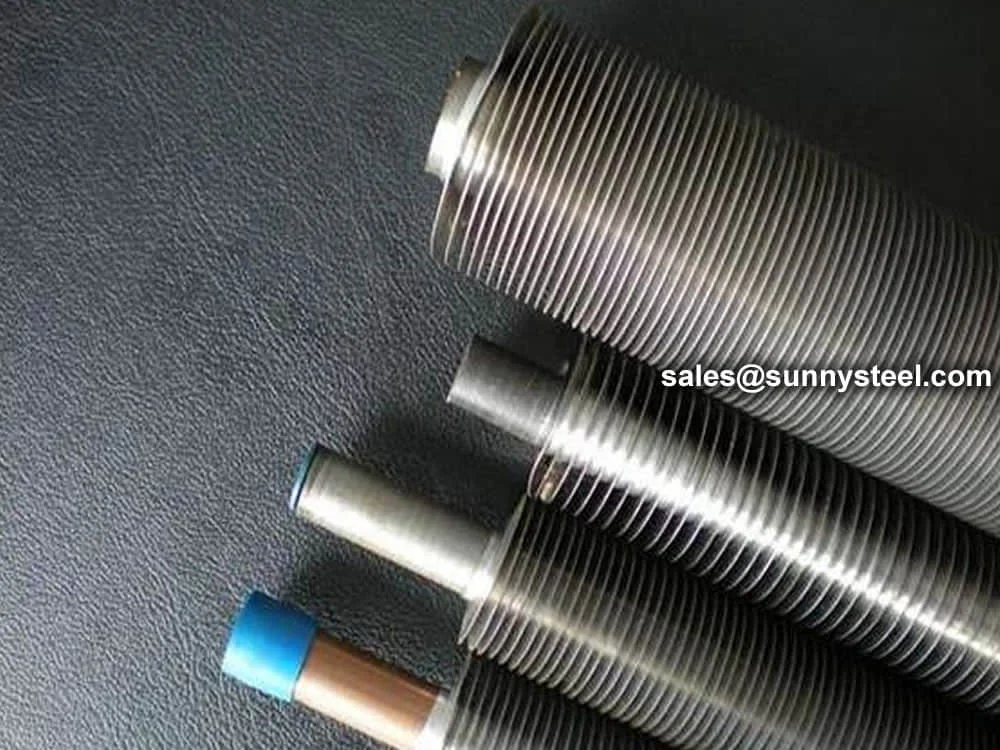

L/LL/KL Finned Tube
High-efficiency Finned Tubing For Enhanced Thermal Transfer
L, ll, and kl finned tubes optimize heat transfer in exchangers with robust, corrosion-resistant designs.

High-efficiency Finned Tubing For Enhanced Thermal Transfer
L, ll, and kl finned tubes optimize heat transfer in exchangers with robust, corrosion-resistant designs.
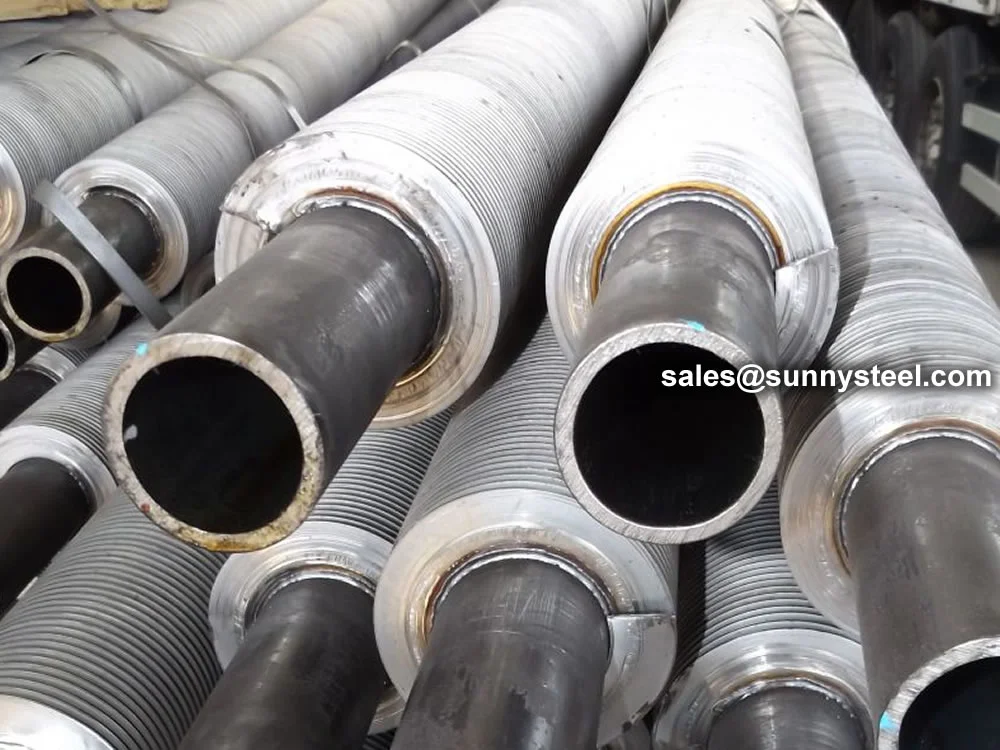
L, LL, and KL Finned Tubes are specialized finned tubing solutions designed to enhance thermal transfer in heat exchanger fins by increasing surface area. These tubes are widely used in petrochemical, power generation, HVAC, and chemical processing industries for applications like air-cooled exchangers, condensers, and boilers. Conforming to standards such as ASTM A179, A213, and ASME SB338, they offer excellent corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for demanding environments requiring efficient heat dissipation.
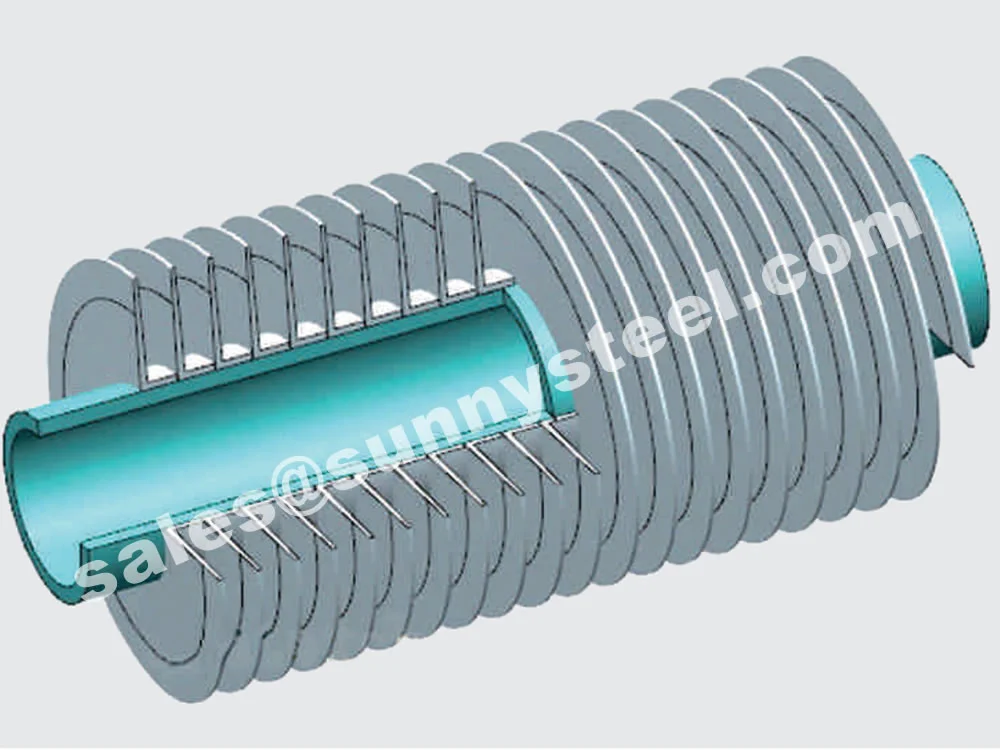
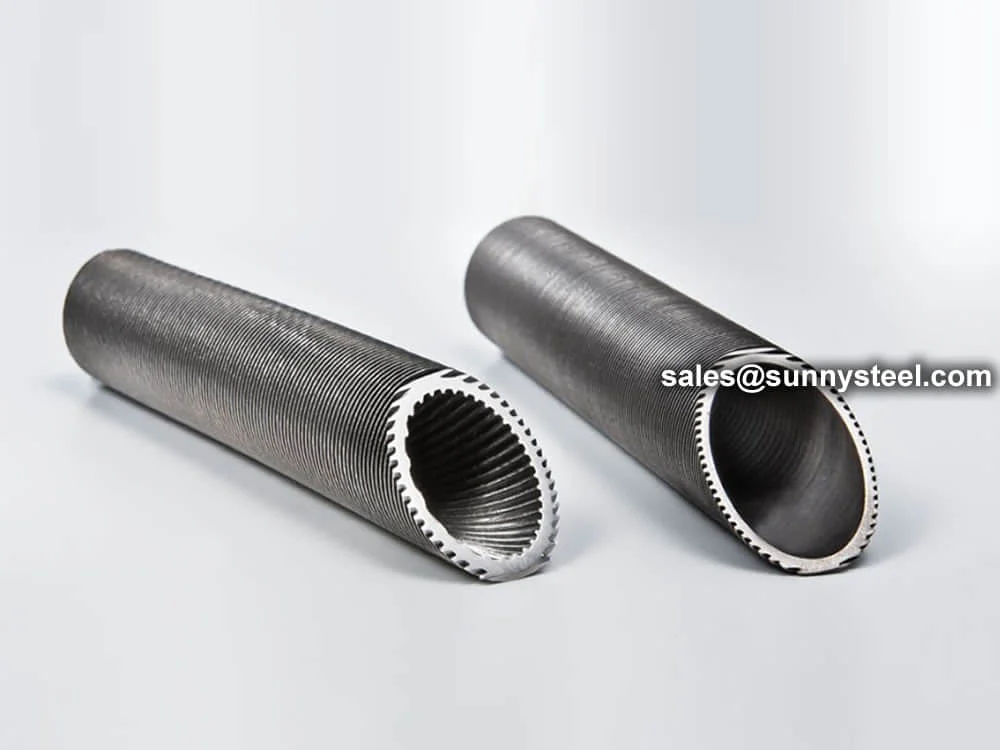
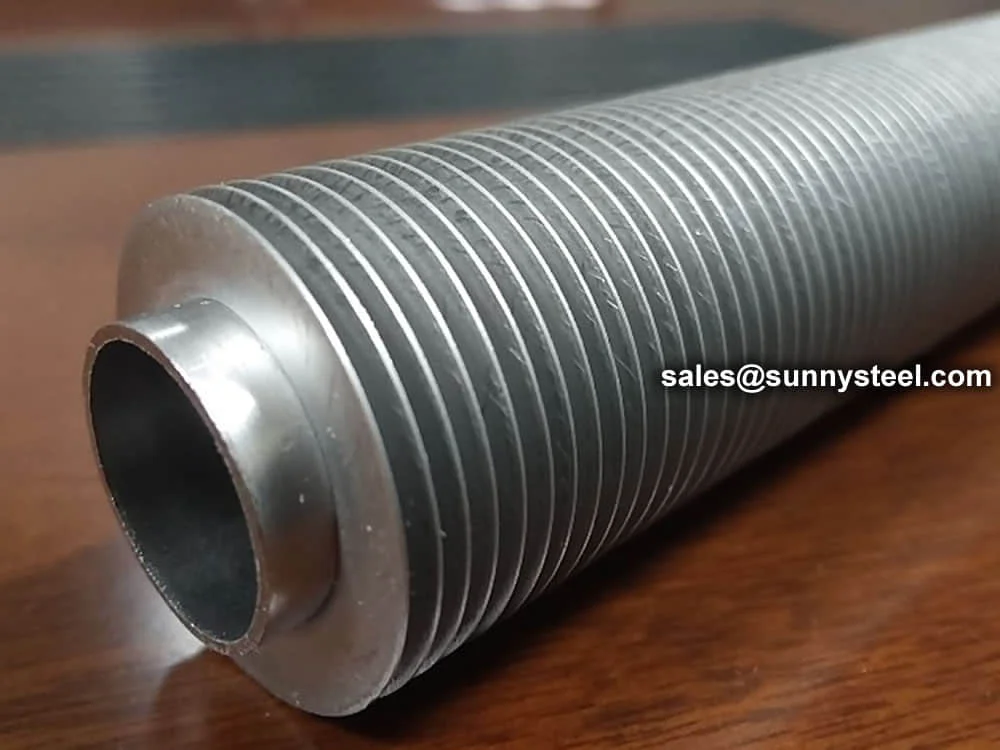
L Finned Tubes feature fins formed by wrapping a metal strip in an L-shape around the base tube, providing a cost-effective solution for temperatures up to 175°C. LL Finned Tubes have overlapping L-fins, offering increased fin contact area and improved heat transfer for applications up to 200°C. KL Finned Tubes incorporate a knurled base tube surface, enhancing fin-to-tube bonding for superior mechanical strength and heat transfer efficiency, suitable for temperatures up to 260°C. Available in base tube sizes from 1/2" to 2" (DN15 to DN50) with fin heights of 8-15mm and fin densities of 7-11 fins per inch, these tubes can be customized for straight or U-bend configurations.
Manufactured using materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, copper, or aluminum, L, LL, and KL Finned Tubes are produced through processes like extrusion or helical winding, followed by rigorous testing (hydrostatic, eddy current, and thermal performance) to ensure compliance with ASTM and TEMA standards. Surface treatments such as galvanization, epoxy coating, or passivation enhance corrosion resistance, protecting against harsh conditions like seawater or acidic fluids. These tubes achieve 5-10 times higher heat transfer rates than plain tubes, making them ideal for compact thermal transfer tubes in air-cooled systems.
The design of L, LL, and KL Finned Tubes addresses challenges like low air-side heat transfer coefficients, enabling efficient cooling in heat exchanger fins. L-finned tubes are cost-effective for general-purpose cooling, LL-finned tubes provide enhanced efficiency for moderate temperatures, and KL-finned tubes excel in high-vibration or high-temperature environments due to their robust fin bonding. These tubes are commonly used in boiler economizers, air preheaters, and refrigeration systems, where their compact design reduces material costs and space requirements while maintaining high performance.
With excellent resistance to fouling and easy maintenance, L, LL, and KL Finned Tubes ensure long-term reliability in applications like petrochemical refineries, power plant condensers, and marine desalination systems. Their ability to handle high-pressure fluids and resist corrosion makes them a preferred choice for engineers seeking durable and efficient finned tubing solutions for advanced heat transfer needs.
Across all wrap-around fin tubes, the fins are secured by spiral tension, requiring tight mechanical bonding, brazing, or similar methods at the ends. An additional advantage is the possibility of using a thinner base tube, which helps reduce production costs.
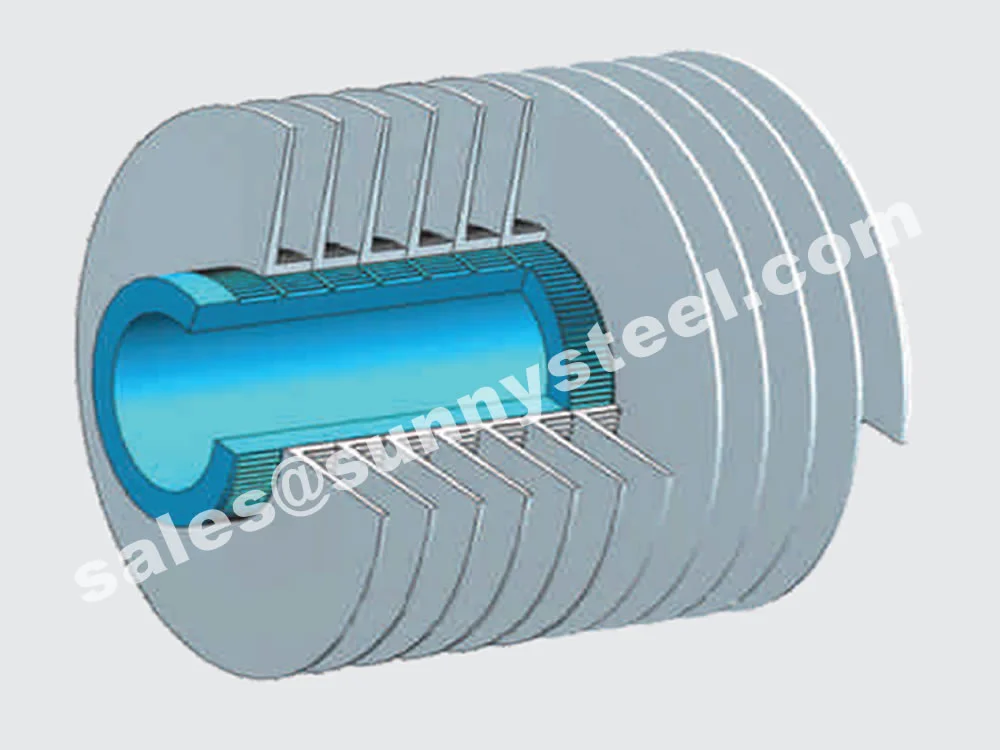
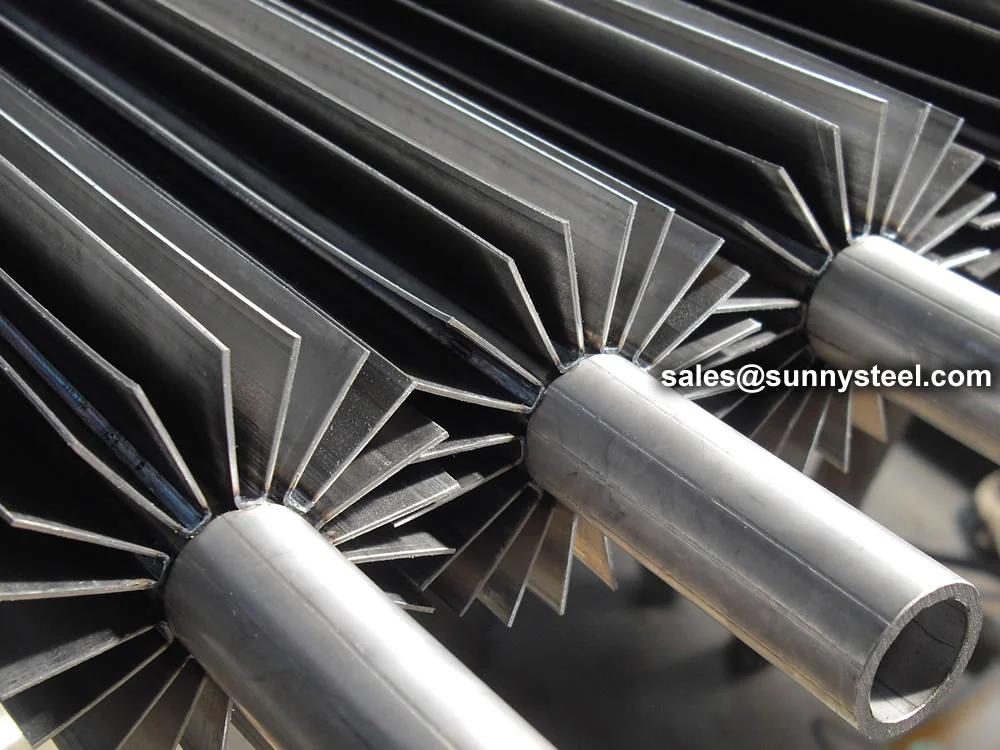
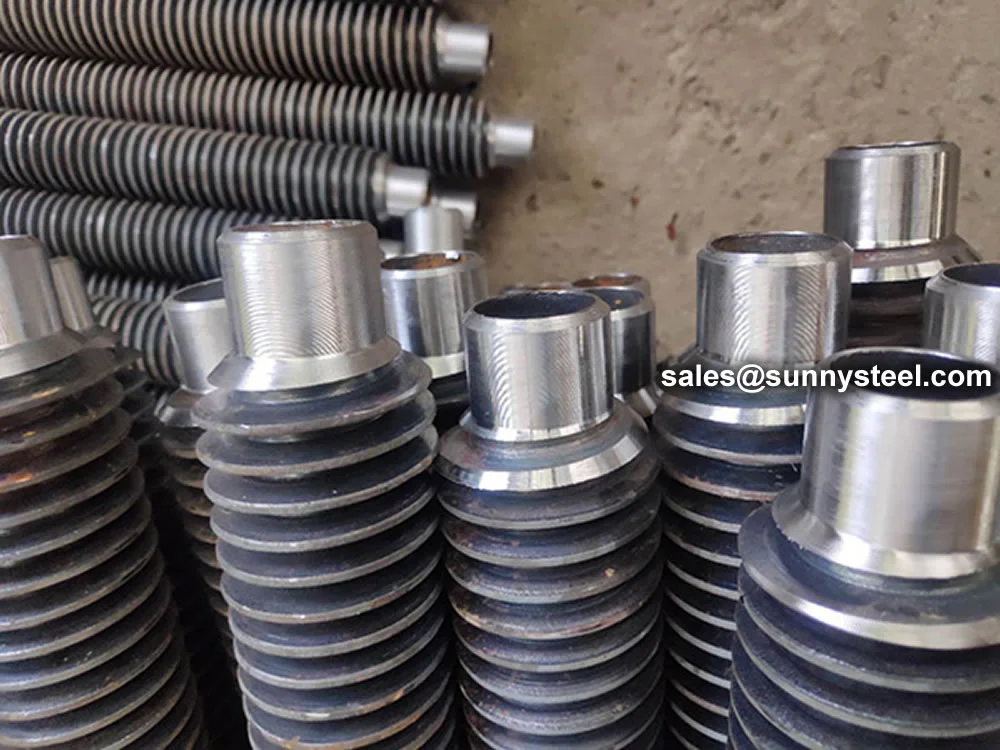
Features a knurled L-shape base fin, fixed by pressure on the tube. Designed to maximize surface contact between fin and tube, ensuring a secure bond and efficient heat transfer.
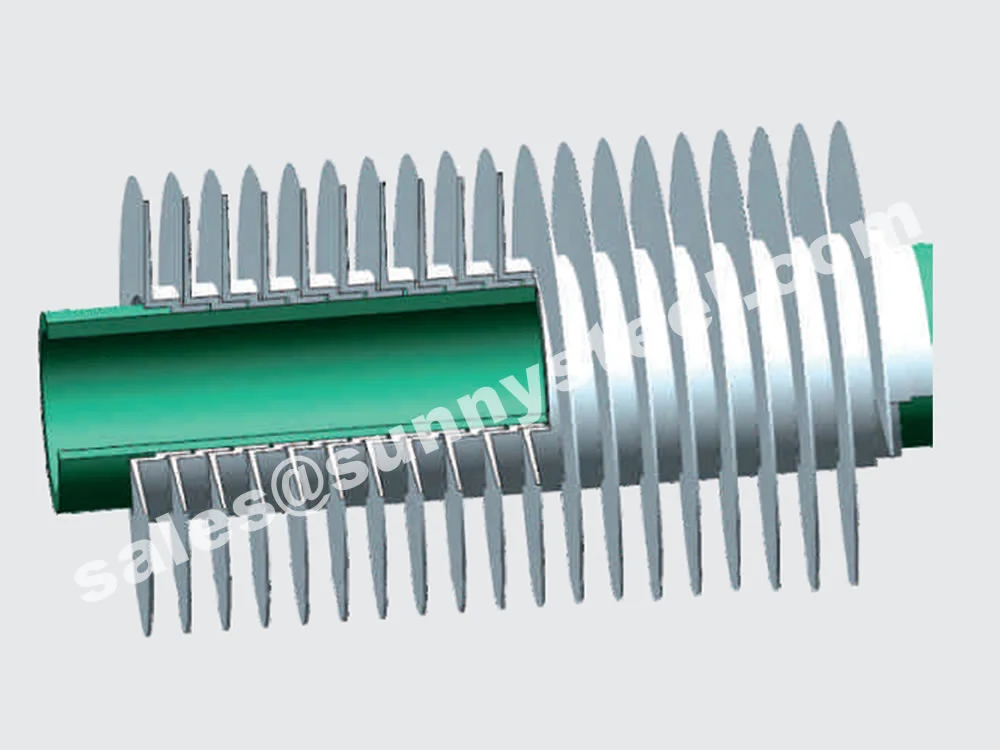
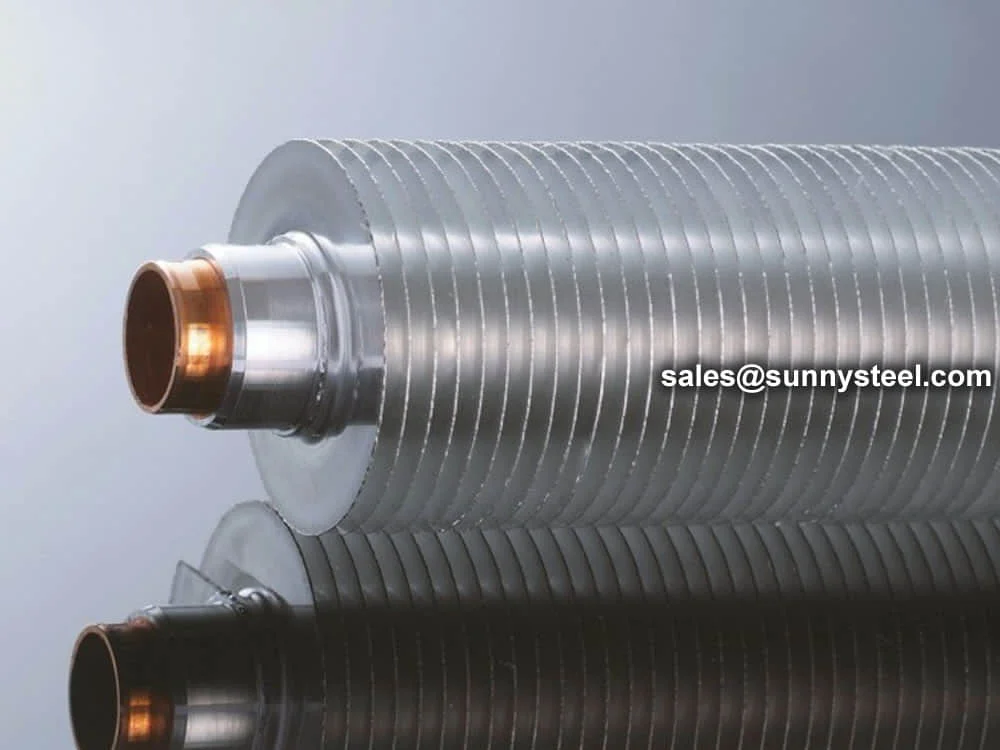
The pre-formed LL foot overlaps one onto another, offering enhanced base tube protection and increased thermal contact area. Its flat fins also minimize resistance to air/gas flow and reduce fouling.
| Sr. No | Particulars | Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base Tube Material | Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Titanium, Copper, Duplex Stainless Steel, Inconel etc. (all material in the theoretical limit) |
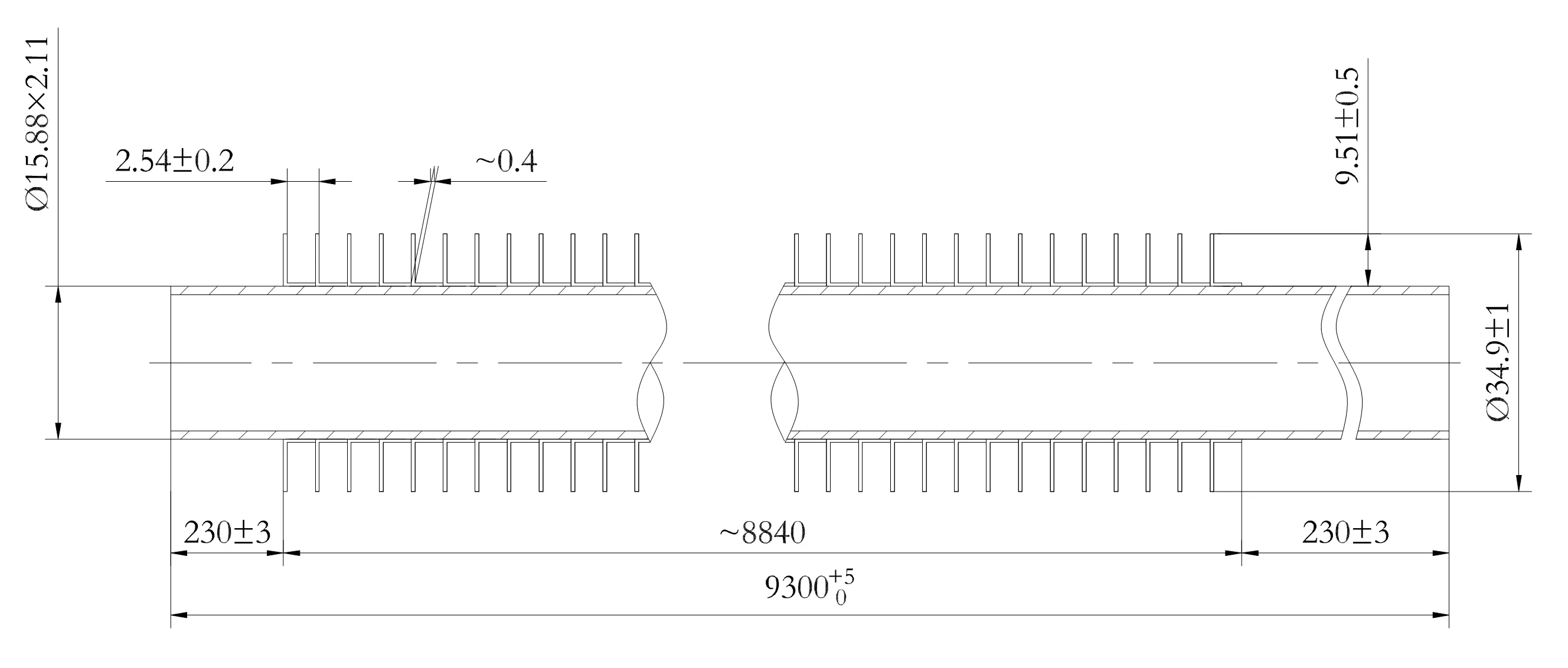
| 2 | Base Tube Diameter | 12.70 mm to 38.10 mm |
| 3 | Base Tube Thickness | 1.25 mm and above |
| 4 | Base Tube Length | 500 mm (Min) to 15000 mm (Max) |
| 5 | Fin Material | Aluminum, Copper, Stainless Steel, etc. |
| 6 | Fin Thickness | 0.3 mm, 0.35 mm, 0.4 mm, 0.45 mm, 0.55 mm, 0.60 mm, 0.65 mm |
| 7 | Fin Density | 236 FPM (6 FPI) to 433 FPM (11 FPI) |
| 8 | Fin Height | 9.8 mm to 16.00 mm |
| 9 | Bare Ends | As per Client Requirement |
| 10 | Manufacturing Capacity | 5,00,000 Meter Per Annum |
We can supply material on an urgent delivery basis due to our large stock and relationships with raw material suppliers. We only use prime quality base tubes and aluminium material.
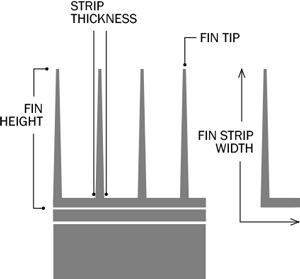
Also referred to as the 'L' foot fin tube or spirally wound fin tube, this design is achieved by wrapping the fin strip around the base tube. The fin base is shaped into an 'L', providing a strong grip and protection against atmospheric corrosion.
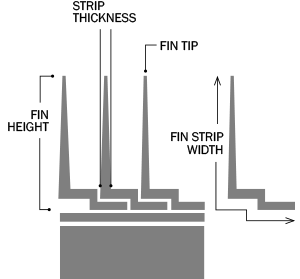
An enhancement of the L type fin tube, the 'LL' design overlaps the 'L' foot of each fin with the next, forming a double 'L' foot. This improves corrosion resistance and ensures a tighter, more durable bond between the fin and tube.
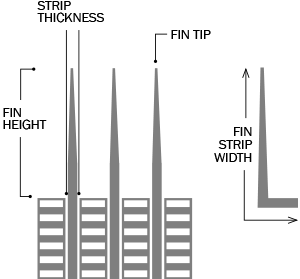
The most widely used wrap-around type, the KLM fin tube is manufactured like the 'L' type but with knurling of both the tube and fin base. This creates a secure mechanical bond and enhances thermal contact efficiency.

We offer you a broad portfolio of materials and can expand our offerings at any time to meet your specific needs regarding thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, or corrosion resistance.
For Aluminum L-Foot finned tubes, the fin material is aluminum, either 1100-0. The tube material is generally carbon steel, stainless steel, or brass; however the tube can be of any material.
For Welded Helical Solid and Welded Helical Serrated finned tubes, the fin and tube materials can be any combination that can be welded together using HIGH FREQUENCY WELDING process.
The materials chosen for a given application are a function of service temperature, corrosive environment, and/or erosive environment. Common tube materials used for our welded product lines include: carbon steel, carbon moly, chrome moly, stainless steel, Inconel, and Incoloy. Common fin materials include: carbon steel; stainless steels of types 304, 310, 316, 321, 409, and 410; Nickel 200, and Inconel.
We offer you a broad portfolio of materials and can expand our offering at any time to meet your specific needs regarding thermal conductivity, mechanical properties, or corrosion resistance.
| Material | Grade |
|---|---|
| Carbon Steel Tubes | A179, A192, SA210 Gr A1/C, A106 Gr B, A333 Gr3/Gr6/Gr8, A334 Gr3/Gr6/Gr8, 09CrCuSb, DIN 17175 St35.8/St45.8, EN 10216 P195/P235/P265, GB/T3087 Gr10/Gr20, GB/T5310 20G/20MnG |
| Alloy Steel Tubes | A209 T1/T1a, A213 T2/T5/T9/T11/T12/T22/T91, A335 P2/P5/P9/P11/P12/P22/P91, EN 10216-2 13CrMo4-5/10CrMo9-10/15NiCuMoNb5-6-4 |
| Stainless Steel Tubes | TP304/304L, TP316/TP316L, TP310/310S, TP347/TP347H |
| Copper Tubes | UNS12200/UNS14200/UNS70600, CuNi70/30, CuNi 90/10 |
| Titanium Tubes | B338 Gr 2 |
Our factory is equipped with professional technical research and design personnel who can provide product optimization design and services.

Quality is the foundation of an enterprise. We adopt advanced production equipment and experienced technical personnel, constantly improve product technology, strictly control every processing step, and strive to compete with first-class quality products.

Testing instrument


Hardness tester

Drawing Machine

Component analyzer
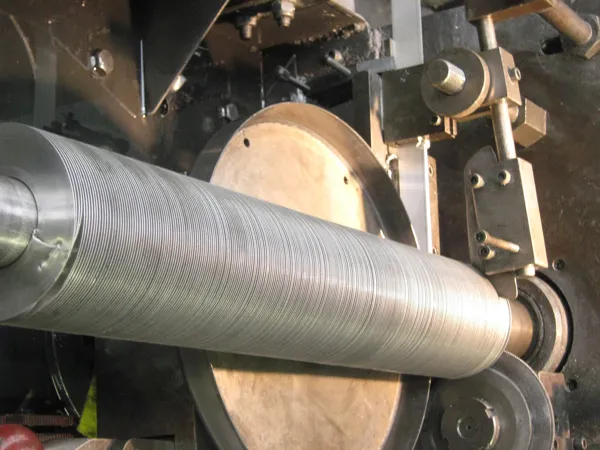

Aluminium KL finned tube

L LL KL G production line
Production equipments


Extrusion equipment

Fin tube bending
Finned tubes are available in many types and configurations. Below is a detailed classification based on fabrication process, fin geometry, material, and applications.

Fin tubes are a type of heat exchanger used in many industries. They are made of aluminum cladded carbon steel and have brazed aluminum fins. The fins increase the surface area of the tubes, which allows them to transfer heat more efficiently. This makes them ideal for applications where high heat transfer rates are required.
Finned tubes are used in applications that involve the transfer of heat from a hot fluid to a colder fluid through a tube wall. They are used in condensers, coolers, and furnaces. The larger surface area means that fewer tubes are needed compared to the use of plain tubes.
The type of finned tube is chosen depending on the specific requirements of each process equipment unit. The fin type and combination of materials are chosen based on the specific requirements of each process equipment unit.
Finned tubes are used in applications where high heat transfer rates are required, such as in power plants and refrigeration systems. The fins increase the surface area of the tube, allowing for more efficient heat transfer between two fluids. This makes them an ideal solution for heat transfer applications where space is limited.
Finned tubes are used in condensers, coolers, and furnaces. The larger surface area means that fewer tubes are needed compared to the use of plain tubes. This can decrease the overall equipment size and can in the long-run decrease the cost of the project.
Finned tube heat exchangers can be used in a broad range of industries including oil & gas, power generation, marine and HVAC&R. They generally use air to cool or heat fluids such as air, water, oil or gas, or they can be used to capture or recover waste heat.
The biggest problem with using a finned tube heat exchanger is with the cleaning and maintenance of the outer surface of the tubes. Because of the fins, mechanical cleaning becomes very difficult and you would have to go for chemical cleaning.
Fin tubes are a type of heat exchanger that are used in many industries. They have a finned surface, which increases their surface area and allows them to transfer heat more efficiently. Finned tubes are typically used in two-phase heat transfer applications, such as condensation or evaporation.
Finned pipes are generally used for single-phase heat transfer applications. Both finned pipes
and finned tubes use fins to increase the surface area for heat transfer.
Finned tubes are used when the heat transfer coefficient on the outside of the tubes is
appreciably lower than that on the inside. They can reduce the equipment cost and also equipment
sizes.
There are several kinds of fin tubes, such as:
High fin tubes are better for applications where the temperature difference between two fluids is high. Low fin tubes are better for applications where the temperature difference is low.
High fin tubes are made of a metal tube surrounded by an aluminum or copper strip. The strip can be applied in different ways, including type L, type KL, type LL, type G (embedded), or type extruded. The higher the fin height, the more surface area and heat transfer capabilities.
Low fin tubes are made of a single material and have a smaller fin of about 1/16th of an inch. They are generally used in liquid to liquid or liquid to gas applications such as coolers, condensers, and chillers.
The profile of the fins has a significant effect on the performance of a finned tube heat exchanger. The larger the fins and the tighter the fin pitch, the more thermal conductivity is achieved.
Finned tubes are a series of tubes with fins on the outside. The fins increase the surface area for heat transfer, which increases the rate of heat exchange. Finned tubes are used in heat exchangers to transfer heat between hot and cold streams. The heat transfer rate depends on the temperature difference between the two fluids and the heat transfer coefficient between each of the fluids.
Finned tube heat exchangers are used in a variety of industries, including:
Finned tube heat exchangers can be used to:
Regular cleaning to prevent fouling, with coatings for corrosion resistance; inspect for wear in high-vibration areas.
Fin tubes are widely used in heat exchangers for industries such as petroleum, petrochemical, steel, power generation, and many more. Different fabrication technologies determine their cost, performance, and efficiency. Below are the main types of fin tube production methods.
Fabricated with punched single fins manually or mechanically placed on the base tube at a certain spacing.
Manual set: Relies on human force; easy to loosen.
Mechanical set: High pressure, stronger bonding, suitable for larger volumes, but noisy and less safe.
Hydraulic set: Quieter, safer, but higher cost and lower productivity.
Produced by winding a steel strip around the tube while applying high-frequency current (skin and proximity effects).
Heat brings the material to a plastic/melt state, ensuring strong bonding under pressure.
Advantages:
- High bonding strength
- Superior quality
- High automation & efficiency
- Widely used in waste heat recovery, power, metallurgy, oil & gas, and petrochemical industries
Made by extruding an outer aluminum or copper tube (muff) over a base tube. Rotating discs squeeze the fins
into a spiral in one operation.
Advantages:
- High production efficiency
- Strong fin-to-tube contact
- Low material cost
- High heat transfer performance
Available as single-metal (copper/aluminum) or bi-metal composite tubes.








Low fin tubes enhance heat transfer in compact hea...

Longitudinal finned tubes boost heat transfer effi...

Laser welded finned tubes enhance heat exchanger e...

Helical solid finned tubes enhance heat transfer e...

High fin tubes maximize heat transfer efficiency i...

Integral low fin tubes optimize heat transfer in c...