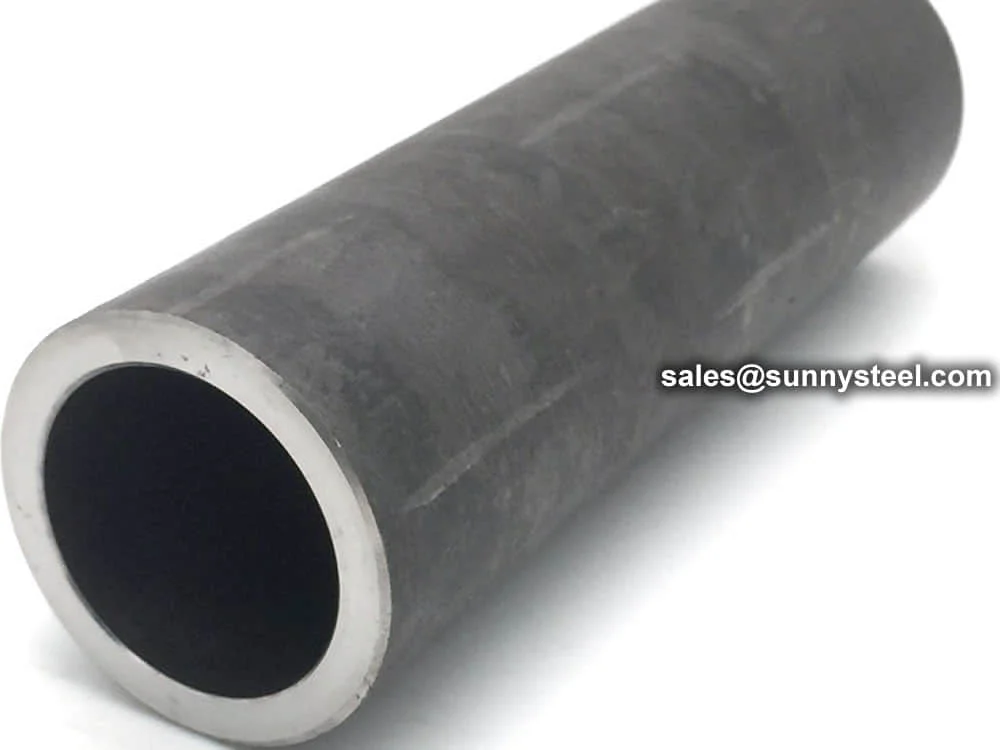

Austenitic Stainless Steel
Corrosion Resistance
Austenitic stainless steel is a type of stainless steel that is widely used in various industrial applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and versatility.

Corrosion Resistance
Austenitic stainless steel is a type of stainless steel that is widely used in various industrial applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and versatility.
Austenitic stainless steel tubes are non-magnetic, face-centered cubic alloys renowned for their outstanding corrosion resistant austenitic pipes and formability, making them a cornerstone for boiler tube erosion protection in harsh industrial settings. With high nickel (8-25%) and chromium (16-26%) compositions, grades like 304, 316, and 310S conform to ASTM A213, A249, and ASME SA213 standards, forming a self-healing passive oxide layer that excels against uniform corrosion, pitting, and stress corrosion cracking in chloride-rich or acidic environments. These high temperature austenitic tubing options are vital for seamless or welded applications in superheaters, economizers, and feedwater heaters, where they withstand cyclic thermal loads up to 800°C and pressures exceeding 10 MPa, preventing tube thinning from fly ash erosion and sulfidation in coal-fired boilers.
Fabricated through cold pilgering or electric resistance welding followed by solution annealing at 1010-1120°C, austenitic stainless steel tubes achieve optimal ductility and weldability, with low-carbon variants like 304L and 316L minimizing sensitization risks during TIG or GTAW joining. Their austenitic structure delivers superior creep resistance and thermal conductivity (14-17 W/m·K), outperforming ferritic grades in fluctuating temperature cycles typical of stainless steel corrosion shields for furnace components and petrochemical reformers. Available in outer diameters from 6.35mm to 50.8mm, wall thicknesses of 0.5-4mm, and lengths up to 20m, these tubes support U-bending with tight radii (3D) and finned enhancements for 20-40% boosted heat transfer rates, ensuring efficient performance in compact shell-and-tube designs.
In boiler tube erosion protection, austenitic grades like 310S provide exceptional scaling resistance in sulfurous flue gases, with erosion shields fabricated from 304 overlaying carbon steel tubes to extend life by 3-5x in high-velocity ash flows. Rigorous quality assurance includes eddy current testing, hydrostatic verification up to 15 MPa, and intergranular corrosion tests per ASTM A262, yielding minimum tensile strengths of 485-620 MPa and elongations of 35-50% for fatigue endurance under vibro-acoustic stresses. Surface treatments range from annealed-pickled to electropolished (Ra
Relative to martensitic steels, corrosion resistant austenitic pipes offer better low-temperature toughness (down to -196°C) and higher work-hardening rates for tube expansion in fixed-tube-sheet exchangers, while duplex hybrids like 2205 combine austenitic corrosion resistance with ferritic strength for sour service. Their non-hardenable nature supports cold forming into baffles and headers per TEMA standards, and magnetic permeability near 1 facilitates non-destructive magnetic particle inspection. This adaptability makes them suitable for high temperature austenitic tubing in LNG vaporizers, desalination plants, and pharmaceutical sterilizers, where hygiene and pitting resistance are critical.
Countering common failures like caustic embrittlement or hydrogen-induced cracking in high-pH waters, stainless steel corrosion shields like these reduce outage frequency by 50% in utility boilers, aligning with NACE MR0175 for sour environments. For operators tackling boiler tube erosion protection in abrasive slurries or seeking versatile corrosion resistant austenitic pipes for multi-phase flows, austenitic stainless steel tubes deliver balanced economy, safety, and longevity, backed by proven deployment in global energy infrastructures.
Austenitic stainless steels are versatile and popular materials, known for their corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and suitability for fabrication. A stable austenite structure contains about 18% Cr, 8–10% Ni, and about 0.1% C. Common grades include the familiar 18Cr-8Ni (TP304) and high Cr-Ni steels with added elements such as Mo, Cu, Si, Nb, and Ti. These steels are non-magnetic with high plasticity and ductility but relatively lower strength. They can be strengthened through cold working. By adding S, Ca, Se, or Te, machinability can be improved.
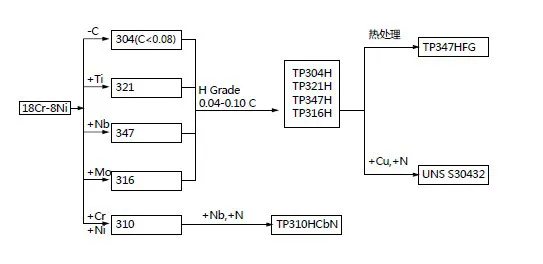
304/L/H/LN, 316/L/H/LN/Ti/LMod, 310S/H, 317/L, 321/H, 347H/HFG
Austenitic steels are non-magnetic stainless steels with high chromium and nickel content and low carbon levels. They are known for their formability, durability, and excellent resistance to corrosion, making them the most commonly used class of stainless steels worldwide.
| AISI grade | C max. | Si max. | Mn max. | Cr | Ni | Mo | Ti | Nb | Al | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 301 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 16-18 | 6-8 | |||||
| 302 | 0.15 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 17-19 | 8-10 | |||||
| 304 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 17.5-20 | 8-10.5 | |||||
| 310 | 0.25 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 24-26 | 19-22 | |||||
| 316 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 16-18 | 10-14 | 2.0-3.0 | ||||
| 321 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 17-19 | 9-12 | 5 x %C min. | ||||
| 347 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 17-19 | 9-13 | 10 x %C min. | ||||
| E 1250 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 6.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 0.25 | ||||
| 20/25-Nb | 0.05 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 20.0 | 25.0 | 0.7 | ||||
| A 286 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 15.0 | 26.0 | 1.2 | ~1.9 | ~0.18 | ~0.25 | |
| 254SMO | 0.02 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 18.5-20.5 | 17.5-18.5 | 6-6.5 | ~1.9 | ~0.18 | ~0.25 | |
| AL-6XN | 0.03 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 20-22 | 23.5-25.5 | 6-7 |
Austenitic stainless steels are primarily categorized into the 300 and 200 series based on alloying elements.
The most common grade is 304, comprising 18% chromium and 8% nickel. The 8% nickel threshold is the minimum required to fully transform ferrite to austenite in an 18% chromium base. For enhanced corrosion resistance, molybdenum is incorporated at about 2% in grade 316.
Developed during the 1940s and 1950s amid nickel shortages, the 200 series—also known as chromium-manganese (CrMn) stainless steels—substitutes nickel with nitrogen, manganese, and copper, all austenite stabilizers. Nitrogen addition is limited to avoid nitride formation and porosity, but manganese enables higher nitrogen levels. This series offers a cost-effective alternative to 300-series steels with superior yield strength.
Reduced surface area minimizes painting, fireproofing, and labor costs.
High weight-to-strength ratio ensures durability and reliability in use.
Used in construction, structural engineering, and various industrial projects.
We stock a wide range of schedules to ensure the right choice for every application, from low-pressure systems to the most demanding industrial conditions.
Lightweight and cost-effective, ideal for low-pressure applications such as water distribution, fire protection systems, and HVAC ductwork.
Stronger than Schedule 10, commonly used in residential plumbing, industrial cooling, and chemical applications.
Designed for high-pressure environments, offering improved durability for industrial processes and oil & gas applications.
Exceptional strength for extreme pressure and temperature conditions. Ideal for power plants, petrochemical industries, and steam lines.
The thickest and most robust pipe schedule, built for the most demanding industrial conditions like deep well drilling and high-pressure hydraulics.
We offer both welded and seamless stainless steel pipes in a range of configurations to meet your specific needs.
Welded pipes are manufactured by bending a sheet of steel into a tube and welding the seam.
Seamless pipes are created by heating a solid billet and piercing it with a mandrel to form a tube.
| Aspect | Seamless Pipes | Welded Pipes |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Higher strength, no weld seam | Lower strength due to weld seam (but improving with technology) |
| Cost | Generally more expensive | More cost-effective to manufacture |
| Usage | High-pressure applications | Low to medium pressure applications |
| Availability | Smaller sizes, limited larger sizes | Wide range of sizes and lengths available |
| Grade | C (% max) | Mn (% max) | Si (% max) | P (% max) | S (% max) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Mo (%) | N (% max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | - | 0.10 |
| 304L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-12.0 | - | 0.10 |
| 316 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
| 316L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
The low carbon content in 304L and 316L enhances weldability, while molybdenum in 316 and 316L improves resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making Austenitic Stainless Steel ideal for harsh environments.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (min, MPa) | Yield Strength (min, MPa) | Elongation (min, %) | Hardness (max, HB) | Hardness (max, HRB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 304L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
These mechanical properties make Austenitic Stainless Steel suitable for applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as architectural structures, marine environments, and chemical processing.
In order to solve the cumbersome and difficult to remember stainless steel grades, improve the practicability of the brand representation, and the contrast with the international standard grades, China has formulated the "Universal Code System for Steel and Alloy Grades", such as 06Cr19Ni10, corresponding to 304. Different grades of stainless steel have different ingredients, but they all have a national standard. The standards of each country are also different.
| No | China (GB) | Japan (JIS) | American | Korea (KS) | EU (BS EN) | India (IS) | Australia (AS) | Taiwan (CNS) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Old | New (07.10) | SUS | ASTM | UNS | STS | EN | IS | AS | CNS | |
| Austenitic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 1 | 1Cr17Mn6Ni5N | 12Cr17Mn6Ni5N | SUS201 | 201 | S20100 | STS201 | 1.4372 | 10Cr17Mn6Ni4N20 | 201-2 | 201 |
| 2 | 1Cr18Mn8Ni5N | 12Cr18Mn9Ni5N | SUS202 | 202 | S20200 | STS202 | 1.4373 | — | — | 202 |
| 3 | 1Cr17Ni7 | 12Cr17Ni7 | SUS301 | 301 | S30100 | STS301 | 1.4319 | 10Cr17Ni7 | 301 | 301 |
| 4 | 0Cr18Ni9 | 06Cr19Ni10 | SUS304 | 304 | S30400 | STS304 | 1.4301 | 07Cr18Ni9 | 304 | 304 |
| 5 | 00Cr19Ni10 | 022Cr19Ni10 | SUS304L | 304L | S30403 | STS304L | 1.4306 | 02Cr18Ni11 | 304L | 304L |
| 6 | 0Cr19Ni9N | 06Cr19Ni10N | SUS304N1 | 304N | S30451 | STS304N1 | 1.4315 | — | 304N1 | 304N1 |
| 7 | 0Cr19Ni10NbN | 06Cr19Ni9NbN | SUS304N2 | XM21 | S30452 | STS304N2 | — | — | 304N2 | 304N2 |
| 8 | 00Cr18Ni10N | 022Cr19Ni10N | SUS304LN | 304LN | S30453 | STS304LN | — | — | 304LN | 304LN |
| 9 | 1Cr18Ni12 | 10Cr18Ni12 | SUS305 | 305 | S30500 | STS305 | 1.4303 | — | 305 | 305 |
| 10 | 0Cr23Ni13 | 06Cr23Ni13 | SUS309S | 309S | S30908 | STS309S | 1.4833 | — | 309S | 309S |
| 11 | 0Cr25Ni20 | 06Cr25Ni20 | SUS310S | 310S | S31008 | STS310S | 1.4845 | — | 310S | 310S |
| 12 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2 | SUS316 | 316 | S31600 | STS316 | 1.4401 | 04Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 316 | 316 |
| 13 | 0Cr18Ni12Mo3Ti | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2Ti | SUS316Ti | 316Ti | S31635 | — | 1.4571 | 04Cr17Ni12MoTi20 | 316Ti | 316Ti |
| 14 | 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 | 022Cr17Ni12Mo2 | SUS316L | 316L | S31603 | STS316L | 1.4404 | 02Cr17Ni12Mo2 | 316L | 316L |
| 15 | 0Cr17Ni12Mo2N | 06Cr17Ni12Mo2N | SUS316N | 316N | S31651 | STS316N | — | — | 316N | 316N |
| 16 | 00Cr17Ni13Mo2N | 022Cr17Ni13Mo2N | SUS316LN | 316LN | S31653 | STS316LN | 1.4429 | — | 316LN | 316LN |
| 17 | 0Cr18Ni12Mo2Cu2 | 06Cr18Ni12Mo2Cu2 | SUS316J1 | — | — | STS316J1 | — | — | 316J1 | 316J1 |
| 18 | 00Cr18Ni14Mo2Cu2 | 022Cr18Ni14Mo2Cu2 | SUS316J1L | — | — | STS316J1L | — | — | — | 316J1L |
| 19 | 0Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 06Cr19Ni13Mo3 | SUS317 | 317 | S31700 | STS317 | — | — | 317 | 317 |
| 20 | 00Cr19Ni13Mo3 | 022Cr19Ni13Mo3 | SUS317L | 317L | S31703 | STS317L | 1.4438 | — | 317L | 317L |
| 21 | 0Cr18Ni10Ti | 06Cr18Ni11Ti | SUS321 | 321 | S32100 | STS321 | 1.4541 | 04Cr18Ni10Ti20 | 321 | 321 |
| 22 | 0Cr18Ni11Nb | 06Cr18Ni11Nb | SUS347 | 347 | S34700 | STS347 | 1.4550 | 04Cr18Ni10Nb40 | 347 | 347 |
| Austenitic-Ferritic Stainless Steel (Duplex) | ||||||||||
| 23 | 0Cr26Ni5Mo2 | — | SUS329J1 | 329 | S32900 | STS329J1 | 1.4477 | — | 329J1 | 329J1 |
| 24 | 00Cr18Ni5Mo3Si2 | 022Cr19Ni5Mo3Si2N | SUS329J3L | — | S31803 | STS329J3L | 1.4462 | — | 329J3L | 329J3L |
| Ferritic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 25 | 0Cr13Al | 06Cr13Al | SUS405 | 405 | S40500 | STS405 | 1.4002 | 04Cr13 | 405 | 405 |
| 26 | — | 022Cr11Ti | SUH409 | 409 | S40900 | STS409 | 1.4512 | — | 409L | 409L |
| 27 | 00Cr12 | 022Cr12 | SUS410L | — | — | STS410L | — | — | 410L | 410L |
| 28 | 1Cr17 | 10Cr17 | SUS430 | 430 | S43000 | STS430 | 1.4016 | 05Cr17 | 430 | 430 |
| 29 | 1Cr17Mo | 10Cr17Mo | SUS434 | 434 | S43400 | STS434 | 1.4113 | — | 434 | 434 |
| 30 | — | 022Cr18NbTi | — | — | S43940 | — | 1.4509 | — | 439 | 439 |
| 31 | 00Cr18Mo2 | 019Cr19Mo2NbTi | SUS444 | 444 | S44400 | STS444 | 1.4521 | — | 444 | 444 |
| Martensitic Stainless Steel | ||||||||||
| 32 | 1Cr12 | 12Cr12 | SUS403 | 403 | S40300 | STS403 | — | — | 403 | 403 |
| 33 | 1Cr13 | 12Cr13 | SUS410 | 410 | S41000 | STS410 | 1.4006 | 12Cr13 | 410 | 410 |
| 34 | 2Cr13 | 20Cr13 | SUS420J1 | 420 | S42000 | STS420J1 | 1.4021 | 20Cr13 | 420 | 420J1 |
| 35 | 3Cr13 | 30Cr13 | SUS420J2 | — | — | STS420J2 | 1.4028 | 30Cr13 | 420J2 | 420J2 |
| 36 | 7Cr17 | 68Cr17 | SUS440A | 440A | S44002 | STS440A | — | — | 440A | 440A |

Stainless steel pipe is one of the more standardiz...

Stainless steel tube is a cylindrical hollow struc...