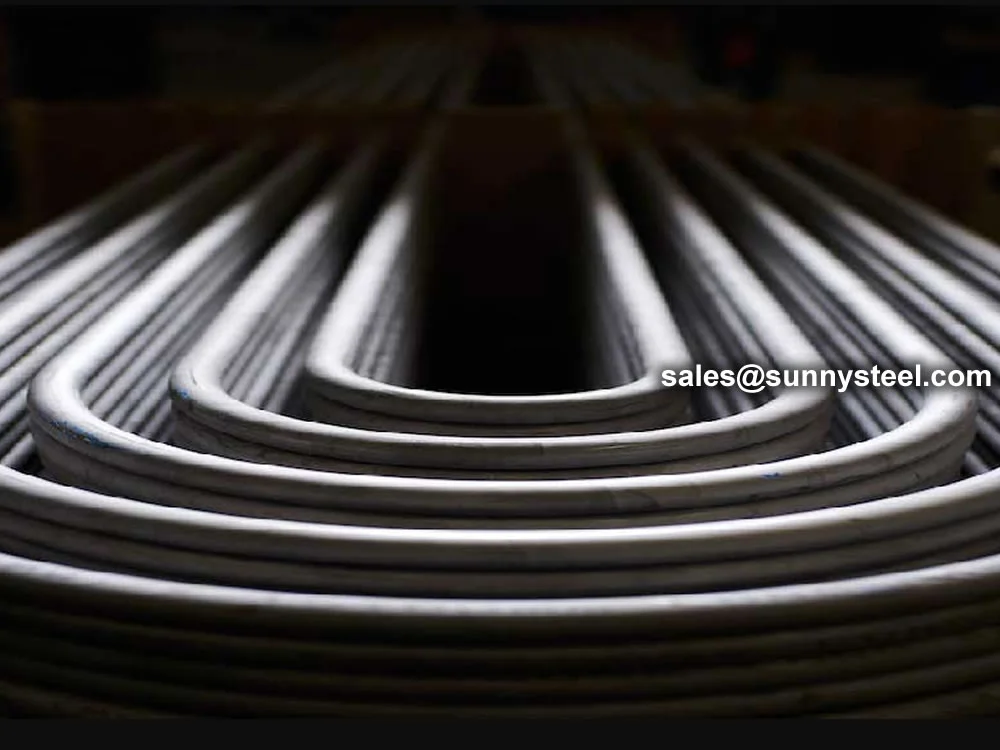
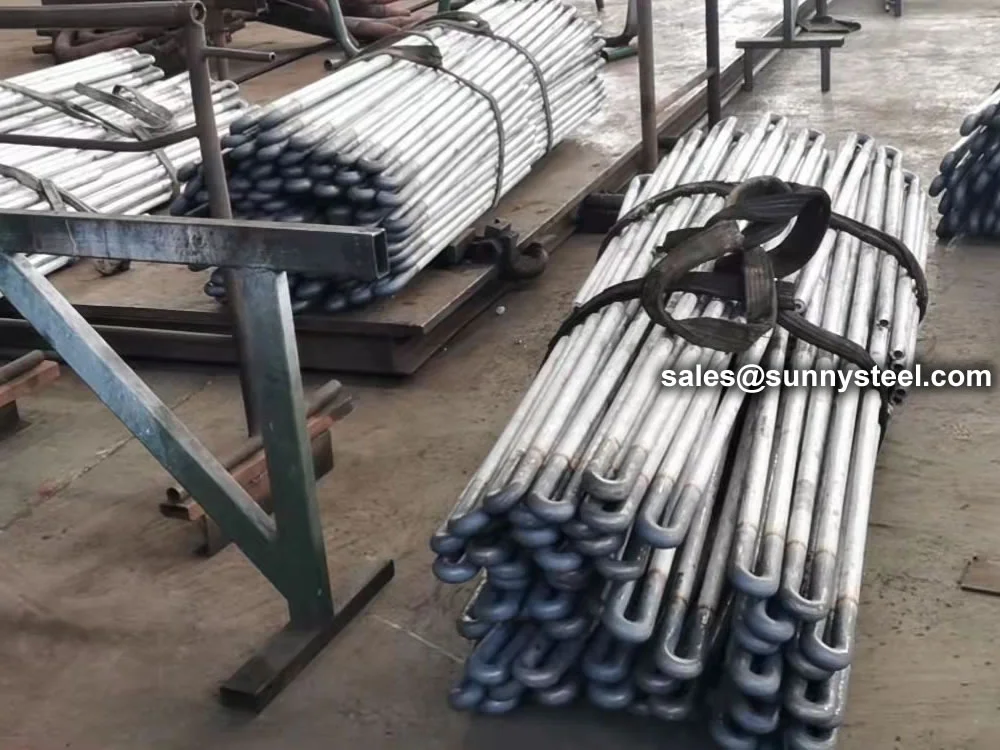
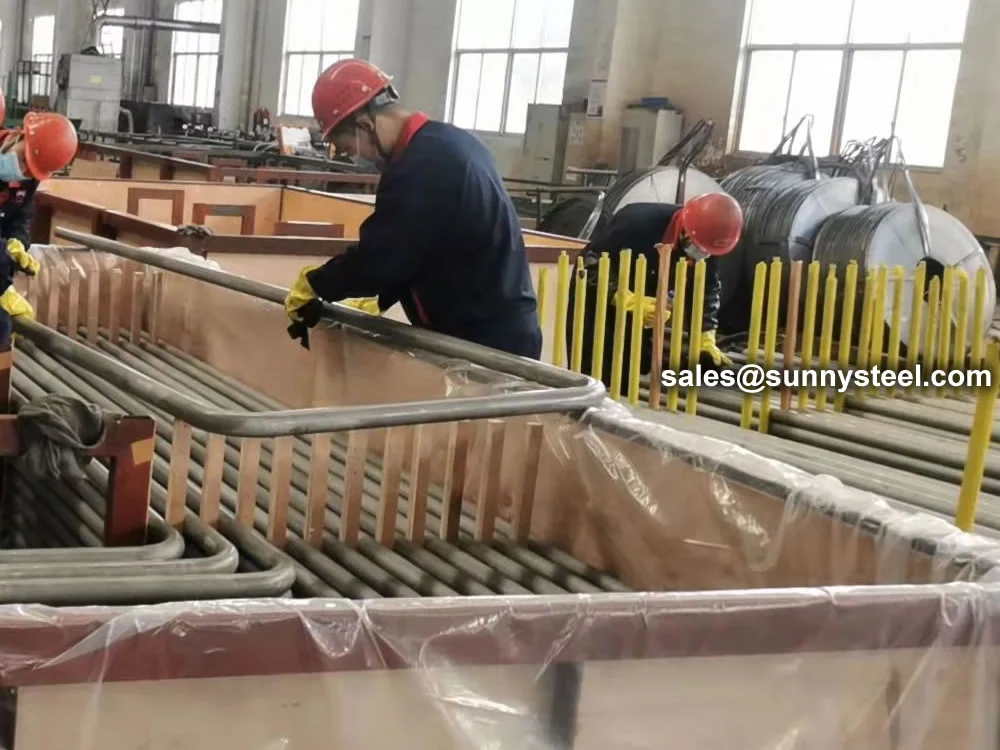
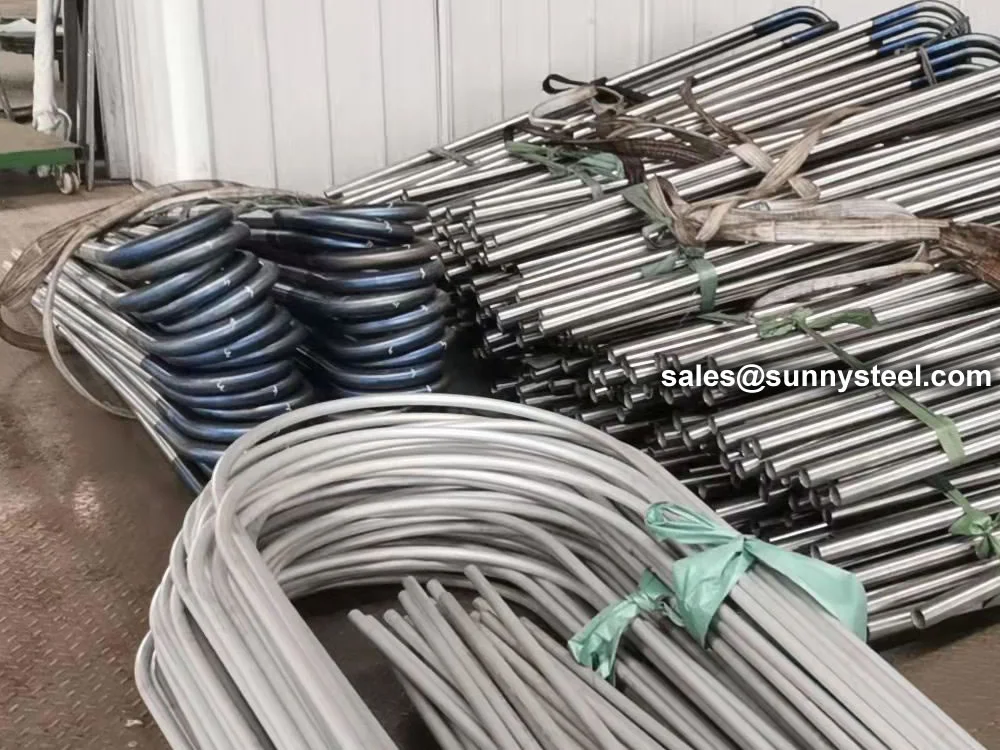
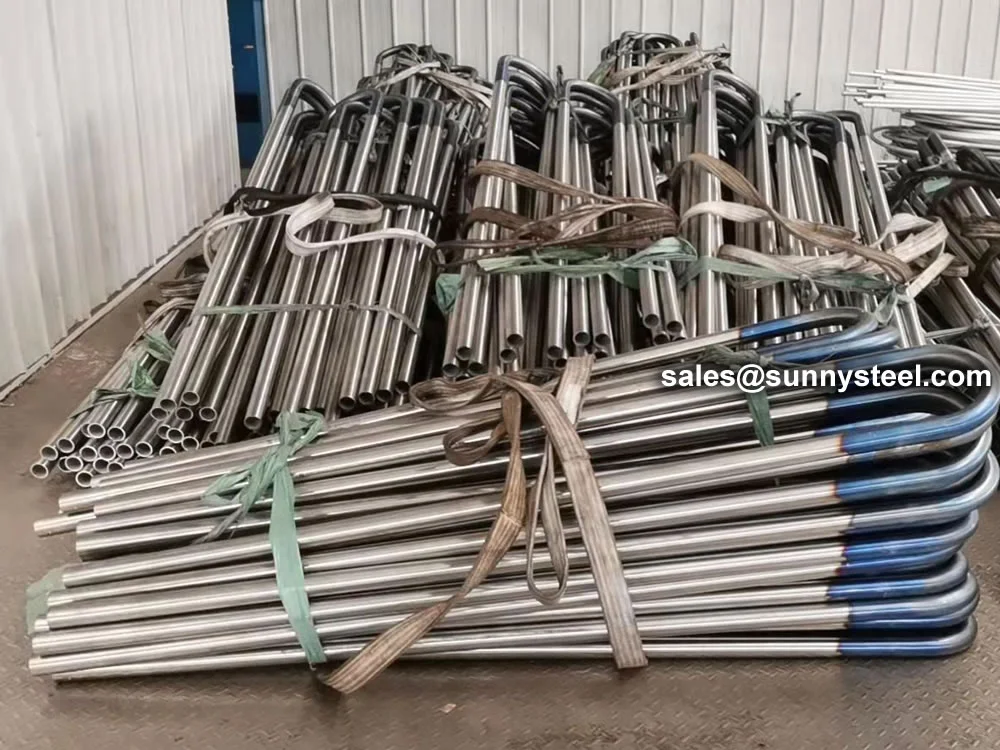
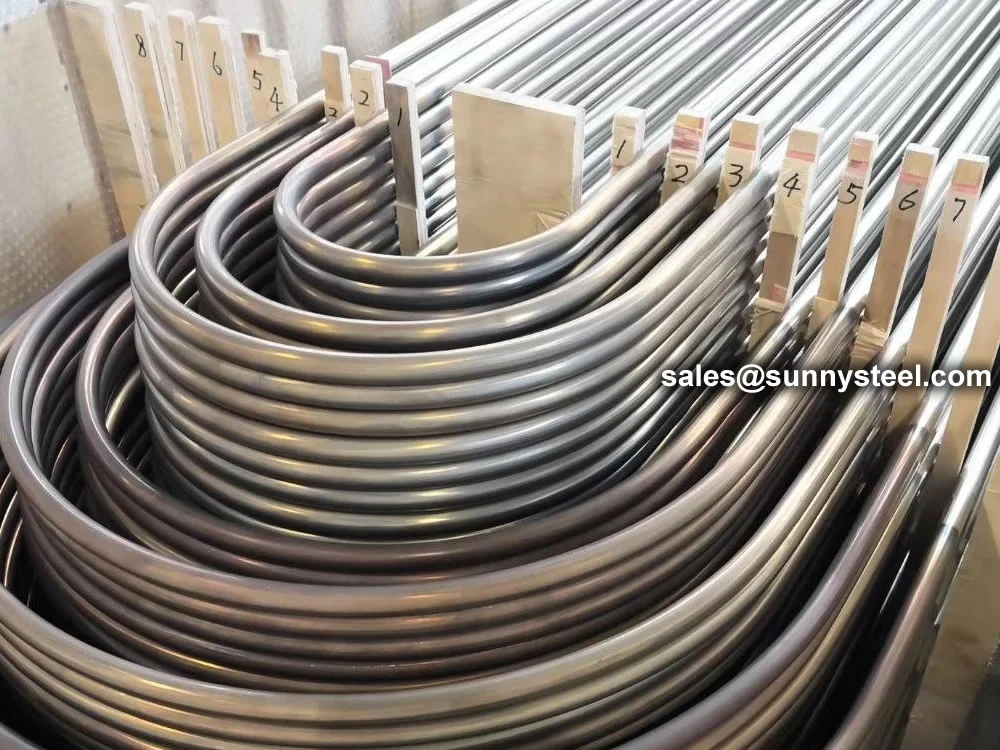
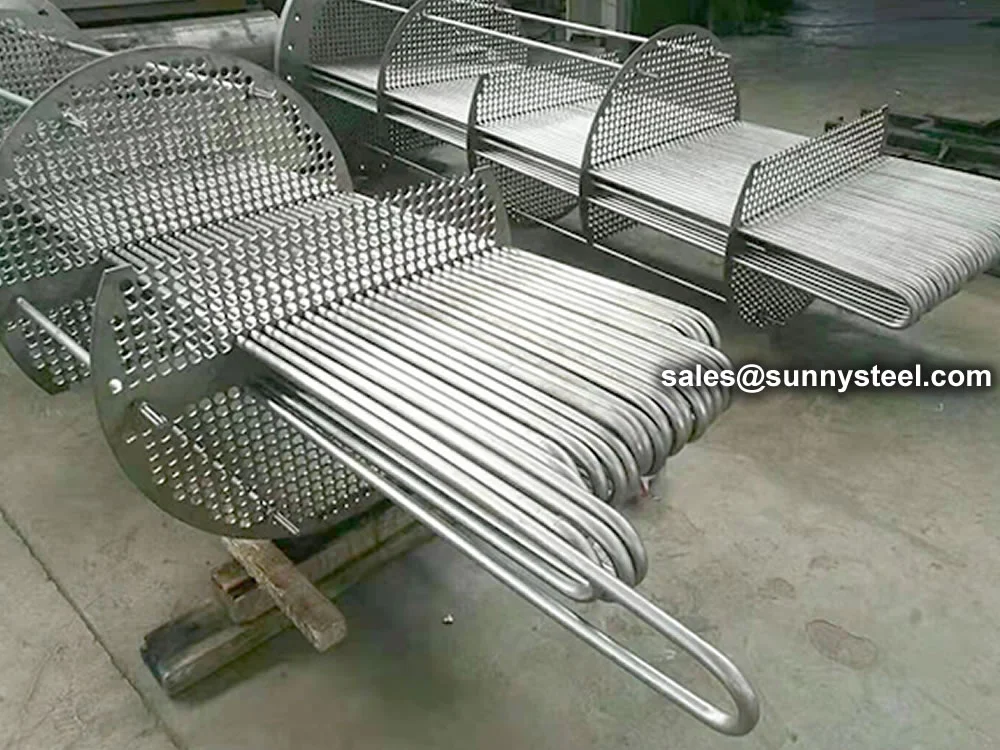
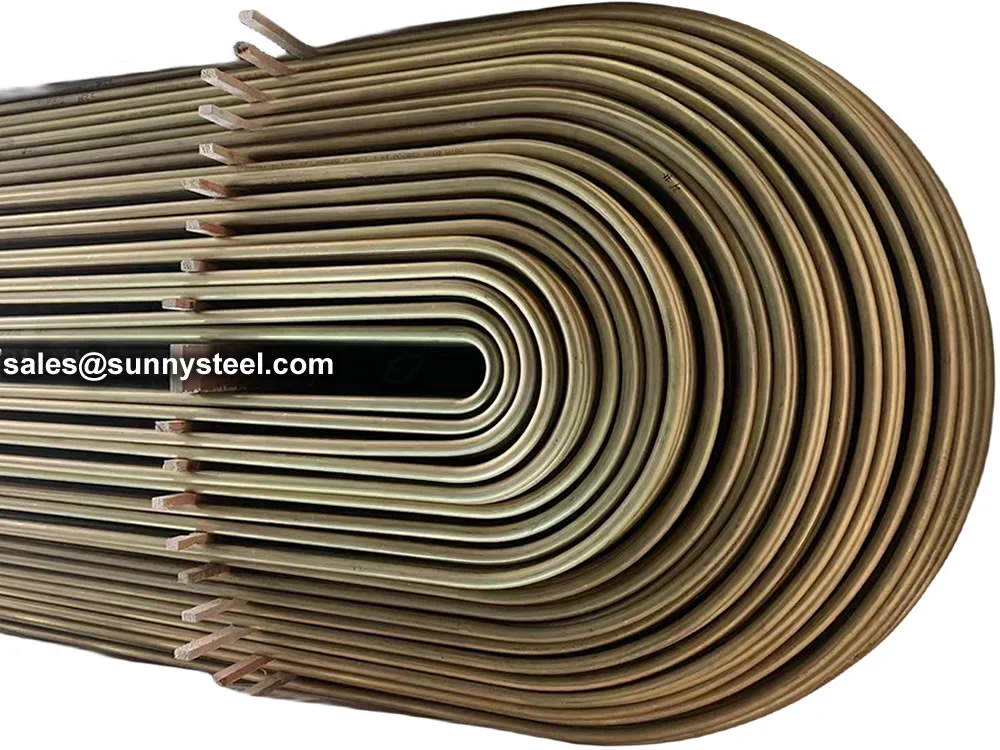
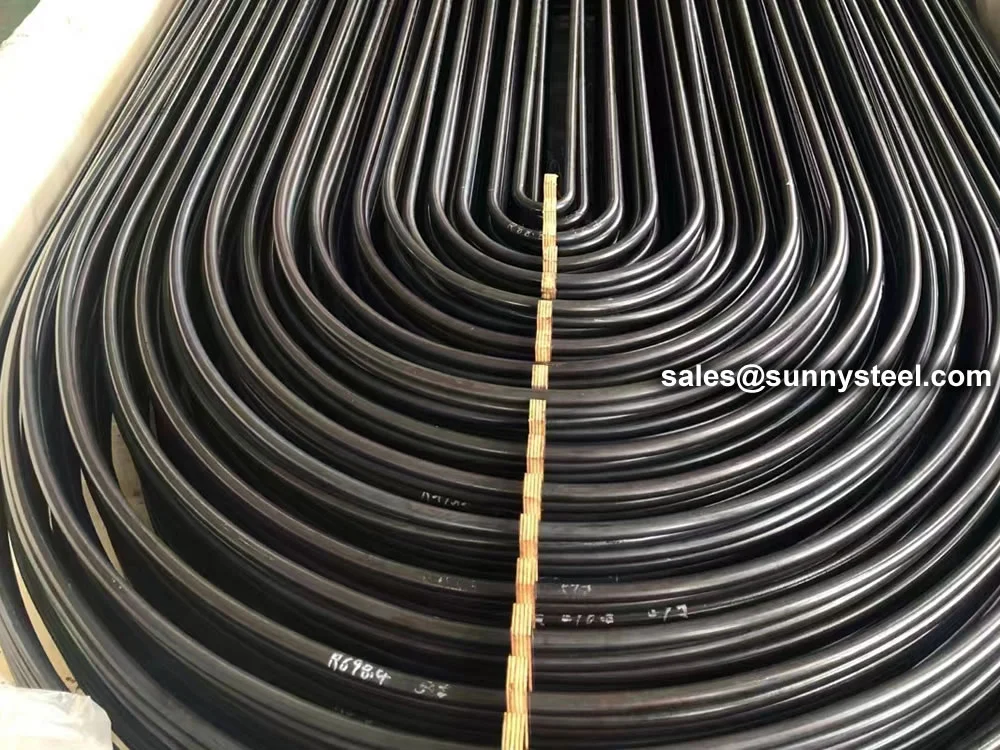
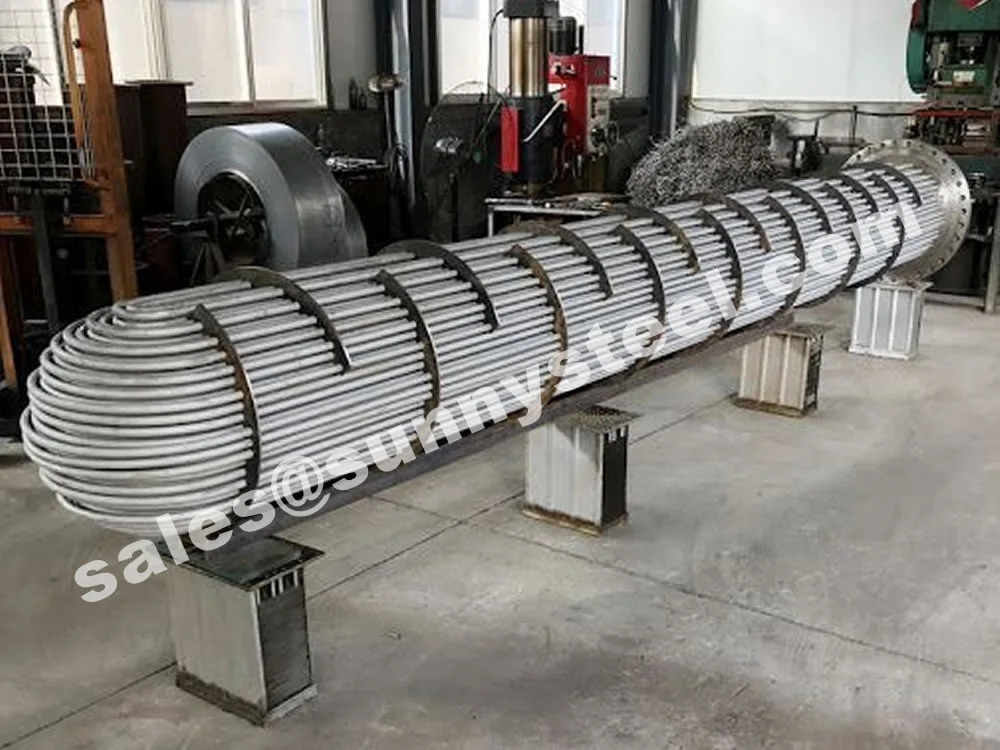
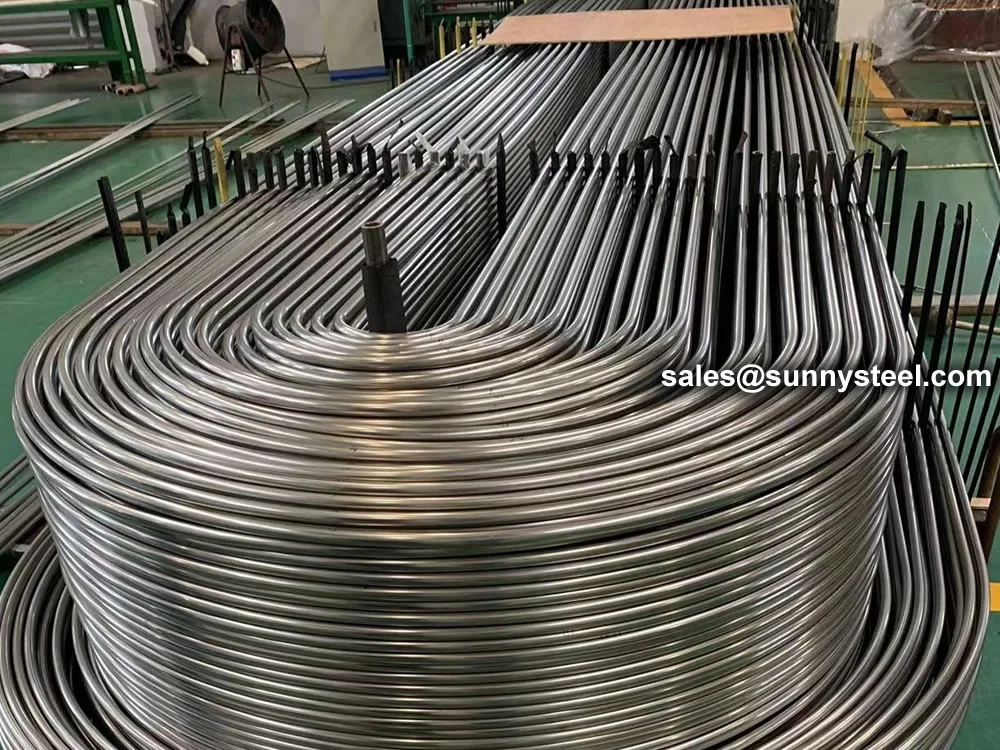
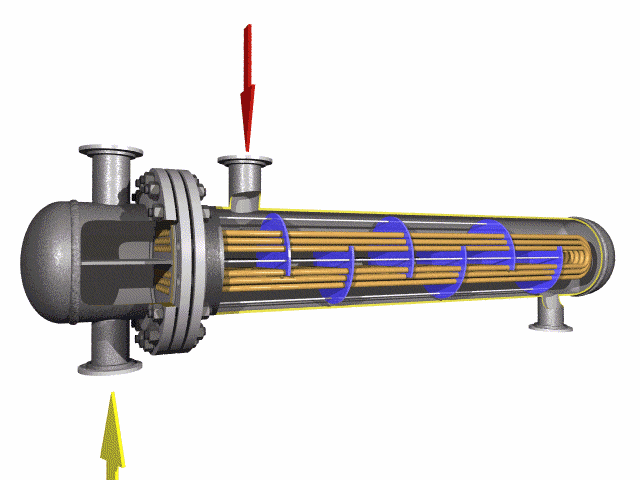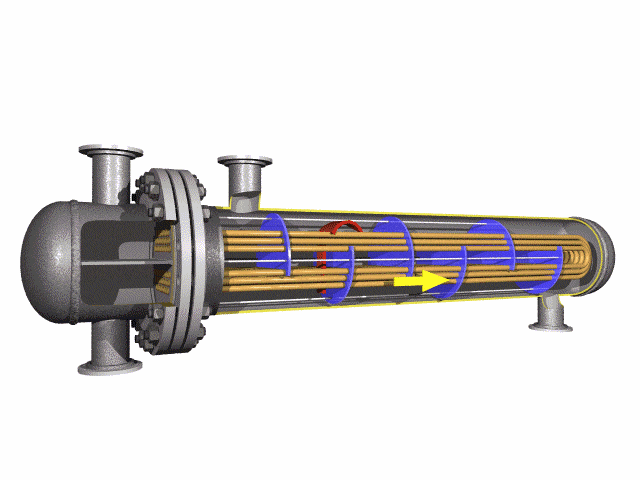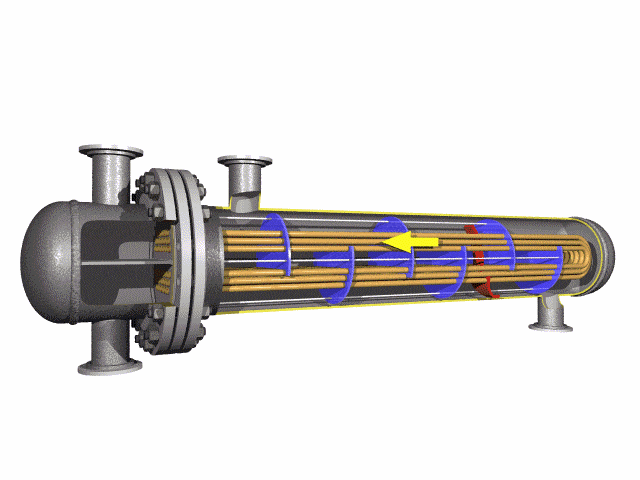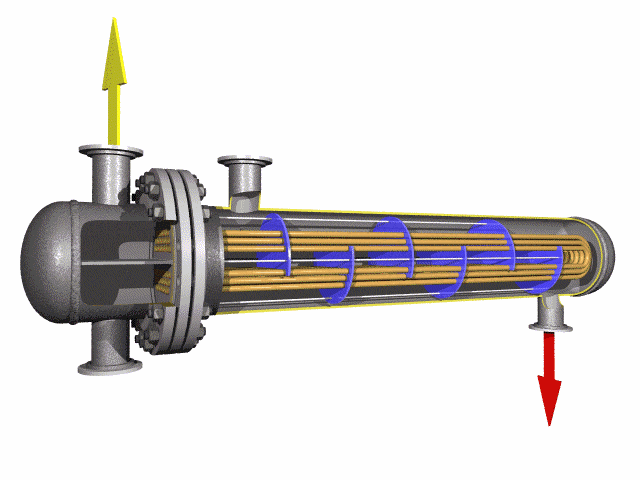
SA-213 TP347H U-Bend Tubes are seamless austenitic stainless steel tubes designed for
high-temperature and high-pressure applications in heat exchanger tubes, superheaters, and boilers.
Conforming to ASME SA-213 and ASTM A213 specifications, these high-temperature tubing solutions are
engineered for industries such as petrochemical, power generation, and chemical processing, where corrosion
resistance and pipeline durability are critical. The U-bend design facilitates compact
layouts and acts as a thermal expansion absorber, reducing stress in piping systems.
The SA-213 TP347H U-Bend Tubes are made from a stabilized austenitic stainless steel alloy
containing niobium (columbium) and a higher carbon content than TP347, enhancing creep strength and intergranular
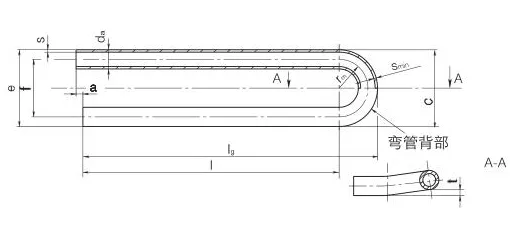
corrosion resistance. Available in outer diameters from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to 3.4mm, and
bend radii from 1.5D to 1500mm, these tubes are customizable for leg lengths up to 16.5 meters. They are
manufactured via cold-drawing or hot-rolling, followed by solution annealing at 1010-1193°C (1850-2000°F) and water
quenching to optimize mechanical properties and ensure corrosion resistance.
These U-shaped tubing solutions undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, eddy current,
flaring, flattening, and positive material identification (PMI) tests, to ensure compliance with ASME SA213/A213M
standards. The high chromium (17.0-19.0%) and nickel (9.0-13.0%) content, combined with niobium (up to 1.0%),
provides excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion in harsh environments, such as those involving sulfuric
acids or high-temperature steam. Surface treatments like pickling, passivation, or bright annealing enhance
durability, while capped ends prevent contamination during transport and installation.
The SA-213 TP347H U-Bend Tubes are particularly suited for ultra-supercritical (USC) coal boilers
and reheaters, operating at temperatures up to 650°C for pressure parts and 850°C for oxidation-resistant
components. Their stabilized composition prevents carbide precipitation, ensuring reliability in applications like
oil and gas pipelines, where hydrogen sulfide corrosion is a concern. Compared to TP304H, TP347H offers superior
creep strength and weldability, with no need for preheating or post-weld heat treatment in most cases, simplifying
installation.
In demanding environments, the SA-213 TP347H U-Bend Tubes minimize pipeline wear, thermal stress,
and corrosion, ensuring long-term performance and safety. Their ability to handle high temperatures and pressures,
combined with low maintenance and compatibility with complex heat exchanger designs, makes them a preferred choice
for engineers seeking reliable heat exchanger tubes for critical applications.
SA 213 TP347H tubes are available in many shapes, including round, square, hollow, rectangular, hydraulic, coiled, straight, and "U" shape. The tubing sizes and thicknesses are usually 1/8 in. or 3.2 mm and inside diameter of 5 inch. The minimum wall thickness is 0.015 to 0.500 inch.
FAQs of SA-213 TP347H U-Bend Tubes
Engineered to meet diverse industrial needs with robust materials and versatile designs.
SA-213 TP347H U-Bend Tubes are seamless austenitic
stainless steel tubes bent into a U-shape, used in heat exchangers and boilers for high-temperature
and high-pressure applications.
They are used in heat exchangers, superheaters, reheaters, and boilers in
petrochemical, power generation, and chemical processing industries.
347H is the higher carbon version of 347 plate. Due to the additional carbon present in 347H plate, it is tougher and generally more durable than 347 plate. These grades of stainless steel plate is available in a wide range of sizes at Penn Stainless Products.
This grade of stainless steel has an elongation of 40%. On the Brinell hardness scale 347 and 347H stainless steel plate has hardness of 201 and on the Rockwell B scale, both 347 and 347H have a hardness of 95.
For TP347H: - Carbon (C): 0.04-0.10% - Manganese (Mn): ≤2.00% - Phosphorus
(P): ≤0.045% - Sulfur (S): ≤0.030% - Silicon (Si): ≤1.00% - Chromium (Cr): 17.0-19.0% - Nickel (Ni):
9.0-13.0% - Columbium + Tantalum (Nb+Ta): 8xC-1.0%
For TP347H: - Tensile Strength: ≥515 MPa - Yield Strength: ≥205 MPa -
Elongation: ≥40% - Hardness: ≤201 HBW
Outer diameters range from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to
3.4mm, with bend radii of 1.5D to 1500mm. Tolerances meet ASTM A213/A688 standards.
Produced via cold-drawing or hot-rolling, followed by mandrel bending,
solution annealing (1010-1193°C), and water quenching to enhance properties.
Tests include hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, PMI, and
dimensional inspections to ensure compliance with ASME SA213/A213M standards.
Installed in heat exchanger tube sheets with welded or expanded ends, with
capped ends to prevent contamination during transport and setup.
TP347H offers superior creep strength and intergranular corrosion
resistance due to niobium stabilization and higher carbon content, making it ideal for
higher-temperature applications than TP304.