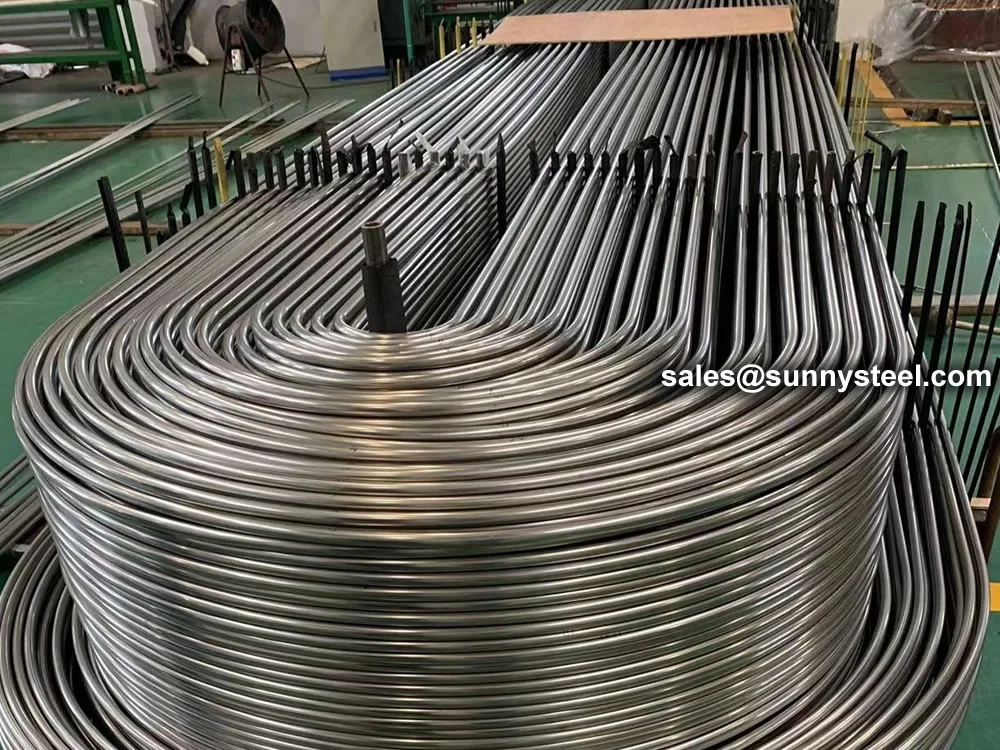
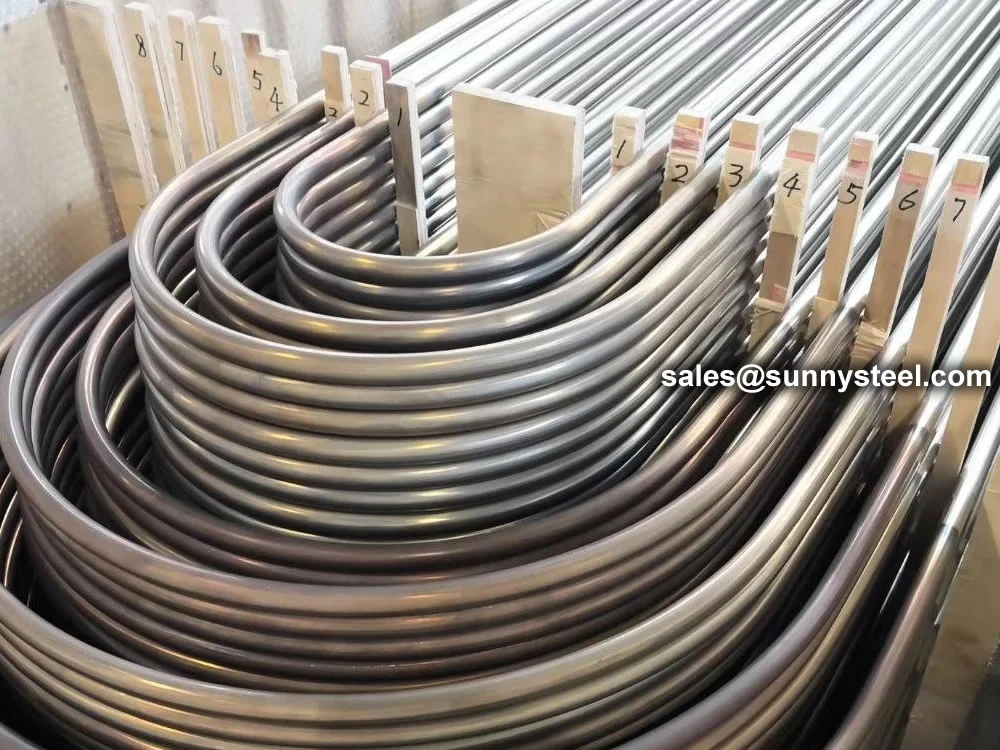
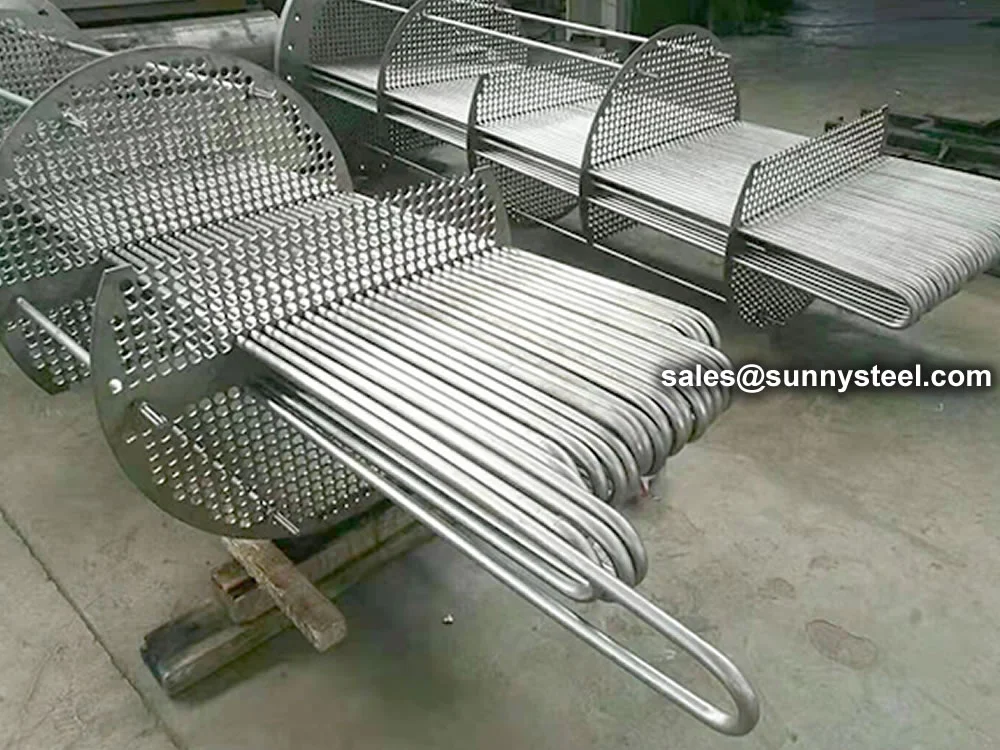
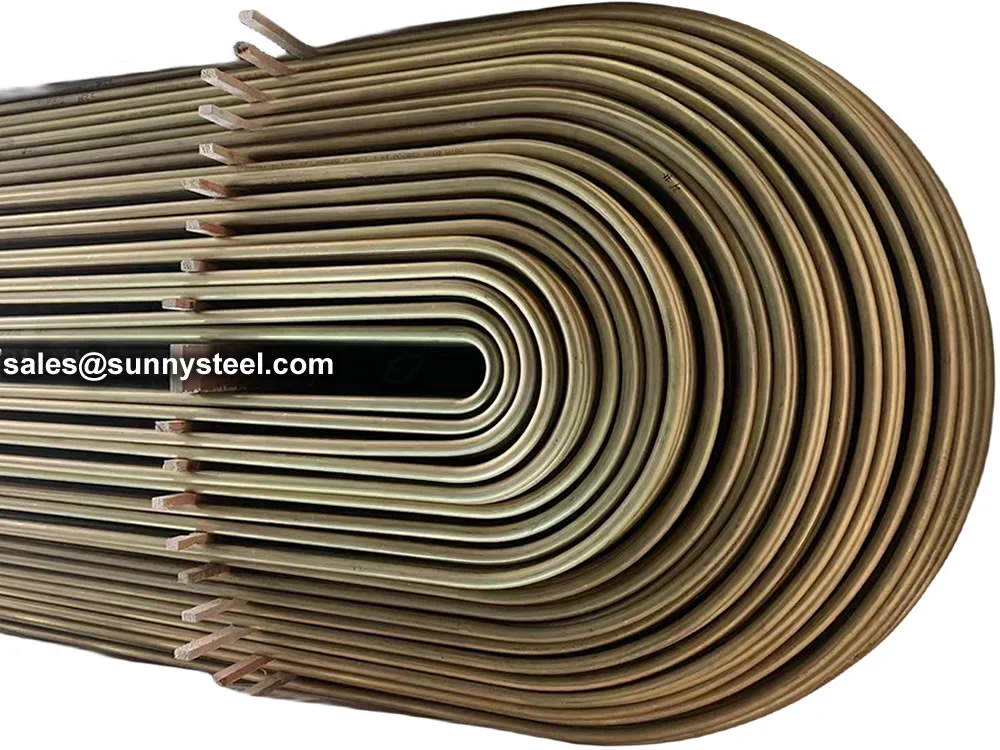
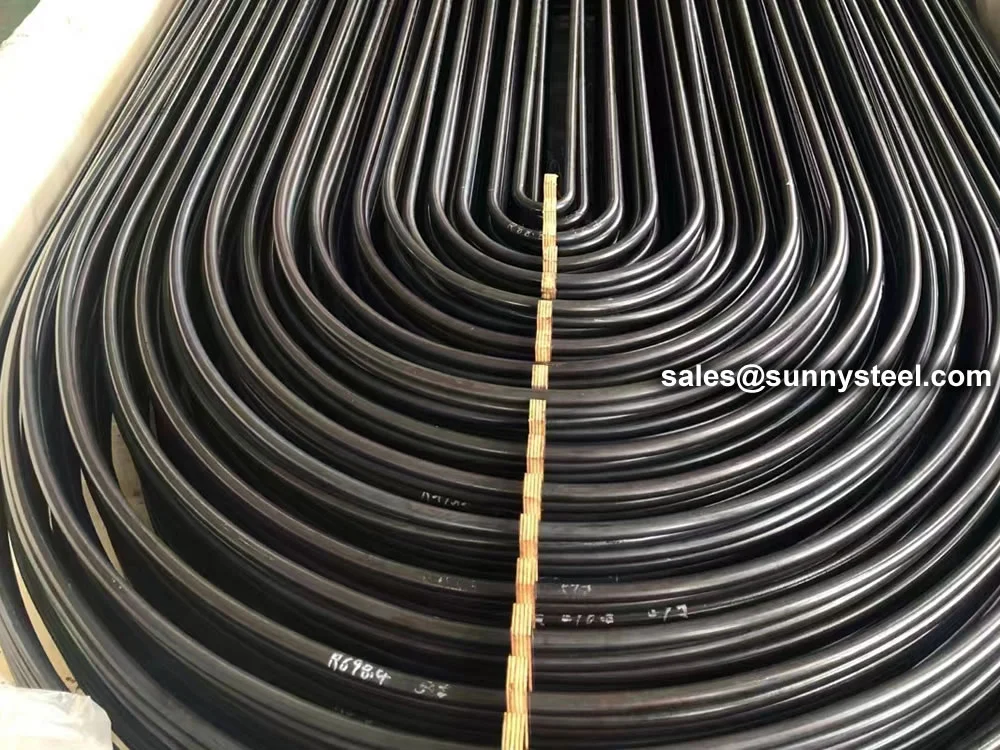
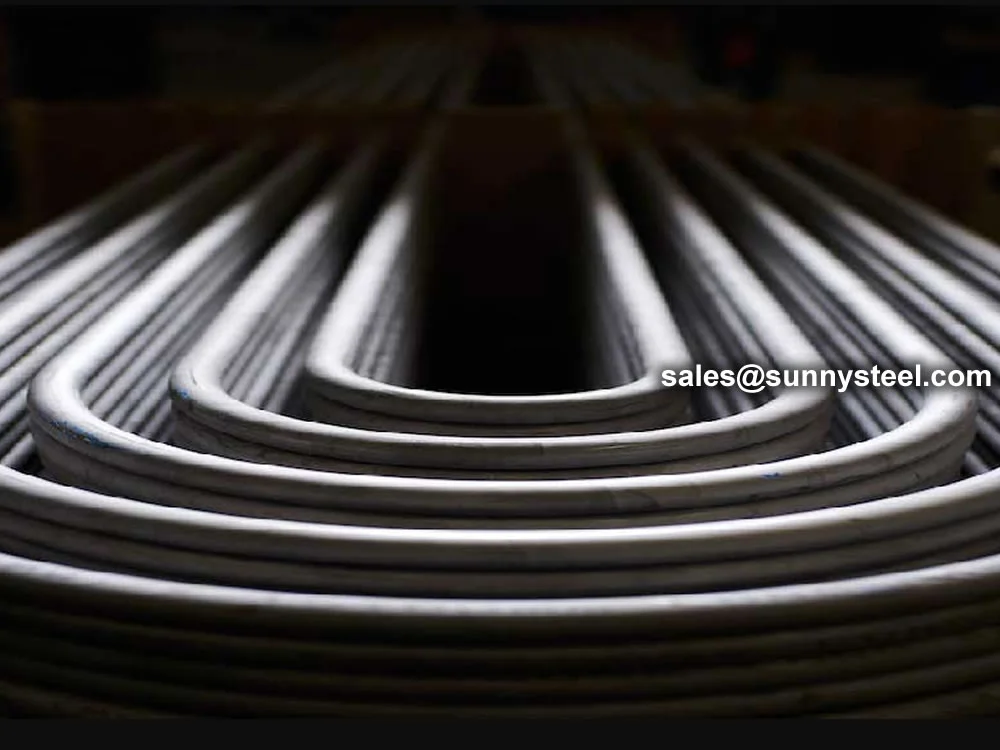
Alloy Steel U-Tubes are seamless or welded tubes made from alloy steel, bent into a
U-shape for use in heat exchanger tubes and boiler tubes. Conforming to standards
like ASTM A213 (T5, T9, T11, T22, T91) and JIS G3462, these tubes are designed for high-temperature and
high-pressure applications in industries such as petrochemical, power generation, oil and gas, and chemical
processing. Their corrosion resistance and role as a thermal expansion absorber
make them ideal for enhancing pipeline durability in harsh environments.
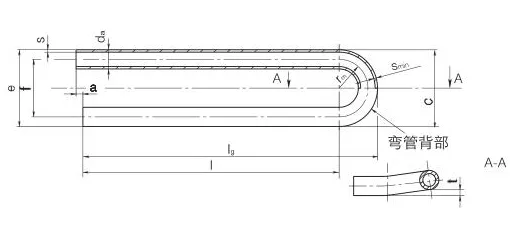
Manufactured through cold-drawing or hot-rolling, Alloy Steel U-Tubes offer outer diameters from
6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to 6mm, and bend radii from 1.5D to 1500mm, customizable to meet
project specifications. Post-bending heat treatments, such as stress relief annealing (650-720°C) or normalizing
(850-950°C), optimize mechanical properties and prevent cracking. Surface treatments like pickling, passivation, or
3LPE coating enhance corrosion resistance, while capped ends protect tubes during transport and
installation.
These tubes undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and hardness tests,
to comply with ASTM A450/A450M and TEMA standards. With tensile strengths ranging from 415 MPa (T11) to 620 MPa
(T91) and yield strengths from 205 MPa to 440 MPa, they are engineered for temperatures up to 650°C and pressures up
to 10 MPa. The U-bend design reduces thermal stress and eliminates the need for expansion joints, making them
cost-effective and space-efficient for heat exchanger tubes.
The alloy steel composition, typically containing 1-9% chromium (Cr) and 0.5-1% molybdenum (Mo), offers superior
creep strength and corrosion resistance compared to carbon steel, while being more economical than
stainless steel. Grades like T11 and T22 are ideal for boiler superheaters, while T91 excels in high-temperature
applications like power plant reheaters. The seamless construction ensures leak-free performance, and their ability
to handle abrasive fluids makes them suitable for pneumatic conveying systems.
Addressing challenges like pipeline wear, corrosion, and thermal stress, Alloy Steel U-Tubes
provide a reliable solution for engineers seeking durable boiler tubes and heat exchanger
tubes. Their high strength, durability, and low maintenance requirements make them a preferred choice
for critical applications in demanding industrial environments, ensuring long-term performance and efficiency.
Alloy steel U tubes are typically constructed from materials containing varying proportions of alloying elements like chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni), and others. These alloys offer exceptional heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength.
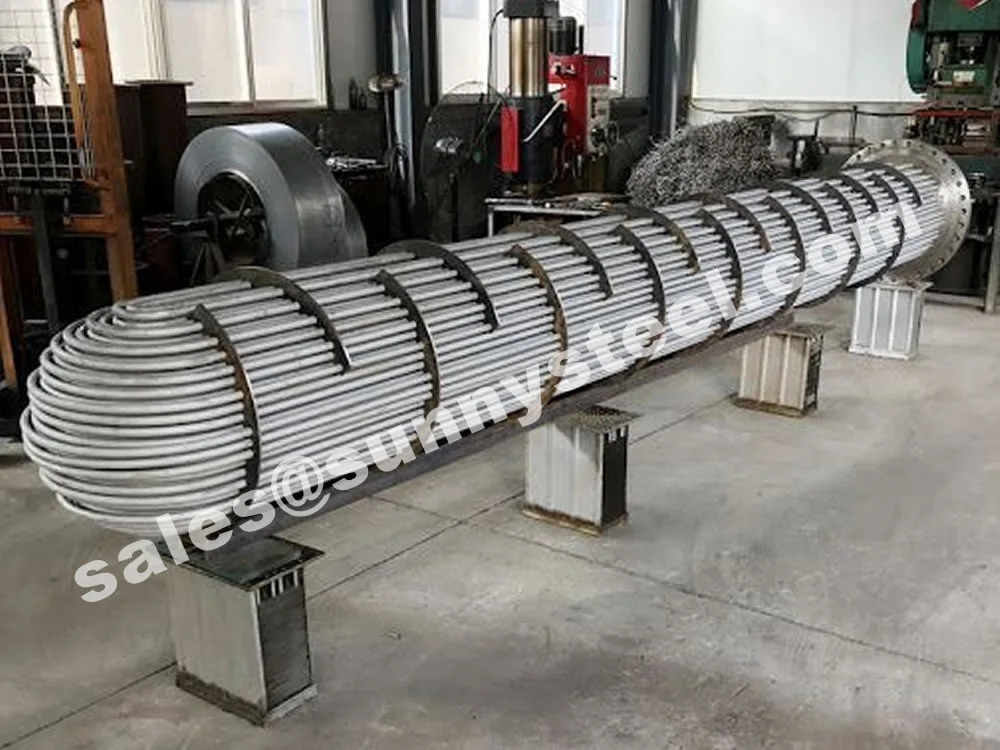
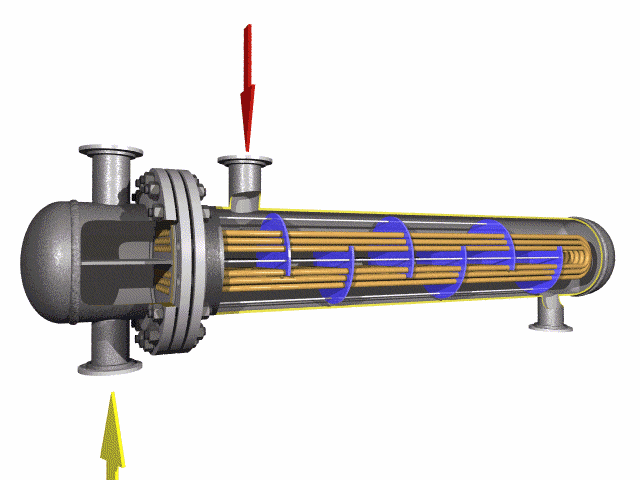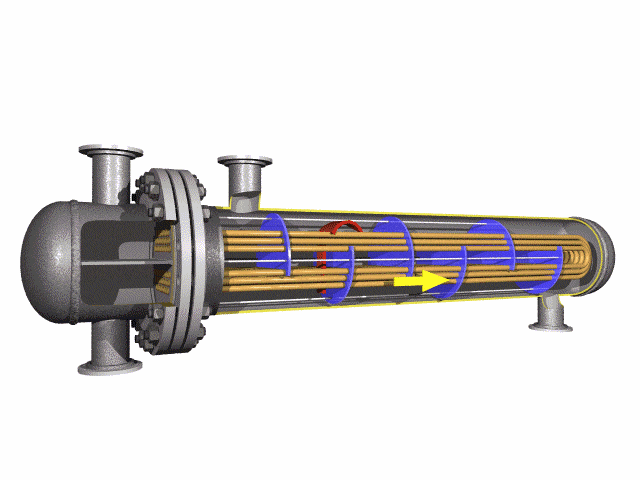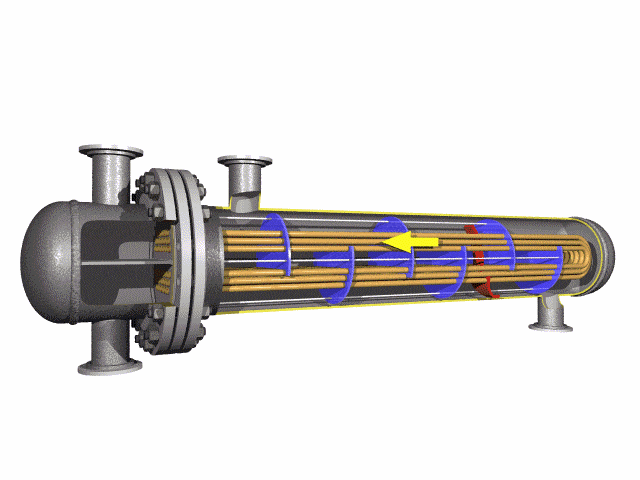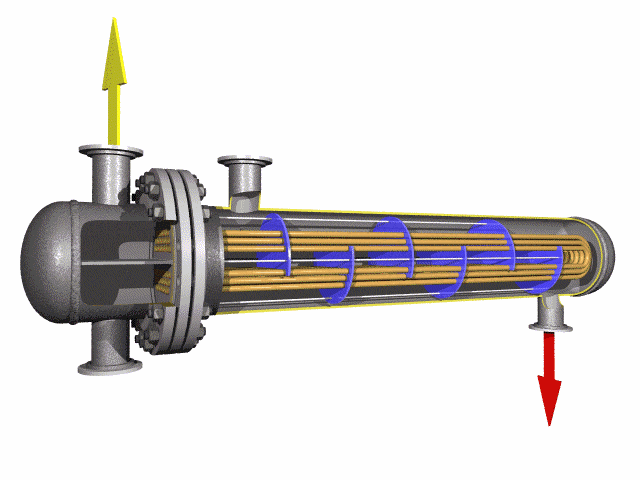
Alloy Steel U-tube heat exchanger tubes are bent into a U-shaped tube, the fluid inlet and outlet were installed in the same side on both sides of the head with partitions into two rooms, each tube is free to expand and retract to solve the heat Compensation problem.
The U tube is an important part of the U tube heat exchanger.
The main structure of the U type tube heat exchanger includes the tube box, the barrel, the head, the heat exchange tube, the nozzle, the baffle plate, the punching plate and the guide tube, the short circuit structure, the support and other accessories.
Alloy Steel U tubes used for heat transfer tubes is usually used for heat transfer tubes and ordinary cold drawn tubes. The former is suitable for non phase transition heat transfer and vibration prone situations, and the latter is suitable for reboiling, condensing heat transfer and non vibration general situations.
Alloy Steel U tubes has a variety of forms, smooth tube is the most traditional form, because it has the advantages of easy manufacturing and low unit length cost, which is the most common in the current application. The pipe should be able to withstand certain temperature and stress. When the tube and shell side fluid are corrosive, the pipe should also have corrosion resistance.
The material of Alloy Steel U tubes:T5, T11, T12, T22, T9, T91, etc.
U Tubes for Heat Transfer
The U-shaped configuration of these tubes significantly enhances their heat transfer capabilities. This design increases the surface area available for heat exchange, resulting in improved efficiency in heat exchangers and condenser systems.
Chemical Composition of Alloy Steel U-Tubes (ASTM A213 T11)
| Element |
Composition (%) |
| Carbon (C) |
0.05-0.15 |
| Manganese (Mn) |
0.30-0.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) |
≤0.025 |
| Sulfur (S) |
≤0.025 |
| Silicon (Si) |
0.50-1.00 |
| Chromium (Cr) |
1.00-1.50 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) |
0.44-0.65 |
Mechanical Properties of Alloy Steel U-Tubes (ASTM A213 T11)
| Property |
Value |
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) |
415 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) |
205 |
| Elongation, min (%) |
30 |
| Hardness, max (HBW) |
163 |
Chemical Composition of Alloy Steel U-Tubes (ASTM A213 T91)
| Element |
Composition (%) |
| Carbon (C) |
0.08-0.12 |
| Manganese (Mn) |
0.30-0.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) |
≤0.020 |
| Sulfur (S) |
≤0.010 |
| Silicon (Si) |
0.20-0.50 |
| Chromium (Cr) |
8.00-9.50 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) |
0.85-1.05 |
| Vanadium (V) |
0.18-0.25 |
| Niobium (Nb) |
0.06-0.10 |
Mechanical Properties of Alloy Steel U-Tubes (ASTM A213 T91)
| Property |
Value |
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) |
620 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) |
440 |
| Elongation, min (%) |
20 |
| Hardness, max (HBW) |
250 |
FAQs
Engineered to meet diverse industrial needs with robust materials and versatile designs.
Alloy Steel U-Tubes are seamless or welded tubes made from alloy steel, bent into a U-shape for heat exchangers and boilers, offering high strength and corrosion resistance.
They are used in heat exchangers, boilers, superheaters, and condensers in petrochemical, power generation, oil and gas, and chemical industries.
Made from alloy steel (e.g., ASTM A213 T11, T91) with 1-9% chromium and 0.5-1% molybdenum, often with coatings like 3LPE or passivation for enhanced corrosion resistance.
Chemical Composition of ASTM A213 T11 & T91 (Unit: %)
| Element |
ASTM A213 T11 |
ASTM A213 T91 |
| Carbon (C) |
0.05-0.15 |
0.08-0.12 |
| Manganese (Mn) |
0.30-0.60 |
0.30-0.60 |
| Phosphorus (P) |
≤0.025 |
≤0.020 |
| Sulfur (S) |
≤0.025 |
≤0.010 |
| Silicon (Si) |
0.50-1.00 |
0.20-0.50 |
| Chromium (Cr) |
1.00-1.50 |
8.00-9.50 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) |
0.44-0.65 |
0.85-1.05 |
| Vanadium (V) |
- |
0.18-0.25 |
| Niobium (Nb) |
- |
0.06-0.10 |
Mechanical Properties of ASTM A213 T11 & T91
| Standard & Grade |
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
Yield Strength (MPa) |
Elongation (%) |
Hardness (HBW) |
| ASTM A213 T11 |
≥415 |
≥205 |
≥30 |
≤163 |
| ASTM A213 T91 |
≥620 |
≥440 |
≥20 |
≤250 |
Outer diameters range from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses from 0.8mm to 6mm, with bend radii of 1.5D to 1500mm. Tolerances comply with ASTM A450/A450M and TEMA standards.
Produced via cold-drawing or hot-rolling, followed by mandrel bending and heat treatment (stress relief at 650-720°C or normalizing at 850-950°C) to enhance properties.
Tests include hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and hardness tests to ensure compliance with ASTM A450/A450M and TEMA standards.
Installed in heat exchanger or boiler tube sheets with welded or expanded ends, with capped ends to prevent contamination during transport.
Alloy Steel U-Tubes offer higher strength and creep resistance at a lower cost than stainless steel, but have less corrosion resistance in highly corrosive environments.