Ultimate Abrasion & Corrosion Protection For Harsh Flows
Robust ss316 stainless steel body with silicon carbide (sic) lining for superior wear resistance in abrasive slurries and corrosive media.
Ultimate Abrasion & Corrosion Protection For Harsh Flows
Robust ss316 stainless steel body with silicon carbide (sic) lining for superior wear resistance in abrasive slurries and corrosive media. swing or ball check design, flanged ends, pn16–pn100 pressure ratings.
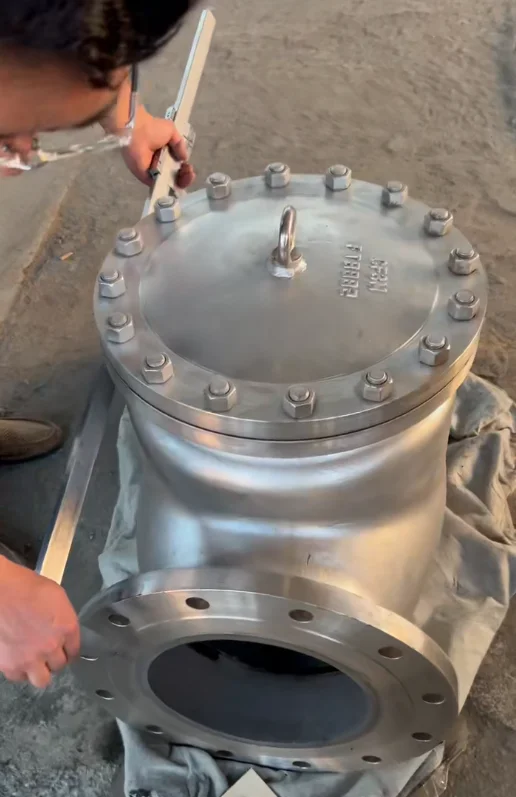
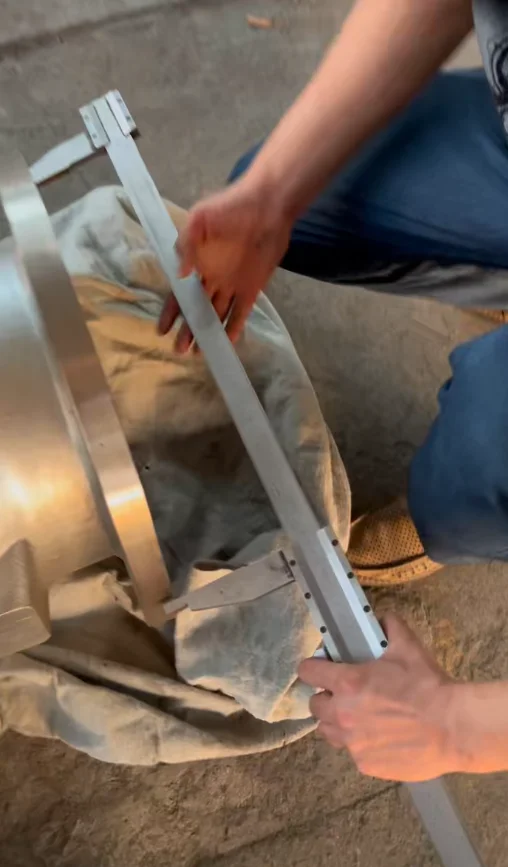
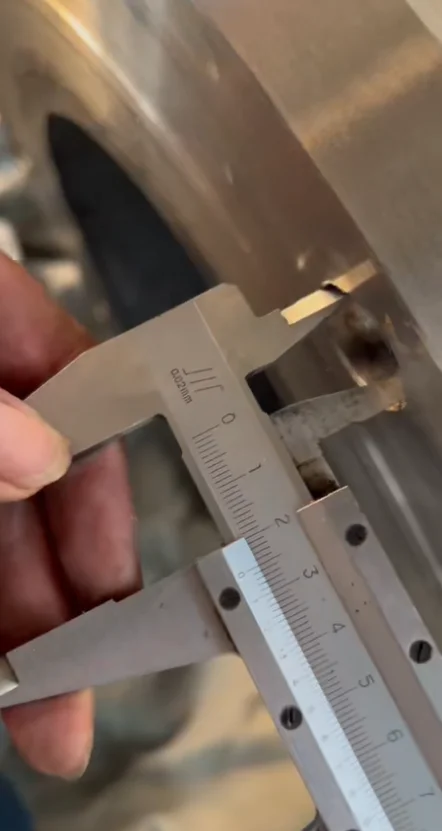
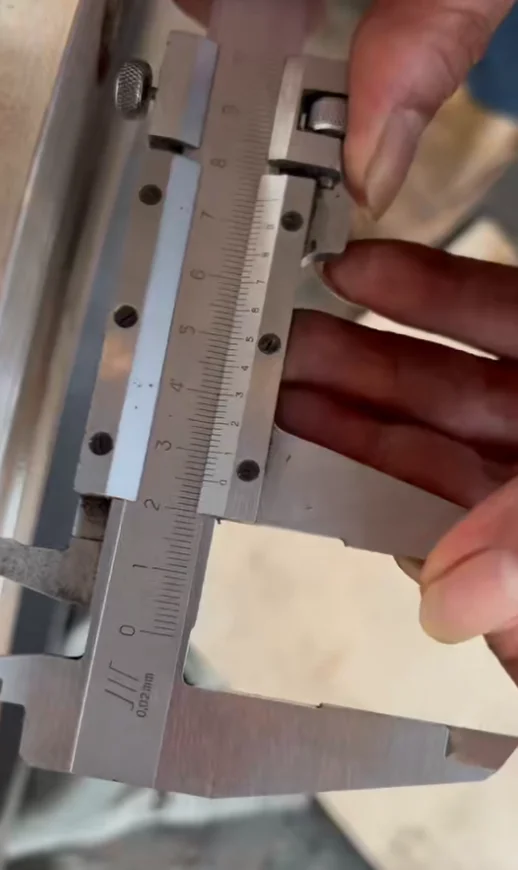
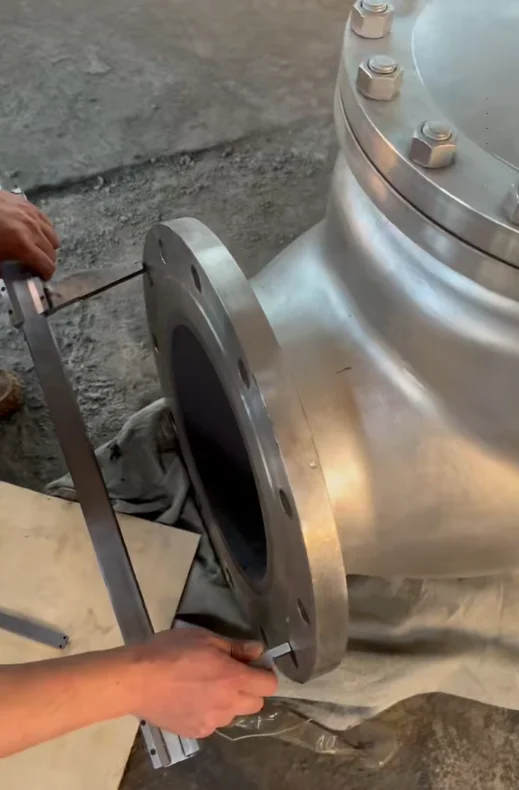
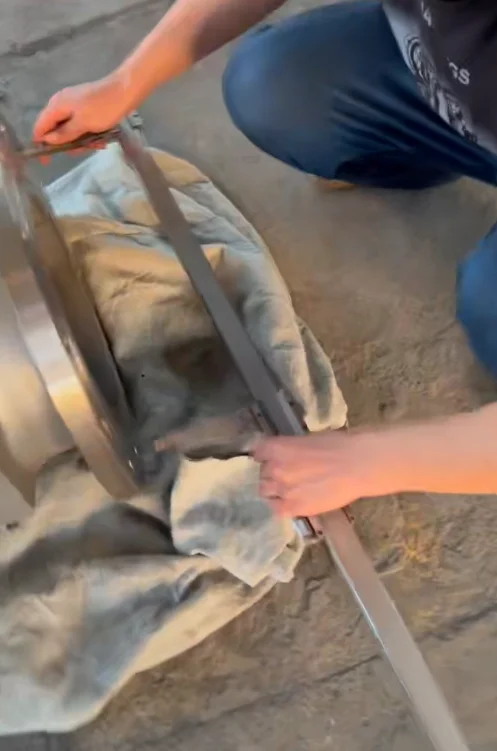

















The SS316 SiC-lined check valve combines the corrosion resistance of AISI 316 stainless steel with the extreme hardness and abrasion resistance of silicon carbide lining. This design prevents backflow in demanding environments where standard valves fail due to wear from slurries, chemicals, or particulates.
Available as swing check (for low-pressure, low-velocity) or ball check (for high-velocity), with bolted body for easy maintenance. SiC lining covers internal surfaces, seats, and discs for full protection.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Body Material | AISI 316 Stainless Steel (1.4401) |
| Lining Material | Silicon Carbide (SiC) – Reaction Bonded or Sintered |
| Design Type | Swing Disc or Ball Check |
| End Connections | Flanged (ANSI B16.5, DIN PN), Butt Weld, Socket Weld |
| Pressure Rating | PN10–PN100 (150–1500 psi) |
| Temperature Rating | -50°C to +200°C (SiC limit; SS316 up to 425°C) |
| Size Range | 1/2″ – 12″ (DN15–DN300) |
| Face-to-Face | ASME B16.10, DIN 3202-F1 |
| Leakage Rate | Zero leakage (metal-seated) |
| Cracking Pressure | 0.05–0.5 bar (adjustable) |
| Standards | API 594, BS 1868, ISO 15761, EN 12366 |
316/316L stainless steel is widely used in chloride and chemical process environments due to its enhanced resistance to corrosion and pitting, attributed to its molybdenum content. These alloys offer excellent mechanical and corrosion-resistant properties across a range of temperatures and environments, making them essential in chemical processing, marine, and high-temperature industrial applications.
Low carbon version of 316, offering superior resistance to intergranular corrosion after welding. Commonly used in marine and chloride-rich environments. Excellent weldability without post-weld annealing.
High carbon content variant suitable for elevated temperature service. Offers greater short and long-term creep strength. Commonly used in high-stress boiler or furnace applications.
Standard molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steel. Excellent resistance to chlorides and moderate acids. Widely used across various chemical and process industries.
| Grade | 316 | 316L |
|---|---|---|
| UNS | S31600 | S31603 |
| Carbon (C) Max. | 0.08 | 0.030 |
| Manganese (Mn) Max. | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Phosphorus (P) Max. | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Sulfur (S) Max. | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon (Si) Max. | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 16.0–18.0 | 16.0–18.0 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 10.0–14.0 | 10.0–14.0 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 2.0–3.0 | 2.0–3.0 |
| Iron (Fe) | Balance | |
Chemical composition details for 316 and 316L stainless steels used in corrosion-resistant applications.
| Material | Form | Tensile Strength (ksi) | Yield Strength (ksi) | Elongation (%) | Hardness (HB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy 316L | Sheet AMS 5507 | 100 max | - | 45 | - |
| Alloy 316 | Sheet AMS 5524 | 75 min | 30 | 45 | 207 max |
Typical mechanical properties for 316 and 316L stainless steel sheets used in industrial applications.
| Electrical Resistivity | Magnetic Permeability |
|---|---|
| 7.2e-005 ohm-cm | 1.008 |
| 1.16e-004 at 650°C | RT |
Electrical resistivity and magnetic permeability values at room and elevated temperatures.
| Alloy | UNS | Tensile (MPa) | Yield (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316 | S31600 | 515 | 205 | 35 | 90 Rb |
| 316L | S31603 | 485 | 170 | - | 90 Rb |
Physical and mechanical properties comparison for 316 and 316L stainless steels.
316L is preferred when welding thick sections is necessary and when resistance to intergranular corrosion is critical. 316H is used for elevated temperature pressure services.

Upstream, midstream, and downstream operations, including drilling, refining, and transportation.
Handling corrosive and hazardous chemicals in various chemical plants.
Steam, water, and fuel systems in thermal, nuclear, and hydroelectric plants.
Municipal water supply, wastewater treatment, and industrial water management.
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in commercial and industrial buildings.
Sterile and hygienic applications, precise flow control in sensitive industries.
Understanding the differences between reaction bonded and pressureless sintered silicon carbide
Reaction bonded silicon carbide offers the lowest cost production technique with excellent overall performance characteristics.
Beams, rollers, cooling air pipes, thermocouple protection pipes, temperature measurement pipes, burner nozzles, wear-resistant parts, corrosion-resistant parts, sealing parts, and various special-shaped structural parts.
Compared with reaction bonded silicon carbide, pressureless sintered silicon carbide offers superior performance in demanding applications.
Can be used in environments where other materials cannot meet requirements, offering significantly longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
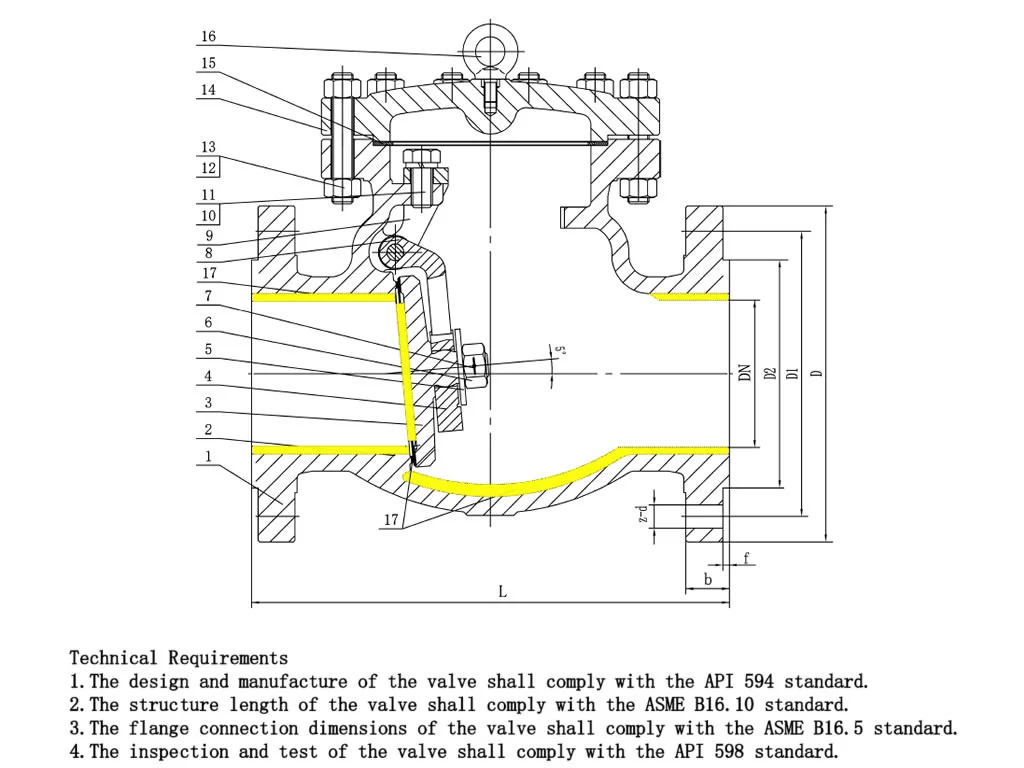
API 6D & API 594 Swing Check Valve
Sort:0
Forged Lift / Piston Check Valve
Sort:0
Rubber Seal Dual Plate Check Valve
Sort:0
Customized Alumina Ceramic Lined Project
Sort:99
High Chromium Alloy Lined Pipe
Sort:99
Sort:0