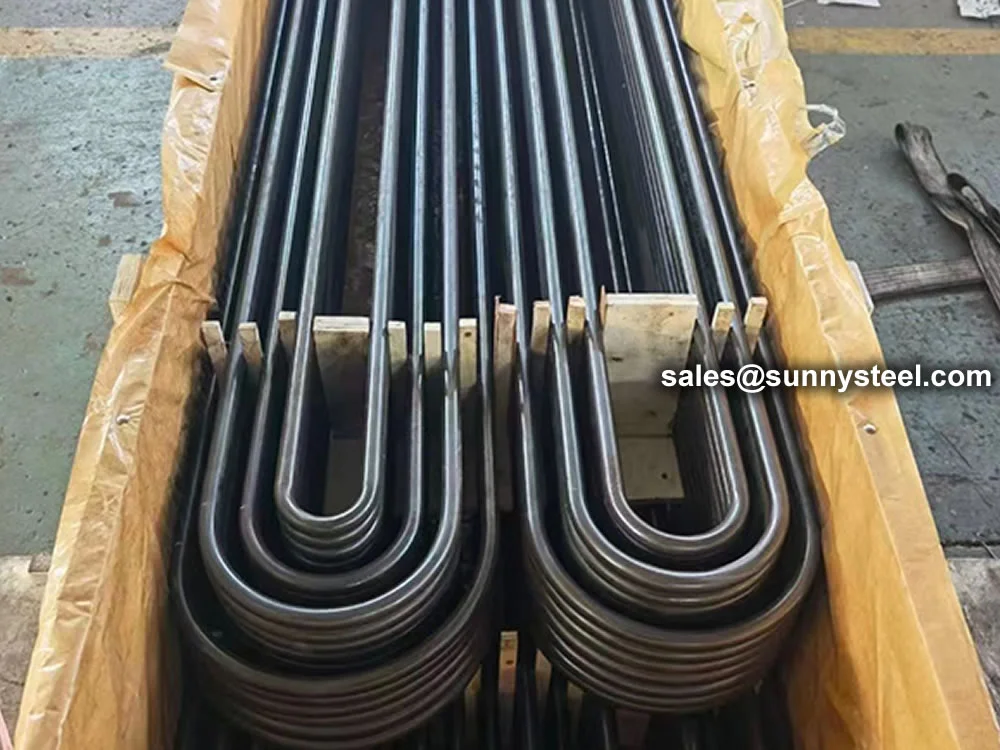
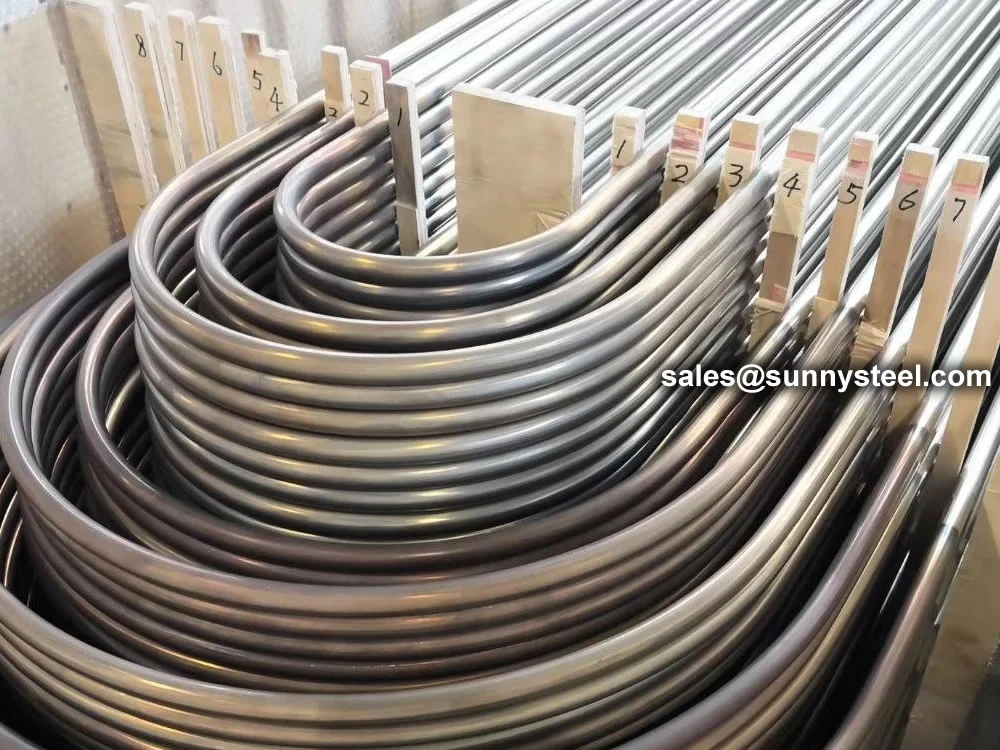
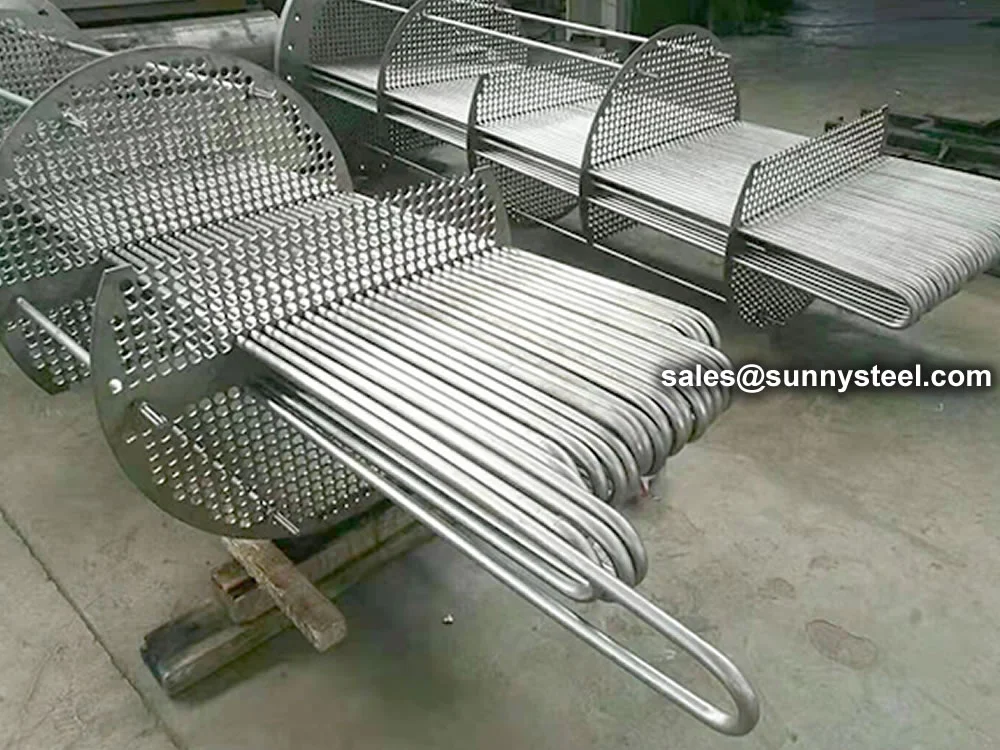
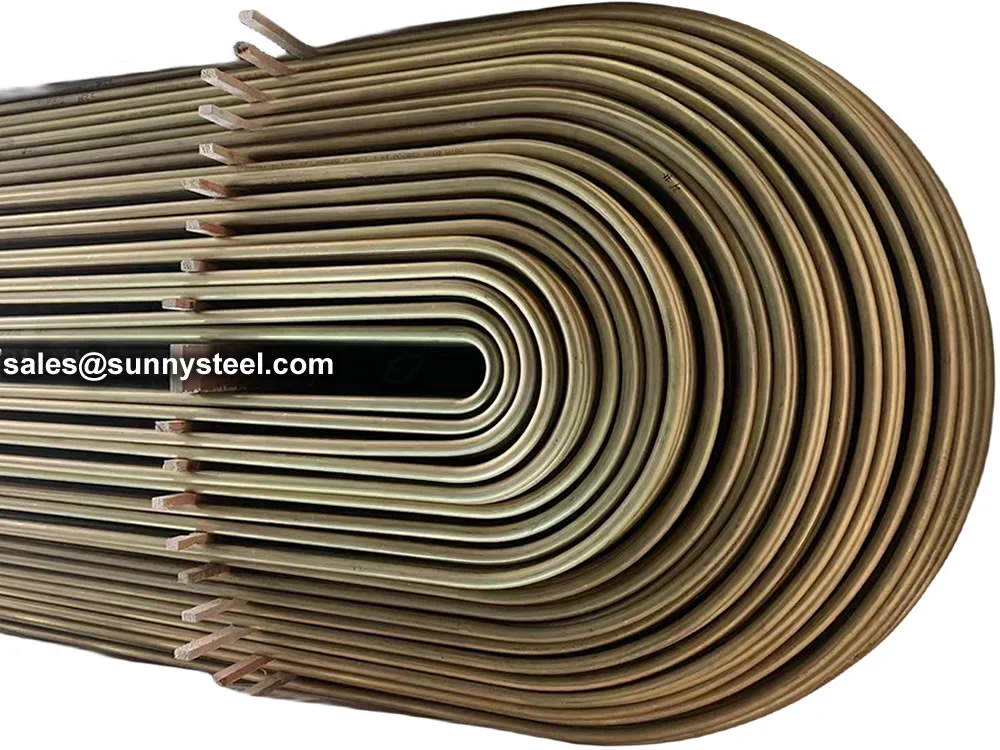
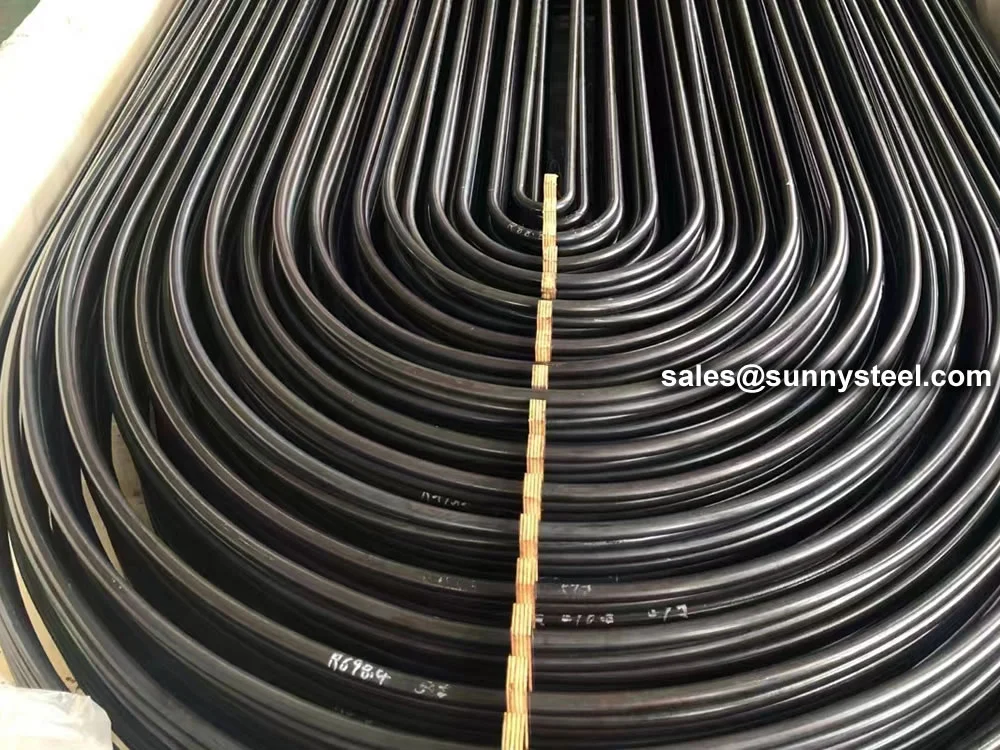
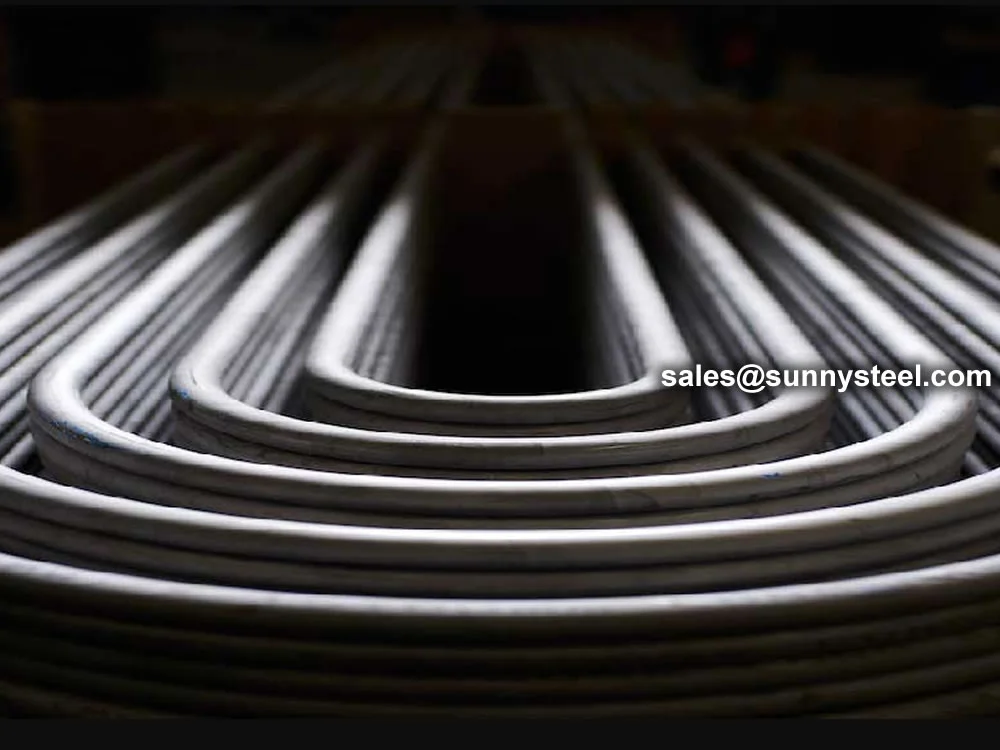
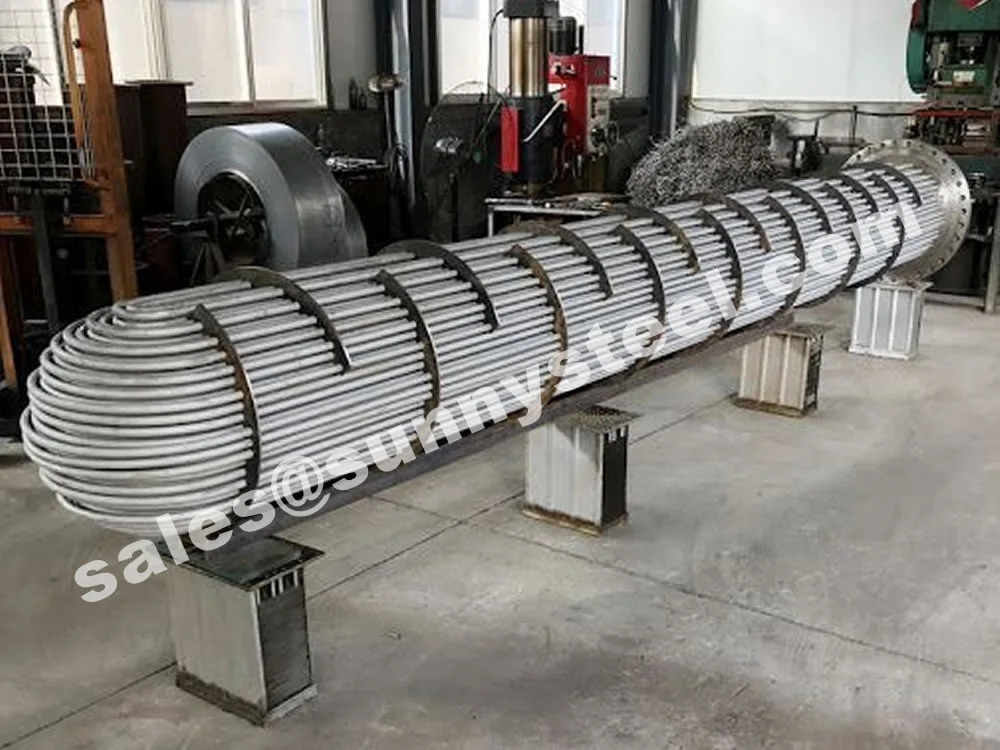
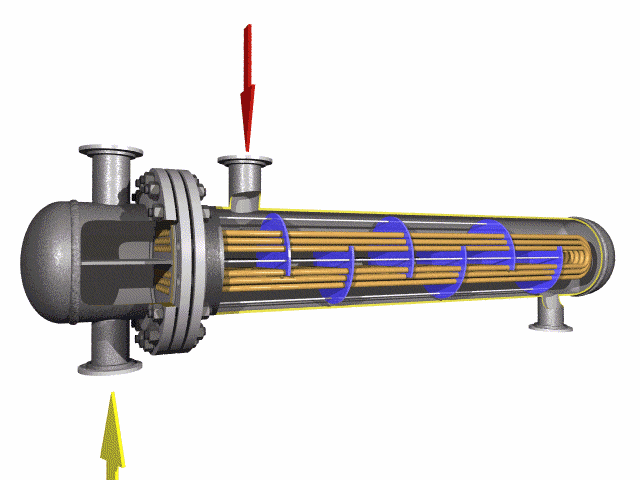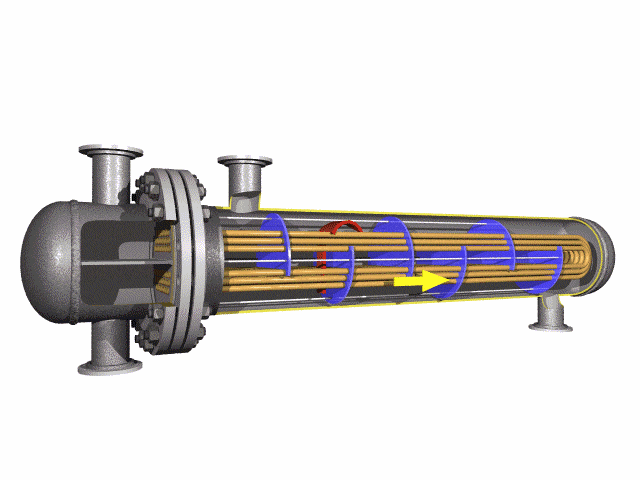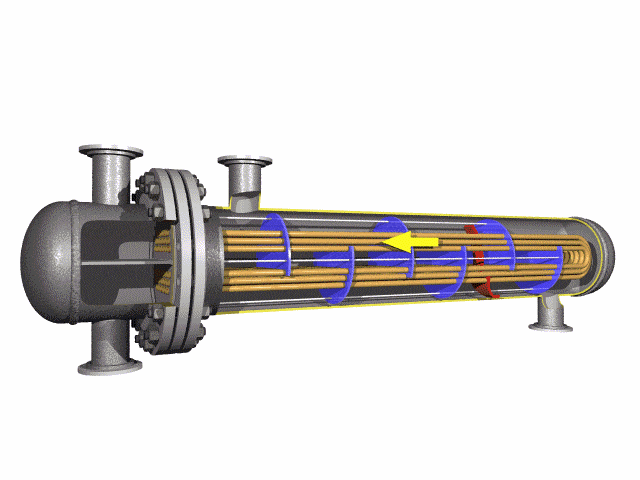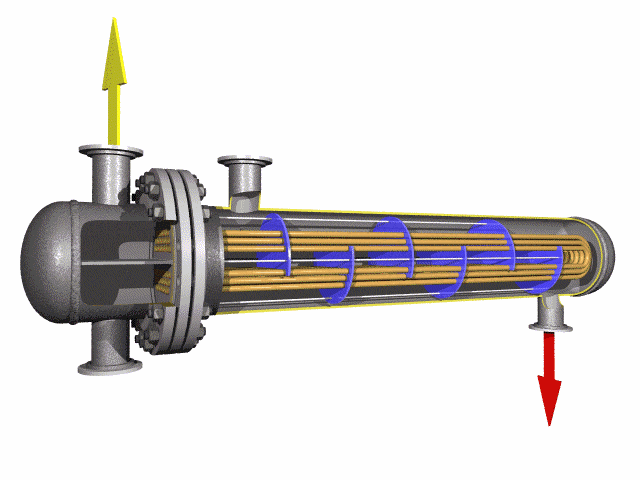
Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes are seamless or welded tubes crafted from low alloy steel, bent
into a U-shape for use in heat exchanger tubes and boiler tubes. Conforming to
standards like ASTM A213 (T5, T9, T11, T22, T91) and JIS G3462, these tubes are engineered for high-pressure and
high-temperature applications in industries such as petrochemical, power generation, oil and gas, and chemical
processing. Their corrosion resistance and ability to act as a thermal expansion
absorber make them ideal for enhancing pipeline durability in demanding environments.
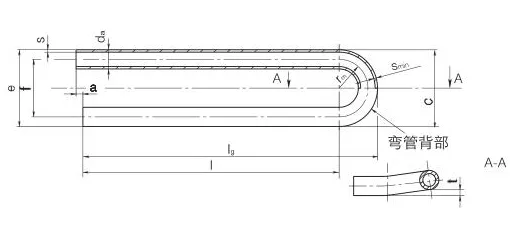
Manufactured using cold-drawing or hot-rolling processes, Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes feature outer
diameters from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to 6mm, and bend radii from 1.5D to 1500mm,
customizable to client specifications. Post-bending heat treatment, such as stress relief annealing at 650-720°C or
normalizing at 850-950°C, ensures optimal mechanical properties and prevents cracking. Surface treatments like
pickling, passivation, or 3LPE coating enhance corrosion resistance, while plastic caps protect
tube ends during transport.
These tubes undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and hardness tests,
to meet ASTM A450/A450M and TEMA standards. With tensile strengths ranging from 415 MPa (T11) to 620 MPa (T91) and
yield strengths from 205 MPa to 440 MPa, they are designed for temperatures up to 650°C and pressures up to 10 MPa.
The U-bend design minimizes thermal stress, eliminates the need for expansion joints, and reduces installation
costs, making them ideal for compact heat exchanger systems.
The low alloy steel composition, typically containing 1-5% chromium (Cr) and 0.5-1% molybdenum (Mo), provides
superior corrosion resistance and creep strength compared to carbon steel, while being more
cost-effective than stainless steel. Common grades like T11 and T22 are suited for boiler superheaters, while T91 is
used in high-temperature, high-pressure applications like power plant reheaters. The seamless construction ensures
leak-free performance, and their ability to handle abrasive fluids makes them suitable for pneumatic conveying
systems.
Addressing challenges like pipeline wear, corrosion, and thermal stress, Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes
offer a robust solution for engineers seeking reliable heat exchanger tubes. Their high
strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and low maintenance requirements make them a preferred choice for critical
applications in harsh industrial environments, ensuring long-term performance and efficiency.
Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes
Engineered for heat exchanger efficiency, low alloy U-bent tubes combine strength, heat resistance,
and cost-effectiveness for industrial applications.
Materials
High & low yield stainless steels
Alloy steels with Cr, Mo, Ni
Carbon steels for cost efficiency
Selection Factors
Mechanical strength
Corrosion resistance
Heat resistance
Purpose of U-Bend
Simplifies fluid routing in piping systems, reducing the need for additional fittings
while enhancing installation flexibility.
Heat Exchangers
Designed for high-pressure, high-temperature service in boilers and condensers.
Chemical & Petrochemical
Withstands aggressive media in refineries and process plants.
Food & Refrigeration
Efficient heat transfer in refrigeration and food processing equipment.
Oil & Gas
Reliable for offshore, refinery, and gas plant heat exchanger units.
Performance Assurance
Low alloy U-bent tubes deliver long service life with excellent heat transfer,
high mechanical strength, and adaptability for critical industries.
Chemical Composition of Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM A213 T11)
| Element |
Composition (%) |
| Carbon (C) |
0.05-0.15 |
| Manganese (Mn) |
0.30-0.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) |
≤0.025 |
| Sulfur (S) |
≤0.025 |
| Silicon (Si) |
0.50-1.00 |
| Chromium (Cr) |
1.00-1.50 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) |
0.44-0.65 |
Mechanical Properties of Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM A213 T11)
| Property |
Value |
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) |
415 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) |
205 |
| Elongation, min (%) |
30 |
| Hardness, max (HBW) |
163 |
Chemical Composition of Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM A213 T91)
| Element |
Composition (%) |
| Carbon (C) |
0.08-0.12 |
| Manganese (Mn) |
0.30-0.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) |
≤0.020 |
| Sulfur (S) |
≤0.010 |
| Silicon (Si) |
0.20-0.50 |
| Chromium (Cr) |
8.00-9.50 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) |
0.85-1.05 |
| Vanadium (V) |
0.18-0.25 |
| Niobium (Nb) |
0.06-0.10 |
Mechanical Properties of Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM A213 T91)
| Property |
Value |
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) |
620 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) |
440 |
| Elongation, min (%) |
20 |
| Hardness, max (HBW) |
250 |
FAQs
Engineered to meet diverse industrial needs with robust materials and versatile designs.
Low Alloy U-Bent Tubes are seamless or welded tubes made
from low alloy steel, bent into a U-shape for heat exchangers and boilers, offering high strength
and corrosion resistance.
They are used in heat exchangers, boilers, superheaters, and condensers in
petrochemical, power generation, oil and gas, and chemical industries.
Made from low alloy steel (e.g., ASTM A213 T11, T91) with 1-5% chromium and
0.5-1% molybdenum, often with coatings like 3LPE or passivation for enhanced corrosion resistance.
For ASTM A213 T11:
- Carbon (C): 0.05-0.15%
- Manganese (Mn):
0.30-0.60%
- Phosphorus (P): ≤0.025%
- Sulfur (S): ≤0.025%
- Silicon (Si):
0.50-1.00%
- Chromium (Cr): 1.00-1.50%
- Molybdenum (Mo): 0.44-0.65%
For ASTM A213
T91:
- Carbon (C): 0.08-0.12%
- Manganese (Mn): 0.30-0.60%
- Phosphorus (P): ≤0.020%
- Sulfur (S): ≤0.010%
- Silicon (Si): 0.20-0.50%
- Chromium (Cr): 8.00-9.50%
-
Molybdenum (Mo): 0.85-1.05%
- Vanadium (V): 0.18-0.25%
- Niobium (Nb): 0.06-0.10%
For ASTM A213 T11:
- Tensile Strength: ≥415 MPa
- Yield Strength:
≥205 MPa
- Elongation: ≥30%
- Hardness: ≤163 HBW
For ASTM A213 T91:
- Tensile
Strength: ≥620 MPa
- Yield Strength: ≥440 MPa
- Elongation: ≥20%
- Hardness: ≤250 HBW
Outer diameters range from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to
6mm, with bend radii of 1.5D to 1500mm. Tolerances comply with ASTM A450/A450M and TEMA standards.
Produced via cold-drawing or hot-rolling, followed by mandrel bending and
heat treatment (stress relief at 650-720°C or normalizing at 850-950°C) to enhance properties.
Tests include hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and hardness
tests to ensure compliance with ASTM A450/A450M and TEMA standards.
Installed in heat exchanger or boiler tube sheets with welded or expanded
ends, with capped ends to prevent contamination during transport.
Low alloy U-bent tubes offer higher strength and creep resistance at a
lower cost than stainless steel, but have less corrosion resistance in highly corrosive
environments.