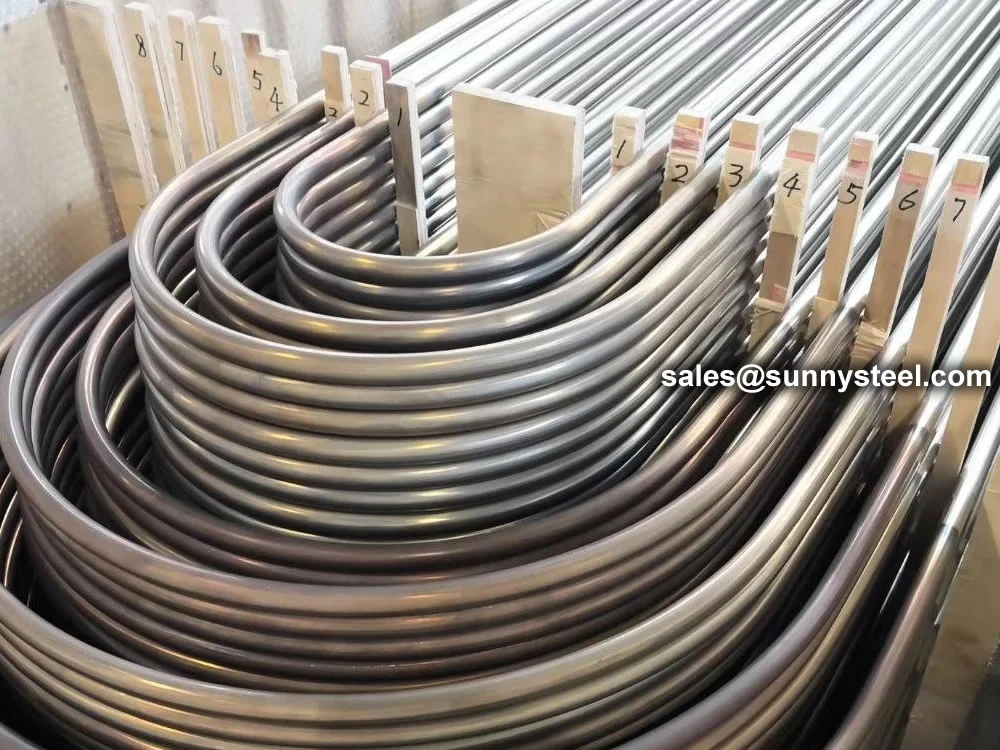
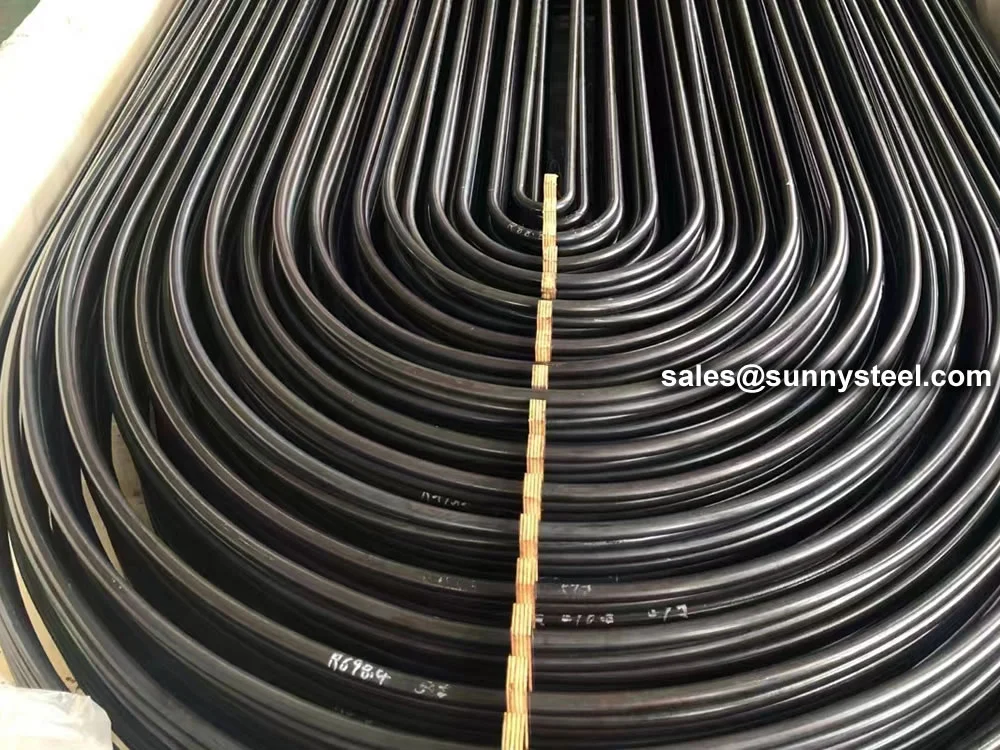
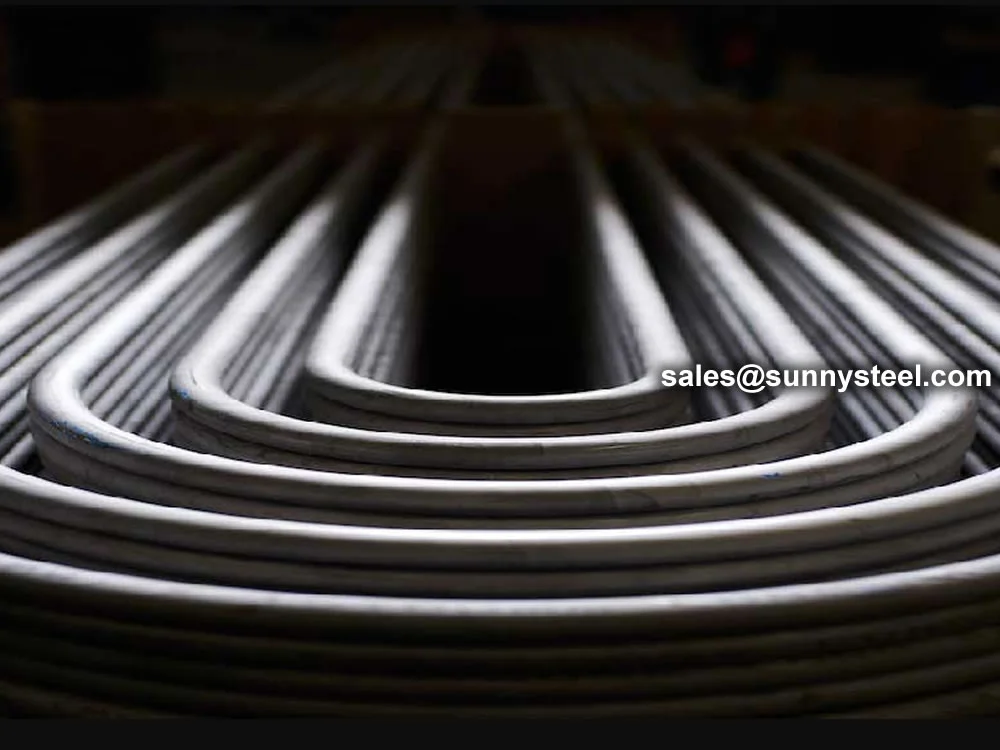
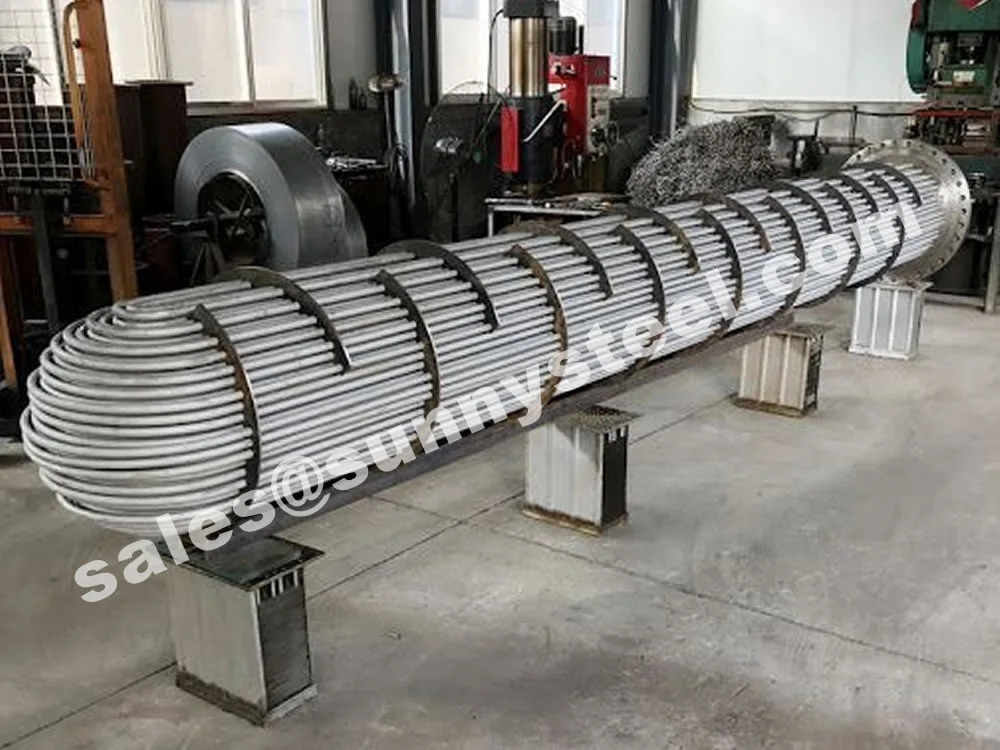
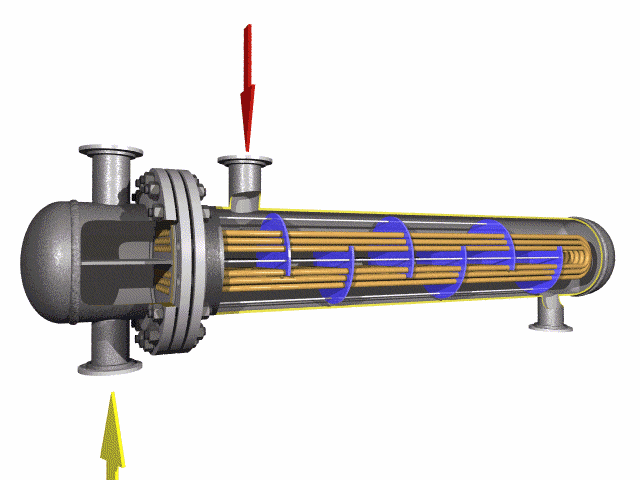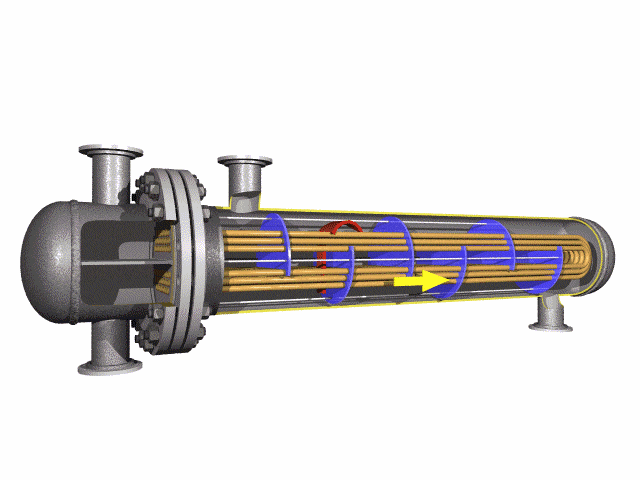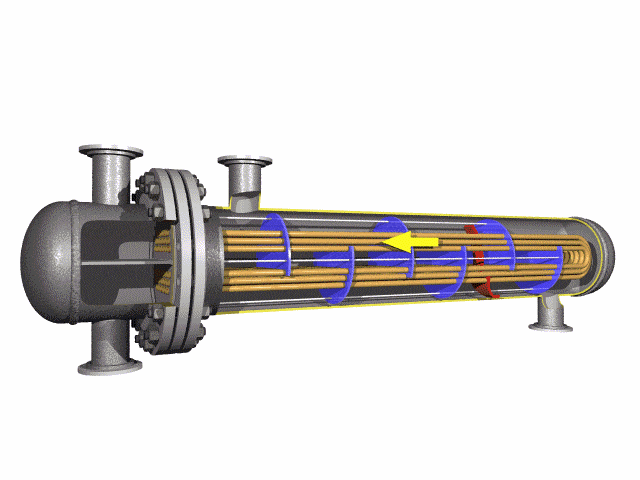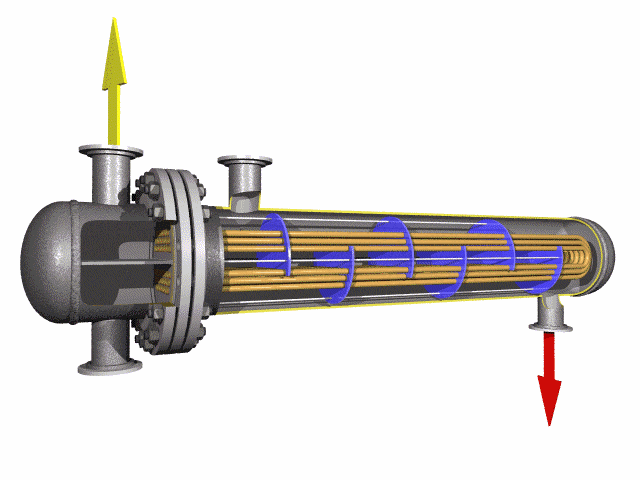
Stainless U-Bend Tubes are seamless or welded stainless steel tubes bent into a U-shape, designed to redirect fluid flow in heat exchanger tubes and ensure efficient thermal expansion absorber performance. Widely used in industries such as petrochemical, power generation, food processing, and pharmaceuticals, these tubes are critical for applications requiring corrosion resistance and high-temperature durability. Conforming to standards like ASTM A213, A269, A688, and ASME SA213, they are engineered for seamless integration into boilers, condensers, and superheaters.
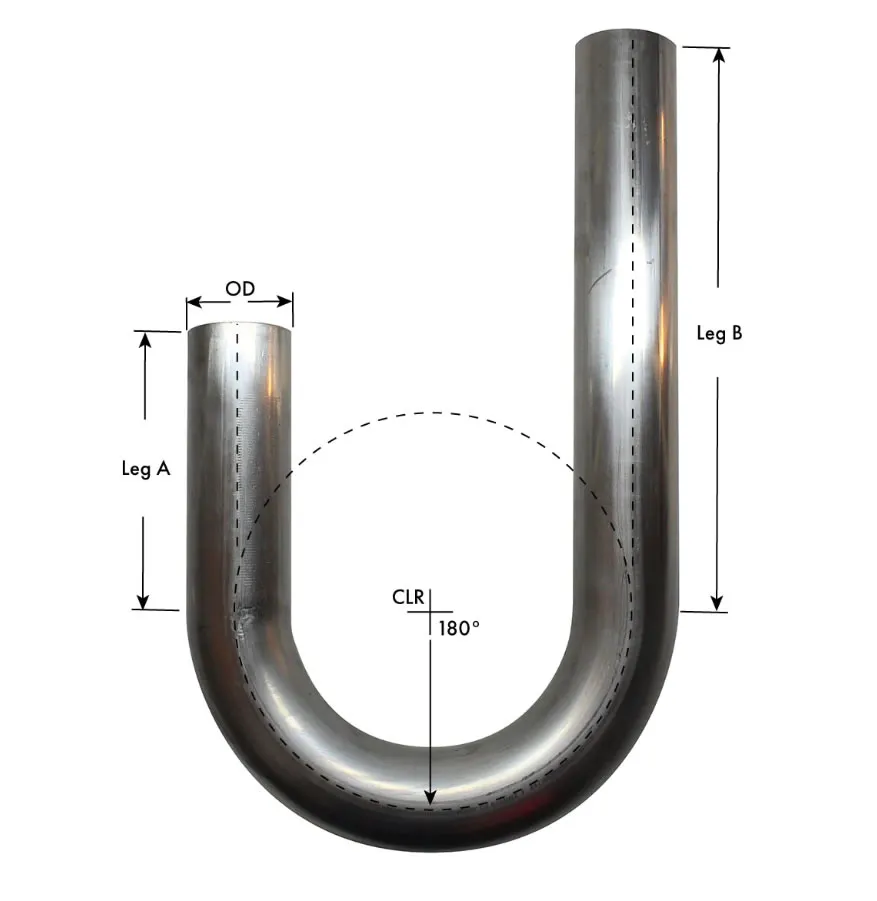
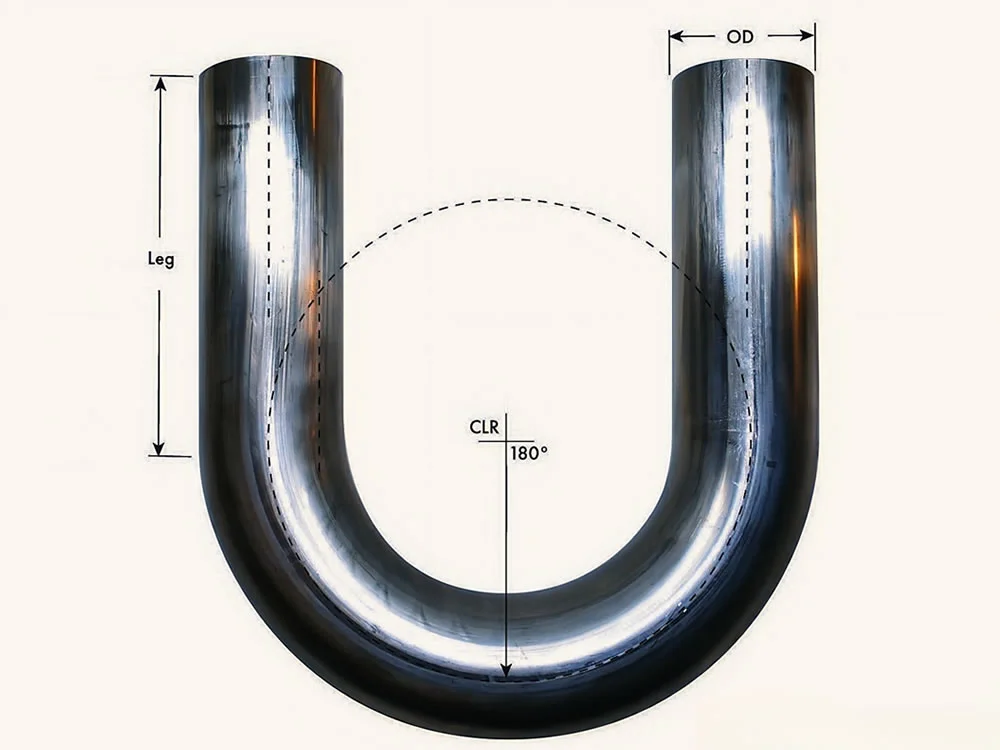
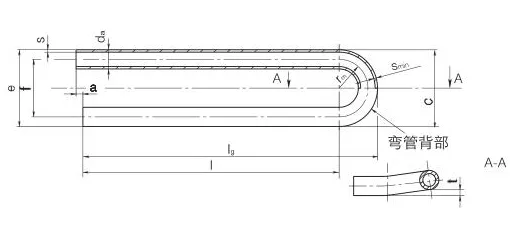
Manufactured through cold-drawing or hot-rolling processes, Stainless U-Bend Tubes are typically made from grades like 304, 304L, 316, 316L, or 321 stainless steel, offering excellent resistance to pitting, crevice corrosion, and oxidation. The U-shape design allows for compact layouts, reducing the need for additional fittings and minimizing thermal stress in pipeline durability. Available in outer diameters from 9.53mm to 50.8mm and wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to 3.0mm, these tubes can be customized for leg lengths up to 12 meters and bend radii of 1.5D to 10D, meeting diverse project requirements.
The U-Shaped Tubing undergoes solution annealing post-bending to relieve residual stresses and enhance corrosion resistance, followed by rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, pneumatic, and dye penetrant tests, to ensure compliance with ASTM A688/A688M or TEMA standards. The tubes are mandrel-bent to maintain a uniform cross-section, preventing wrinkles or ovality, which ensures optimal flow and heat transfer efficiency. Surface treatments like pickling, passivation, or polishing further enhance durability, while capped ends prevent contamination during transport and installation.
Compared to straight tubes, Stainless U-Bend Tubes offer superior thermal compensation, allowing free expansion and contraction without the need for expansion joints, which reduces costs. Their high chromium (18-20%) and nickel (8-12%) content in grades like 304/316L ensures resistance to corrosive fluids, making them ideal for harsh environments like refineries or chemical plants. The tubes are also suitable for hygienic applications, such as food and beverage processing, due to their smooth, crevice-free surfaces that meet AS 1528.1 standards for cleanliness.
The Stainless U-Bend Tubes address challenges like pipeline wear, corrosion, and thermal stress in demanding systems. Their versatility, combined with easy maintenance and long service life, makes them a preferred choice for engineers seeking reliable heat exchanger tubes for critical applications in extreme conditions. Whether used in nuclear power plants or pharmaceutical processing, these tubes deliver unmatched performance and safety.
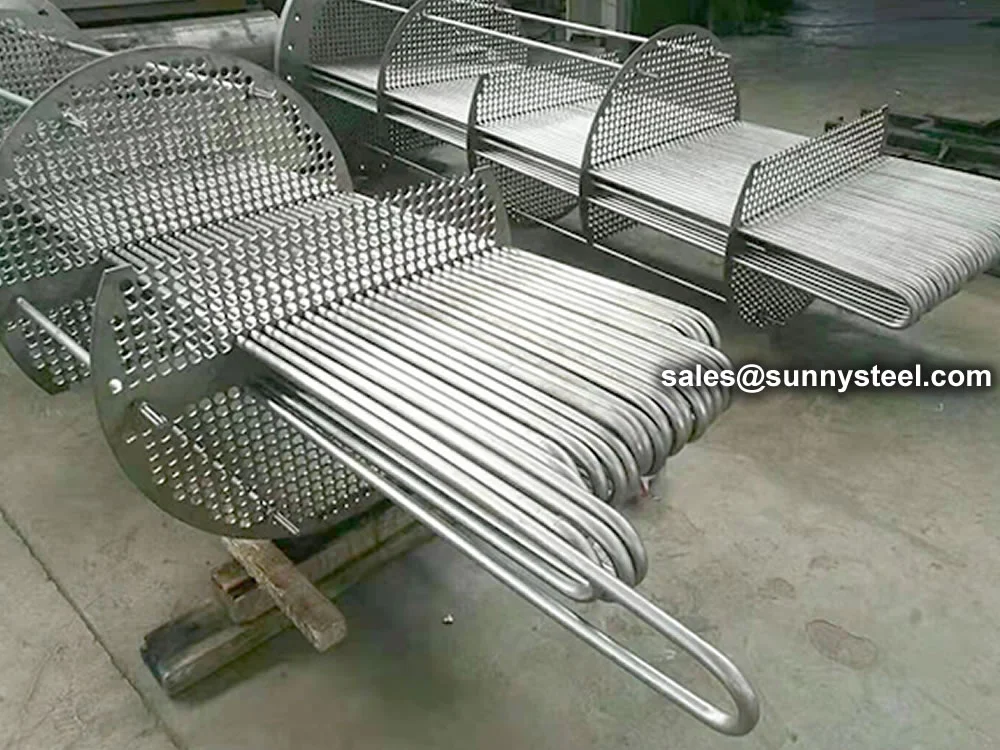
Heat exchanger equipment on the basis of stainless steel U-tube is essential in strategically important and critical fields nuclear and petrochemical machine building.
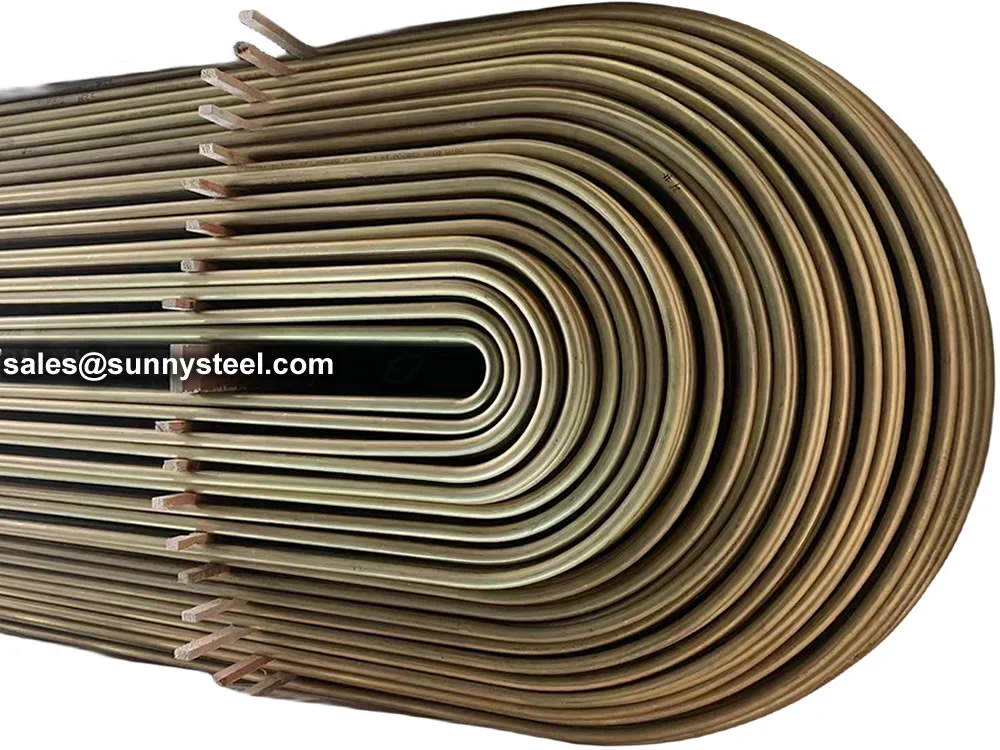
Surface condition Finished U Bend Tube shall be free of scale, without scratches after bending
Heat exchanger tubes can also be delivered as U-bent tube / U bend pipe, manufactured according to the common heat exchanger standards. Our basic specification for u bend pipes is ASTM A213/A213M, ASTM A 312/312M, EN 10216-5, and we can also follow various specifications on customers' requests.
Stainless U bends in the tube help to change the direction of the flow of the medium being transported, which helps to reduce the need for additional piping that would otherwise be required to accomplish the same effect. These tubes are often used in industries where cleanliness and hygiene are critical, such as food and beverage processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processes, because stainless steel is non-corrosive and resistant to high temperatures and pressure.