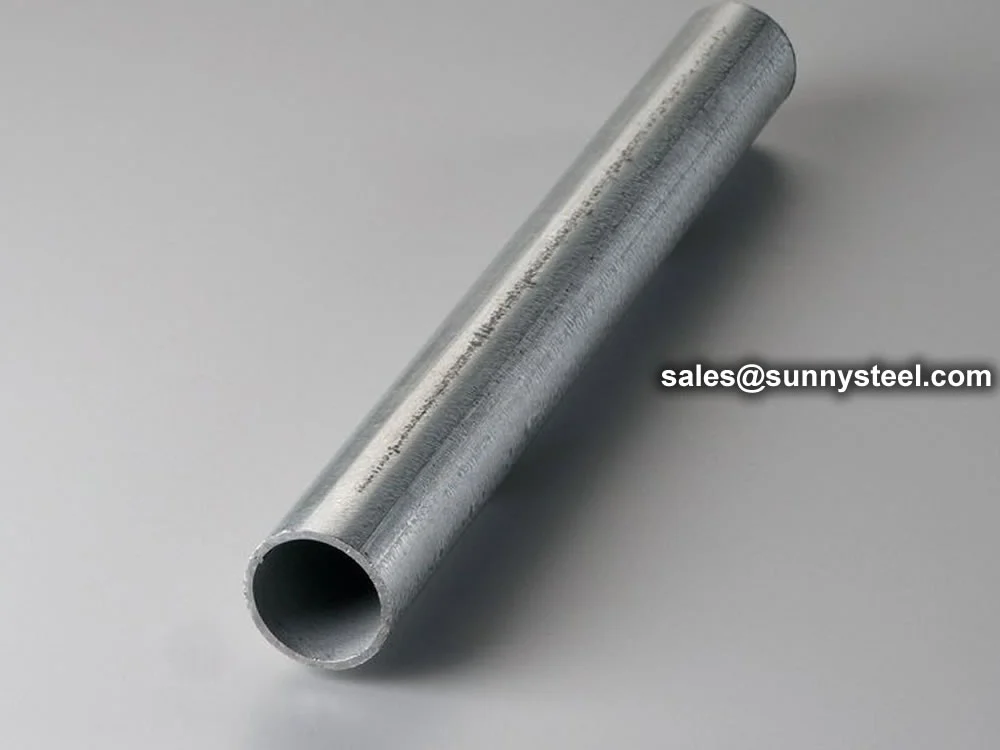

Corrosion-resistant And Durable Piping Solutions
Hot-dip galvanized pipes provide superior corrosion resistance for water supply, construction, and industrial applications.

Hot-Galvanized electrical steel Pipe
Galvanized pipes, coated with zinc, offer superior corrosion resistance and cost-effective durability for a wide range of applications.
In addition to this, galvanized pipe also provides:

Galvanized Threaded end steel pipe
Typically used on pipe 3" and smaller, threaded connections are referred to as screwed pipe.
With tapered grooves cut into the ends of a run of pipe, screwed pipe and screwed fittings can easily be assembled without welding or other permanent means of attachment. In the United States, the standard pipe thread is National Pipe Thread (NPT).
The reason for this is that as NPT connections are assembled, they become increasingly more difficult for the process to leak. The standard taper for NPT pipe is 3/4" for every foot. Threaded End is abbreviated on drawings as TE.
Threaded fittings have threads that are either male or female. Male threads are cut into the outside of a pipe or fitting, while female threads are cut into the inside of the fitting. As screwed pipe and fittings are assembled, two pieces are pulled together. The distance that is pulled together is called the thread engagement.
Galvanized Schedule 40 Pipe
Schedule 40 pipe is the most common wall thickness designation for pipe; the size refers to the inside diameter. The wall thickness will increase proportionally to the inside diameter.
Galvanized steel should be used anywhere rust protection is required or desired to create durable, long lasting products and structures. The quick fix options to prevent rust, like that of painting or coatings of grease and oil, tend to be unreliable and only provide short-term corrosion protection requiring continued maintenance.
Galvanized materials require less maintenance, less repair costs, have a longer life expectancy than that of uncoated steel, and have a lower initial cost than other coating options.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes are carbon steel pipes coated with a zinc layer through a hot-dip galvanizing process, ensuring exceptional corrosion resistance and durability. Compliant with ASTM A123 and A53 standards, these pipes are ideal for water supply systems, construction frameworks, and agricultural irrigation, offering a minimum tensile strength of 330 MPa and a zinc coating thickness of at least 1.5 oz/ft² (458 g/m²).
The manufacturing process involves cleaning, pickling, and immersing the steel pipes in molten zinc at approximately 450°C (842°F), creating a metallurgical bond that protects against rust and corrosion. Available in sizes from DN15 (1/2”) to DN200 (8”) with wall thicknesses from SCH 40 to SCH 80, and lengths from 5.8 to 12 meters, Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes meet diverse project requirements. Surface treatments like passivation enhance longevity, and plain or threaded ends ensure easy installation.
These pipes undergo stringent testing, including tensile, hydrostatic, and coating thickness tests, to ensure compliance with ASTM standards. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial anode, protecting the steel even if scratched, making Corrosion-Resistant Galvanized Pipes suitable for harsh environments like marine and industrial settings. Their durability supports high-pressure applications in gas pipelines and industrial piping.
Compared to pre-galvanized or stainless steel pipes, Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes offer superior corrosion protection and cost-effectiveness, though they may require periodic maintenance in highly corrosive environments. Their versatility and long lifespan (up to 50 years) make them a preferred choice for fencing, railings, and structural applications.
Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes address challenges like pipeline corrosion, environmental exposure, and maintenance costs, providing reliable, long-lasting solutions for industrial and residential applications.
Hot-dip galvanizing (HDG) is the process of coating iron, steel or ferrous materials with a layer of zinc. This done by passing the metal through molten zinc at a temperature of 860°F (460°C) to form zinc carbonate (ZNC03). Zinc carbonate is a strong material that protects steel and can prevent corrosion in many circumstances. Hot-dip galvanizing can be carried out cheaply and in large batches.
| Feature | Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipe | Pre-Galvanized Pipe | Stainless Steel Pipe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating | Zinc (80-100 microns) | Zinc (thinner, coil-coated) | None (inherent corrosion resistance) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (sacrificial anode) | Moderate (weaker at welds) | Superior (no coating needed) |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Lower initial cost | Higher cost |
| Lifespan | Up to 50 years | 20-30 years | 50+ years |
| Applications | Water, gas, construction | Light structural, fencing | Chemical, marine, hygienic |
Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes offer distinct advantages over pre-galvanized and stainless steel pipes. Below is a comparison of key features.
High chromium and molybdenum content for harsh environments.
Polished or brushed finishes for decorative applications.
Tensile strength up to 515 MPa for structural integrity.
Oval shape for tight spaces and better maneuverability.
Easily welded for complex designs and installations.
Meets ASTM A554, A269, and A312 standards.
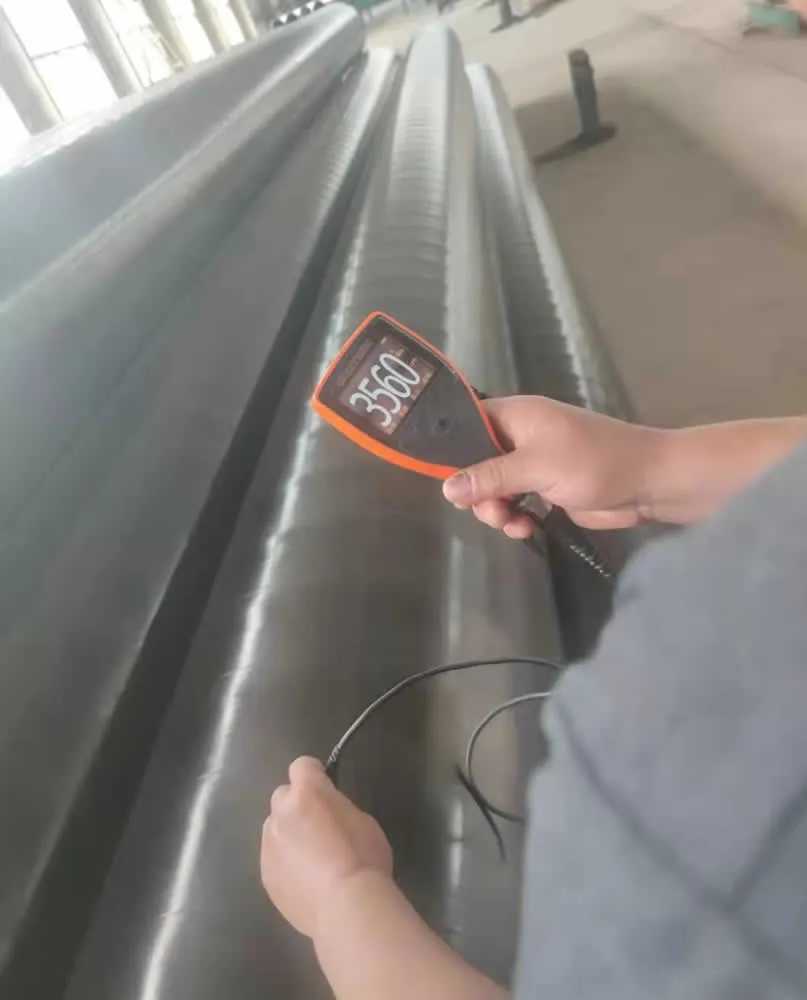

Preparation: The galvanizing reaction will only occur on a chemically clean surface, so the first step of the process involves removing contamination. First, the metal is degreased using a caustic solution and then dipped in hydrochloric acid to remove rust, mill scale, welding slag, paint and grease. This followed by a rinse and a dip in a flux solution, which is usually about 30 percent zinc ammonium chloride.
Galvanizing: When the clean iron or steel component is dipped into the molten zinc (at 842°F (450°C)), zinc-iron alloy layers form as a result of a metallurgical reaction between the iron and zinc. When the material is pulled from the galvanizing bath, a layer of molten zinc is present on top of the alloy layer. When it cools, it has the bright, shiny appearance associated with galvanized products.
Inspection: After galvanizing, the coated materials are inspected for coating thickness and coating appearance. A variety of simple physical and laboratory tests may be performed to determine thickness, uniformity, adherence and appearance of the zinc coating.

Explore Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes with targeted long-tail keywords for specifications, applications, and materials.
Note: Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes meet international standards, ensuring high performance and reliability. Contact suppliers for detailed specifications.
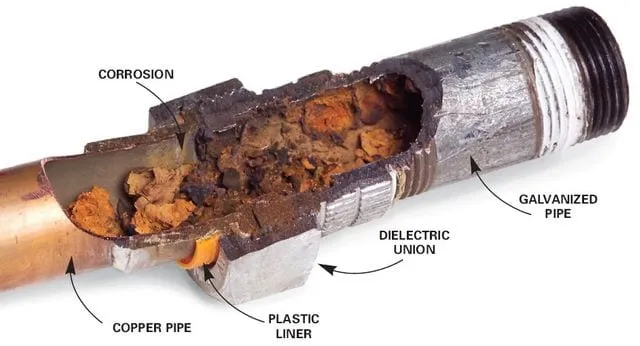
The properties of galvanized steel are a unique combination that make it ideal for use in interior and exterior applications such as car bodies, appliances, nuts and bolts, roofs, and rebar.
| Grade | C (% max) | Mn (% max) | P (% max) | S (% max) | Cu (% max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade A | 0.25 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 0.045 | 0.40 |
| Grade B | 0.30 | 1.20 | 0.05 | 0.045 | 0.40 |
The zinc coating (80-100 microns) enhances the corrosion resistance of Galvanized Steel Pipe , protecting the carbon steel base in harsh environments. The chemical composition ensures weldability and durability for
| Grade | Tensile Strength (min, MPa) | Yield Strength (min, MPa) | Elongation (min, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade A | 330 | 205 | 28 |
| Grade B | 415 | 240 | 30 |
These properties ensure Galvanized Steel Pipe eliver robust performance in structural and high-pressure applications.
| Feature | Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipe | Pre-Galvanized Pipe | Stainless Steel Pipe |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating | Zinc (80-100 microns) | Zinc (thinner, coil-coated) | None (inherent corrosion resistance) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (sacrificial anode) | Moderate (weaker at welds) | Superior (no coating needed) |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Lower initial cost | Higher cost |
| Lifespan | Up to 50 years | 20-30 years | 50+ years |
| Applications | Water, gas, construction | Light structural, fencing | Chemical, marine, hygienic |
Hot-Dip Galvanized Pipes offer distinct advantages over pre-galvanized and stainless steel pipes.
| Grade | C (% max) | Mn (% max) | Si (% max) | P (% max) | S (% max) | Cr (%) | Ni (%) | Mo (%) | N (% max) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-11.0 | - | 0.10 |
| 304L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-12.0 | - | 0.10 |
| 316 | 0.08 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
| 316L | 0.03 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 0.045 | 0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 | 0.10 |
The low carbon content in 304L and 316L enhances weldability, while molybdenum in 316 and 316L improves resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, making Galvanized Steel Pipe ideal for harsh environments.
| Grade | Tensile Strength (min, MPa) | Yield Strength (min, MPa) | Elongation (min, %) | Hardness (max, HB) | Hardness (max, HRB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 304L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 201 | 92 |
| 316 | 515 | 205 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
| 316L | 485 | 170 | 40 | 217 | 95 |
These mechanical properties make Galvanized Steel Pipe suitable for applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as architectural structures, marine environments, and chemical processing.
Galvanized seamless tubes are widely used in various industries, including construction, plumbing, automotive, and infrastructure projects.

Astm a135 grade b erw pipe offers high-strength so...

Astm a53 grade b pipes offer high-strength, corros...

Astm a178 tubes offer reliable, cost-effective erw...

Astm a214 erw boiler tubes offer high-strength, co...