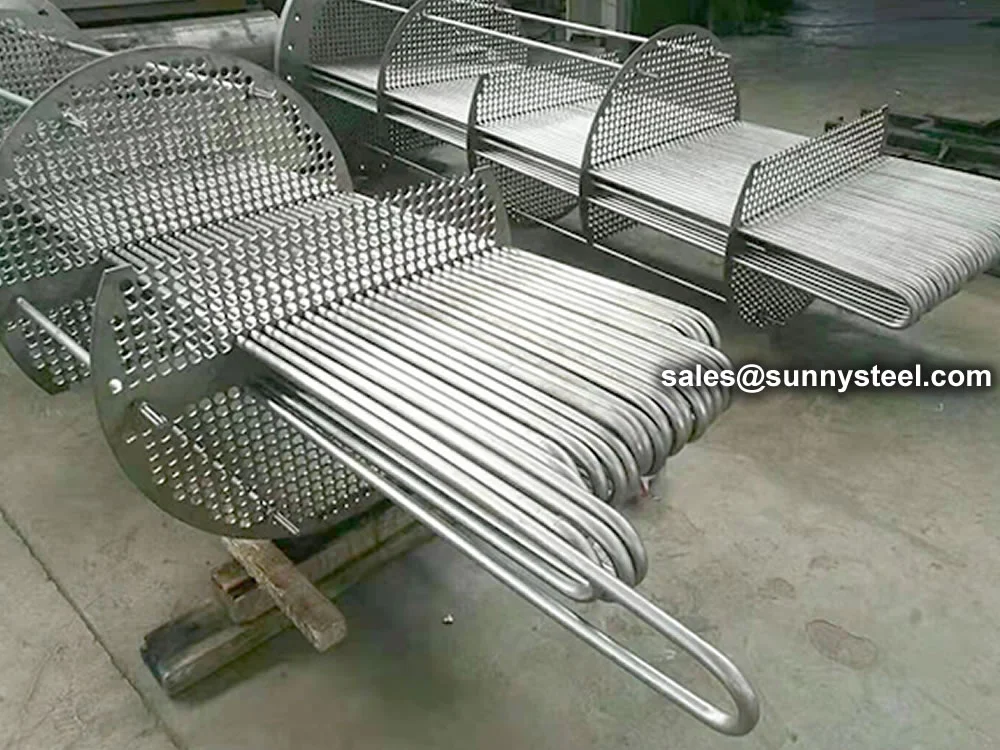
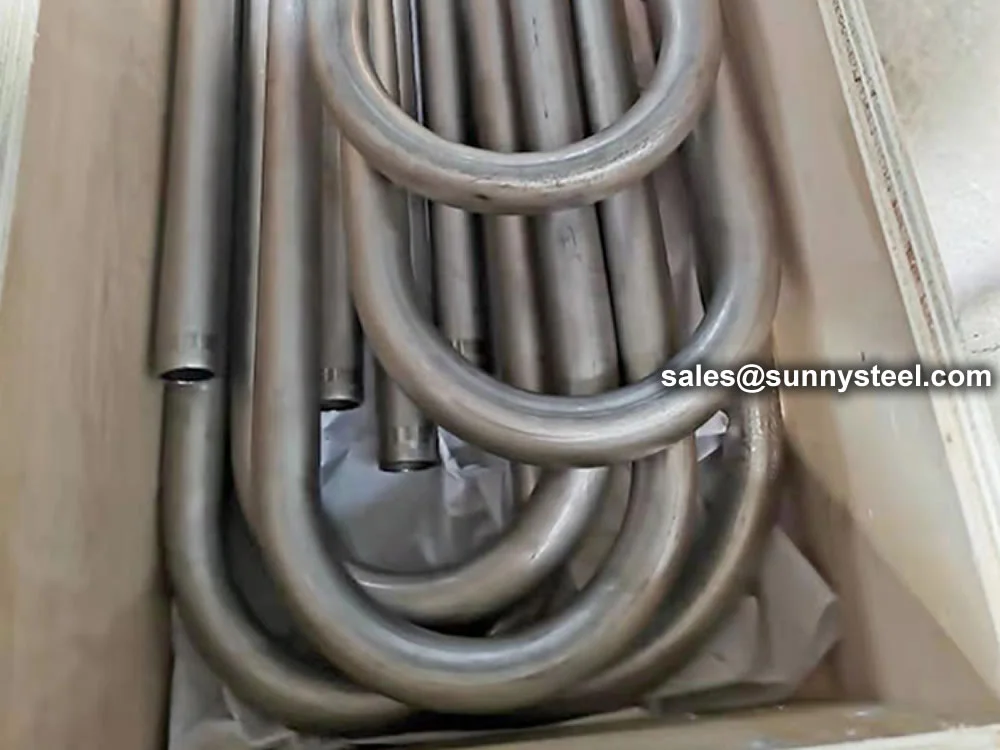
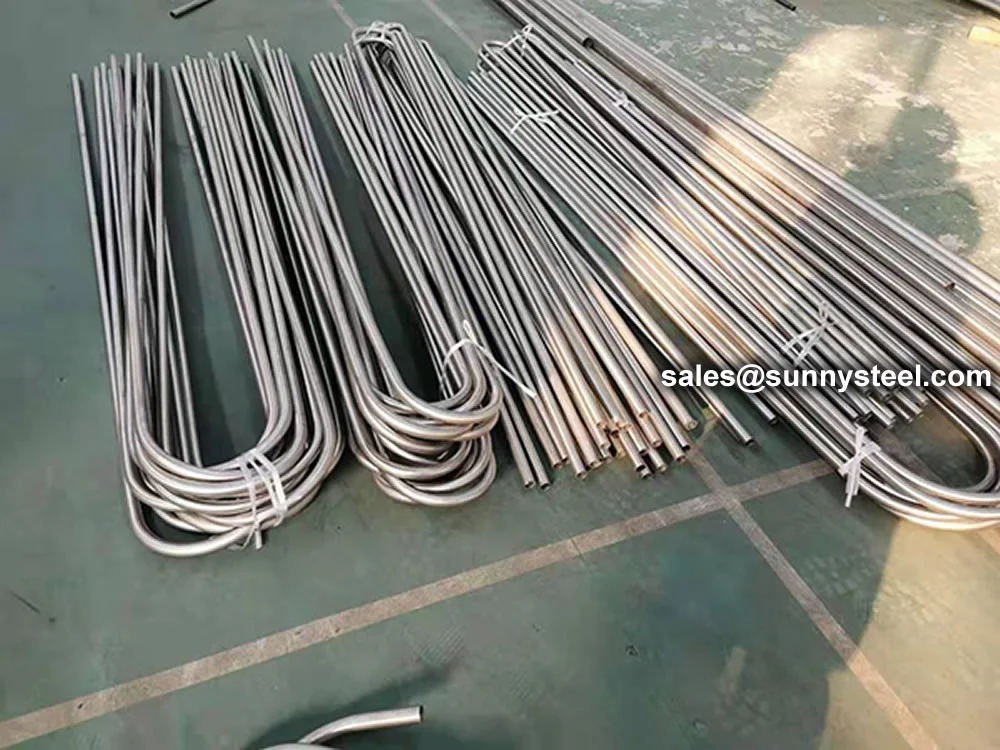
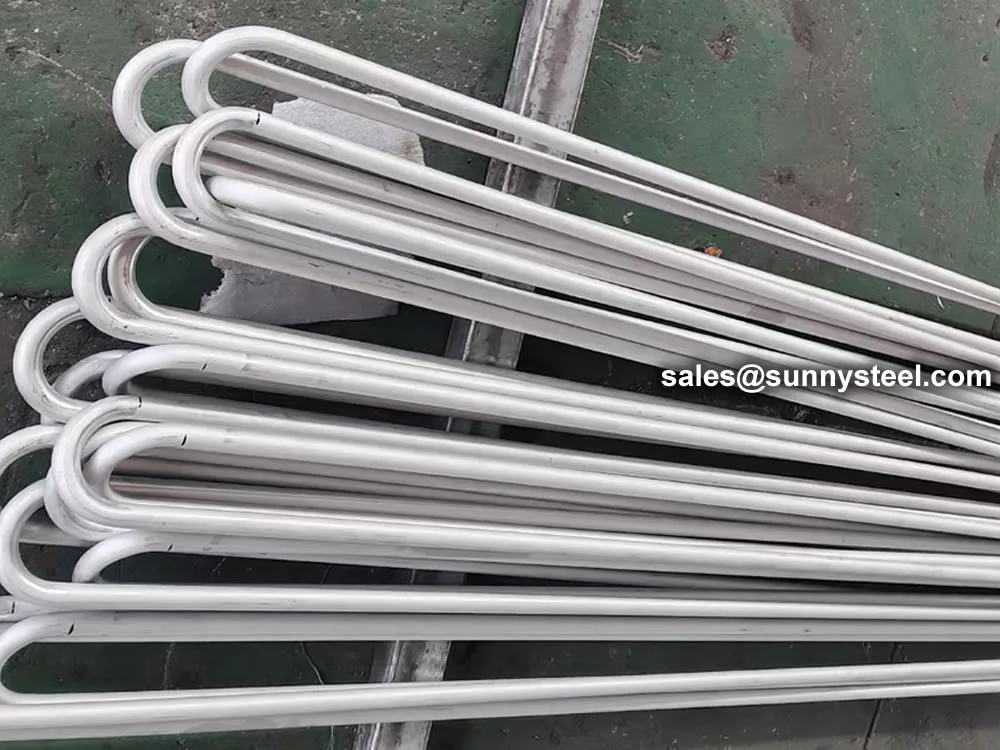
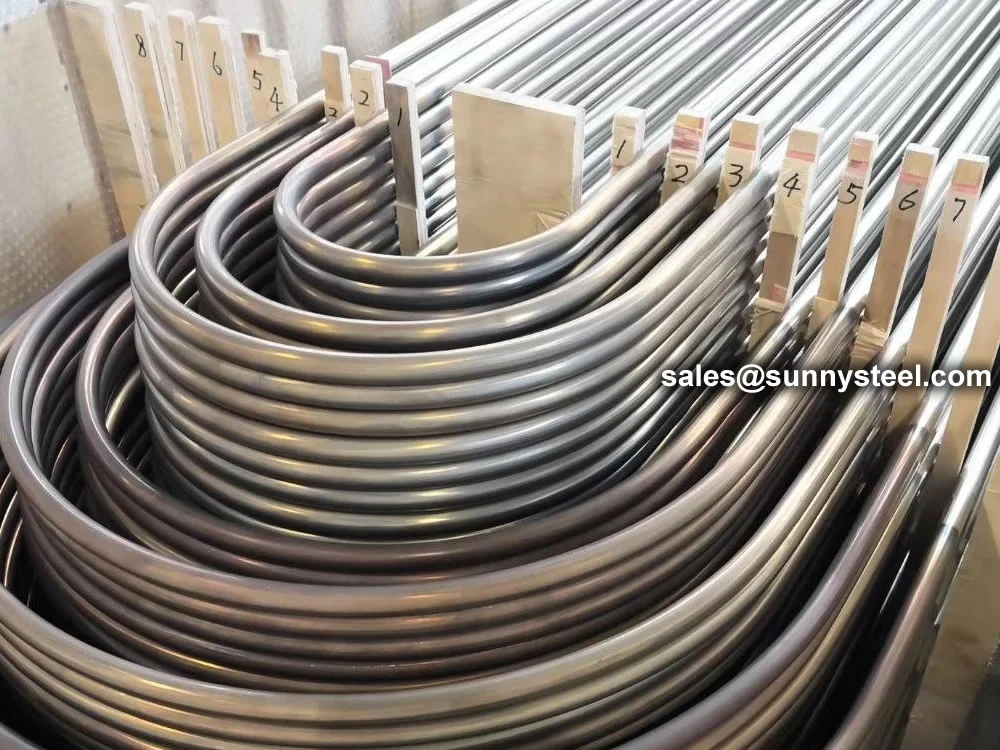
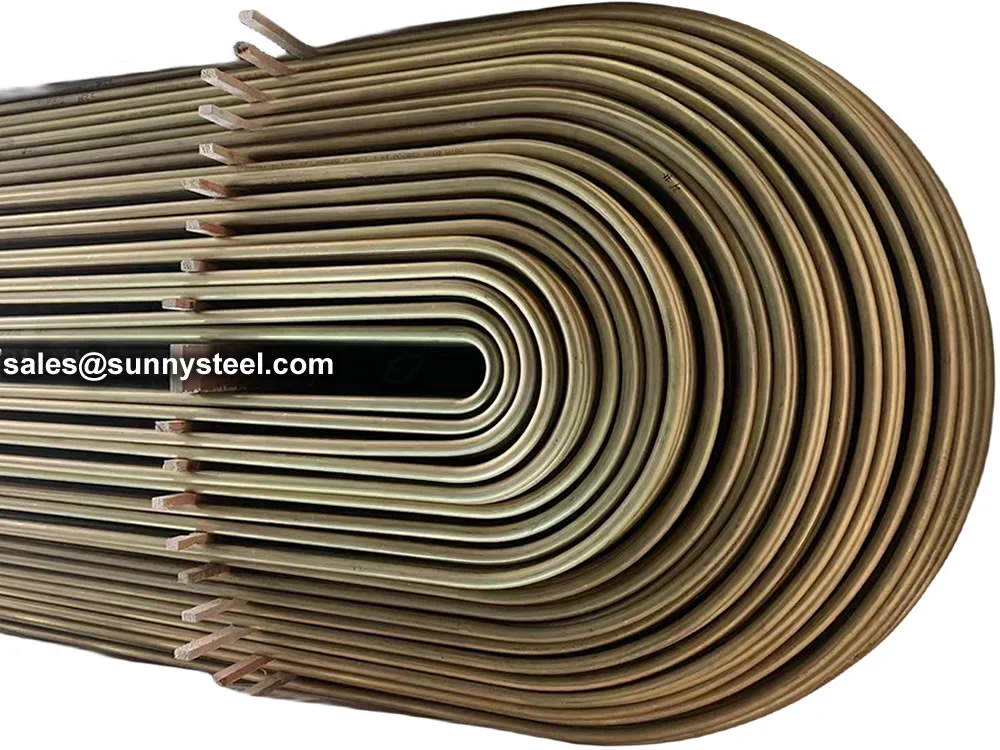
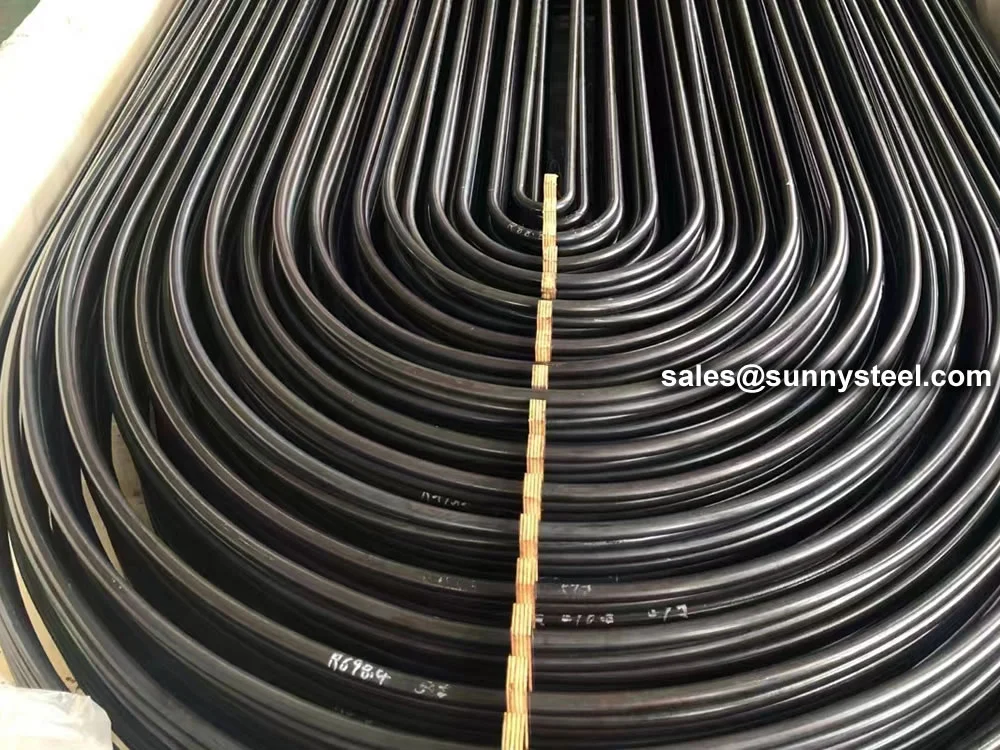
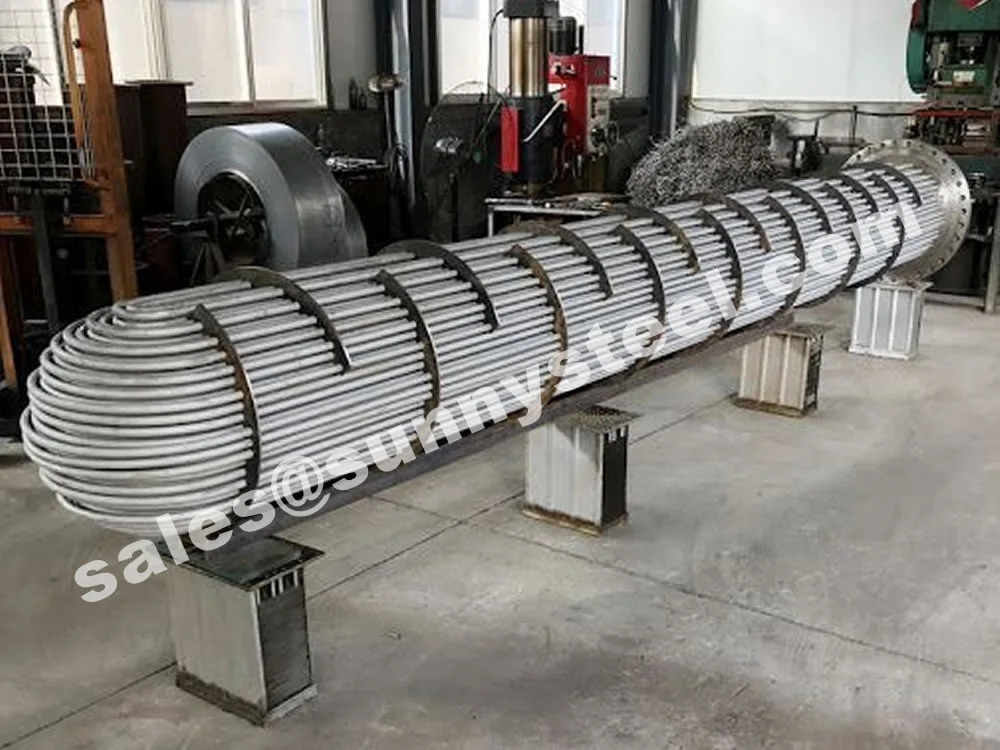
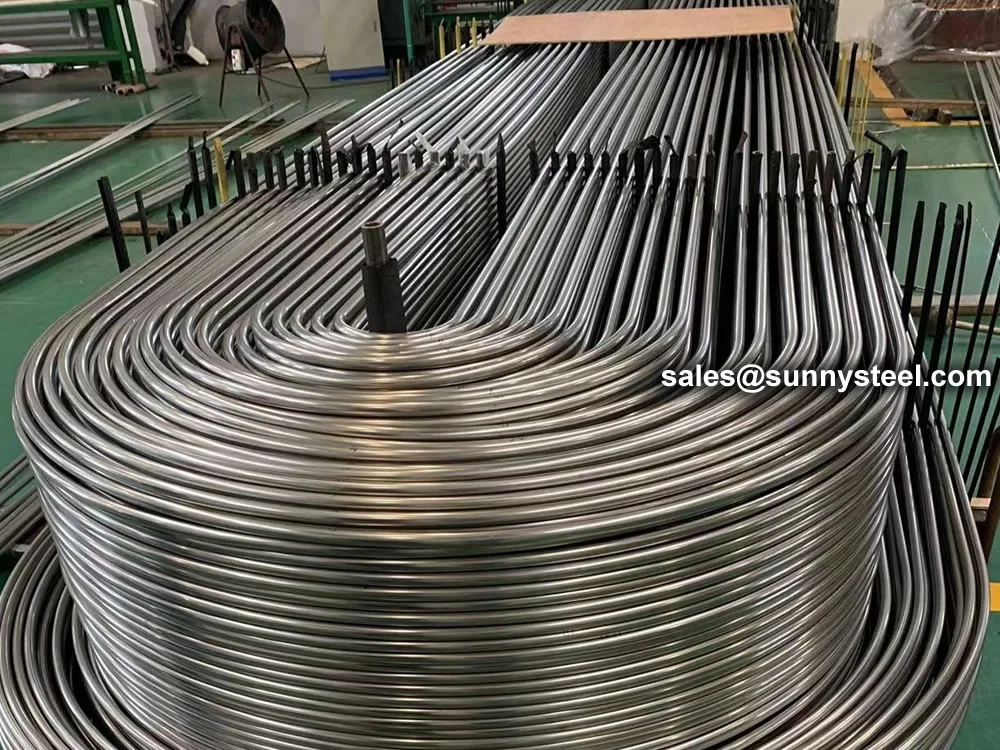
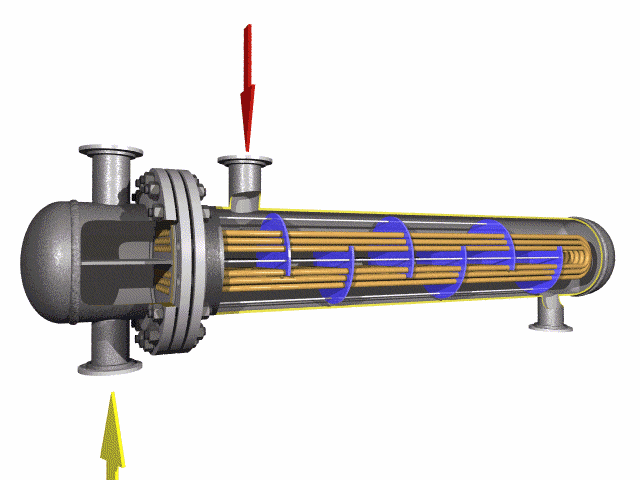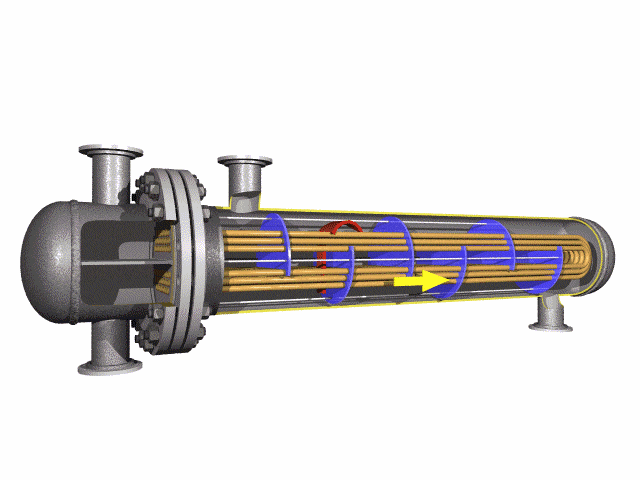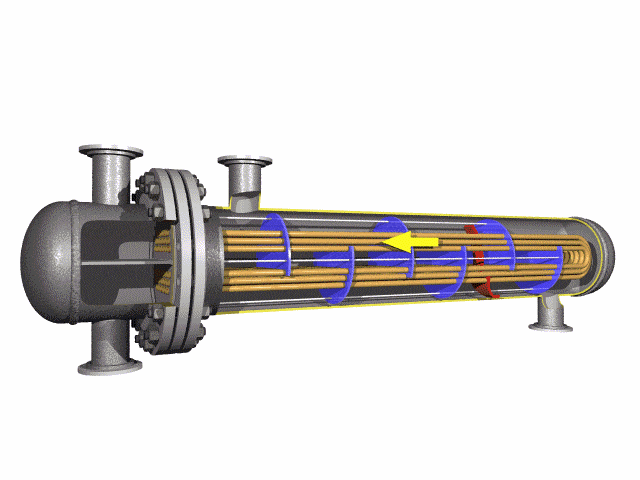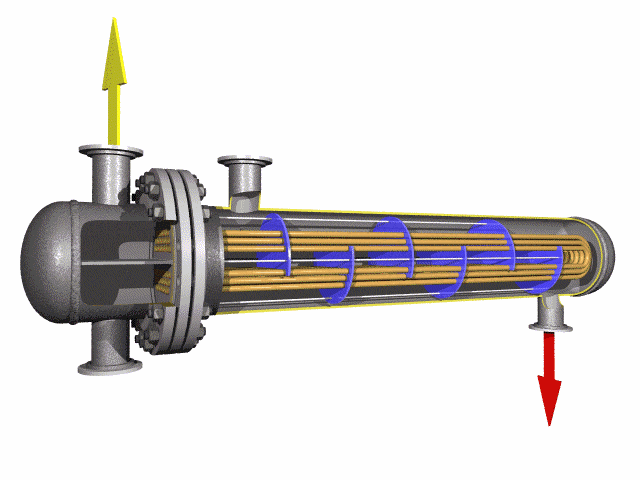
Titanium Alloy U-Bent Tubes are seamless or welded tubes made from titanium alloys
(e.g., Grades 2, 5, 9) bent into a U-shape for use in heat exchanger tubes and boiler
tubes. Conforming to standards like ASTM B338 and ASME SB338, these tubes are designed for
high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosive environments in industries such as aerospace, marine, chemical
processing, and power generation. Their exceptional corrosion resistance, lightweight
tubing properties, and ability to act as a thermal expansion absorber ensure
pipeline durability in demanding applications.
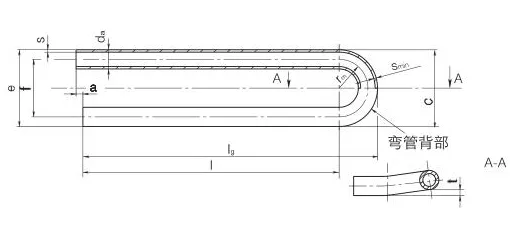
Manufactured via cold-working methods, Titanium Alloy U-Bent Tubes feature outer diameters from
9.53mm to 38.1mm, wall thicknesses from 0.7mm to 5mm, and bend radii from 1.5D to 1500mm, customizable per client
specifications. Post-bending heat treatments, such as stress relief annealing at 540-650°C, optimize mechanical
properties and prevent cracking. Surface treatments like pickling or polishing enhance corrosion
resistance, and plastic caps protect tube ends during transport. The alloy’s low density (4.51 g/cm³)
and high strength make it ideal for weight-sensitive applications.
These tubes undergo rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and ultrasonic
tests, to comply with ASTM B338 and TEMA standards. With tensile strengths ranging from 345 MPa (Grade 2) to 860 MPa
(Grade 5) and yield strengths from 275 MPa to 550 MPa, they are engineered for temperatures up to 600°C and
pressures up to 10 MPa. The U-bend design minimizes thermal stress, eliminates expansion joints, and reduces
installation costs, making them ideal for compact heat exchanger systems in corrosive environments like seawater or
chemical fluids.
Titanium alloys, such as Grade 2 (commercially pure) and Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), offer a high strength-to-weight ratio
and excellent resistance to seawater, acids, and chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking. Compared to stainless
steel, titanium alloys provide superior corrosion resistance in marine and chemical applications,
while their biocompatibility makes them suitable for medical and food processing equipment. These tubes are ideal
for heat exchangers, condensers, evaporators, and intercoolers in industries requiring lightweight
tubing with robust performance.
Addressing challenges like pipeline wear, corrosion, and thermal stress, Titanium Alloy U-Bent
Tubes provide a reliable solution for engineers seeking durable heat exchanger tubes.
Their high strength, low thermal expansion, and long-term durability make them a preferred choice for critical
applications in extreme environments, ensuring efficiency and minimal maintenance
Advantages of Titanium Alloy U Bent Tubes
Titanium U-bend tubes are widely used in boilers, condensers, heat exchangers, coolers,
and critical process equipment across industries including oil & gas, chemical, power,
steel, sugar, and renewable energy plants.
Corrosion Resistance
Outstanding resistance to seawater and chemical corrosion,
ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Titanium alloys deliver excellent mechanical strength
while remaining significantly lighter than steel.
Lightweight
Reduces overall equipment weight, improving handling and
efficiency in transport and installation.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
U-bend design increases surface area, enhancing heat transfer performance
for critical applications in power and process industries.
Longevity
Exceptional fatigue and wear resistance ensures extended
service life and reduced maintenance downtime.
Chemical Composition of Titanium Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM B338 Grade 2)
| Element |
Composition (%) |
| Titanium (Ti) |
Balance |
| Iron (Fe) |
≤0.30 |
| Oxygen (O) |
≤0.25 |
| Carbon (C) |
≤0.08 |
| Nitrogen (N) |
≤0.03 |
| Hydrogen (H) |
≤0.015 |
Mechanical Properties of Titanium Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM B338 Grade 2)
| Property |
Value |
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) |
345 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) |
275 |
| Elongation, min (%) |
20 |
| Hardness, max (HBW) |
160 |
Chemical Composition of Titanium Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM B338 Grade 5)
| Element |
Composition (%) |
| Titanium (Ti) |
Balance |
| Aluminum (Al) |
5.5-6.75 |
| Vanadium (V) |
3.5-4.5 |
| Iron (Fe) |
≤0.40 |
| Oxygen (O) |
≤0.20 |
| Carbon (C) |
≤0.08 |
| Nitrogen (N) |
≤0.05 |
| Hydrogen (H) |
≤0.015 |
Mechanical Properties of Titanium Alloy U-Bent Tubes (ASTM B338 Grade 5)
| Property |
Value |
| Tensile Strength, min (MPa) |
860 |
| Yield Strength, min (MPa) |
550 |
| Elongation, min (%) |
10 |
| Hardness, max (HBW) |
334 |
FAQs
Engineered to meet diverse industrial needs with robust materials and versatile designs.
Titanium Alloy U-Bent Tubes are seamless or welded tubes made from titanium alloys (e.g., Grades 2, 5) bent into a U-shape for heat exchangers and boilers, offering superior corrosion resistance and lightweight properties.
Used in heat exchangers, condensers, evaporators, and intercoolers in aerospace, marine, chemical processing, and power generation industries.
Titanium alloys offer excellent corrosion resistance to seawater, acids, and chlorides, high strength-to-weight ratio, and biocompatibility, ideal for marine, chemical, and medical applications.
For Grade 2:
- Titanium (Ti): Balance
- Iron (Fe): ≤0.30%
- Oxygen (O): ≤0.25%
- Carbon (C): ≤0.08%
- Nitrogen (N): ≤0.03%
- Hydrogen (H): ≤0.015%
For Grade 5:
- Titanium (Ti): Balance
- Aluminum (Al): 5.5-6.75%
- Vanadium (V): 3.5-4.5%
- Iron (Fe): ≤0.40%
- Oxygen (O): ≤0.20%
- Carbon (C): ≤0.08%
- Nitrogen (N): ≤0.05%
- Hydrogen (H): ≤0.015%
For Grade 2:
- Tensile Strength: ≥345 MPa
- Yield Strength: ≥275 MPa
- Elongation: ≥20%
- Hardness: ≤160 HBW
For Grade 5:
- Tensile Strength: ≥860 MPa
- Yield Strength: ≥550 MPa
- Elongation: ≥10%
- Hardness: ≤334 HBW
Outer diameters range from 9.53mm to 38.1mm, wall thicknesses from 0.7mm to 5mm, with bend radii of 1.5D to 1500mm. Tolerances comply with ASTM B338 and TEMA standards.
Produced via cold-working, followed by mandrel bending and stress relief annealing at 540-650°C to enhance properties and prevent cracking.
Tests include hydrostatic, eddy current, flaring, flattening, and ultrasonic tests to ensure compliance with ASTM B338 and TEMA standards.
Installed in heat exchanger or boiler tube sheets with welded or expanded ends, using gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) with inert gas shielding to prevent oxidation.
Titanium alloy U-bent tubes offer superior corrosion resistance in seawater and chemical environments, and a higher strength-to-weight ratio, but are more expensive than stainless steel.