pipeline expansion without buckling; flexible or sliding options available.
Enhances heat transfer when the outside coefficient is lower than the inside, improving efficiency.
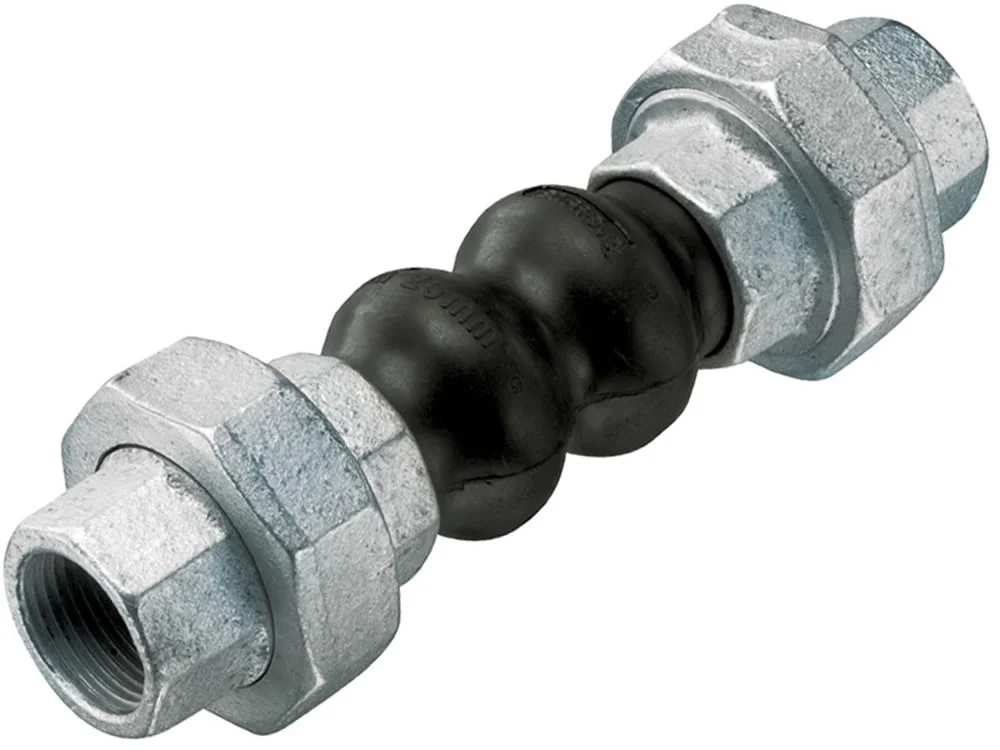

Threaded rubber expansion joints absorb vibration,...

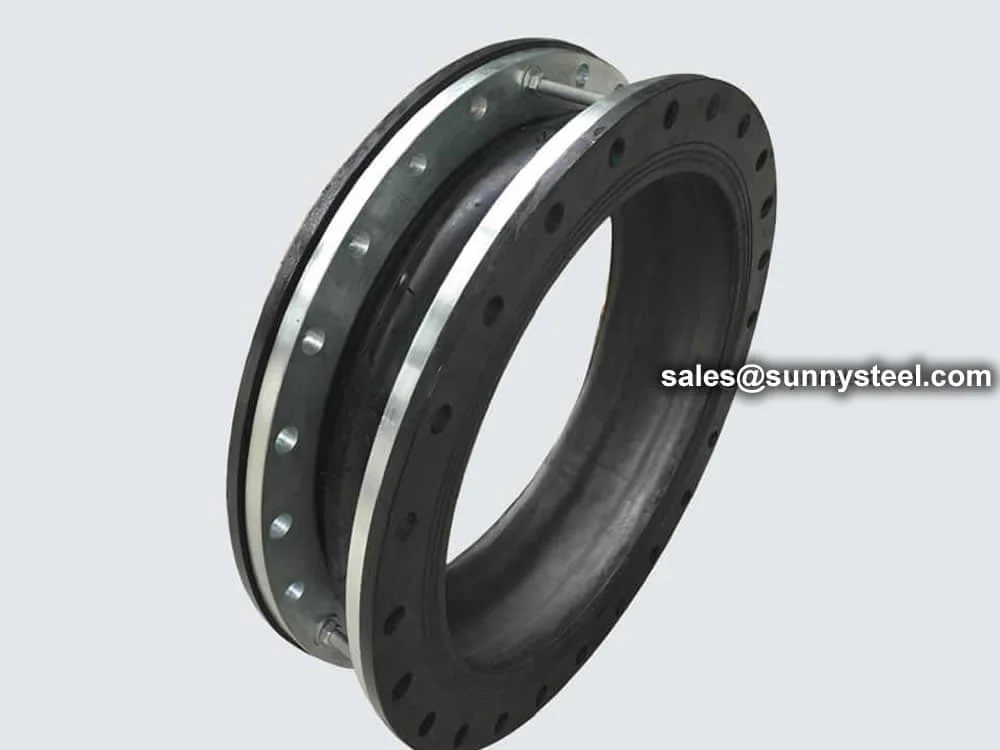
Flexible rubber joints absorb vibration, reduce no...

Food grade rubber expansion joints ensure hygienic...

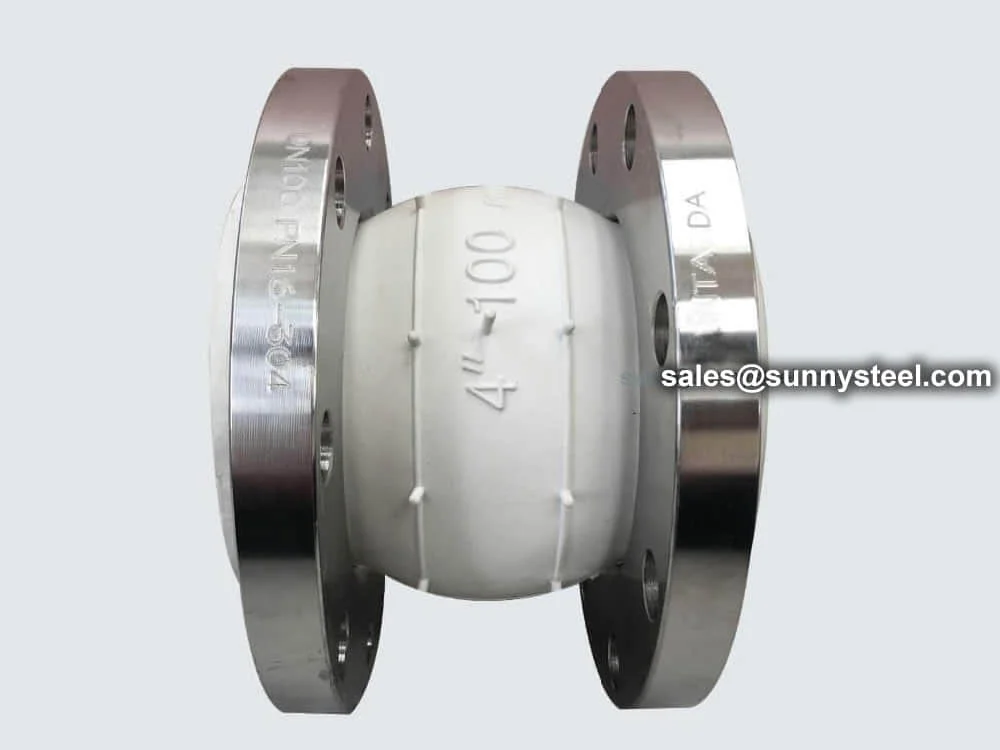
Limited flexible rubber joints absorb vibration, r...

Flexible rubber elbow joints redirect flow in pipi...

Ein gummi-kompensator ist ein flexibles verbindung...