
The gate valve provides reliable on-off flow control for oil, gas, and water pipelines, featuring corrosion-resistant materials and robust design for high-pressure systems up to pn40 and 425°c.
The Gate Valve is a robust, linear-motion valve engineered for reliable on-off flow control in industrial pipelines, offering full flow capacity and tight shutoff for oil, gas, water, and chemical systems. Featuring a wedge-shaped gate and durable construction from materials like ASTM A216 WCB carbon steel or ASTM A351 CF8M stainless steel, this industrial gate valve ensures superior corrosion resistance and longevity in harsh environments. Designed for high-pressure applications up to PN40 (ANSI Class 150-600) and temperatures up to 425°C, it is ideal for pipeline isolation in refineries, petrochemical plants, power generation, and water treatment facilities.
Compliant with API 600 for cast steel valves and ASME B16.34 for pressure-temperature ratings, the wedge gate valve is available in sizes from 1/2" to 48" (DN15 to DN1200) with flanged, butt-weld, or threaded end connections per ASME B16.5 and B16.25. The valve’s solid or flexible wedge design ensures tight sealing against bidirectional pressure, with metal or resilient seats (e.g., PTFE or Stellite) providing Class VI shutoff per API 598. Rigorous testing, including hydrostatic, pneumatic, and shell tests, confirms tensile strengths above 485 MPa and leak-free performance under high-pressure conditions. Optional features like bellows seals or extended stems enhance safety in hazardous or high-temperature applications.
The pipeline isolation valve is designed for minimal pressure drop and unobstructed flow when fully open, making it ideal for systems requiring maximum throughput. Its corrosion resistant gate valve properties are enhanced by coatings such as epoxy or 3LPE, protecting against aggressive media like seawater, acids, or slurries. The valve’s robust bonnet (bolted or pressure-sealed) withstands thermal cycling and vibration, while non-rising or rising stem options (OS&Y) offer flexibility for manual or actuated operation. With a cycle life exceeding 10,000 operations, it ensures low maintenance and extended service in demanding industrial gate valve applications.
Compared to ball or butterfly valves, the gate valve excels in applications requiring infrequent operation and complete flow isolation, offering lower leakage rates and higher durability under pressure surges. Its ability to handle high-viscosity fluids and abrasive media without clogging makes it superior for slurry pipelines or crude oil systems. Customizable features like gear operators, pneumatic actuators, or API 6D compliance for pipeline service ensure versatility across oil and gas transmission, steam systems, and HVAC networks. The valve’s full-bore design minimizes turbulence, reducing wear on downstream equipment and extending system life.
Addressing challenges like pipeline corrosion, leakage, and thermal stress, the wedge gate valve incorporates double-disc or parallel-slide configurations for enhanced sealing and reduced stem thrust. Its compatibility with global flange standards (ANSI, DIN, JIS) and certifications like SIL 3 for safety-critical systems ensures broad applicability. Whether isolating high-pressure steam in boilers or controlling flow in offshore platforms, the Gate Valve delivers reliable, low-maintenance pipeline isolation valve performance, ensuring safety and efficiency in critical industrial operations.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Fluid Resistance | Straight-through body design allows fluid to pass with minimal resistance when fully open. |
| Superior Sealing | Provides better sealing performance than shut-off valves, ensuring reliable shutoff. |
| Wide Application Range | Suitable for steam, oil, granular solids, high viscosity media, venting, and low vacuum systems. |
| Bidirectional Flow | Allows flow in both directions, making it suitable for pipelines where flow direction changes. |
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Slow Operation | The gate must travel a long distance to open or close, leading to longer actuation time. |
| Not for Rapid Actuation | Unsuitable for applications requiring quick shutoff or frequent operation. |
| Surface Damage Risk | Friction between the gate and seat may cause scratches on the sealing surface. |
| Reduced Sealing Performance | Scratches eventually impair sealing efficiency and shorten service life. |
| Repair Difficulty | Damaged sealing surfaces are difficult to repair, though valves are easy to replace. |
Engineered for reliable pipeline isolation with corrosion-resistant materials and robust design.
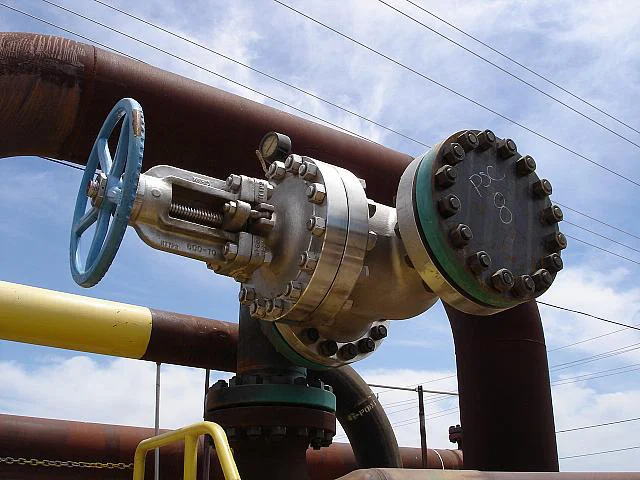
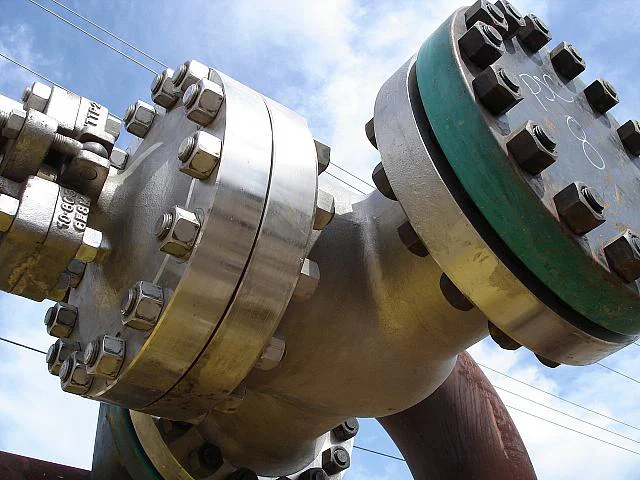
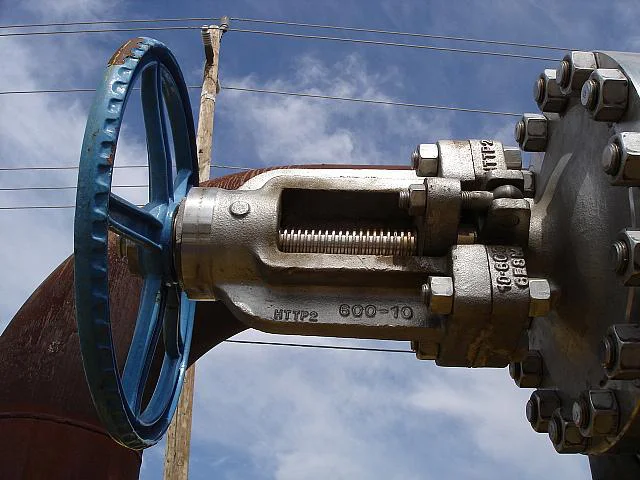
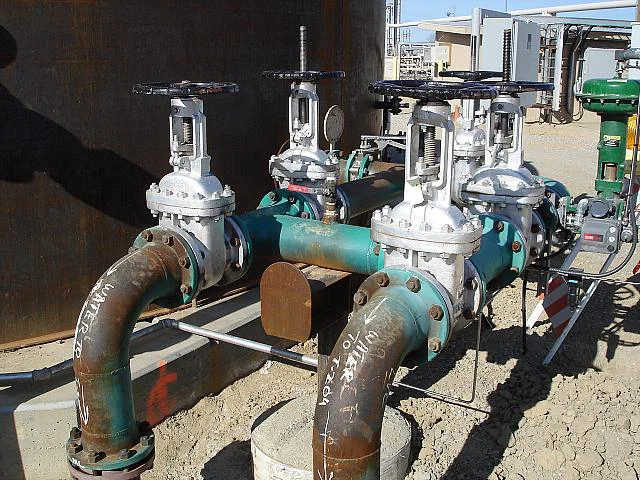
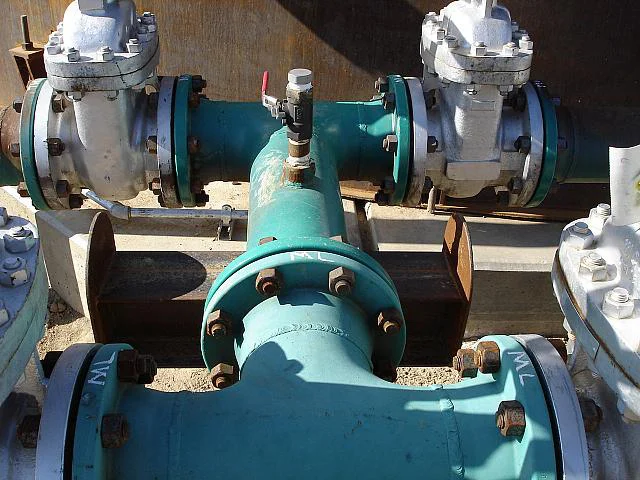



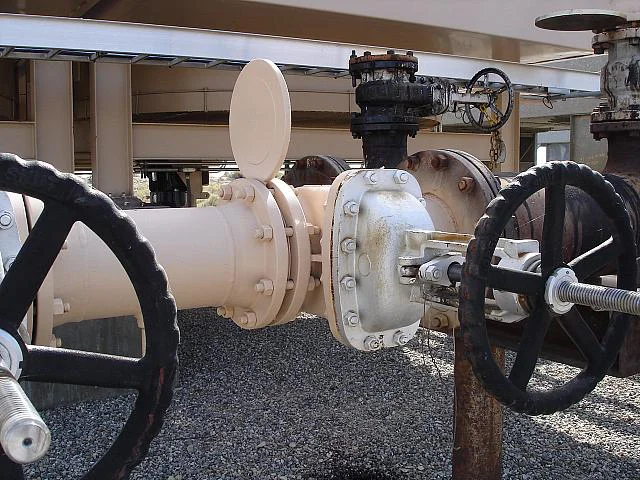


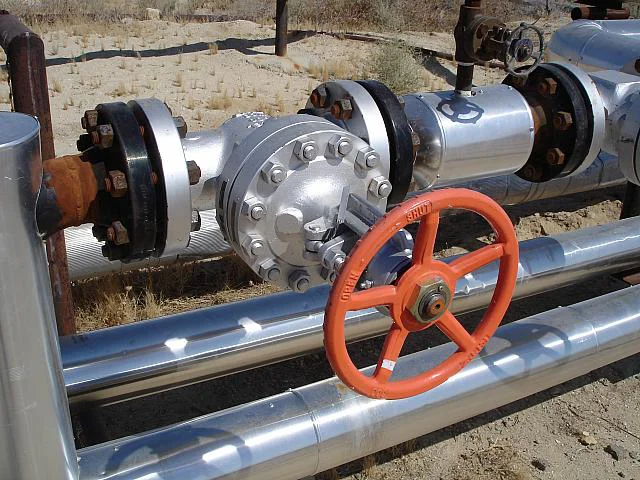
Gate valves have a simple design, widely used in low pressure-drop services. Their full-port design ensures unobstructed flow and no pressure drop, while also allowing pipeline cleaning with a pigging system.
A resilient seated gate valve with a non-rising spindle consists of the following parts. The body is the largest element of the valve, with the bonnet bolted for cleaning and maintenance. The wedge slides down to press the valve seat for complete shutoff and moves upward to allow flow. Over the last century, the construction has remained consistent, with improvements in service life, sealing performance, and corrosion resistance.
Modern gate valve bodies are more compact and sleek, enabling installation in limited space conditions while maintaining durability and efficiency.
Moves vertically to open or close, sealing against the seat for shutoff.
Made of ductile iron, it is the main housing that contains the fluid flow.
Ensures tight sealing when the wedge presses against it.
Transfers rotational motion to vertical movement of the wedge.
Supports the stem to reduce wear during operation.
Bolted to the body for easy cleaning and maintenance access.
Provides sealing around the stem to prevent leakage.

Comprehensive list of key international valve standards from major organizations, updated as of 2025.
| Organization | Standard | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ANSI | American National Standards Institute | General industrial standards |
| API | American Petroleum Institute | Standards for oil and gas industry |
| ASME | American Society of Mechanical Engineers | Boiler and pressure vessel codes |
| BS | British Standards | UK national standards |
| GB, JB, HG | China Valve Standards | Chinese national and industry standards |
| FCI | Fluid Control Institute | Standards for fluid control and conditioning equipment |

American National Standards Institute
| Code | ANSI Standard Name |
|---|---|
| ANSI A126 | Grey Iron Castings for Valves, Flanges, and Pipe Fittings |
| ANSI A181 | Forged or Rolled Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts for General Service |
| ANSI B16.10 | Face-to-Face and End-to-End Dimensions of Valves |
| ANSI B16.34 | Valves - Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End |
| ANSI B16.5 | Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings |
| ANSI/FCI 70-2 | Control Valve Seat Leakage |
| ANSI B127.1 | Constant-Level Oilers |
American Petroleum Institute
| Code | API Standard Name |
|---|---|
| API 526 | Flanged Steel Pressure-Relief Valves |
| API 527 | Seat Tightness of Pressure Relief Valves |
| API 594 | Check Valves: Flanged, Lug, Bolted Bonnet |
| API 595 | Cast Iron Gate Valves - Flanged Bonnet |
| API 597 | Steel Venturi Gate Valves - Flanged and Welding Ends |
| API 598 | Valve Inspection and Testing |
| API 599 | Steel and Ductile Iron Plug Valves |
| API 600 | Bolted Bonnet Steel Gate Valves for Refinery Service |
| API 602 | Compact Steel Gate Valves - Flanged, Threaded, and Welding Ends |
| API 603 | Corrosion-Resistant Gate Valves - Flanged Ends |
| API 604 | Ductile Iron Gate Valves - Flanged Ends |
| API 607 | Fire Test for Quarter-Turn Valves |
| API 608 | Metal Ball Valves - Flanged, Threaded, and Welding Ends |
| API 609 | Butterfly Valves: Double Flanged, Lug- and Wafer-Type |
| API 6D | Pipeline and Piping Valves |
| API 6FA | Fire Test for Valves |
| API RP 574 | Inspection Practices for Piping System Components |
| API RP 576 | Inspection of Pressure-Relieving Devices |
American Society of Mechanical Engineers
| Code | ASME Standard Name |
|---|---|
| ASME A105/A105M | Carbon Steel Forgings for Piping Applications |
| ASME A181/A181M | Carbon Steel Forgings, for General-Purpose Pipes |
| ASME A182/A182M | Forged or Rolled Alloy and Stainless Steel Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, and Valves and Parts for High-Temperature Service |
| ASME A350/A350M | Carbon and Low-Alloy Steel Forgings for Low-Temperature Service |
| ASME A694/A694M | Carbon and Alloy Steel Forgings for Pipe Flanges, Fittings, Valves, and Parts for High-Pressure Transmission Service |
| ASME B16.5 | Pipe Flanges and Flanged Fittings: NPS 1/2 Through NPS 24 Metric/Inch Standard |
| ASME B16.10 | Face-to-Face and End-to-End Dimensions of Valves |
| ASME B16.11 | Forged Fittings, Socket-Welding and Threaded |
| ASME B16.34 | Valves - Flanged, Threaded, and Welding End |
| ASME B31.1 | Power Piping |
| ASME B31.3 | Process Piping |
| ASME F1508 | Standard Specification for Angle Style, Pressure Relief Valves for Steam, Gas, and Liquid Services |
| ASME F1565 | Pressure-Reducing Valves for Steam Service |
British Standards Institution
| Code | British Standard Name |
|---|---|
| BS 1212 | Float Operated Valves - Automatic Valves (Including Float Valves) for Tanks, Cisterns, Hot-Water Cylinders and Feed Cisterns |
| BS 1414 | Specification for Steel Wedge Gate Valves (Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends) for the Petroleum, Petrochemical and Allied Industries |
| BS 1552 | Specification for Control Plug Cocks for Low Pressure Gases |
| BS 1868 | Specification for Steel Check Valves (Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends) for the Petroleum, Petrochemical and Allied Industries |
| BS 1873 | Specification for Steel Globe and Globe Stop and Check Valves (Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends) for the Petroleum, Petrochemical and Allied Industries |
| BS 1952 | Specification for Copper Alloy Gate Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 2080 | Specification for Face-to-Face, Centre-to-Face, End-to-End and Centre-to-End Dimensions for Flanged and Butt-Welding End Steel Valves for the Petroleum, Petrochemical and Allied Industries |
| BS 2995 | Specification for Cast and Forged Steel Wedge Gate, Globe, Check and Plug Valves Screwed and Socket-Welding Sizes 1/2 in and Smaller for the Petroleum Industry |
| BS 3464 | Specification for Cast Iron Gate Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5150 | Specification for Cast Iron Wedge and Double Disk Gate Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5151 | Specification for Cast Iron Gate (Parallel Slide) Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5152 | Specification for Cast Iron Globe and Globe Stop and Check Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5153 | Specification for Cast Iron Check Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5154 | Specification for Copper Alloy Globe, Globe Stop and Check, Check and Gate Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5155 | Specification for Butterfly Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5156 | Specification for Screw-Down Diaphragm Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5157 | Specification for Steel Gate (Parallel Slide) Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5159 | Specification for Cast Iron and Carbon Steel Ball Valves for General Purposes |
| BS 5160 | Specification for Steel Globe Valves, Globe Stop Valves, Stop and Check Valves and Lift Type Check Valves |
| BS 5351 | Specification for Steel Ball Valves for Petroleum, Petrochemical and Allied Industries |
| BS EN 12266-1 | Industrial Valves - Testing of Metallic Valves Part 1: Pressure Tests - Test Procedures |
China National Standards
| Code | GB Standard Name | Adopting Standard |
|---|---|---|
| GB 12220 | General Valve - Marking | ISO 5209 |
| GB 12221 | Flanged Ends Metal Valve - Face-to-Face Dimensions | ISO 5752 |
| GB 12222 | Multi-Turn Valve - The Connection of the Driving Device | ISO 5210/1-3 |
| GB 12223 | Part-Turn Valve - The Connection of the Driving Device | ISO 5211/1-3 |
| GB 12224 | Steel Valve - General Requirements | ANSI B16.34 |
| GB 12225 | General Valve - Copper Alloy Casting Ware Technology Requirements | ASTM B584 |
| GB 12226 | General Valve - Gray Cast Iron Technology Requirements | ISO 185, BS 1452 |
| GB 12228 | General Valve - Carbon Forging Steel Technology Requirements | ASTM A105, A181 |
| GB 12229 | General Valve - Carbon Casting Steel Technology Requirements | ASTM A703 |
| GB 12230 | General Valve - Austenitic Casting Steel Technology Requirements | ASTM A351 |
| GB 12232 | General Valve - Flanged Ends Iron Gate Valve | ISO 5996-1982, API 595 |
| GB 12233 | General Valve - Iron Gate Valve and Lift Check Valve | BS 5152, 5153 |
| GB 12234 | General Valve - Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends Copper Gate Valve | API 600 |
| GB 12237 | General Valve - Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends Steel Ball Valve | ISO 7121, API 607 |
| GB 12238 | General Valve - Flanged and Wafer Ends Butterfly Valve | BS 5155 |
| GB 12239 | General Valve - Diaphragm Valve | BS 5156, NFE 29 |
| GB 12240 | General Valve - Iron Plug Valve | API 593 |
| GB 12241 | Safety Valve - General Requirements | ISO 4126 |
| GB 12242 | Safety Valve - Characteristic Testing Solution | ANSI/ASME PTC 25.3 |
| GB 12243 | Direct Spring-Loaded Safety Valve | JIS B 8210 |
| GB 12244 | Pressure Reducing Valve - General Requirements | JIS B 8372, B8410 |
| GB 12245 | Pressure Reducing Valve - Characteristic Testing Solution | JIS B 8372, B8410 |
| GB 12246 | Pilot Operated Pressure Reducing Valve | JIS B 8372, DSS 405 |
| GB 12247 | Steam Trap Valve - Classification | ISO 6704 |
| GB 12248 | Steam Trap Valve - Technology Terms | ISO 6552 |
| GB 12249 | Steam Trap Valve - Marking | ISO 6553 |
| GB 12250 | Steam Trap Valve - Face-to-Face Dimensions | ISO 6554 |
| GB 12251 | Steam Trap Valve - Testing Solution | ISO 6948, 7841, 7842 |
| GB/T 13927 | General Valve - Pressure Testing | ISO 5208 |
| JB/T 6899-93 | Valve Fire-Proof Test | ISO 10497 |
| JB/T 7927-95 | Valve Casting Steelware Out-Form Quality Requirements | MSS SP-55 |
| ZBJ 16006-90 | Inspection and Testing of Valve | API 598 |
| Code | GB Standard Name |
|---|---|
| GB 12227 | General Valve - Ductile Cast Iron Technology Requirements |
| GB 12235 | General Valve - Flanged Steel Stop and Lift Check Valve |
| GB 12236 | General Valve - Steel Swing Check Valve |
| GB/T 13932 | General Valve - Iron Swing Check Valve |
| GB/T 15185 | Iron and Copper Ball Valve |
| GB/T 15188.1 | Valve Face-to-Face Dimensions - Butt-Welding Ends Valve |
| GB/T 15188.2 | Valve Face-to-Face Dimensions - Wafer Ends Valve |
| GB/T 15188.3 | Valve Face-to-Face Dimensions - Female Screw-Down Valve |
| GB/T 15188.4 | Valve Face-to-Face Dimensions - Male Screw-Down Valve |
| JB 93 | Handle |
| JB/T 450 | PN16-32.0 MPa Forging Angle Type High-Pressure Valve, Fastener, and Technology Requirements |
| JB/T 7745-95 | Pipeline Ball Valve |
| JB/T 8527-97 | Metal Sealing Butterfly Valve |
| JB/T 8473-96 | Instrument Valve Series |
| ZBJ 16004-88 | Reducing Valve Type and Basing Coefficient |
| ZBJ 16007-90 | Steam Trap Valve Technology Terms |
| ZBJ 16009-90 | Valve Pneumatic Actuator Technology Terms |
Standards for fluid control and conditioning equipment
The Fluid Control Institute (FCI) provides standards to assist in understanding and using control valves, solenoid valves, and regulators.
| Code | FCI Standard Name |
|---|---|
| ANSI/FCI 70-2 | Control Valve Seat Leakage |
| ANSI/FCI 70-3 | Control Valve Aerodynamic Noise Prediction |
| ANSI/FCI 91-1 | Qualification of Control Valve Stem Seals |
| ANSI/FCI 85-1 | Method of Determining the Thermal Expansion of a Filled Thermal System |
| FCI 68-2 | Procedure in Rating Flow and Pressure Characteristics of Solenoid Valves for Liquid Service |
| FCI 75-1 | Test Conditions and Procedures for Measuring Electrical Characteristics of Solenoid Valves |
| FCI 82-1 | Recommended Methods for Testing and Classifying the Water Hammer Characteristics of Electrically Operated Valves |
| ANSI/FCI 69-1 | Pressure Ratings of Traps |
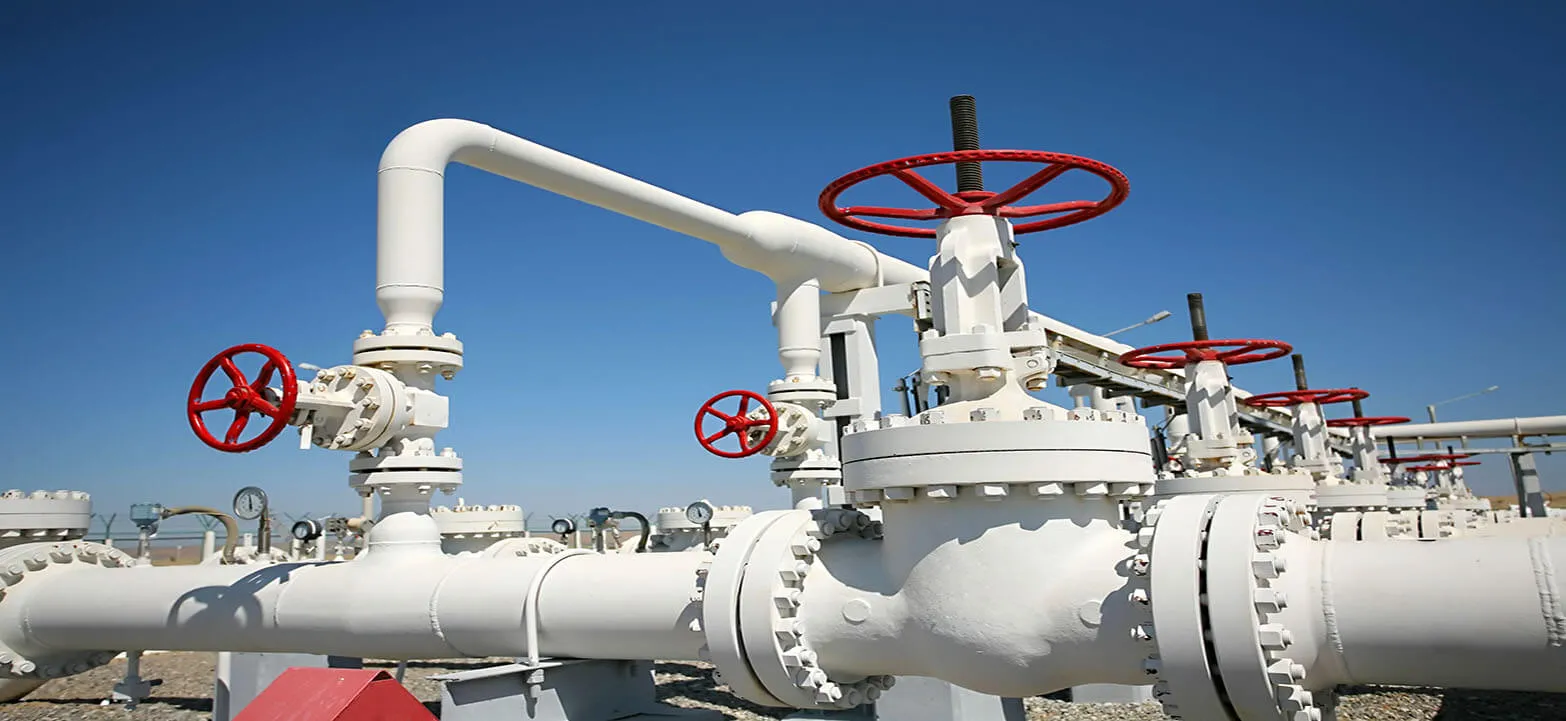

Upstream, midstream, and downstream operations, including drilling, refining, and transportation.
Handling corrosive and hazardous chemicals in various chemical plants.
Steam, water, and fuel systems in thermal, nuclear, and hydroelectric plants.
Municipal water supply, wastewater treatment, and industrial water management.
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems in commercial and industrial buildings.
Sterile and hygienic applications, precise flow control in sensitive industries.
Customized Alumina Ceramic Lined Project
Sort:99
High Chromium Alloy Lined Pipe
Sort:99
Sort:0