
High-strength Tubes For Boilers And Heat Exchangers
Seamless boiler tubes for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, offering excellent corrosion resistance and thermal stability for power generation and petrochemicals."
Seamless Boiler Tubes are engineered for high-pressure and high-temperature environments, delivering exceptional corrosion resistance and thermal stability. Conforming to standards like ASTM A192, ASTM A213, and JIS G3461, these tubes are ideal for high-pressure boiler piping, heat exchanger tubes, and superheater applications in power generation, petrochemicals, and industrial heating systems. Their seamless construction ensures reliability and durability under extreme conditions.
Manufactured through hot-rolling or cold-drawing processes, Seamless Boiler Tubes are available in outer diameters from 12.7 mm to 168.3 mm and wall thicknesses from 1 mm to 15 mm. Lengths can be standard (6m, 12m) or customized (up to 25m) to meet project specifications. Heat treatments such as normalizing, quenching, and tempering optimize mechanical properties, ensuring resistance to pipeline wear and thermal stress. The seamless design eliminates weld imperfections, making these tubes suitable for critical applications requiring leak-proof performance.
The chemical composition of boiler tubes varies by grade, typically including carbon (0.06–0.25%), silicon (0.10–0.50%), manganese (0.27–1.20%), phosphorus (≤0.035%), sulfur (≤0.035%), and alloying elements like chromium and molybdenum in grades like T11 or T22 for enhanced corrosion resistance. Rigorous testing, including tensile, hardness, flattening, flaring, and hydrostatic tests, ensures compliance with industry standards. Surface treatments such as phosphating, varnishing, or 3LPE coatings protect against corrosion, while plain or beveled ends facilitate installation.
Seamless Boiler Tubes are critical for applications like power plant boilers, petrochemical refineries, and industrial heat exchangers, where they handle high-pressure steam, hot water, or corrosive fluids. Compared to welded tubes, seamless boiler tubes offer superior strength and pressure resistance, making them the preferred choice for high-temperature environments (up to 650°C). Their ability to withstand thermal fatigue and oxidation ensures reliable performance in demanding conditions.
These tubes address challenges like high-pressure containment, corrosion, and thermal stress in boiler systems. Their seamless construction, compliance with stringent standards, and advanced alloy compositions make them a reliable choice for engineers seeking durable power generation piping and petrochemical boiler tubes, ensuring safety, efficiency, and long service life.

WHAT WE DO?
Sunny Steel, a top-tier boiler tube manufacturer, delivers ASME standard steel boiler tubes and pipes globally. With over 20 years of expertise, we’ve perfected our manufacturing process to ensure exceptional quality for industrial applications.
Our industrial boiler feed tubes are crafted with precision, meeting rigorous ASME standards. We implement advanced inspection and testing protocols to guarantee performance under the toughest conditions. Key features include:
Our skilled engineers provide precise specifications or custom designs tailored to your needs, offered at competitive prices with fast delivery. We collaborate closely with clients to identify optimal designs, ensuring cost-effectiveness and maximizing return on investment.
Partner with Sunny Steel for high-quality, ASME-compliant boiler tubes designed to meet your specific requirements.
With all boilers, heat is transferred from the inside of tubes to the outside (firetube boilers), or, from the outside of tubes to the inside (watertube boilers).
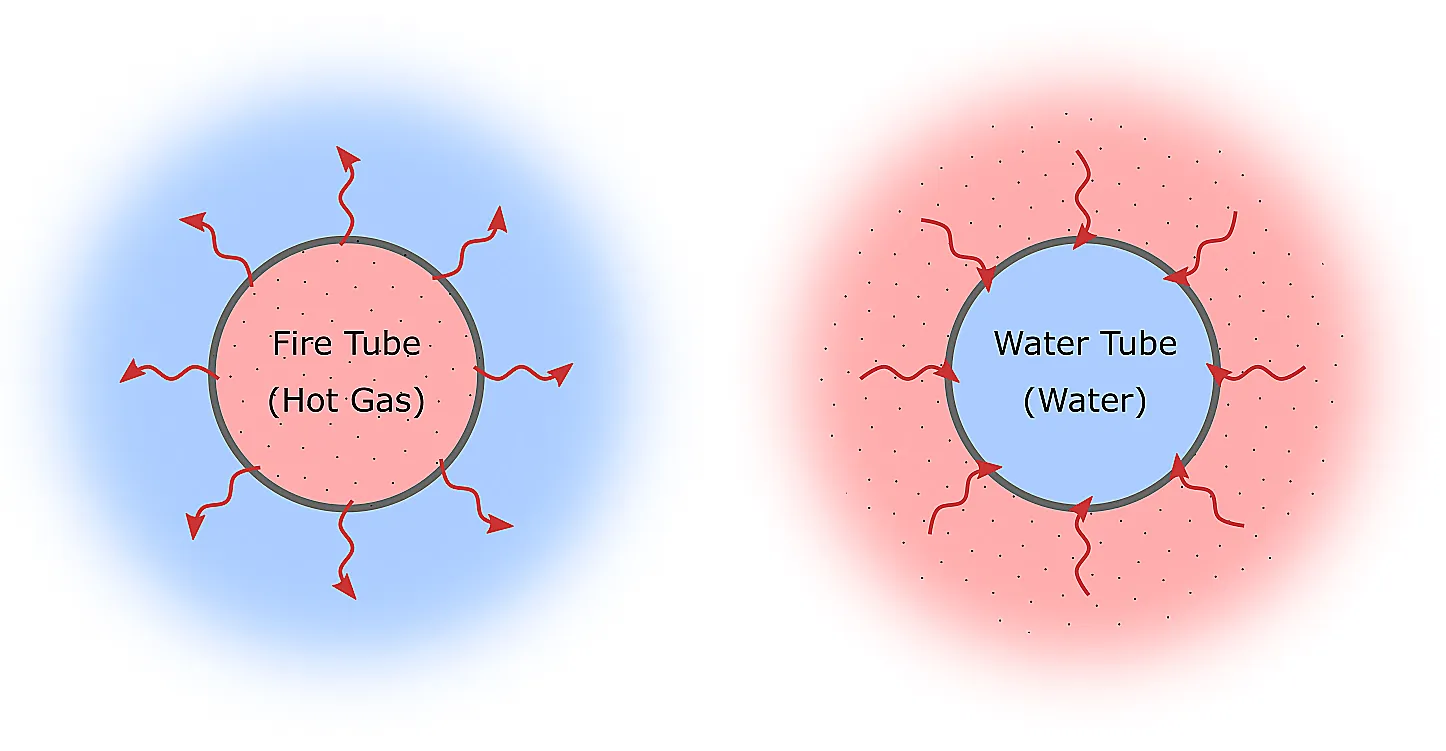
Fire Tube and Water Tube Boiler Tubes
The number of tubes within a boiler ranges from hundreds to thousands within a single boiler, depending upon the size and design of the boiler. The primary purpose of boiler tubes is to transfer the heat produced by the combustion of fuel into water or steam.
Our vast experience and global relationships enable us to adapt to your needs, guiding your growth with tailored solutions for industrial boiler applications.
We provide top-tier ASME standard boiler tubes made from durable, high-quality steel, ensuring long-lasting performance in demanding industrial environments.
At Industrial Boilers America, we prioritize customer satisfaction over profit, building strong relationships to meet your specific needs.
Our cost-effective solutions reduce expenses, allowing you to reinvest in your operations and expand your impact.
These tubes are ideal for industrial processes, including power generation, chemical processing and oil refining.
Handles extreme pressures in boiler and heat exchanger systems.
Performs reliably at temperatures up to 650°C.
Resists oxidation and corrosion with alloyed grades and coatings.
Eliminates weld defects for leak-proof performance.
Durable materials reduce maintenance and replacement costs.
Certified with rigorous testing to meet ASTM and JIS standards.
Boiler tubes face challenges from harsh operating conditions, requiring proper design and maintenance.
High temperatures, pressures, and corrosive fluids weaken tubes, risking leaks or ruptures.
Mineral buildup reduces heat transfer, causing overheating and potential tube failure.
Rapid temperature changes cause fatigue, especially at welds, leading to failure.
High-velocity fluids or abrasive substances thin tube walls, risking failure.
Slow deformation under high temperature and pressure causes tube distortion.
Poor control of pH, oxygen, or conductivity leads to corrosion and scaling.
Incorrect materials fail under specific temperature, pressure, or corrosion conditions.
Note: Proper design, material selection, and regular maintenance are essential for boiler tube reliability.
Standards for seamless and welded boiler tubes used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
| Country | Standard | Example Grades |
|---|---|---|
| China | GB 5310 | 20G, 15CrMoG |
| USA | ASME SA213 | T11, T22 |
| Europe | EN 10216-2 | P235GH, 16Mo3 |
| Japan | JIS G3462 | STBA 22, STBA 24 |
Note: Boiler tubes are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Refer to specific standards or contact suppliers for detailed specifications.
| Specifications | Steel Grades |
|---|---|
| ASTM A-210 / ASME SA-210 | Gr. A1; C |
| BS 3059-1 | Gr. 320 |
| BS 3059-2 | Gr. 360; 440; 620; 622; |
| EN 17175 | 16Mo3 |
| EN 10216/1 |
P235TR1; P235TR2; P265TR1; P265TR2 |
| EN 10216/2 |
P235GHTC1; P235GHTC2; P265GHTC1; P265GHTC2 |
|
ASTM A-209 ASTM A-213 ASME SA-213 |
Gr. T1; T11; T12; T22; T5; T9; T91; T92 |
| ASTM A-335 / ASME SA-335 | Gr. P1; P11; P12; P22; P5; P9; P91; P92 |
| Properties | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk modulus (typical for steel) | 140 GPa | 20300 ksi |
| Shear modulus (typical for steel) | 80 GPa | 11600 ksi |
| Elastic modulus | 190-210 GPa | 27557-30458 ksi |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.27-0.30 | 0.27-0.30 |
| Hardness, Brinell | – | – |
| Hardness, Knoop (converted from Rockwell C hardness) | 875 | 875 |
| Hardness, Rockwell C (quenched in oil from 150°C tempered) | 62 | 62 |
| Hardness, Rockwell C (quenched in water from 150°C tempered) | 64 | 64 |
| Hardness, Rockwell C (quenched in oil) | 64 | 64 |
| Hardness, Rockwell C (quenched in water) | 66 | 66 |
| Hardness, Vickers (converted from Rockwell C hardness) | 848 | 848 |
| Machinability (spheroidized annealed and cold drawn. Based on 100 machinability for AISI 1212 steel) | 40 | 40 |
| Feature | Seamless Boiler Tubes | Welded Boiler Tubes | Stainless Steel Tubes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon/Alloy Steel | Carbon/Alloy Steel | Stainless Steel |
| Temperature Range | Up to 650°C | Up to 500°C | Up to 800°C |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 325–415 | 300–400 | 515–690 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 180–205 | 150–200 | 205–345 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate (with coatings) | Moderate (weld areas vulnerable) | Excellent |
| Pressure Resistance | High | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Moderate | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Boilers, heat exchangers, superheaters | Low-pressure boilers | Corrosive environments, high-temperature |
| Key Advantage | High-pressure reliability | Cost-effective | Superior corrosion resistance |
| Manufacturing Process | Seamless, heat-treated | Welded (ERW, SAW) | Seamless or welded |
Tube ends are vertical to the longitudinal axis and burr-free.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Tube OD | 26.7–114.3 mm |
| Tube WT | 3.2–12.5 mm |
| Tube Lengths | 4–13 meters |
| Deburring Angle (a) | 30° ± 5° or 37° ± 2.5° |
| Dimension (c) | 1.6 ± 0.8 mm |
Tubes have deburred ends or are customized for welding.

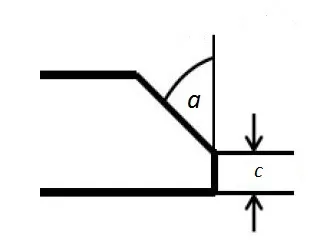
Note: Images of tube ends are available upon request from suppliers.
Ensured through dimensional examination, visual checks, chemical composition, mechanical properties, and 100% eddy current testing.
Hot gas passes through tubes in a sealed water container, transferring heat to generate steam.
Water circulates in tubes heated externally by fire, producing steam in a steam drum.
Explore seamless boiler tubes with targeted long-tail keywords, covering specifications, applications, manufacturing, procurement, and dimensions for high-pressure boiler systems.
Note: Seamless boiler tubes are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. For detailed specifications, refer to ASTM A192, A213, JIS G3461, or contact a certified supplier.

Seamless Boiler Tubes are essential for high-pressure and high-temperature applications in power generation, petrochemicals, and industrial heating systems.
Handles high-pressure steam in thermal power plants.
Resists corrosion in high-temperature processing.
Ensures efficient heat transfer in industrial systems.
Handles superheated steam in power generation.
Supports high-temperature fluid transport in heating systems.
Used in high-pressure fluid transport systems.

Other structural pipes provide high strength and v...

Steel pipe for gas cylinder offers high-strength, ...

Seamless pipes for high-temperature applications o...