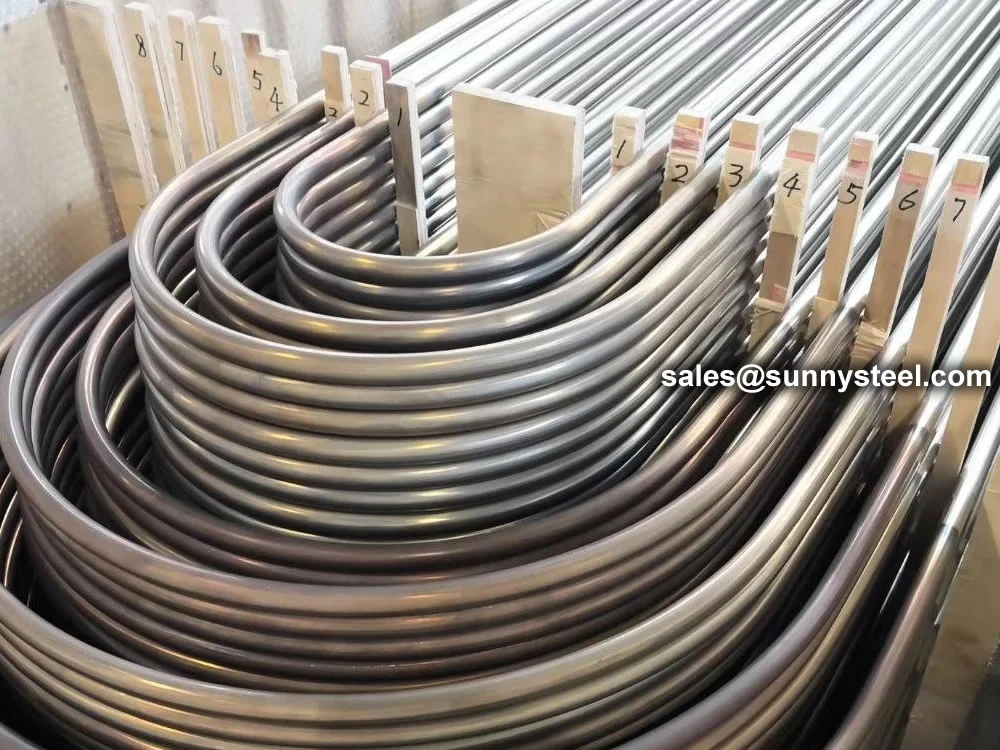
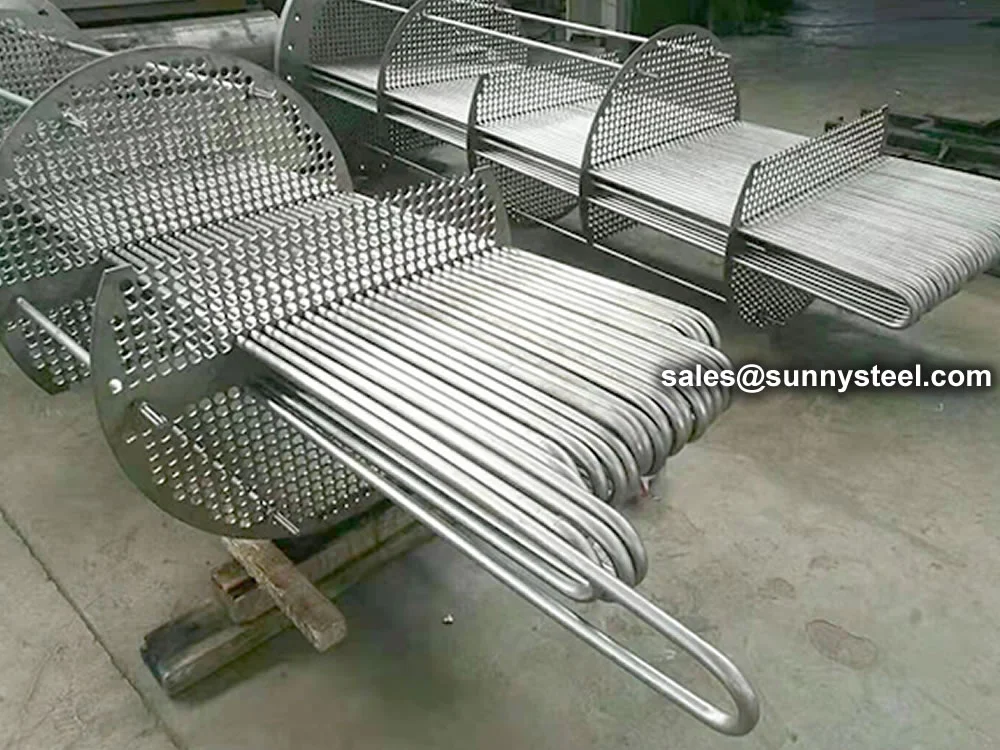
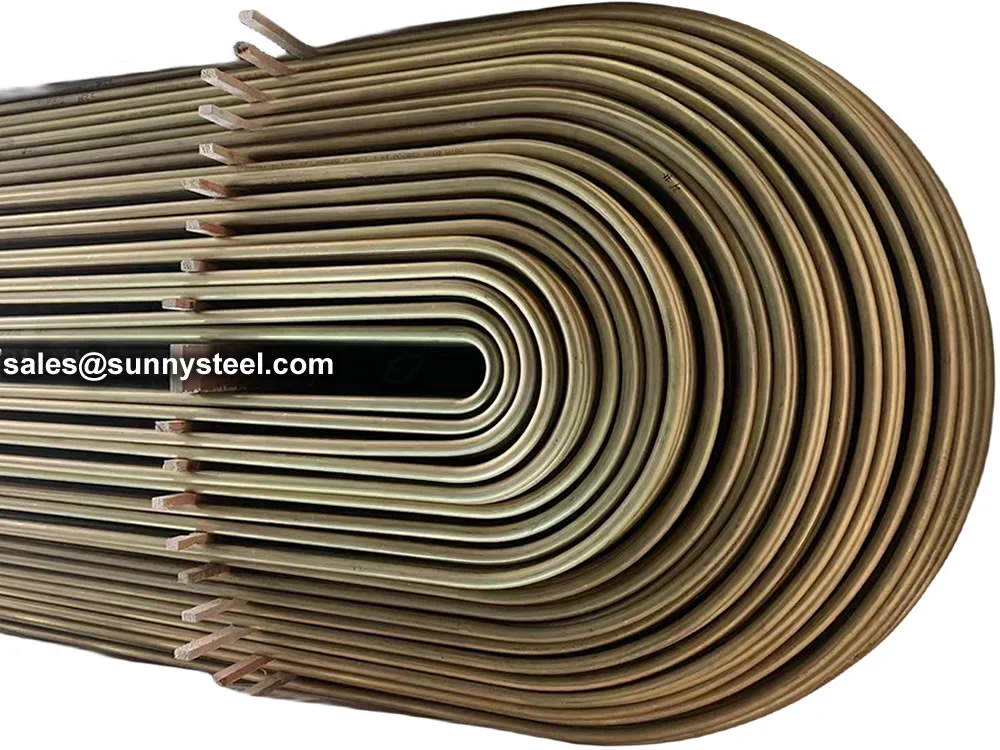
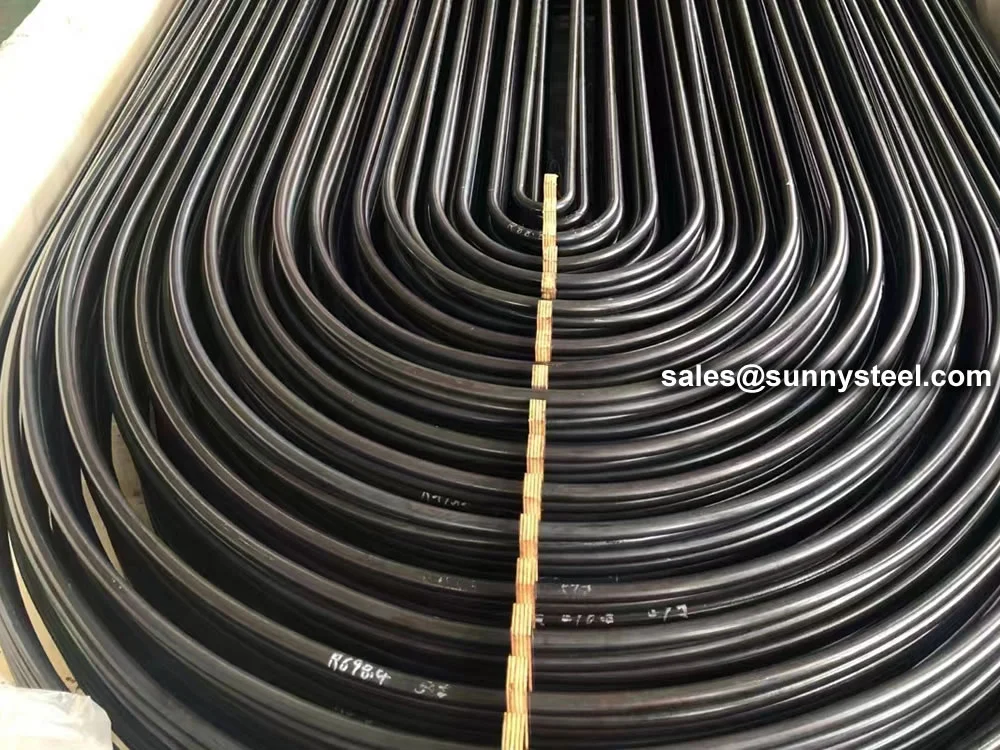
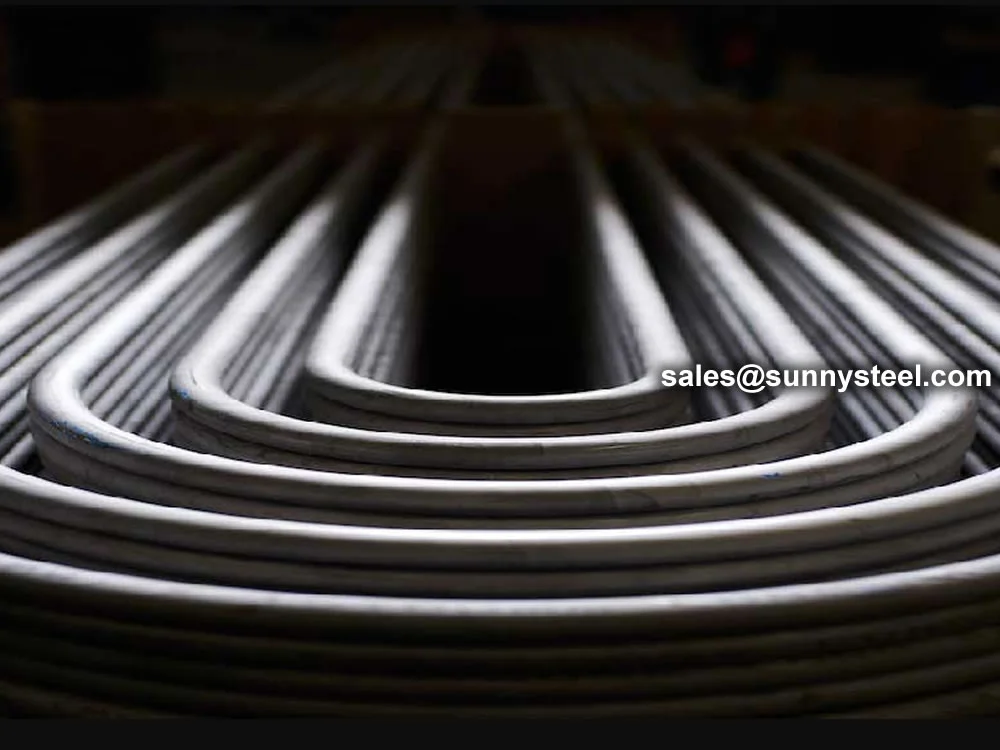
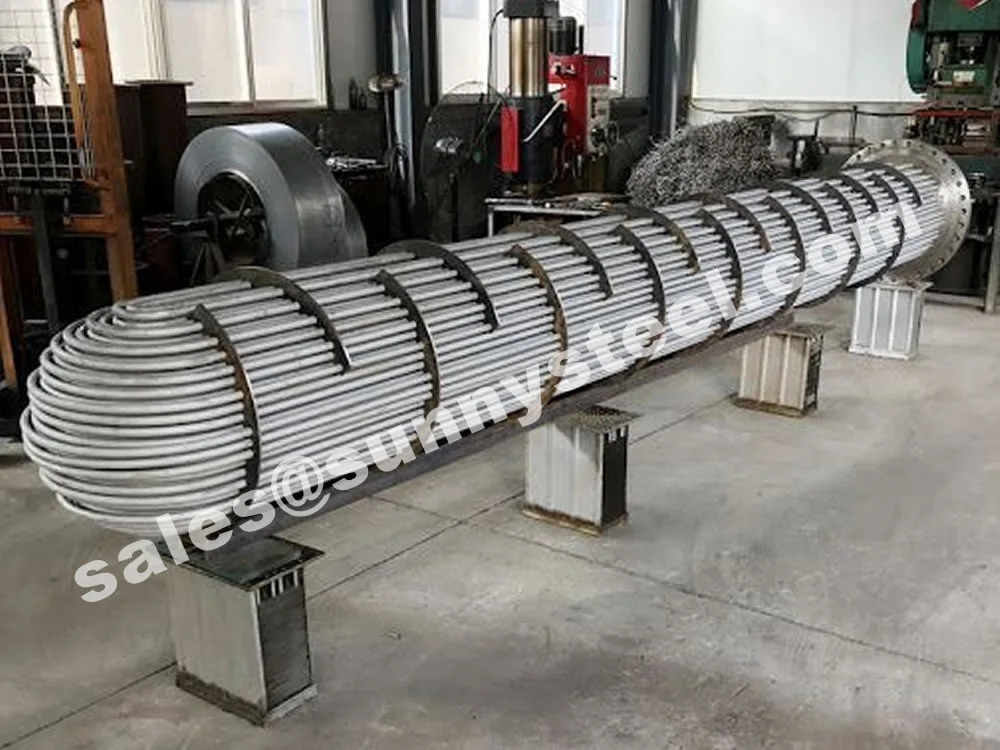
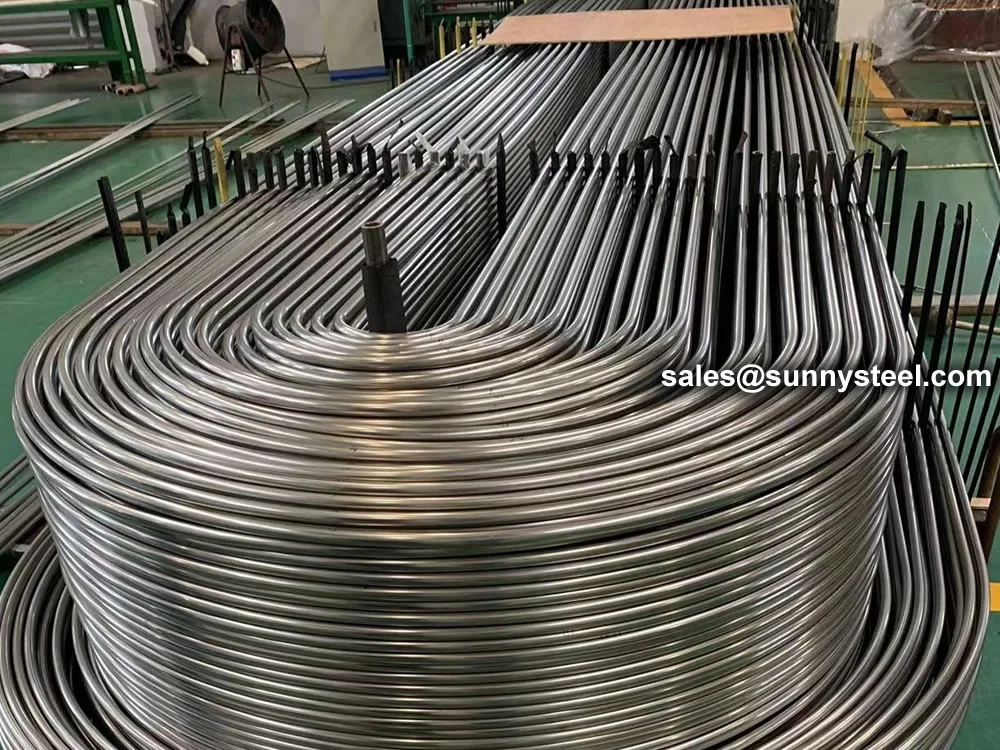
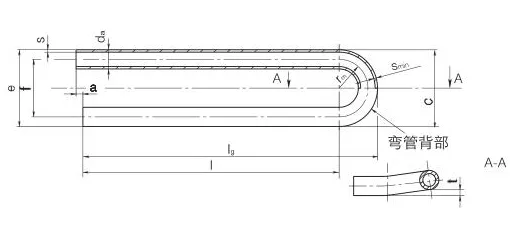
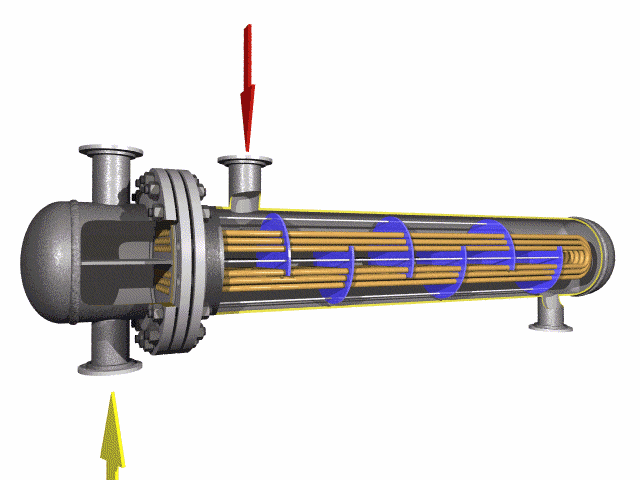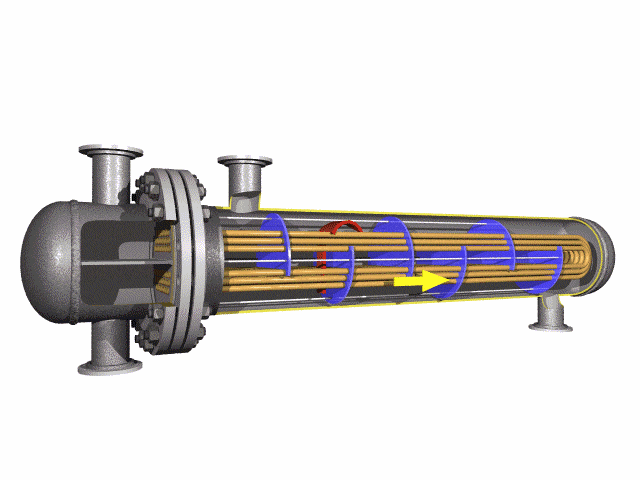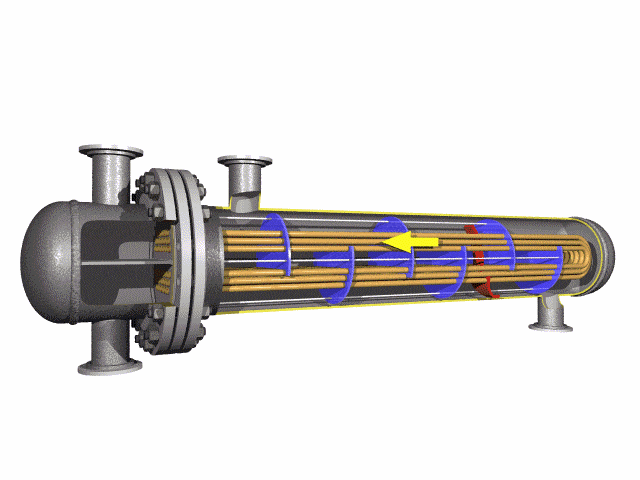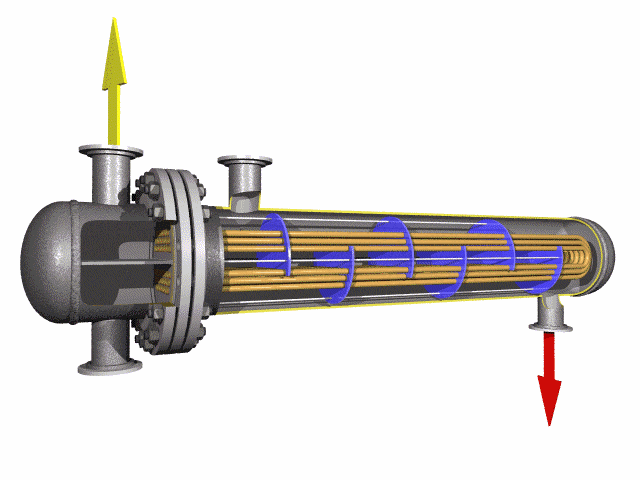
U-Bent Heat Exchanger Tubes are seamless or welded tubes bent into a U-shape, designed to optimize heat transfer in heat exchanger tubes and boiler tubes. Conforming to standards like ASTM A179, A192, A213, and ASME SA213, these tubes are critical for industries such as petrochemical, power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC, where corrosion resistance and pipeline durability are essential. The U-bend configuration acts as a thermal expansion absorber, minimizing stress and eliminating the need for additional expansion joints.
Available in materials like low-carbon steel, stainless steel (304, 316, 347H), and alloy steels, U-Bent Heat Exchanger Tubes are manufactured through cold-drawing or hot-rolling processes, followed by precise mandrel bending to maintain uniform wall thickness and prevent ovality. Outer diameters range from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, with wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to 3.4mm and bend radii from 1.5D to 1500mm. Post-bending heat treatment, such as solution annealing (1010-1193°C for stainless steel) or stress relief (≥650°C for carbon steel), enhances mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Surface treatments like pickling, passivation, or galvanization further improve durability.
These tubes undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and dimensional inspections, to comply with ASTM A450/A450M or TEMA standards. With tensile strengths ranging from 325 MPa (carbon steel) to 515 MPa (stainless steel), they are designed for operating temperatures up to 650°C (stainless steel) or 450°C (carbon steel) and pressures up to 9.8 MPa for high-pressure applications. The U-bend design ensures compact layouts, reducing installation costs and space requirements in heat exchangers and condensers.
The U-Bent Heat Exchanger Tubes excel in applications requiring high thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosive fluids, such as water, steam, or chemical solutions. Their seamless construction minimizes leak risks, while their ability to absorb thermal expansion enhances system longevity. Compared to straight tubes, U-bent tubes reduce the need for additional fittings, making them ideal for complex heat exchanger designs. Optional end finishes, such as plain, beveled, or capped ends, ensure compatibility with various tube sheet configurations.
Addressing challenges like pipeline wear, corrosion, and thermal stress, U-Bent Heat Exchanger Tubes provide a reliable solution for engineers seeking efficient heat exchanger tubes. Their versatility, durability, and low maintenance requirements make them a preferred choice for high-performance heat transfer systems in demanding industrial environments.
FAQs
Engineered to meet diverse industrial needs with robust materials and versatile designs.
U-Bent Heat Exchanger Tubes are seamless or welded tubes bent into a U-shape, used in heat exchangers and boilers for efficient heat transfer and thermal expansion absorption.
They are used in heat exchangers, condensers, boilers, and superheaters in petrochemical, power generation, chemical processing, and HVAC industries.
Common materials include low-carbon steel (ASTM A179), stainless steel (304, 316, 347H), and alloy steels, with coatings like galvanization or passivation for corrosion resistance.
For ASTM A179 (Carbon Steel):
- Carbon (C): 0.06-0.18%
- Manganese (Mn): 0.27-0.63%
- Phosphorus (P): ≤0.035%
- Sulfur (S): ≤0.035%
- Silicon (Si): ≤0.25%
For ASTM A213 TP347H (Stainless Steel):
- Carbon (C): 0.04-0.10%
- Manganese (Mn): ≤2.00%
- Phosphorus (P): ≤0.045%
- Sulfur (S): ≤0.030%
- Silicon (Si): ≤1.00%
- Chromium (Cr): 17.0-19.0%
- Nickel (Ni): 9.0-13.0%
- Columbium + Tantalum (Nb+Ta): 8xC-1.0%
For ASTM A179:
- Tensile Strength: ≥325 MPa
- Yield Strength: ≥180 MPa
- Elongation: ≥35%
- Hardness: ≤72 HRB
For ASTM A213 TP347H:
- Tensile Strength: ≥515 MPa
- Yield Strength: ≥205 MPa
- Elongation: ≥40%
- Hardness: ≤201 HBW
Outer diameters range from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to 3.4mm, with bend radii of 1.5D to 1500mm. Tolerances comply with ASTM A450/A450M or TEMA standards.
Produced via cold-drawing or hot-rolling, followed by mandrel bending and heat treatment (e.g., solution annealing at 1010-1193°C for stainless steel or ≥650°C for carbon steel).
Tests include hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and dimensional inspections to ensure compliance with ASTM A450/A450M or TEMA standards.
Installed in heat exchanger tube sheets with welded or expanded ends, with capped ends to prevent contamination during transport and setup.
U-Bent tubes reduce the need for additional fittings and absorb thermal expansion, unlike straight tubes, which may require expansion joints, increasing costs and space.